| [1] |
DATE RS, KAUSHAL M, RAMESH A. A review of the management of gallstone disease and its complications in pregnancy[J]. Am J Surg, 2008, 196( 4): 599- 608. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2008.01.015. |
| [2] |
HUANG CL, LIU J, LU YY, et al. Clinical features and treatment of hypertriglyceridemia-induced acute pancreatitis during pregnancy: A retrospective study[J]. J Clin Apher, 2016, 31( 6): 571- 578. DOI: 10.1002/jca.21453. |
| [3] |
BANKS PA, BOLLEN TL, DERVENIS C, et al. Classification of acute pancreatitis: 2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus[J]. Gut, 2013, 62( 1): 102- 111. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302779. |
| [4] |
WEI P, ZHAO XL, HOU WH, et al. Clinical characteristics and maternal and fetal outcomes of 166 patients with acute pancreatitis in pregnancy[J]. Chin J Pract Gynecol Obstet, 2022, 38( 7): 756- 759. DOI: 10.19538/j.fk2022070119. |
| [5] |
DUCARME G, MAIRE F, CHATEL P, et al. Acute pancreatitis during pregnancy: A review[J]. J Perinatol, 2014, 34( 2): 87- 94. DOI: 10.1038/jp.2013.161. |
| [6] |
TSUANG W, NAVANEETHAN U, RUIZ L, et al. Hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis: Presentation and management[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2009, 104( 4): 984- 991. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2009.27. |
| [7] |
JIANG X, YAN YF, ZHONG R, et al. Clinical features of biliary acute pancreatitis versus hypertriglyceridemic acute pancreatitis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36( 9): 2050- 2055. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.09.028. |
| [8] |
ONG Y, SHELAT VG. Ranson score to stratify severity in acute pancreatitis remains valid-old is gold[J]. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 15( 8): 865- 877. DOI: 10.1080/17474124.2021.1924058. |
| [9] |
Chinese Society for Emergency Medicine, Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Alliance of Emergency Treatment and First Aid, Emergency Medicine Branch, Beijing Medical Association, et al. Expert consensus on emergency diagnosis and treatment of acute pancreatitis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37( 5): 1034- 1041. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.05.012. |
| [10] |
PITCHUMONI CS, YEGNESWARAN B. Acute pancreatitis in pregnancy[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2009, 15( 45): 5641. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.15.5641. |
| [11] |
GARG PK, SINGH VP. Organ failure due to systemic injury in acute pancreatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2019, 156( 7): 2008- 2023. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.12.041. |
| [12] |
SZATMARY P, GRAMMATIKOPOULOS T, CAI WH, et al. Acute pancreatitis: Diagnosis and treatment[J]. Drugs, 2022, 82( 12): 1251- 1276. DOI: 10.1007/s40265-022-01766-4. |
| [13] |
TANG SJ, RODRIGUEZ-FRIAS E, SINGH S, et al. Acute pancreatitis during pregnancy[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2010, 8( 1): 85- 90. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2009.08.035. |
| [14] |
KMN V, SHEELA CN, BANKA S, et al. Maternal and perinatal outcome of acute pancreatitis during pregnancy: A 5 year experience at a tertiary care centre[J]. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol, 2016: 4041- 4045. DOI: 10.18203/2320-1770.ijrcog20163886. |
| [15] |
GENG YX, LI WQ, SUN LQ, et al. Severe acute pancreatitis during pregnancy: Eleven years experience from a surgical intensive care unit[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2011, 56( 12): 3672- 3677. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-011-1809-5. |
| [16] |
PAPADAKIS EP, SARIGIANNI M, MIKHAILIDIS DP, et al. Acute pancreatitis in pregnancy: An overview[J]. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol, 2011, 159( 2): 261- 266. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2011.07.037. |
| [17] |
ZHANG TT, WANG GX, CAO Z, et al. Acute pancreatitis in pregnancy: A 10-year, multi-center, retrospective study in Beijing[J]. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth, 2022, 22( 1): 414. DOI: 10.1186/s12884-022-04742-8. |
| [18] |
YANG ZY, GUO GY, LI H. Predicting fetal loss in severe acute pancreatitis during pregnancy: A 5-year single-tertiary-center retrospective analysis[J]. Postgrad Med, 2020, 132( 5): 473- 478. DOI: 10.1080/00325481.2020.1752010. |
| [19] |
RAUSCHERT S, GÁZQUEZ A, UHL O, et al. Phospholipids in lipoproteins: Compositional differences across VLDL, LDL, and HDL in pregnant women[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2019, 18( 1): 20. DOI: 10.1186/s12944-019-0957-z. |
| [20] |
RUSSI G. Severe dyslipidemia in pregnancy: The role of therapeutic apheresis[J]. Transfus Apher Sci, 2015, 53( 3): 283- 287. DOI: 10.1016/j.transci.2015.11.008. |
| [21] |
PENG R, ZHANG XM, ZHANG L, et al. CT findings of acute pancreatitis with pneumonia and its clinical correlation analysis[J]. Radiol Pract, 2020, 35( 1): 68- 73. DOI: 10.13609/j.cnki.1000-0313.2020.01.013. |
| [22] |
SHEN HN, CHANG YH, CHEN HF, et al. Increased risk of severe acute pancreatitis in patients with diabetes[J]. Diabet Med, 2012, 29( 11): 1419- 1424. DOI: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2012.03680.x. |
| [23] |
URUSHIHARA H, TAKETSUNA M, LIU Y, et al. Increased risk of acute pancreatitis in patients with type 2 diabetes: An observational study using a Japanese hospital database[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7( 12): e53224. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053224. |
| [24] |
SCHÜTTE K, MALFERTHEINER P. Markers for predicting severity and progression of acute pancreatitis[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol, 2008, 22( 1): 75- 90. DOI: 10.1016/j.bpg.2007.10.013. |
| [25] |
ZHOU HJ, MEI X, HE XH, et al. Severity stratification and prognostic prediction of patients with acute pancreatitis at early phase: A retrospective study[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2019, 98( 16): e15275. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015275. |
| [26] |
KONG WH, HE YY, BAO HR, et al. Diagnostic value of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio for predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis: A meta-analysis[J]. Dis Markers, 2020, 2020: 9731854. DOI: 10.1155/2020/9731854. |
| [27] |
LIU DL, WEN LL, WANG ZD, et al. The mechanism of lung and intestinal injury in acute pancreatitis: A review[J]. Front Med(Lausanne), 2022, 9: 904078. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.904078. |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
CASQUEIRO J, CASQUEIRO J, ALVES C. Infections in patients with diabetes mellitus: A review of pathogenesis[J]. Indian J Endocrinol Metab, 2012, 16( Suppl1): S27- S36. DOI: 10.4103/2230-8210.94253. |



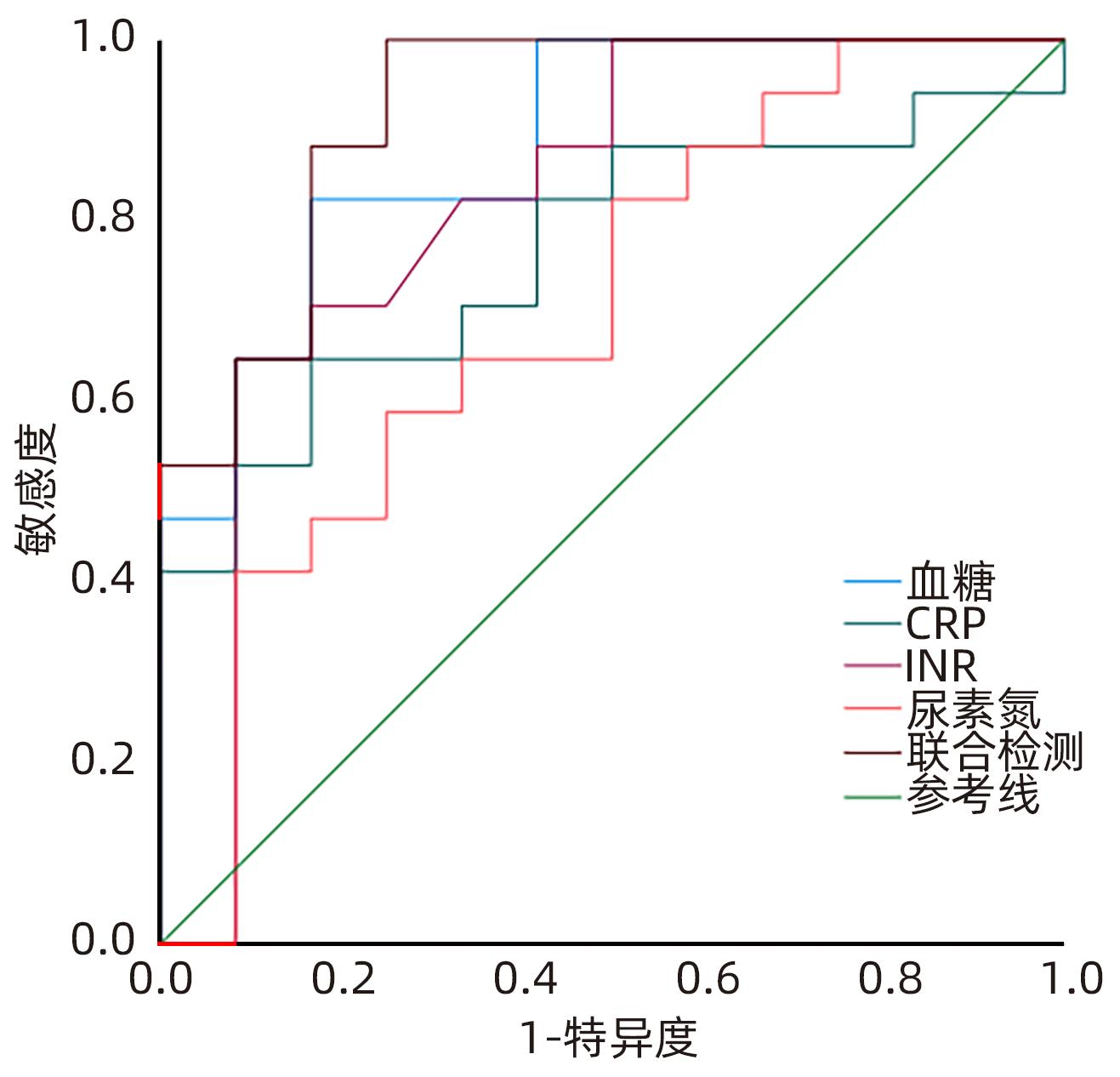




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: