| [1] |
DU GH, LI L, YANG XY, et al. An overview of the ancient and modern researches on the toxicity of Chinese medicinal materials[J]. Pharmacol Clin Chin Mater Med, 2018, 34( 4): 187- 189. DOI: 10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.2018.04.045. |
| [2] |
Branch of Hepatobiliary Diseases, China Association of Chinese Medicine; Branch of Chinese Patent Medicine, China Association of Chinese Medicine. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of herb-induced liver injury[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2016, 32( 5): 835- 843. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2016.05.003. |
| [3] |
WANG JB, ZHU Y, BAI ZF, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of herb-induced liver injury[J]. Chin J Integr Med, 2018, 24( 9): 696- 706. DOI: 10.1007/s11655-018-3000-8. |
| [4] |
HU ZX, ZHOU SZ, ZHANG N, et al. Development of polyclonal antibodies for detection of diosbulbin B-derived cis-enedial protein adducts[J]. Chem Res Toxicol, 2018, 31( 4): 231- 237. DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.7b00299. |
| [5] |
LIU BS, WANG GJ, WANG ZH, et al. One case of acute liver injury caused by tripterygium glycosides tablets[J]. Chin J Pharmacovigil, 2023, 20( 5): 511- 513, 535. DOI: 10.19803/j.1672-8629.20220672. |
| [6] |
WANG MH, WANG X, YAN YJ, et al. Correlation between triptolide in Tripterygium glycoside tablets and hepatotoxicity in vitro[J]. Mod Chin Med, 2021, 23( 8): 1344- 1351. DOI: 10.13313/j.issn.1673-4890.20200520001. |
| [7] |
GE FL, NIU M, HAN ZX, et al. Analysis of epidemiological characteristics of drug induced liver injury associated with Baixianpi Preparations[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2019, 44( 5): 1048- 1052. DOI: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20181217.001. |
| [8] |
ZHAO SQ, WU M. Acute renal failure and liver injury caused by Xanthium seed poisoning: a case report[J]. J Pract Diagn Ther, 2004, 18( 6): 514. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3474.2004.06.036. |
| [9] |
PENG WX, LI X, LIU FQ. Analysis of drug-induced liver injury induced by cassia seed extract: a case report[J]. Pharm J Chin People’s Liberation Army, 2016, 32( 5): 487. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9926.2016.05.033. |
| [10] |
ZHAO YM, WU L, ZHANG S, et al. Safety evaluation and risk control measures of Cassiae Semen[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2017, 42( 21): 4074- 4078. DOI: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20170919.013. |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
SUN MH, LIU YY, LEI X, et al. Hepatic veno-occlusive syndrome and multiple organ dysfunction caused by food-borne poisoning of Panax notoginseng: Report of one case[J/CD]. Chin J Hyg Rescue Electron Ed, 2019, 5( 3): 191- 192. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-9133.2019.03.017. |
| [13] |
PAN HL, PAN WJ, CHEN CY, et al. Progress in the study of the effects of medicinal components of traditional Chinese medicine on liver toxicity[J]. Chin J Clin Ration Drug Use, 2020, 13( 27): 179- 181. DOI: 10.15887/j.cnki.13-1389/r.2020.27.078. |
| [14] |
Technology Committee on DILI Prevention and Management, Chinese Medical Biotechnology Association; Study Group of Drug Induced Liver Disease, Chinese Medical Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Chinese guideline for diagnosis and management of drug-induced liver injury(2023 version)[J]. Chin J Gastroenterol, 2023, 28( 7): 397- 431. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20230419-00176. |
| [15] |
LI M, LI RR, LIU CH. Clinic diagnosis and treatment of herb-induced liver injury[J]. Chin J Pharmacovigil, 2023, 20( 2): 127- 131. DOI: 10.19803/j.1672-8629.20220661. |
| [16] |
WANG CY, DENG Y, LI P, et al. Prediction of biochemical nonresolution in patients with chronic drug-induced liver injury: A large multicenter study[J]. Hepatology, 2022, 75( 6): 1373- 1385. DOI: 10.1002/hep.32283. |
| [17] |
HUANG A, ZHU Y, LIU SH, et al. An optimized short-term steroid therapy for chronic drug-induced liver injury: A prospective randomized clinical trial[J]. Liver Int, 2024, 44( 6): 1435- 1447. DOI: 10.1111/liv.15899. |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
ZHAN XY, LUO Q, XIONG WY, et al. Comparison of effects of different aconite products on liver injury toxicity[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2023, 34( 3): 609- 613. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2023.03.25. |
| [22] |
GAO Y, XIE LY, LU ZQ. Research progress on toxicity of aconite and compatibility of attenuating toxicity and enhancing effect[J]. Tianjin Pharm, 2020, 32( 1): 65- 69. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5687.2020.01.018. |
| [23] |
WANG TL, ZHAO XY, SHAO C, et al. A proposed pathologic sub-classification of drug-induced liver injury[J]. Hepatol Int, 2019, 13( 3): 339- 351. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-019-09940-9. |
| [24] |
SHI W, GAO Y, GUO YM, et al. Idiosyncratic hepatotoxicity evaluation of Cortex Dictamni based on immune stress[J]. Acta Pharm Sin, 2019, 54( 4): 678- 686. DOI: 10.16438/j.0513-4870.2018-1045. |
| [25] |
CHEN H, GAO SQ, XIAO JR, et al. Clinical analysis of drug-induced liver damage caused by huangyaozi( Dioscorea bulbifera L.) and its preparation[J]. J Hunan Univ Chin Med, 2021, 41( 9): 1442- 1446. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-070X.2021.09.023. |
| [26] |
QIU BY, ZHANG BY, HUANG NL. A commonly used Chinese medicine that can cause liver side effects[J]. Asia Pac Tradit Med, 2011, 7( 8): 188- 189.
邱宝玉, 张碧玉, 黄南龙. 可引起肝脏不良反应的常用中药[J]. 亚太传统医药, 2011, 7( 8): 188- 189.
|
| [27] |
HE TT, GONG M, WANG LF, et al. Prospective study on pathological features and traditional Chinese medicine syndrome types of patients with herb-induced liver injury[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med, 2019, 39( 8): 932- 936. DOI: 10.7661/j.cjim.20190318.044. |
| [28] |
HOOFNAGLE JH, BJÖRNSSON ES. Drug-induced liver injury-types and phenotypes[J]. N Engl J Med, 2019, 381( 3): 264- 273. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1816149. |
| [29] |
GAO YJ, ZHAO X, BAI ZF, et al. Prevention and control of safety risks of traditional Chinese medicine based on indirect knowledge of toxicity[J]. Chin J Pharmacovigil, 2021, 18( 11): 1004- 1008. DOI: 10.19803/j.1672-8629.2021.11.02. |
| [30] |
XIAO XH, ZHAO X, BAI ZF, et al. New outlook on safety of traditional Chinese medicine: Concept and practice[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2023, 48( 10): 2557- 2564. DOI: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230309.601. |
| [31] |
BAI ZF, WANG JB, XIAO XH. Cognition innovation of toxicity of Chinese medicine and safe and precise medication[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2022, 47( 10): 2557- 2564. DOI: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220211.601. |
| [32] |
YU LQ, ZHENG J, LI JY, et al. Mechanism of hepatotoxicity induced by neem seed in mice based on serum exosome and liver miRNA expression profiles[C]// The Professional Committee of Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology of the Chinese Society of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine. 2019 Abstracts of the Third Academic Seminar of the Professional Committee of Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology of the Chinese Society of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine. 2019: 2.
俞铃琪, 郑洁, 李俊颖, 等. 基于血清外泌体和肝脏miRNA表达谱的川楝子致小鼠肝毒性机制研究[C]//中国中西医结合学会临床药理与毒理专业委员会. 2019中国中西医结合学会临床药理与毒理专业委员会第三届学术研讨会论文摘要集. 2019: 2.
|
| [33] |
JI C, ZHENG J, TONG W, et al. Revealing the mechanism of Fructus meliae toosendan-induced liver injury in mice by integrating microRNA and mRNA-based toxicogenomics data[J]. RSC Adv, 2015, 5( 100): 81774- 81783. DOI: 10.1039/C5RA10112C. |
| [34] |
LIU Y, WU H, WANG Z, et al. Integrated expression profiles of mRNA and miRNA in a gerbil model of fatty liver fibrosis treated with exenatide[J]. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol, 2021, 45( 2): 101312. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinre.2019.07.013. |
| [35] |
YANG XW, ZHANG YH, LIU Y, et al. Emodin induces liver injury by inhibiting the key enzymes of FADH/NADPH transport in rat liver[J]. Toxicol Res, 2018, 7( 5): 888- 896. DOI: 10.1039/c7tx00307b. |
| [36] |
HASNAT M, YUAN ZQ, NAVEED M, et al. Drp1-associated mitochondrial dysfunction and mitochondrial autophagy: A novel mechanism in triptolide-induced hepatotoxicity[J]. Cell Biol Toxicol, 2019, 35( 3): 267- 280. DOI: 10.1007/s10565-018-9447-8. |
| [37] |
LI FJ, YAO GT, JIN RM, et al. Mechanism studies on hepatotoxicity of rats induced by Sophorae Tonkinensis radix et Rhizoma in rat[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2011, 36( 13): 1821- 1823. DOI: 10.4268/cjcmm20111327. |
| [38] |
LI CP, RAO T, CHEN XP, et al. HLA-B*35:01 allele is a potential biomarker for predicting Polygonum multiflorum-induced liver injury in humans[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 70( 1): 346- 357. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30660. |
| [39] |
TU C. The identification for susceptible individuals of idiosyncratic liver injury induced by traditional Chinese medicines and rational use[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of TCM, 2019.
涂灿. 中药特异质肝损伤易感人群识别及安全合理用药研究: 以何首乌为例[D]. 成都: 成都中医药大学, 2019.
|
| [40] |
ZHANG L, NIU M, WEI AW, et al. Risk profiling using metabolomic characteristics for susceptible individuals of drug-induced liver injury caused by Polygonum multiflorum[J]. Arch Toxicol, 2020, 94( 1): 245- 256. DOI: 10.1007/s00204-019-02595-3. |
| [41] |
ZHANG L, BAI ZF, LI CY, et al. Study on idiosyncratic liver injury and content of cis-2, 3, 5, 4′-tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside in radix Polygoni multiflori Preparata[J]. Acta Pharm Sin, 2017, 52( 7): 1041- 1047. DOI: 10.16438/j.0513-4870.2017-0307. |
| [42] |
ZHANG L, LIU XY, TU C, et al. Components synergy between stilbenes and emodin derivatives contributes to hepatotoxicity induced by Polygonum multiflorum[J]. Xenobiotica, 2020, 50( 5): 515- 525. DOI: 10.1080/00498254.2019.1658138. |
| [43] |
GUAN SB, ZHANG WT, GUO H. A case of the syndrome of disappearing intrahepatic bile ducts caused by Polygonum multiflorum[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2024, 32( 3): 248- 250. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20231203-00260. |
| [44] |
WANG ZL. Susceptible components and mechanism studies of epimedii folium-induced immunological idiosyncratic liver injury based on NLRP3 inflammasome[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of TCM, 2021.
王智磊. 基于NLRP3炎症小体的淫羊藿致免疫特异质肝损伤易感成分及作用机制研究[D]. 成都: 成都中医药大学, 2021.
|
| [45] |
LIU Q, GUO YL, DONG TW, et al. Research progress on hepatotoxicity mechanism and attenuation methods of psoraleae fructus[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae, 2021, 27( 11): 233- 239. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20210626. |
| [46] |
HUANG Y, LIU YL, MA RR, et al. Clinical case analysis and disassembled prescription study of liver injury related to Xianling Gubao[J]. Acta Pharm Sin, 2021, 56( 1): 266- 273. DOI: 10.16438/j.0513-4870.2020-1477. |
| [47] |
BAI ZF, MENG YK, HE LZ, et al. Immune idiosyncratic liver injury induced by traditional non-toxic traditional Chinese medicine and a hypothesis of its mechanism[J]. Chin Pharm J, 2017, 52( 13): 1105- 1109. DOI: 10.11669/cpj.2017.13.001. |
| [48] |
BAI ZF, GAO Y, ZUO XB, et al. Progress in research on the pathogenesis of immune regulation and idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury[J]. Acta Pharm Sin, 2017, 52( 7): 1019- 1026. DOI: 10.16438/j.0513-4870.2017-0315. |
| [49] |
WANG ZL, XU G, WANG HB, et al. Icariside II, a main compound in Epimedii Folium, induces idiosyncratic hepatotoxicity by enhancing NLRP3 inflammasome activation[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2020, 10( 9): 1619- 1633. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.03.006. |
| [50] |
GAO Y, XU G, MA L, et al. Icariside I specifically facilitates ATP or nigericin-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation and causes idiosyncratic hepatotoxicity[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2021, 19( 1): 13. DOI: 10.1186/s12964-020-00647-1. |
| [51] |
FU SB, XU G, GAO Y, et al. Inhibitory effect and mechanism of licochalcone A on NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. Acta Pharm Sin, 2018, 53( 12): 2050- 2056. DOI: 10.16438/j.0513-4870.2018-0713. |
| [52] |
WANG JB, CUI HR, BAI ZF, et al. Precision medicine-oriented safety assessment strategy for traditional Chinese medicines: Disease-syndrome-based toxicology[J]. Acta Pharm Sin, 2016, 51( 11): 1681- 1688. DOI: 10.16438/j.0513-4870.2016-0812. |



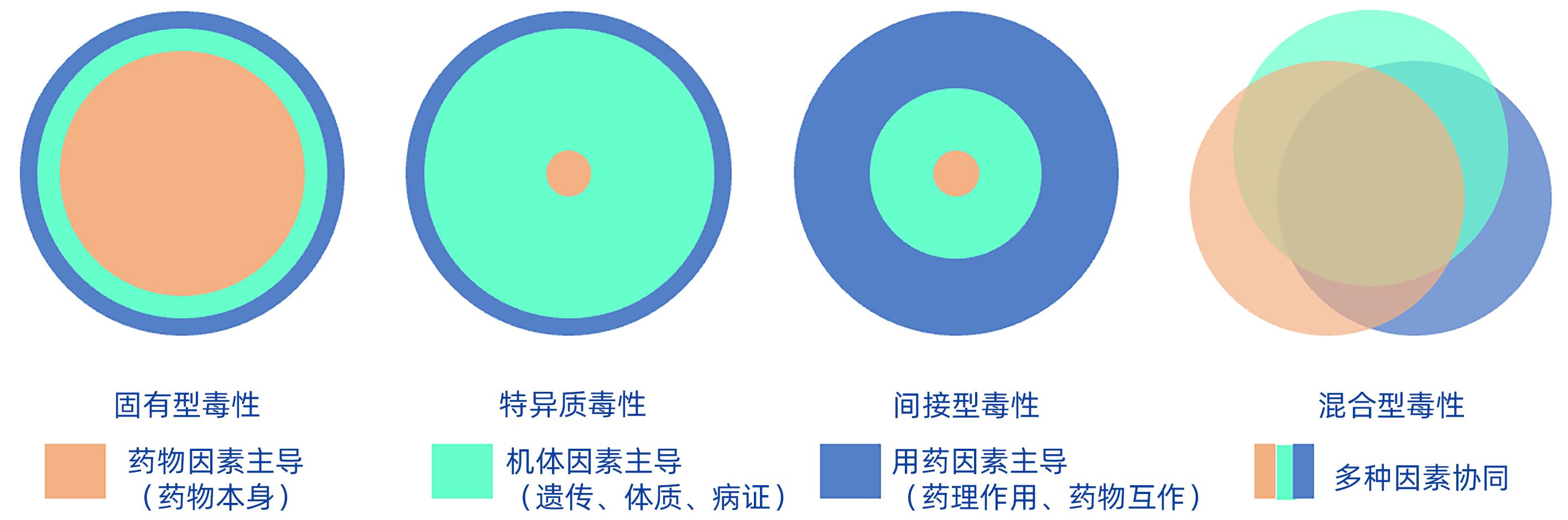




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: