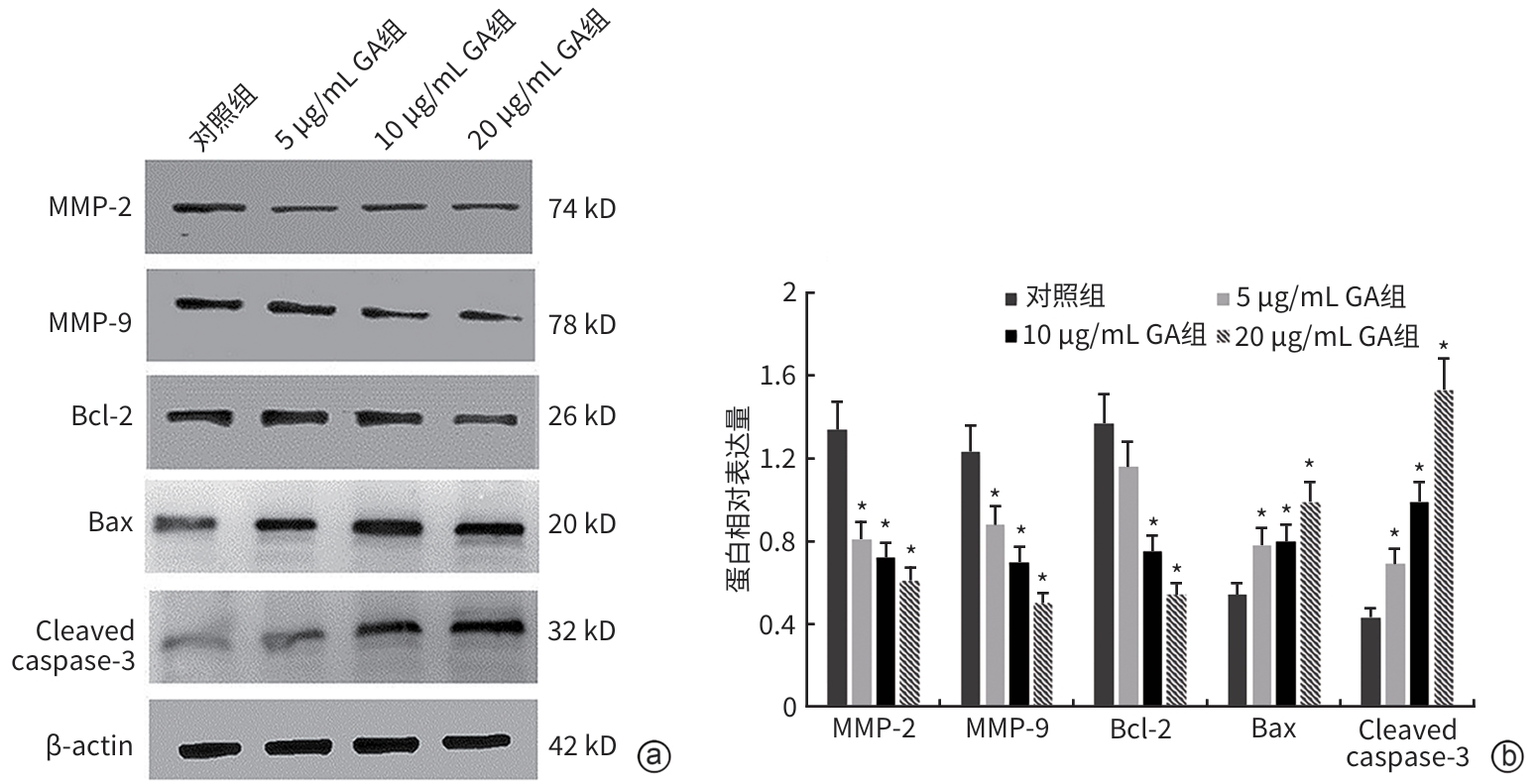
| [1] |
SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71( 3): 209- 249. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21660. |
| [2] |
JIN AH, ZHU JB, YIN XZ, et al. Effect of iridoid glycosides from Boschniakia rossica on epithelial-mesenchymal transition of HepG2 cells induced by transforming growth factor-beta 1[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2024, 40( 6): 1175- 1182. DOI: 10.12449/JCH240617. 金爱花, 朱洁波, 尹学哲, 等. 草苁蓉环烯醚萜苷(IGBR)对TGF-β1诱导的HepG2细胞上皮间质转化模型的影响[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40( 6): 1175- 1182. DOI: 10.12449/JCH240617. |
| [3] |
XIE DY, SHI JY, ZHOU J, et al. Clinical practice guidelines and real-life practice in hepatocellular carcinoma: A Chinese perspective[J]. Clin Mol Hepatol, 2023, 29( 2): 206- 216. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2022.0402. |
| [4] |
FAN R, PAPATHEODORIDIS G, SUN J, et al. aMAP risk score predicts hepatocellular carcinoma development in patients with chronic hepatitis[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 73( 6): 1368- 1378. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.07.025. |
| [5] |
ZHOU J, SUN HC, WANG Z, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma(2019 edition)[J]. Liver Cancer, 2020, 9( 6): 682- 720. DOI: 10.1159/000509424. |
| [6] |
SUN GL, WANG D. Gallic acid from Terminalia chebula inhibited the growth of esophageal carcinoma cells by suppressing the Hippo signal pathway[J]. Iran J Basic Med Sci, 2020, 23( 11): 1401- 1408. DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.42283.9982. |
| [7] |
CHOI HJ, SONG JH, BHATT LR, et al. Anti-human rhinovirus activity of Gallic acid possessing antioxidant capacity[J]. Phytother Res, 2010, 24( 9): 1292- 1296. DOI: 10.1002/ptr.3101. |
| [8] |
LIN XM, WANG GF, LIU P, et al. Gallic acid suppresses colon cancer proliferation by inhibiting SRC and EGFR phosphorylation[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2021, 21( 6): 638. DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.10070. |
| [9] |
ZHANG TX, MA LJ, WU PF, et al. Gallic acid has anticancer activity and enhances the anticancer effects of cisplatin in non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells via the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. Oncol Rep, 2019, 41( 3): 1779- 1788. DOI: 10.3892/or.2019.6976. |
| [10] |
YANG XL, XUE JH, CHEN TY, et al. Effect of atractylone on the viability and apoptosis of hepatoma HepG2 cells and related mechanism[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37( 11): 2589- 2594. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.11.020. |
| [11] |
QU Y, ZHANG WJ, CHEN FF, et al. Progress in research and development of chemical drugs and treatment of liver cancer[J]. Gansu Sci Technol, 2023, 39( 8): 114- 119, 127. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0952.2023.08.028. |
| [12] |
ZHAO YY, HAN ZQ, ZOU YP, et al. Effect of lysophosphatidic acid on hepatoma cells and related mechanism[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 11): 2623- 2628. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.11.016. |
| [13] |
XU HC, WANG FL, XIE LH. Current status and perspectives in clinical treatment of intermediate and advanced primary hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Changchun Univ Chin Med, 2024, 40( 1): 103- 107. DOI: 10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2024.01.024. |
| [14] |
YANG C, ZHANG HL, ZHANG LM, et al. Evolving therapeutic landscape of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 20( 4): 203- 222. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-022-00704-9. |
| [15] |
WU H, NULAN BDL, LIU LY, et al. Inhibitory effects of Gallic acid on human esophageal cancer TE-1 cells in vitro and its mechanism[J]. China Pharm, 2022, 33( 12): 1448- 1454. DOI: 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2022.12.07. |
| [16] |
HAN QQ, YE MR, JIN QL. Demethylzeylasteral inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion and promotes apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting the AKT/CREB signaling pathway[J]. J South Med Univ, 2024, 44( 2): 280- 288. DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.02.10. |
| [17] |
XU GS, JIANG HB, PAN J, et al. Inhibitory effects of betulinic acid on migration and invasion of gastric cancer MGC-803 cells and their mechanisms[J]. J Jilin Univ(Med Edit), 2022, 48( 1): 122- 128. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220115. |
| [18] |
JIANG B, YANG T, FENG LF, et al. Effects of salidroside on proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of 97H cells[J]. Chin Pharmacol Bull, 2023, 39( 3): 445- 452. DOI: 10.12360/CPB202202019. 蒋兵, 杨韬, 封龙飞, 等. 红景天苷对97H细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭及凋亡的影响[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2023, 39( 3): 445- 452. DOI: 10.12360/CPB202202019. |
| [19] |
PANG LL, HU Y, LUO J, et al. Study of the mechanism of combretastatin a-4 derivative LGD5 induced G2/M cycle arrest and apoptosis in human cervical cancer HeLa cells[J]. Chin J Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2024, 29( 10): 1100- 1109. DOI: 10.12092/j.issn.1009-2501.2024.10.003. |
| [20] |
YUAN CL, CHEN GP, JING CB, et al. Eriocitrin, a dietary flavonoid suppressed cell proliferation, induced apoptosis through modulation of JAK2/STAT3 and JNK/p38 MAPKs signaling pathway in MCF-7 cells[J]. J Biochem Mol Toxicol, 2022, 36( 1): e22943. DOI: 10.1002/jbt.22943. |
| [21] |
WANG ZY, ZHANG H, ZHOU JH, et al. Eriocitrin from lemon suppresses the proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through inducing apoptosis and arresting cell cycle[J]. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, 2016, 78( 6): 1143- 1150. DOI: 10.1007/s00280-016-3171-y. |
| [22] |
ZHOU H, ZHANG YQ, GAN C, et al. Eriocitrin suppresses proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells by promoting ROS production and activating the MAPK pathway[J]. J South Med Univ, 2023, 43( 3): 412- 419. DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.03.11. |



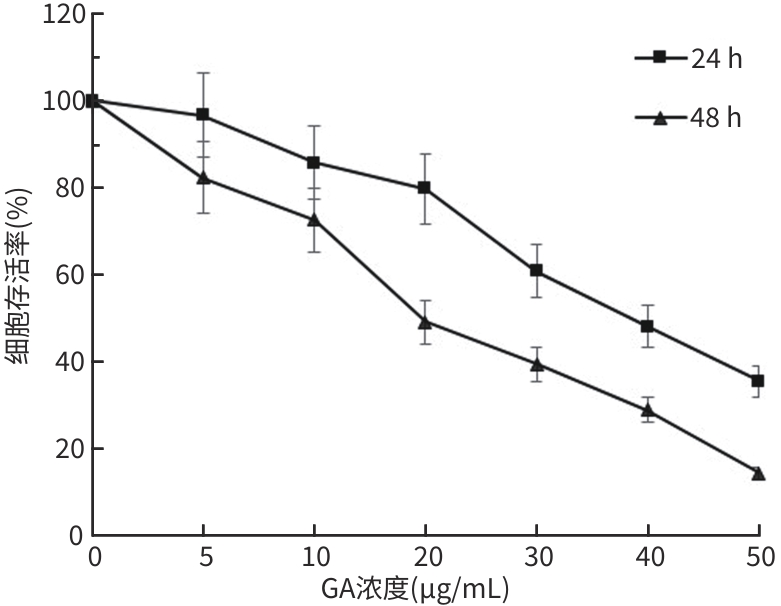




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: