| [1] |
JOHNSON CA, GISSEN P, SERGI C. Molecular pathology and genetics of congenital hepatorenal fibrocystic syndromes[J]. J Med Genet, 2003, 40( 5): 311- 319. DOI: 10.1136/jmg.40.5.311. |
| [2] |
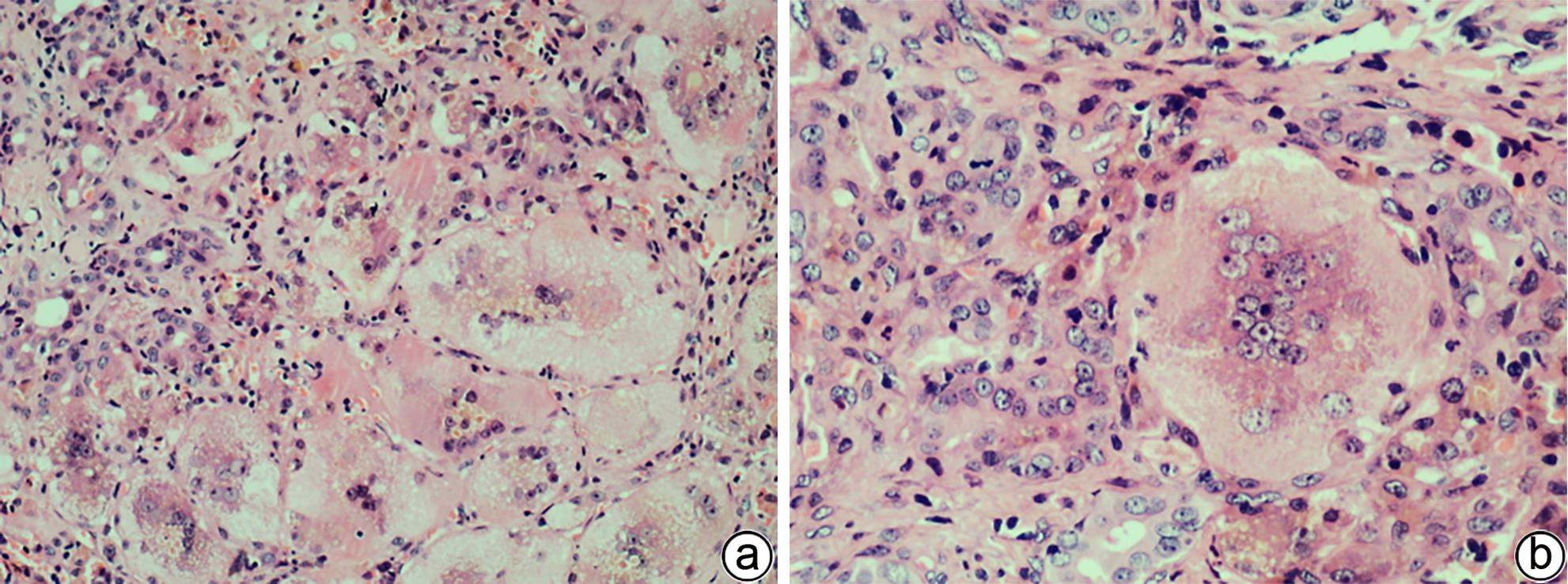
ESTRADAS J, PASCUAL-RAMOS V, MARTÍNEZ B, et al. Autoimmune hepatitis with giant-cell transformation[J]. Ann Hepatol, 2009, 8( 1): 68- 70.
|
| [3] |
SARCOGNATO S, SACCHI D, GRILLO F, et al. Autoimmune biliary diseases: Primary biliary cholangitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Pathologica, 2021, 113( 3): 170- 184. DOI: 10.32074/1591-951X-245. |
| [4] |
ZEN Y, HUBSCHER SG, NAKANUMA Y. Bile duct diseases. BurtAD, FerrellLD, HübscherSG, eds. MacSween’s pathology of the liver[M]. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier, 2018: 515.
|
| [5] |
TAKAHASHI T, MIURA T, NAKAMURA J, et al. Plasma cells and the chronic nonsuppurative destructive cholangitis of primary biliary cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2012, 55( 3): 846- 855. DOI: 10.1002/hep.24757. |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
KARLSEN TH, FOLSERAAS T, THORBURN D, et al. Primary sclerosing cholangitis-a comprehensive review[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 67( 6): 1298- 1323. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.07.022. |
| [8] |
HIRSCHFIELD GM, KARLSEN TH, LINDOR KD, et al. Primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Lancet, 2013, 382( 9904): 1587- 1599. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60096-3. |
| [9] |
PORTMANN B, ZEN Y. Inflammatory disease of the bile ducts-cholangiopathies: Liver biopsy challenge and clinicopathological correlation[J]. Histopathology, 2012, 60( 2): 236- 248. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2011.03853.x. |
| [10] |
COLLING R, VERRILL C, FRYER E, et al. Bile duct basement membrane thickening in primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Histopathology, 2016, 68( 6): 819- 824. DOI: 10.1111/his.12857. |
| [11] |
FIEL MI, SIMA HR, AZARIAN A, et al. A morphometric study of the hepatic arterioles in end-stage primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Virchows Arch, 2015, 466( 2): 143- 149. DOI: 10.1007/s00428-014-1680-9. |
| [12] |
CARRASCO-AVINO G, SCHIANO TD, WARD SC, et al. Primary sclerosing cholangitis: Detailed histologic assessment and integration using bioinformatics highlights arterial fibrointimal hyperplasia as a novel feature[J]. Am J Clin Pathol, 2015, 143( 4): 505- 513. DOI: 10.1309/AJCPVKFVIPRBXQR2. |
| [13] |
NAKAZAWA T, NAITOH I, HAYASHI K, et al. Diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis based on cholangiographic classification[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2012, 47( 1): 79- 87. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-011-0465-z. |
| [14] |
ZHANG JP, HOU XT, YIN ZC, et al. Gilbert syndrome: Clinicopathological and genetic analyses of 29 cases[J]. Chin J Diagn Pathol, 2018, 25( 2): 85- 89. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8096.2018.02.002. |
| [15] |
ATAOLLAHI M, DEHGHANI SM, ANBARDAR MH, et al. Liver histologic changes in children with type 1 of Crigler-Najjar syndrome[J]. Arkh Patol, 2021, 83( 5): 27- 30. DOI: 10.17116/patol20218305127. |
| [16] |
FATA CR, GILLIS LA, PACHECO MC. Liver fibrosis associated with crigler-najjar syndrome in a compound heterozygote: A case report[J]. Pediatr Dev Pathol, 2017, 20( 6): 522- 525. DOI: 10.1177/1093526617697059. |
| [17] |
WU ZB. Ultramicro-pathological diagnostics[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific& Technical Publishers, 2003.
武忠弼. 超微病理诊断学[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2003.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
WENG YH, XIONG QF, LIU DX, et al. Clinical and pathological features of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 1): 154- 159. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.01.024. |
| [20] |
QIU YL, GONG JY, FENG JY, et al. Defects in myosin VB are associated with a spectrum of previously undiagnosed low γ-glutamyltransferase cholestasis[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 65( 5): 1655- 1669. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29020. |
| [21] |
GOMEZ-OSPINA N, POTTER CJ, XIAO R, et al. Mutations in the nuclear bile acid receptor FXR cause progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis[J]. Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 10713. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10713. |
| [22] |
HALAWI A, IBRAHIM N, BITAR R. Triggers of benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis and its pathophysiology: A review of literature[J]. Acta Gastroenterol Belg, 2021, 84( 3): 477- 486. DOI: 10.51821/84.3.013. |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
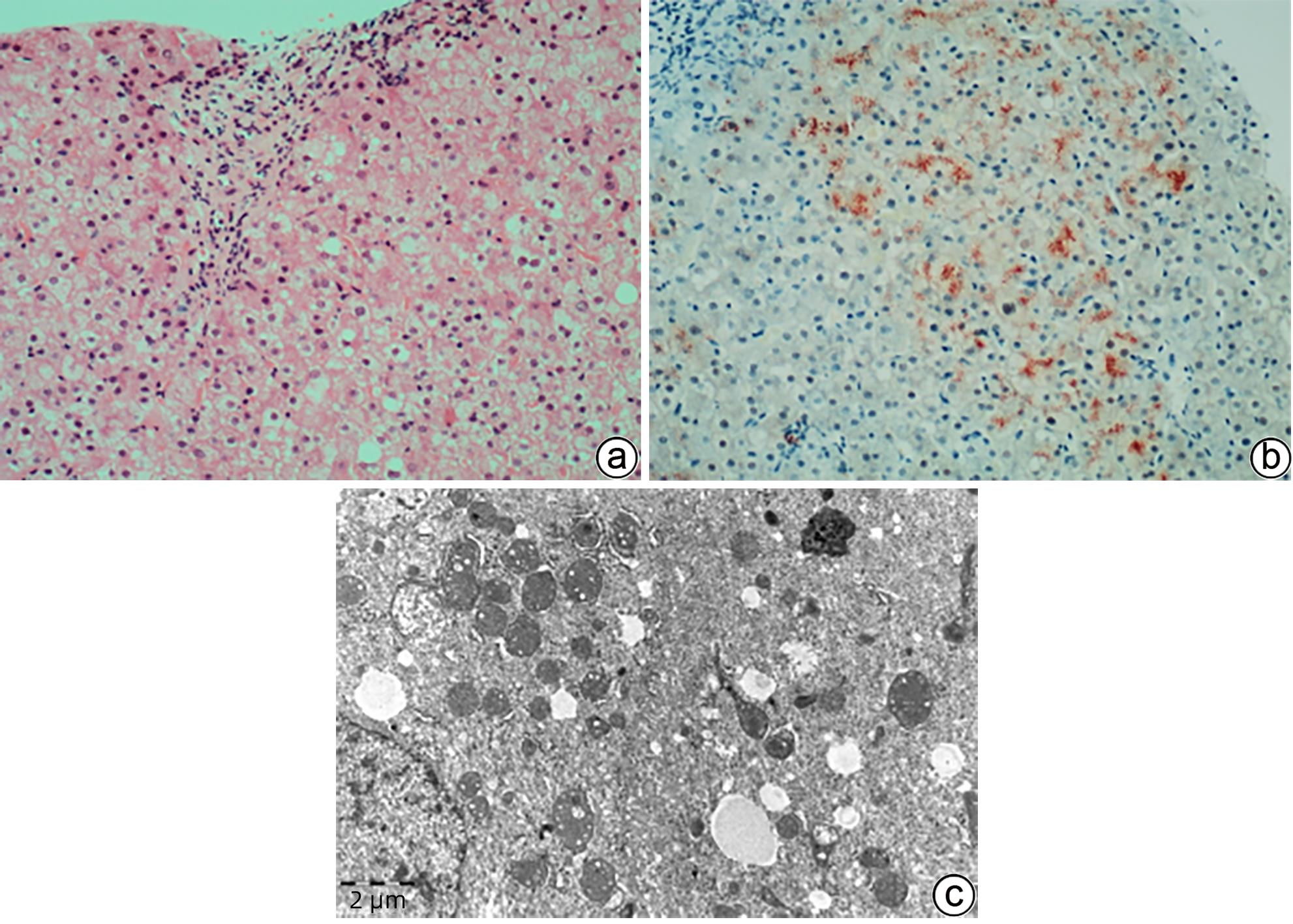
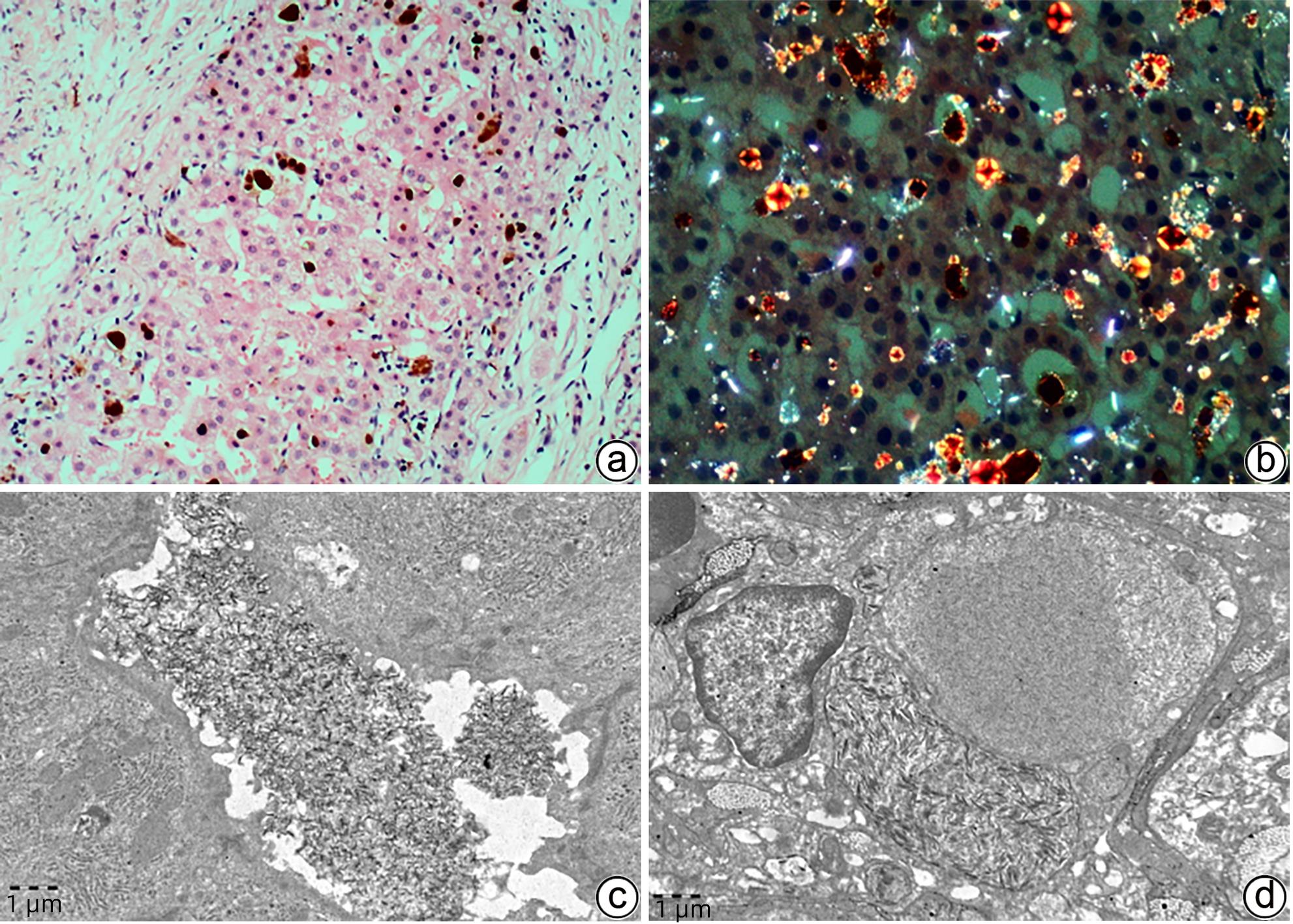
FANNI D, GUIDO M, GEROSA C, et al. Liver changes in Wilson’s disease: The full spectrum. A report of 127 biopsies from 43 patients[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2021, 25( 12): 4336- 4344. DOI: 10.26355/eurrev_202106_26142. |
| [25] |
ZHAO XY, HE ZY, LIU LW, et al. Comparative study of pathological characteristics of 45 patients with primary and secondary hemochromatosis[J]. Infect Dis Inf, 2019, 32( 2): 127- 131. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8134.2019.02.007. |
| [26] |
MIYAMOTO R, JUN SD, OTA K, et al. Neonatal intrahepatic cholestasis caused by citrin deficiency with no hepatic steatosis: A case report[J]. BMC Pediatr, 2021, 21( 1): 237. DOI: 10.1186/s12887-021-02717-w. |
| [27] |
ZHANG JP, CHENG YB, ZHOU XJ, et al. Neonatal intrahepatic cholestasis caused by citrin deficiency: A clinicopathological analysis of two cases[J]. Chin J Diagn Pathol, 2018, 25( 4): 261- 265. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8096.2018.04.006. |
| [28] |
FABRIS L, MILANI C, FIOROTTO R, et al. Dysregulation of the Scribble/YAP/β-catenin axis sustains the fibroinflammatory response in a PKHD1 -/- mouse model of congenital hepatic fibrosis[J]. FASEB J, 2022, 36( 6): e22364. DOI: 10.1096/fj.202101924R. |
| [29] |
SAXENA R. Practical hepatic pathology: A diagnostic approach[M]. 2nd Ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2018.
|
| [30] |
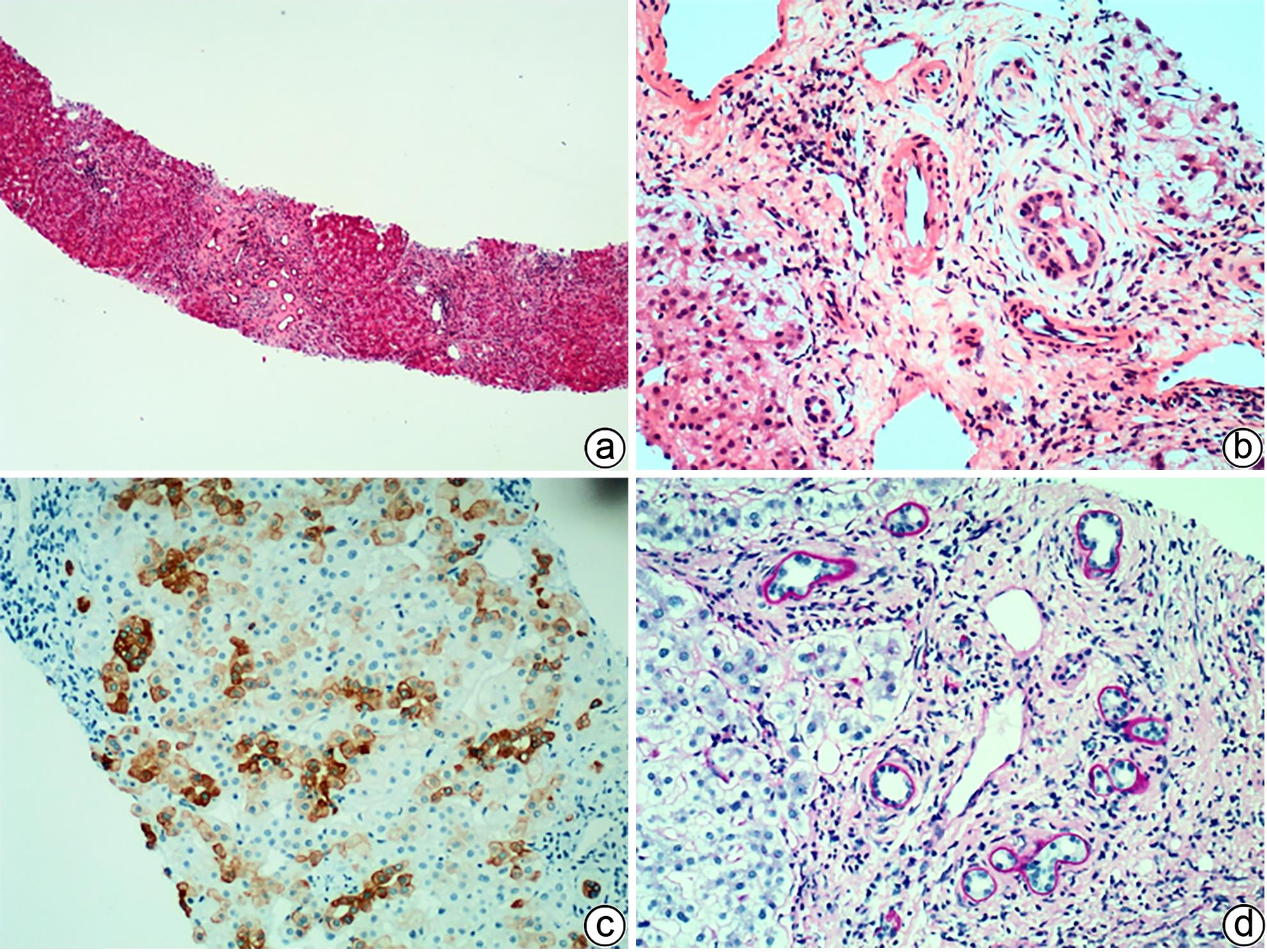
DESMET VJ. Congenital diseases of intrahepatic bile ducts: Variations on the theme“ductal plate malformation”[J]. Hepatology, 1992, 16( 4): 1069- 1083. DOI: 10.1002/hep.1840160434. |
| [31] |
CHEN IY, WHITNEY-MILLER CL, LIAO XY. Congenital hepatic fibrosis and its mimics: A clinicopathologic study of 19 cases at a single institution[J]. Diagn Pathol, 2021, 16( 1): 81. DOI: 10.1186/s13000-021-01142-y. |
| [32] |
GILBERT MA, BAUER RC, RAJAGOPALAN R, et al. Alagille syndrome mutation update: Comprehensive overview of JAG1 and NOTCH2 mutation frequencies and insight into missense variant classification[J]. Hum Mutat, 2019, 40( 12): 2197- 2220. DOI: 10.1002/humu.23879. |
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
CASANOVA-GONZÁLEZ MJ, TRAPERO-MARUGÁN M, JONES EA, et al. Liver disease and erythropoietic protoporphyria: A concise review[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2010, 16( 36): 4526- 4531. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i36.4526. |
| [35] |
ANSTEY AV, HIFT RJ. Liver disease in erythropoietic protoporphyria: Insights and implications for management[J]. Gut, 2007, 56( 7): 1009- 1018. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2006.097576. |
| [36] |
MACDONALD DM, GERMAIN D, PERROT H. The histopathology and ultrastructure of liver disease in erythropoietic protoporphyria[J]. Br J Dermatol, 1981, 104( 1): 7- 17. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1981.tb01705.x. |
| [37] |
VIJ M, RELA M. Biliary atresia: Pathology, etiology and pathogenesis[J]. Future Sci OA, 2020, 6( 5): FSO466. DOI: 10.2144/fsoa-2019-0153. |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: