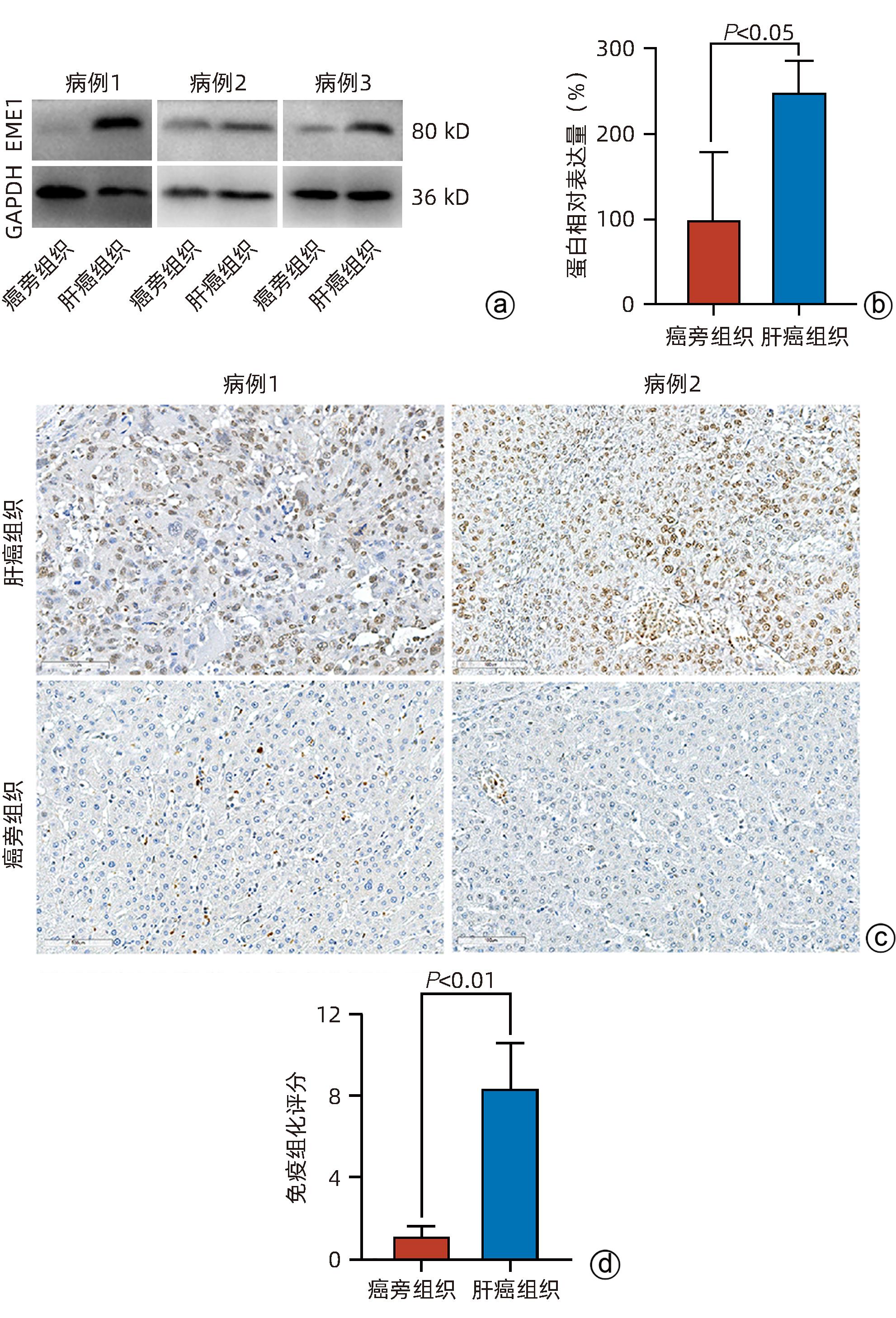
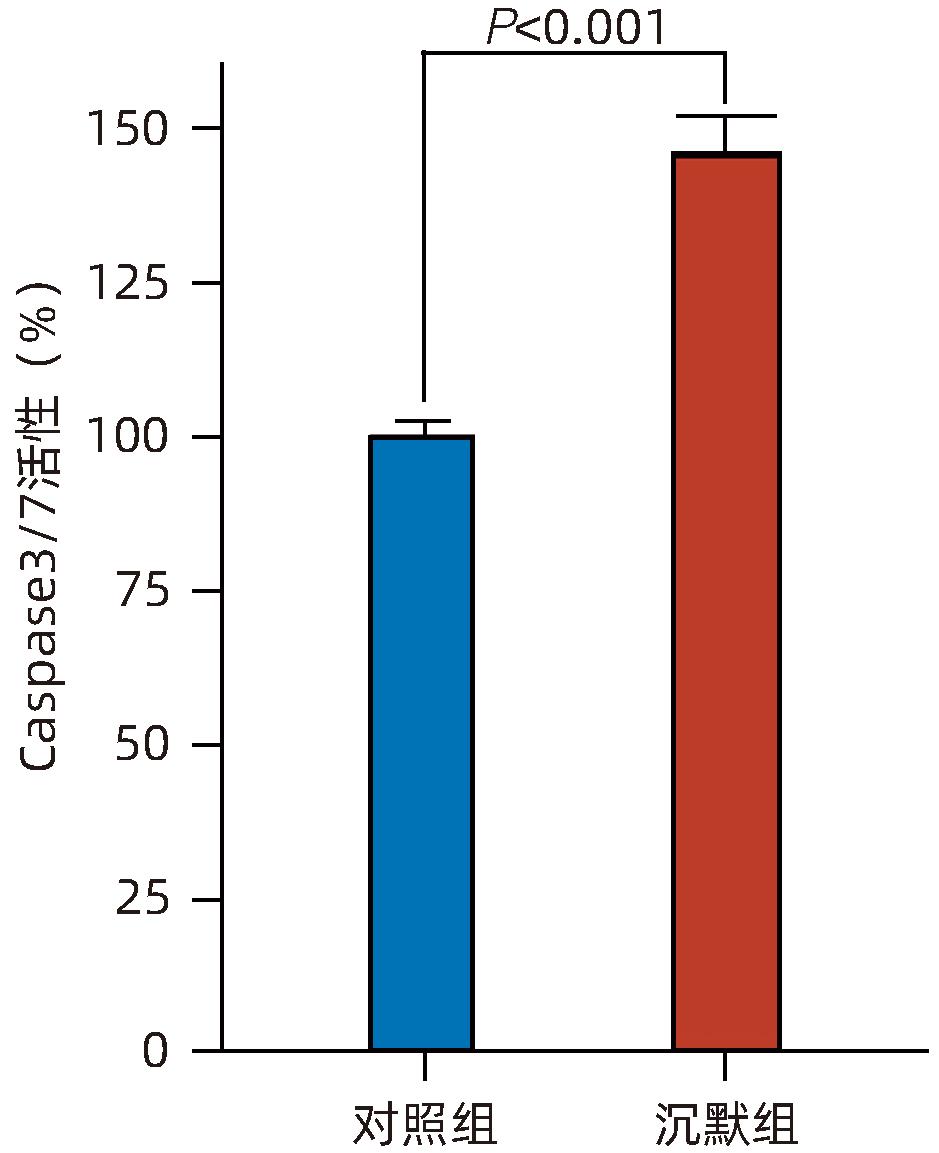
| [1] |
SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71( 3): 209- 249. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21660. |
| [2] |
LLOVET JM, KELLEY RK, VILLANUEVA A, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2021, 7: 6. DOI: 10.1038/s41572-020-00240-3. |
| [3] |
CHEN SH, WANG CY, GUO C, et al. Establishment of a nomogram model for predicting the survival of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 7): 1566- 1571. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.07.020. |
| [4] |
WANG JJ, WANG KX, CHEN C, et al. Survival analysis and development of a prognostic nomogram for patients with hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9( 10): e20850. DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20850. |
| [5] |
JI D, CHEN Y, BI JF, et al. Entecavir plus Biejia-Ruangan compound reduces the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 77( 6): 1515- 1524. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.07.018. |
| [6] |
GWON GH, JO A, BAEK K, et al. Crystal structures of the structure-selective nuclease Mus81-Eme1 bound to flap DNA substrates[J]. EMBO J, 2014, 33( 9): 1061- 1072. DOI: 10.1002/embj.201487820. |
| [7] |
HAN YY, ZHENG QY, TIAN Y, et al. Identification of a nine-gene panel as a prognostic indicator for recurrence with muscle-invasive bladder cancer[J]. J Surg Oncol, 2019, 119( 8): 1145- 1154. DOI: 10.1002/jso.25446. |
| [8] |
VÉQUAUD E, DESPLANQUES G, JÉZÉQUEL P, et al. Survivin contributes to DNA repair by homologous recombination in breast cancer cells[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2016, 155( 1): 53- 63. DOI: 10.1007/s10549-015-3657-z. |
| [9] |
PENG L, LIANG J, WANG Q, et al. A DNA damage repair gene signature associated with immunotherapy response and clinical prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Front Genet, 2022, 13: 798846. DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.798846. |
| [10] |
GUO ZG, LIANG EB, LI W, et al. Essential meiotic structure-specific endonuclease1(EME1) promotes malignant features in gastric cancer cells via the Akt/GSK3B/CCND1 pathway[J]. Bioengineered, 2021, 12( 2): 9869- 9884. DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1999371. |
| [11] |
WANG YX, HUANG XL, SU ZH, et al. The Glu69Asp polymorphism of EME1 gene is associated with an increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in Guangxi population, China[J]. Int J Gen Med, 2022, 15: 7855- 7866. DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S383261. |
| [12] |
ZHAO JW, LIU L, ZHANG AQ, et al. Effect of EME1 exon variant Ile350Thr on risk and early onset of breast cancer in southern Chinese women[J]. J Biomed Res, 2013, 27( 3): 193- 201. DOI: 10.7555/JBR.27.20130013. |
| [13] |
SUZUKI T, YASUI M, HONMA M. Mutator phenotype and DNA double-strand break repair in BLM helicase-deficient human cells[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2016, 36( 23): 2877- 2889. DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00443-16. |
| [14] |
SHAMMAS MA, SHMOOKLER REIS RJ, KOLEY H, et al. Dysfunctional homologous recombination mediates genomic instability and progression in myeloma[J]. Blood, 2009, 113( 10): 2290- 2297. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-05-089193. |
| [15] |
FULDA S. Tumor resistance to apoptosis[J]. Int J Cancer, 2009, 124( 3): 511- 515. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.24064. |
| [16] |
SZAKAL B, BRANZEI D. Premature Cdk1/Cdc5/Mus81 pathway activation induces aberrant replication and deleterious crossover[J]. EMBO J, 2013, 32( 8): 1155- 1167. DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2013.67. |
| [17] |
PALMA A, PUGLIESE GM, MURFUNI I, et al. Phosphorylation by CK2 regulates MUS81/EME1 in mitosis and after replication stress[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2018, 46( 10): 5109- 5124. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gky280. |
| [18] |
GUO YG, ZHU ZH, HUANG ZY, et al. CK2-induced cooperation of HHEX with the YAP-TEAD4 complex promotes colorectal tumorigenesis[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13( 1): 4995. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-32674-6. |
| [19] |
KWON J, ZHANG JM, MOK B, et al. CK2-mediated phosphorylation upregulates the stability of USP13 and promotes ovarian cancer cell proliferation[J]. Cancers, 2022, 15( 1): 200. DOI: 10.3390/cancers15010200. |
| [20] |
PITRODA SP, PASHTAN IM, LOGAN HL, et al. DNA repair pathway gene expression score correlates with repair proficiency and tumor sensitivity to chemotherapy[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2014, 6( 229): 229ra42. DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3008291. |
| [21] |
XU YH, LI J, ZHU KK, et al. FIBP interacts with transcription factor STAT3 to induce EME1 expression and drive radioresistance in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2023, 19( 12): 3816- 3829. DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.83134. |
| [22] |
WEINANDY A, PIROTH MD, GOSWAMI A, et al. Cetuximab induces eme1-mediated DNA repair: A novel mechanism for cetuximab resistance[J]. Neoplasia, 2014, 16( 3): 207- 220, 220.e1- 220. e4. DOI: 10.1016/j.neo.2014.03.004. |



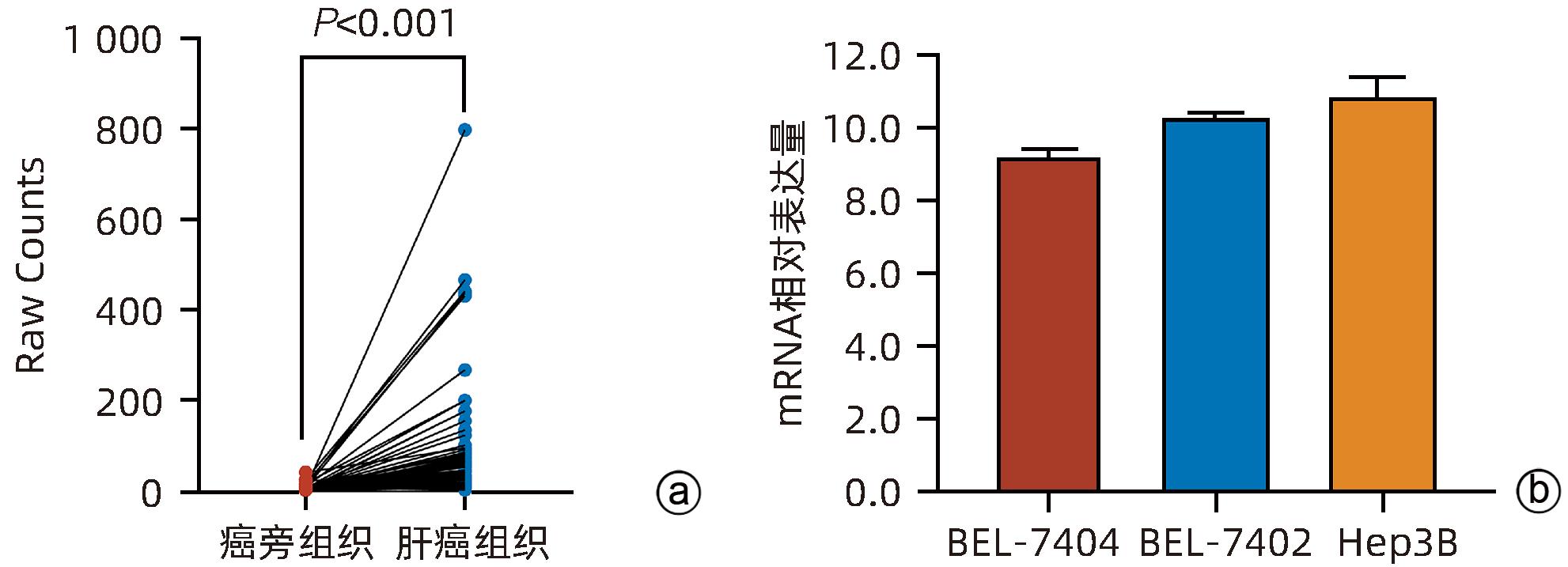




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: