| [1] |
SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71( 3): 209- 249. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21660. |
| [2] |
REHMAN O, JAFERI U, PADDA I, et al. Overview of lenvatinib as a targeted therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Clin Exp Hepatol, 2021, 7( 3): 249- 257. DOI: 10.5114/ceh.2021.109312. |
| [3] |
KUDO M, FINN RS, QIN SK, et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial[J]. Lancet, 2018, 391( 10126): 1163- 1173. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30207-1. |
| [4] |
MATSUKI M, HOSHI T, YAMAMOTO Y, et al. Lenvatinib inhibits angiogenesis and tumor fibroblast growth factor signaling pathways in human hepatocellular carcinoma models[J]. Cancer Med, 2018, 7( 6): 2641- 2653. DOI: 10.1002/cam4.1517. |
| [5] |
OGASAWARA S, MIHARA Y, KONDO R, et al. Antiproliferative effect of lenvatinib on human liver cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo[J]. Anticancer Res, 2019, 39( 11): 5973- 5982. DOI: 10.21873/anticanres.13802. |
| [6] |
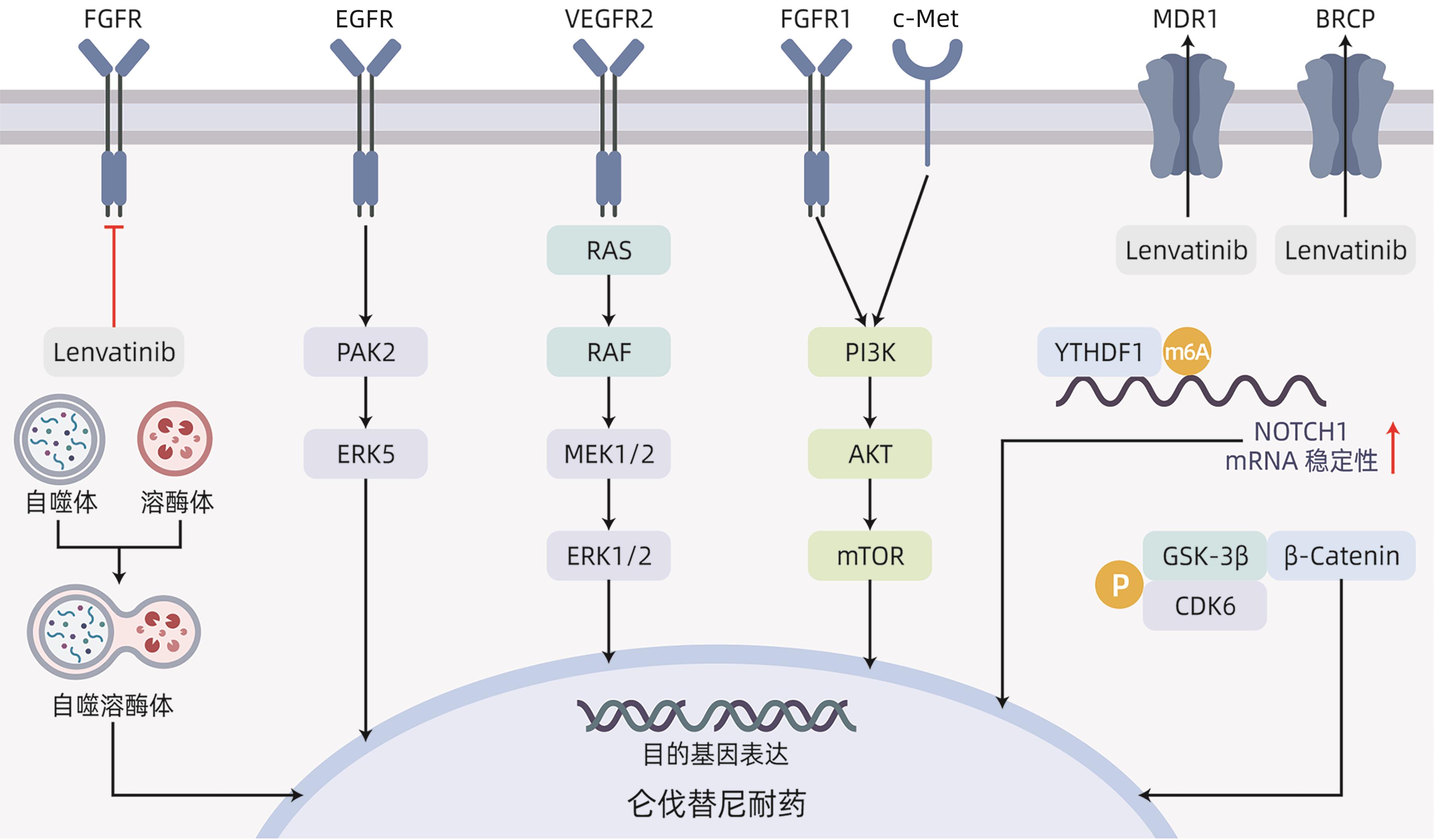
JIN HJ, SHI YP, LV YY, et al. EGFR activation limits the response of liver cancer to lenvatinib[J]. Nature, 2021, 595( 7869): 730- 734. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-03741-7. |
| [7] |
HE XP, HIKIBA Y, SUZUKI Y, et al. EGFR inhibition reverses resistance to lenvatinib in hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12( 1): 8007. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-12076-w. |
| [8] |
WANG LN, YANG QX, ZHOU QY, et al. METTL3-m 6A-EGFR-axis drives lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Lett, 2023, 559: 216122. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216122. |
| [9] |
HUANG ML, LONG JT, YAO ZJ, et al. METTL1-mediated m7G tRNA modification promotes lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Res, 2023, 83( 1): 89- 102. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-0963. |
| [10] |
ZHAO ZW, ZHANG DK, WU FZ, et al. Sophoridine suppresses lenvatinib-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma growth by inhibiting RAS/MEK/ERK axis via decreasing VEGFR2 expression[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2021, 25( 1): 549- 560. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.16108. |
| [11] |
BYRON SA, CHEN HB, WORTMANN A, et al. The N550K/H mutations in FGFR2 confer differential resistance to PD173074, dovitinib, and ponatinib ATP-competitive inhibitors[J]. Neoplasia, 2013, 15( 8): 975- 988. DOI: 10.1593/neo.121106. |
| [12] |
ZHAO ZW, SONG JJ, ZHANG DK, et al. Oxysophocarpine suppresses FGFR1-overexpressed hepatocellular carcinoma growth and sensitizes the therapeutic effect of lenvatinib[J]. Life Sci, 2021, 264: 118642. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118642. |
| [13] |
WANG JQ, WU ZX, YANG YQ, et al. ATP-binding cassette(ABC) transporters in cancer: A review of recent updates[J]. J Evid Based Med, 2021, 14( 3): 232- 256. DOI: 10.1111/jebm.12434. |
| [14] |
SHUMAKER RC, ALURI J, FAN J, et al. Effect of rifampicin on the pharmacokinetics of lenvatinib in healthy adults[J]. Clin Drug Investig, 2014, 34( 9): 651- 659. DOI: 10.1007/s40261-014-0217-y. |
| [15] |
SHUMAKER R, ALURI J, FAN J, et al. Effects of ketoconazole on the pharmacokinetics of lenvatinib(E7080) in healthy participants[J]. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev, 2015, 4( 2): 155- 160. DOI: 10.1002/cpdd.140. |
| [16] |
SUN DW, LIU J, WANG YF, et al. Co-administration of MDR1 and BCRP or EGFR/PI3K inhibitors overcomes lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 944537. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.944537. |
| [17] |
ONORATI AV, DYCZYNSKI M, OJHA R, et al. Targeting autophagy in cancer[J]. Cancer, 2018, 124( 16): 3307- 3318. DOI: 10.1002/cncr.31335. |
| [18] |
HU FQ, SONG D, YAN YM, et al. IL-6 regulates autophagy and chemotherapy resistance by promoting BECN1 phosphorylation[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12( 1): 3651. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23923-1. |
| [19] |
XU WP, LIU JP, FENG JF, et al. MiR-541 potentiates the response of human hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib treatment by inhibiting autophagy[J]. Gut, 2020, 69( 7): 1309- 1321. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318830. |
| [20] |
PAN JM, ZHANG M, DONG LQ, et al. Genome-Scale CRISPR screen identifies LAPTM5 driving lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Autophagy, 2023, 19( 4): 1184- 1198. DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2117893. |
| [21] |
ZHANG YX, ZHANG YJ, TAO HS, et al. Targeting LINC01607 sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma to lenvatinib via suppressing mitophagy[J]. Cancer Lett, 2023, 576: 216405. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216405. |
| [22] |
FERNÁNDEZ-PALANCA P, PAYO-SERAFÍN T, SAN-MIGUEL B, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma cells loss lenvatinib efficacy in vitro through autophagy and hypoxia response-derived neuropilin-1 degradation[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2023, 44( 5): 1066- 1082. DOI: 10.1038/s41401-022-01021-2. |
| [23] |
WANG BJ, TIAN T, KALLAND KH, et al. Targeting Wnt/β-catenin signaling for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2018, 39( 7): 648- 658. DOI: 10.1016/j.tips.2018.03.008. |
| [24] |
RUSSELL JO, MONGA SP. Wnt/β-catenin signaling in liver development, homeostasis, and pathobiology[J]. Annu Rev Pathol, 2018, 13: 351- 378. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-020117-044010. |
| [25] |
GUO YR, XU J, DU Q, et al. IRF2 regulates cellular survival and Lenvatinib-sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC) through regulating β-catenin[J]. Transl Oncol, 2021, 14( 6): 101059. DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2021.101059. |
| [26] |
WANG JH, YU HM, DONG W, et al. N6-methyladenosine-mediated up-regulation of FZD10 regulates liver cancer stem cells’ properties and lenvatinib resistance through WNT/β-catenin and hippo signaling pathways[J]. Gastroenterology, 2023, 164( 6): 990- 1005. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.01.041. |
| [27] |
LEUNG CON, YANG Y, LEUNG RWH, et al. Broad-spectrum kinome profiling identifies CDK6 upregulation as a driver of lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14( 1): 6699. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42360-w. |
| [28] |
VENKATESH V, NATARAJ R, THANGARAJ GS, et al. Targeting Notch signalling pathway of cancer stem cells[J]. Stem Cell Investig, 2018, 5: 5. DOI: 10.21037/sci.2018.02.02. |
| [29] |
TAKEBE N, MIELE L, HARRIS PJ, et al. Targeting Notch, Hedgehog, and Wnt pathways in cancer stem cells: Clinical update[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2015, 12( 8): 445- 464. DOI: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2015.61. |
| [30] |
ZHANG XY, SU TH, WU YF, et al. N6-methyladenosine reader YTHDF1 promotes stemness and therapeutic resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by enhancing NOTCH1 expression[J]. Cancer Res, 2024, 84( 6): 827- 840. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-1916. |
| [31] |
FENG WQ, ZHANG HX, YU Q, et al. Study on the mechanism of Notch pathway mediates the role of lenvatinib-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma based on organoids[J]. Curr Mol Med, 2024. DOI: 10.2174/0115665240268201231213095302.[ Online ahead of print] |
| [32] |
YANG SB, ZHOU ZH, LEI J, et al. TM4SF1 upregulates MYH9 to activate the NOTCH pathway to promote cancer stemness and lenvatinib resistance in HCC[J]. Biol Direct, 2023, 18( 1): 18. DOI: 10.1186/s13062-023-00376-8. |
| [33] |
MOON H, RO SW. MAPK/ERK signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancers, 2021, 13( 12): 3026. DOI: 10.3390/cancers13123026. |
| [34] |
HUANG SZ, MA ZY, ZHOU Q, et al. Genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 library screening identified that DUSP4 deficiency induces lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2022, 18( 11): 4357- 4371. DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.69969. |
| [35] |
CHEN HF, CHUANG HC, TAN TH. Regulation of dual-specificity phosphatase(DUSP) ubiquitination and protein stability[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20( 11): 2668. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20112668. |
| [36] |
LU YG, SHEN HM, HUANG WJ, et al. Genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screening in hepatocellular carcinoma with lenvatinib resistance[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2021, 7( 1): 359. DOI: 10.1038/s41420-021-00747-y. |
| [37] |
MOOSAVI F, GIOVANNETTI E, SASO L, et al. HGF/MET pathway aberrations as diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive biomarkers in human cancers[J]. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci, 2019, 56( 8): 533- 566. DOI: 10.1080/10408363.2019.1653821. |
| [38] |
FU RD, JIANG ST, LI JY, et al. Activation of the HGF/c-MET axis promotes lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells with high c-MET expression[J]. Med Oncol, 2020, 37( 4): 24. DOI: 10.1007/s12032-020-01350-4. |
| [39] |
XU X, JIANG WJ, HAN P, et al. MicroRNA-128-3p mediates lenvatinib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by downregulating c-met[J]. J Hepatocell Carcinoma, 2022, 9: 113- 126. DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S349369. |
| [40] |
JIANG XJ, STOCKWELL BR, CONRAD M. Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2021, 22( 4): 266- 282. DOI: 10.1038/s41580-020-00324-8. |
| [41] |
ISEDA N, ITOH S, TOSHIDA K, et al. Ferroptosis is induced by lenvatinib through fibroblast growth factor receptor-4 inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Sci, 2022, 113( 7): 2272- 2287. DOI: 10.1111/cas.15378. |
| [42] |
DUAN AQ, LI H, YU WL, et al. Long noncoding RNA XIST promotes resistance to lenvatinib in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via epigenetic inhibition of NOD2[J]. J Oncol, 2022, 2022: 4537343. DOI: 10.1155/2022/4537343. |
| [43] |
WANG Y, TAN K, HU W, et al. LncRNA AC026401.3 interacts with OCT1 to intensify sorafenib and lenvatinib resistance by activating E2F2 signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2022, 420( 1): 113335. DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2022.113335. |
| [44] |
YU T, YU JJ, LU L, et al. MT1JP-mediated miR-24-3p/BCL2L2 axis promotes Lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting apoptosis[J]. Cell Oncol, 2021, 44( 4): 821- 834. DOI: 10.1007/s13402-021-00605-0. |
| [45] |
ZHANG PF, SUN HX, WEN PH, et al. circRNA circMED27 acts as a prognostic factor and mediator to promote lenvatinib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2022, 27: 293- 303. DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.12.001. |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: