| [1] |
YOUNOSSI ZM, GOLABI P, PAIK JM, et al. The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis(NASH): A systematic review[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 77( 4): 1335- 1347. DOI: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000004. |
| [2] |
ESTES C, ANSTEE QM, ARIAS-LOSTE MT, et al. Modeling NAFLD disease burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the period 2016-2030[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 69( 4): 896- 904. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.05.036. |
| [3] |
WU CM, ZHANG CY, XU HL, et al. Epidemiological research and diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in China[J]. China Med Herald, 2023, 20( 11): 158- 161. DOI: 10.20047/j.issn1673-7210.2023.11.36. |
| [4] |
SARDANA O, GOYAL R, BEDI O. Molecular and pathobiological involvement of fetuin-A in the pathogenesis of NAFLD[J]. Inflammopharmacology, 2021, 29( 4): 1061- 1074. DOI: 10.1007/s10787-021-00837-4. |
| [5] |
CHEKOL ABEBE E, TILAHUN MUCHE Z, BEHAILE T/MARIAM A, et al. Role of fetuin-A in the pathogenesis of psoriasis and its potential clinical applications[J]. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol, 2022, 15: 595- 607. DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S356801. |
| [6] |
STEFAN N, FRITSCHE A, WEIKERT C, et al. Plasma fetuin-A levels and the risk of type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetes, 2008, 57( 10): 2762- 2767. DOI: 10.2337/db08-0538. |
| [7] |
SONG AY, XU M, BI YF, et al. Serum fetuin-A associates with type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance in Chinese adults[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6( 4): e19228. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019228. |
| [8] |
SUN JR, ZHANG D, XU J, et al. Circulating FABP4, nesfatin-1, and osteocalcin concentrations in women with gestational diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2020, 19( 1): 199. DOI: 10.1186/s12944-020-01365-w. |
| [9] |
XIAO Y, SHU LL, WU XP, et al. Fatty acid binding protein 4 promotes autoimmune diabetes by recruitment and activation of pancreatic islet macrophages[J]. JCI Insight, 2021, 6( 7): e141814. DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.141814. |
| [10] |
OLIVIER E, SOURY E, RUMINY P, et al. Fetuin-B, a second member of the fetuin family in mammals[J]. Biochem J, 2000, 350( Pt 2): 589- 597.
|
| [11] |
MUSTAFA AI, KADAH AS, FAWZY EM, et al. Serum fetuin-A: A novel potential link between post-adolescent acne and insulin resistance[J]. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol, 2022, 15( 12): 33- 37.
|
| [12] |
DENG WJ, GU J, ZUO LJ, et al. The level changes and influencing factors of serum fetuin-B in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Chin J Diabetes, 2019, 27( 3): 198- 201. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6187.2019.03.007. |
| [13] |
National Workshop on Fatty Liver and Alcoholic Liver Disease, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Fatty Liver Expert Committee, Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Guidelines of prevention and treatment for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A 2018 update[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34( 5): 947- 957. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.05.007. |
| [14] |
YOUNOSSI ZM, HENRY L, BUSH H, et al. Clinical and economic burden of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2018, 22( 1): 1- 10. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2017.08.001. |
| [15] |
STEFAN N, HENNIGE AM, STAIGER H, et al. Alpha2-heremans-schmid glycoprotein/fetuin-A is associated with insulin resistance and fat accumulation in the liver in humans[J]. Diabetes Care, 2006, 29( 4): 853- 857. DOI: 10.2337/diacare.29.04.06.dc05-1938. |
| [16] |
CHEKOL ABEBE E, TILAHUN MUCHE Z, BEHAILE T/MARIAM A, et al. The structure, biosynthesis, and biological roles of fetuin-A: A review[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2022, 10: 945287. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.945287. |
| [17] |
LI LN, SPRANGER L, STOBÄUS N, et al. Fetuin-B, a potential link of liver-adipose tissue cross talk during diet-induced weight loss-weight maintenance[J]. Nutr Diabetes, 2021, 11( 1): 31. DOI: 10.1038/s41387-021-00174-z. |
| [18] |
DI MINNO A, ZANOBINI M, MYASOEDOVA VA, et al. Could circulating fetuin A be a biomarker of aortic valve stenosis?[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2017, 249: 426- 430. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.05.040. |
| [19] |
Low serum fetuin-a as a biomarker to predict pneumococcal necrotizing pneumonia and hemolytic uremic syndrome in children: Erratum[J]. Medicine, 2018, 97( 3): e9684. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009684. |
| [20] |
ZHOU ZW, SUN MZ, JIN H, et al. Fetuin-A to adiponectin ratio is a sensitive indicator for evaluating metabolic syndrome in the elderly[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2020, 19( 1): 61. DOI: 10.1186/s12944-020-01251-5. |
| [21] |
ZHAO LL, SHANG Y, LUO QZ, et al. Decreased plasma fetuin-A level as a novel bioindicator of poor prognosis in community-acquired pneumonia: A multi-center cohort study[J]. Front Med, 2022, 9: 807536. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.807536. |
| [22] |
DIAO WQ, SHEN N, DU YP, et al. Fetuin-B(FETUB): A plasma biomarker candidate related to the severity of lung function in COPD[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 30045. DOI: 10.1038/srep30045. |
| [23] |
YURTCU N, ORAL S, CELIK S, et al. Predıctıve value of pregnancy of follıcular fluıd fetuın-A and-B levels ın infertıle women after intra-cytoplasmic sperm injection[J]. J Obstet And Gynaecol, 2022, 48( 1): 178- 187. DOI: 10.1111/jog.15070. |
| [24] |
LIU SS, XIAO JH, ZHAO ZZ, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of circulating fetuin-a levels in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2021, 9( 1): 3- 14. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2020.00081. |
| [25] |
LU CW, LEE YC, CHIANG CH, et al. Independent dose-response associations between fetuin-A and lean nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13( 9): 2928. DOI: 10.3390/nu13092928. |
| [26] |
BALLESTRI S, MESCHIARI E, BALDELLI E, et al. Relationship of serum fetuin-a levels with coronary atherosclerotic burden and NAFLD in patients undergoing elective coronary angiography[J]. Metab Syndr Relat Disord, 2013, 11( 4): 289- 295. DOI: 10.1089/met.2012.0149. |
| [27] |
IX JH, SHARMA K. Mechanisms linking obesity, chronic kidney disease, and fatty liver disease: The roles of fetuin-A, adiponectin, and AMPK[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2010, 21( 3): 406- 412. DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2009080820. |
| [28] |
LANTHIER N, LEBRUN V, MOLENDI-COSTE O, et al. Liver fetuin-A at initiation of insulin resistance[J]. Metabolites, 2022, 12( 11): 1023. DOI: 10.3390/metabo12111023. |
| [29] |
PETER A, KOVAROVA M, STAIGER H, et al. The hepatokines fetuin-A and fetuin-B are upregulated in the state of hepatic steatosis and may differently impact on glucose homeostasis in humans[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2018, 314( 3): E266- E273. DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00262.2017. |
| [30] |
CHOI JW, LIU H, MUKHERJEE R, et al. Downregulation of fetuin-B and zinc-α2-glycoprotein is linked to impaired fatty acid metabolism in liver cells[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2012, 30( 2): 295- 306. DOI: 10.1159/000339065. |
| [31] |
DABROWSKA AM, TARACH JS, WOJTYSIAK-DUMA B, et al. Fetuin-A(AHSG) and its usefulness in clinical practice. Review of the literature[J]. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub, 2015, 159( 3): 352- 359. DOI: 10.5507/bp.2015.018. |
| [32] |
ZHAO CL, SHANG DF, ZHOU C, et al. Mechanism of lipid metabolism mediated by hepatokines and adipokines in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 1): 168- 174. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.01.026. |



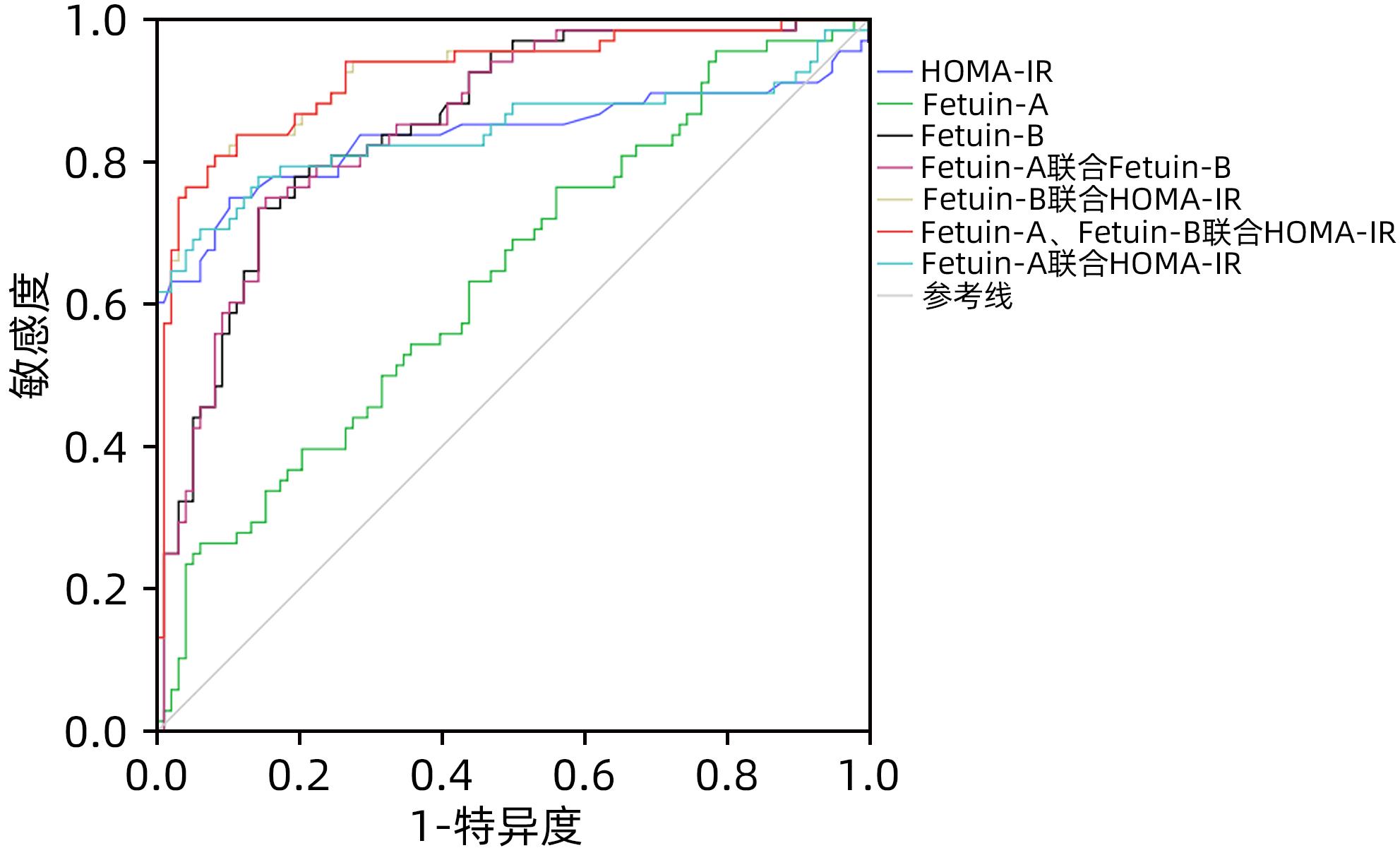




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: