| [1] |
ZHENG YL, LI L, JIA YX, et al. LINC01554-mediated glucose metabolism reprogramming suppresses tumorigenicity in hepatocellular carcinoma via downregulating PKM2 expression and inhibiting Akt/mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Theranostics, 2019, 9( 3): 796- 810. DOI: 10.7150/thno.28992. |
| [2] |
RUMGAY H, ARNOLD M, FERLAY J, et al. Global burden of primary liver cancer in 2020 and predictions to 2040[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 77( 6): 1598- 1606. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.08.021. |
| [3] |
Department of Medical Emergency, National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Healthy China action-implementation plan of cancer prevention action(2023-2030)[J]. China Cancer, 2023, 32( 12): 887- 890. DOI: 10.11735/j.issn.1004-0242.2023.12.A001. |
| [4] |
NONG SQ, HAN XY, XIANG Y, et al. Metabolic reprogramming in cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutics[J]. MedComm(2020), 2023, 4( 2): e218. DOI: 10.1002/mco2.218. |
| [5] |
FOGLIA B, BELTRÀ M, SUTTI S, et al. Metabolic reprogramming of HCC: A new microenvironment for immune responses[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24( 8): 7463. DOI: 10.3390/ijms24087463. |
| [6] |
PAGET S. The distribution of secondary growths in cancer of the breast. 1889[J]. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 1989, 8( 2): 98- 101.
|
| [7] |
ZHANG Q, LOU Y, BAI XL, et al. Immunometabolism: A novel perspective of liver cancer microenvironment and its influence on tumor progression[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2018, 24( 31): 3500- 3512. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i31.3500. |
| [8] |
KOTSARI M, DIMOPOULOU V, KOSKINAS J, et al. Immune system and hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC): New insights into HCC progression[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24( 14): 11471. DOI: 10.3390/ijms241411471. |
| [9] |
PAULUSMA CC, LAMERS WH, BROER S, et al. Amino acid metabolism, transport and signalling in the liver revisited[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2022, 201: 115074. DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115074. |
| [10] |
ZHENG Y, YAO YR, GE TX, et al. Amino acid metabolism reprogramming: Shedding new light on T cell anti-tumor immunity[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2023, 42( 1): 291. DOI: 10.1186/s13046-023-02845-4. |
| [11] |
ZHANG XH, ZHANG SY, LI L. Amino acid metabolic reprogramming in tumorigenesis and development[J]. Chin J Biochem Mol Biol, 2023, 39( 2): 174- 188. DOI: 10.13865/j.cnki.cjbmb.2022.06.1105. |
| [12] |
YANG F, HILAKIVI-CLARKE L, SHAHA A, et al. Metabolic reprogramming and its clinical implication for liver cancer[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 78( 5): 1602- 1624. DOI: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000005. |
| [13] |
WANG YY, BAI CS, RUAN YX, et al. Coordinative metabolism of glutamine carbon and nitrogen in proliferating cancer cells under hypoxia[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10( 1): 201. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-08033-9. |
| [14] |
JIN HJ, WANG SY, ZAAL EA, et al. A powerful drug combination strategy targeting glutamine addiction for the treatment of human liver cancer[J]. eLife, 2020, 9: e56749. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.56749. |
| [15] |
LIN J, RAO DN, ZHANG M, et al. Metabolic reprogramming in the tumor microenvironment of liver cancer[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2024, 17( 1): 6. DOI: 10.1186/s13045-024-01527-8. |
| [16] |
TIAN LY, SMIT DJ, JÜCKER M. The role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma metabolism[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24( 3): 2652. DOI: 10.3390/ijms24032652. |
| [17] |
MERLIN J, IVANOV S, DUMONT A, et al. Non-canonical glutamine transamination sustains efferocytosis by coupling redox buffering to oxidative phosphorylation[J]. Nat Metab, 2021, 3( 10): 1313- 1326. DOI: 10.1038/s42255-021-00471-y. |
| [18] |
MA GF, ZHANG ZL, LI P, et al. Reprogramming of glutamine metabolism and its impact on immune response in the tumor microenvironment[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2022, 20( 1): 114. DOI: 10.1186/s12964-022-00909-0. |
| [19] |
YE YY, YU BD, WANG H, et al. Glutamine metabolic reprogramming in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Front Mol Biosci, 2023, 10: 1242059. DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1242059. |
| [20] |
PENG H, WANG YF, LUO WB. Multifaceted role of branched-chain amino acid metabolism in cancer[J]. Oncogene, 2020, 39( 44): 6747- 6756. DOI: 10.1038/s41388-020-01480-z. |
| [21] |
BONVINI A, ROGERO MM, COQUEIRO AY, et al. Effects of different branched-chain amino acids supplementation protocols on the inflammatory response of LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages[J]. Amino Acids, 2021, 53( 4): 597- 607. DOI: 10.1007/s00726-021-02940-w. |
| [22] |
LING ZN, JIANG YF, RU JN, et al. Amino acid metabolism in health and disease[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8( 1): 345. DOI: 10.1038/s41392-023-01569-3. |
| [23] |
HU GY, CUI Z, CHEN XY, et al. Suppressing mesenchymal stromal cell ferroptosis via targeting a metabolism-epigenetics axis corrects their poor retention and insufficient healing benefits in the injured liver milieu[J]. Adv Sci(Weinh), 2023, 10( 13): e2206439. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202206439. |
| [24] |
MOSSMANN D, MÜLLER C, PARK S, et al. Arginine reprograms metabolism in liver cancer via RBM39[J]. Cell, 2023, 186( 23): 5068- 5083. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.09.011. |
| [25] |
LÍNDEZ AA MI, REITH W. Arginine-dependent immune responses[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2021, 78( 13): 5303- 5324. DOI: 10.1007/s00018-021-03828-4. |
| [26] |
SICA A, PORTA C, MORLACCHI S, et al. Origin and functions of tumor-associated myeloid cells(TAMCs)[J]. Cancer Microenviron, 2012, 5( 2): 133- 149. DOI: 10.1007/s12307-011-0091-6. |
| [27] |
YANG LM, CHU ZL, LIU M, et al. Amino acid metabolism in immune cells: Essential regulators of the effector functions, and promising opportunities to enhance cancer immunotherapy[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2023, 16( 1): 59. DOI: 10.1186/s13045-023-01453-1. |
| [28] |
MISSIAEN R, ANDERSON NM, KIM LC, et al. GCN2 inhibition sensitizes arginine-deprived hepatocellular carcinoma cells to senolytic treatment[J]. Cell Metab, 2022, 34( 8): 1151- 1167. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.06.010. |
| [29] |
TRÉZÉGUET V, FATROUNI H, MERCHED AJ. Immuno-metabolic modulation of liver oncogenesis by the tryptophan metabolism[J]. Cells, 2021, 10( 12): 3469. DOI: 10.3390/cells10123469. |
| [30] |
SOLVAY M, HOLFELDER P, KLAESSENS S, et al. Tryptophan depletion sensitizes the AHR pathway by increasing AHR expression and GCN2/LAT1-mediated kynurenine uptake, and potentiates induction of regulatory T lymphocytes[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2023, 11( 6): e006728. DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2023-006728. |
| [31] |
CAMPESATO LF, BUDHU S, TCHAICHA J, et al. Blockade of the AHR restricts a Treg-macrophage suppressive axis induced by L-Kynurenine[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11( 1): 4011. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-17750-z. |
| [32] |
DEY S, MONDAL A, DUHADAWAY JB, et al. IDO1 signaling through GCN2 in a subpopulation of gr-1 + cells shifts the IFNγ/IL6 balance to promote neovascularization[J]. Cancer Immunol Res, 2021, 9( 5): 514- 528. DOI: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-20-0226. |
| [33] |
HEZAVEH K, SHINDE RS, KLÖTGEN A, et al. Tryptophan-derived microbial metabolites activate the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in tumor-associated macrophages to suppress anti-tumor immunity[J]. Immunity, 2022, 55( 2): 324- 340. DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.01.006. |
| [34] |
GIRITHAR HN, STAATS PIRES A, AHN SB, et al. Involvement of the kynurenine pathway in breast cancer: Updates on clinical research and trials[J]. Br J Cancer, 2023, 129( 2): 185- 203. DOI: 10.1038/s41416-023-02245-7. |
| [35] |
LONG G, WANG D, TANG JN, et al. Development of tryptophan metabolism patterns to predict prognosis and immunotherapeutic responses in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Aging(Albany NY), 2023, 15( 15): 7593- 7615. DOI: 10.18632/aging.204928. |
| [36] |
PASCALE RM, PEITTA G, SIMILE MM, et al. Alterations of methionine metabolism as potential targets for the prevention and therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Medicina(Kaunas), 2019, 55( 6): 296. DOI: 10.3390/medicina55060296. |
| [37] |
ROY DG, CHEN J, MAMANE V, et al. Methionine metabolism shapes T helper cell responses through regulation of epigenetic reprogramming[J]. Cell Metab, 2020, 31( 2): 250- 266. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.006. |
| [38] |
HUNG MH, LEE JS, MA C, et al. Tumor methionine metabolism drives T-cell exhaustion in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12( 1): 1455. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-21804-1. |
| [39] |
SINCLAIR LV, HOWDEN AJ, BRENES A, et al. Antigen receptor control of methionine metabolism in T cells[J]. eLife, 2019, 8: e44210. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.44210. |
| [40] |
SAINI N, NAAZ A, METUR SP, et al. Methionine uptake via the SLC43A2 transporter is essential for regulatory T-cell survival[J]. Life Sci Alliance, 2022, 5( 12): e202201663. DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202201663. |
| [41] |
LI JT, YANG H, LEI MZ, et al. Dietary folate drives methionine metabolism to promote cancer development by stabilizing MAT IIA[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2022, 7( 1): 192. DOI: 10.1038/s41392-022-01017-8. |
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
ENDICOTT M, JONES M, HULL J. Amino acid metabolism as a therapeutic target in cancer: A review[J]. Amino Acids, 2021, 53( 8): 1169- 1179. DOI: 10.1007/s00726-021-03052-1. |



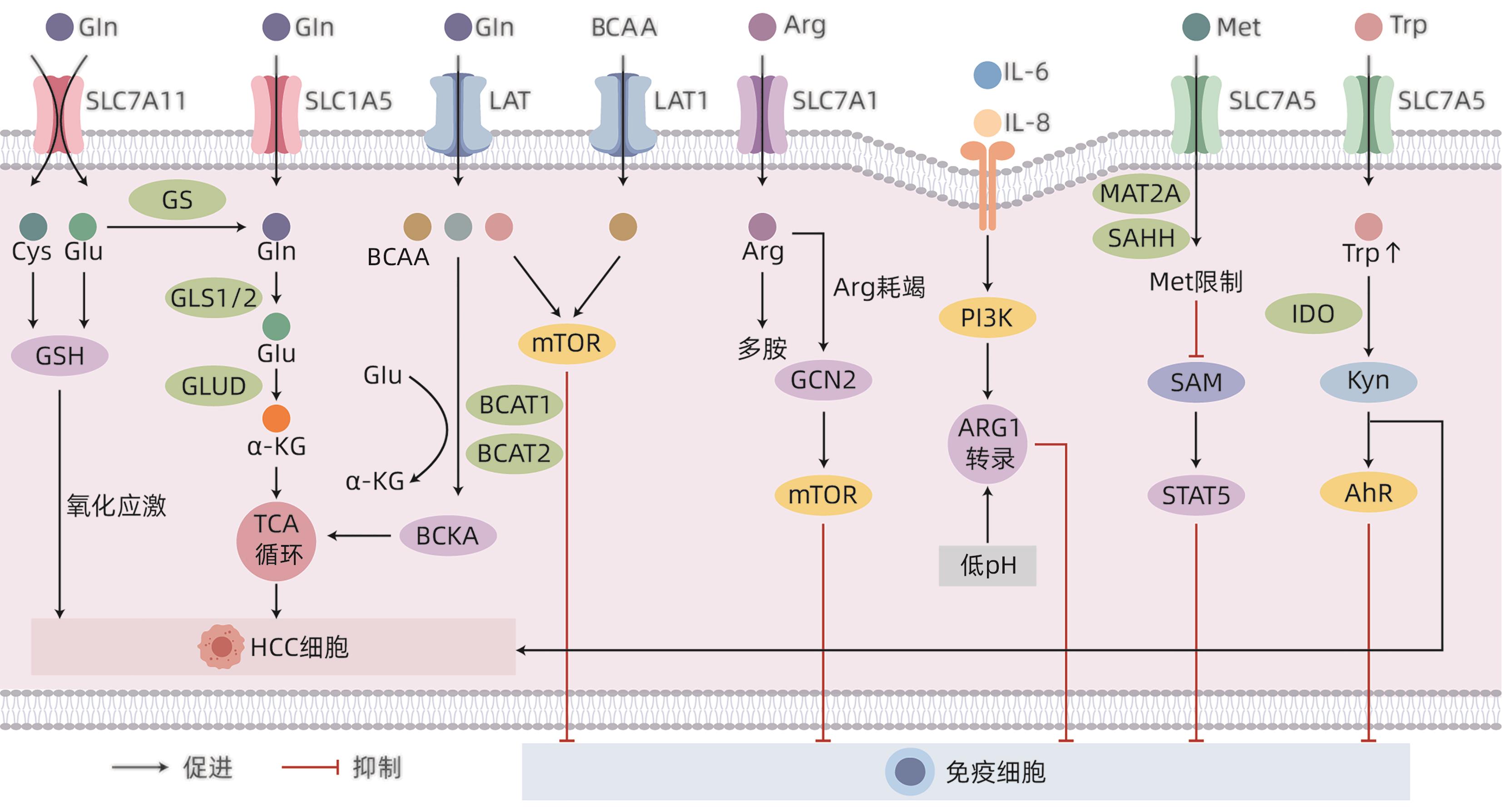




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: