18F-FDG PET/CT、超声造影及联合应用对胰腺良恶性病变的鉴别诊断价值比较
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.12.017
Value of 18F-FDG PET/CT, contrast-enhanced ultrasound, and their combined use in differential diagnosis of benign and malignant pancreatic lesions: A comparative study
-
摘要:
目的 探讨18F-FDG PET/CT、超声造影及联合应用对胰腺病变良恶性鉴别的诊断价值。 方法 回顾性分析2015年1月—2020年12月于唐山市工人医院行18F-FDG PET/CT和超声造影检查的胰腺病变患者资料,以病理结果为标准,分析18F-FDG P ET/CT、超声造影及两者联合时对胰腺病变良恶性鉴别诊断的灵敏度、特异度、准确度、阳性预测值及阴性预测值。计量资料组间比较采用t检验;计数资料组间比较采用χ2检验。 结果 108例病变中恶性83例、良性25例,18F-FDG PET/CT诊断灵敏度、特异度、准确度、阳性预测值及阴性预测值分别为86.75%、80.00%、85.19%、93.51%及64.52%,超声造影分别为69.88%、76.00%、71.30%、90.63%及43.18%,两者联合应用时分别为90.36%、84.00%、88.89%、94.94%及72.41%。18F-FDG PET/CT与超声造影两者间灵敏度、准确度比较差异均有统计学意义(P值均<0.05)。 结论 18F-FDG PET/CT对胰腺病变良恶性鉴别具有较高的诊断价值,高于超声造影,两者联合应用时可进一步提高诊断价值。 -
关键词:
- 胰腺肿瘤 /
- 正电子发射断层显像计算机体层摄影术 /
- 体层摄影术, X线计算机 /
- 氟脱氧葡萄糖F18
Abstract:Objective To assess the value of 18F-FDG PET/CT, contrast-enhanced ultrasound, and their combination in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant pancreatic lesions. Methods A retrospective analysis was performed on patients with pancreatic lesions who underwent18F-FDG PET/CT and contrast-enhanced ultrasound who were admitted to Tangshan Gongren Hospital from January 2015 to December 2020. The imaging results were confirmed by pathology examination to evaluate diagnostic sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive and negative predictive value. The t-test was used for comparison of continuous data between two groups, and the chi-square test was used for comparison of categorical data between groups. Results There were 83 malignant lesions and 25 benign lesions in 108 patients. The sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive and negative predictive value were 86.75%, 80.00%, 85.19%, 93.51% and 64.52% for 18F-FDG PET/CT; and 69.88%, 76.00%, 71.30%, 90.63% and 43.18% for contrast-enhanced ultrasound, respectively. The two methods differed significantly in sensitivity and accuracy (all P < 0.05), but not in specificity, negative and positive predictive value (all P > 0.05). When combined with the contrast-enhanced ultrasound, 18F-FDG PET/CT had an increased sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive and negative predictive value of 90.36%, 84.00%, 88.89%, 94.94% and 72.41%, respectively, though this was not statistically significant due to the increased signal of blood supply in the lesions. Conclusion 18F-FDG PET/CT has a better performance than contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant pancreatic lesions, and their combination can improve the diagnostic value. -
由于胰腺解剖位置较深,胰腺病变临床症状及体征不明显,胰腺癌恶性程度高,进展快,很容易发生淋巴结及远处器官转移,发现时多为晚期,病死率较高,成为临床中诊治最为困难的肿瘤之一[1-3],缺乏有效的影像学诊断方法。正电子发射型体层摄影/计算机体层摄影(positron emission tomography / computed tomography, PET/CT) 在多种肿瘤的诊治中有较高价值,临床中最常用的是18氟脱氧葡萄糖(18F-fluorodeoxyglucose, 18F-FDG)代谢显像[4-5]。超声造影可以对病变进行常规超声诊断,同时还可显示病变的血供情况,从而对病变进行良恶性诊断[6]。本研究探讨18F-FDG PET/CT显像对胰腺病变良恶性鉴别的诊断价值,并与超声造影进行对比及联合应用,旨在提高对胰腺病变良恶性鉴别的诊断效能。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
回顾性分析2015年1月—2020年12月在本院确诊存在胰腺病变患者的临床资料,入选标准:(1)未经治疗患者;(2)同期(2周)内先后行18F-FDG PET/CT显像及超声造影。排除标准:(1)治疗后行18F-FDG PET/CT显像者;(2)临床资料不全者;(3)无病理结果者。
1.2 PET/CT显像剂及显像仪器
显像剂18F-FDG由天津原子高科同位素有限公司提供,放化纯度>95%。PET/CT为PHILIPS GEMINI TF机型。患者空腹6 h以上,血糖水平在11 mmol/L以下,按体质量3.7 MBq/kg静脉注射18F-FDG,闭目安静休息50~60 min后进行低剂量CT成像及18F-FDG代谢显像,扫描范围由颅底至股骨上段。图像经处理工作站EBW进行PET/CT图像融合,并勾画病灶感兴趣,自动得出最大标准化摄取值(maximum standardized uptake value, SUVmax),连续测量3次,取其平均值。
1.3 超声仪器及造影剂
超声检查使用GE Logiq E9、Philips Iu22超声诊断仪,探头频率为1~5 MHz,患者行常规超声检查后行超声造影检查,造影剂使用Sonovue,经肘正中静脉快速团注1.5~2 mL,在注入造影剂瞬间开始计时,不间断观察病灶灌注过程,存储并记录3 min内病灶的动态增强-消退过程。
1.4 胰腺病变18F-FDG PET/CT显像评估方法
观察胰腺病灶组织放射性显像剂摄取的形态及摄取程度,当出现结节状或肿块状18F-FDG摄取增高灶,摄取程度高于肝脏或周围正常胰腺组织,SUVmax>3.0,伴或不伴有远端胰管扩张,或发现周围淋巴结或肝脏、肺等远处脏器存在转移性病灶时诊断为恶性,否则诊断为良性。
1.5 胰腺病变超声造影评估方法
观察胰腺病灶的常规超声表现及造影增强程度与模式,胰腺造影时相分为动脉期(10~30 s)和静脉期(31~120 s),将肿瘤增强程度分为高增强(病灶强化程度高于周边正常胰腺实质)、等增强(病灶强化程度与周边正常胰腺实质一致)和低增强(病灶强化程度低于周边正常胰腺实质),综合常规超声及造影表现进行诊断,病灶呈低回声、形态不规则、边界不清晰、伴有胰管扩张或截断,超声造影显示动脉期及静脉期均呈低增强,或伴有周围淋巴结转移或肝转移时诊断为恶性,余诊断为良性。
1.6 统计学方法
应用SPSS 20.0软件进行数据统计分析。计量资料以x±s表示,组间比较采用t检验;计数资料组间比较采用χ2检验。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 一般资料及病理结果
共入组病例108例,其中男65例,女43例,年龄27~78岁。67例通过穿刺活检取得病理结果,41例通过手术切除取得病理结果,最终病理结果恶性72例,交界性肿瘤11例,良性25例。72例恶性中,病理确诊43例胰腺导管腺癌(pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, PDAC),15例神经内分泌肿瘤(pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, PNET),6例实性假乳头状瘤(solid pseudopapillary tumors, SPT),5例囊腺癌,淋巴瘤3例;交界性肿瘤11例,4例为导管内乳头状黏液性肿瘤(intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm, IPMN),黏液性囊腺瘤4例,导管内管状乳头状肿瘤3例(intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm, ITPN),由于世界卫生组织指出交界性肿瘤存在恶性倾向,本研究将其列入恶性组,年龄(63.7±11.4)岁;25例良性病变中12例为慢性胰腺炎,7例为自身免疫性胰腺炎(autoimmune pancreatitis,AIP),5例浆液性囊腺瘤,1例胰尾部副脾,年龄(44.7±15.1)岁,两组患者年龄差异有统计学意义(t=2.894,P=0.002)。
2.2 18F-FDG PET/CT显像诊断结果
83例恶性病灶中检出72例,25例良性病灶中检出20例,诊断灵敏度、特异度、准确度、阳性预测值及阴性预测值分别为86.75%、80.00%、85.19%、93.51%及64.52%(表 1、2)。其中11例恶性病变被漏诊,5例良性病变被误诊。本研究中恶性病变SUVmax范围为1.9~13.0,均值为5.1±2.5,良性病变的SUVmax范围为0.7~4.9,均值为2.3±1.2,比较良恶性两组间的SUVmax,差异有统计学意义(t=7.563,P=0.001)。11例被漏诊的恶性病变分别为4例PDAC,2例PNET,2例SPT,2例黏液性囊腺瘤,1例ITPN,在这11例中有6例病灶直径<1 cm;5例被误诊的良性病变中2例为慢性胰腺炎,2例AIP,1例胰腺内副脾(图 1、2)。
表 1 3种诊断方法分别对胰腺良恶性病变检出的数目比较Table 1. Comparison of 3 diagnostic results with the number of benign and malignant pancreatic lesions病理 例数 PET/CT(例) 超声造影(例) PET/CT+超声造影(例) + - + - + - 恶性 83 72 11 58 25 75 8 良性 25 5 20 6 19 4 21 表 2 3种诊断方法对胰腺良恶性病变诊断指标比较Table 2. Comparison of 3 diagnostic indexes of benign and malignant pancreatic lesions组别 灵敏度 特异度 准确度 阳性预测值 阴性预测值 PET/CT 86.75%1) 80.00% 85.19%1) 93.51% 64.52% 超声造影 69.88% 76.00% 71.30% 90.63% 43.18% PET/CT+超声造影 90.36%1) 84.00% 88.89%1) 94.94% 72.41% χ2值 6.952 0.117 6.119 0.403 3.316 P值 0.008 0.733 0.013 0.546 0.069 注:与超声造影比,1)P<0.05。 2.3 超声造影诊断结果
83例恶性病灶超声造影共检出58例,25例良性病灶共检出19例,诊断灵敏度、特异度、准确度、阳性预测值及阴性预测值分别为69.88%、76.00%、71.30%、90.63%及43.18%。其中25例恶性病变被漏诊,6例良性病变被误诊(表 1、2)。25例漏诊的恶性病变中分别为13例PDAC,4例PNET,3例囊腺癌,2例IPMN,1黏液性囊腺瘤,1例ITPN,1例淋巴瘤;6例误诊的良性病变中为4例慢性胰腺炎,1例AIP,1例胰尾部副脾(图 3~6)。
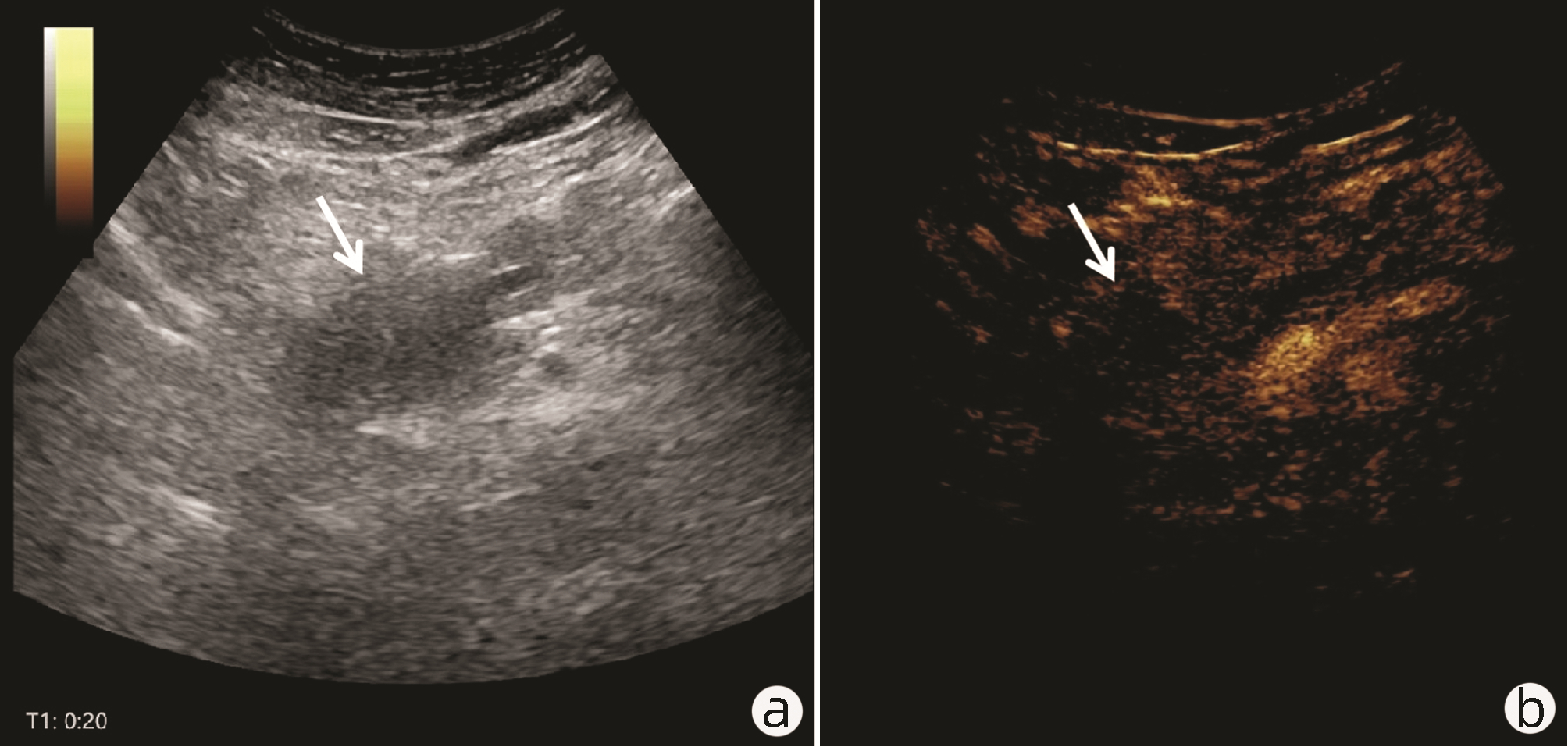
 图 3 PDAC超声造影动脉期图像注:患者,男,58岁,胰头导管腺癌(与图 1同一患者),超声造影显示胰头病变动脉期呈低增强(箭头)。a,常规超声;b,超声造影动脉期。Figure 3. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in arterial phase
图 3 PDAC超声造影动脉期图像注:患者,男,58岁,胰头导管腺癌(与图 1同一患者),超声造影显示胰头病变动脉期呈低增强(箭头)。a,常规超声;b,超声造影动脉期。Figure 3. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in arterial phase 图 4 PDAC超声造影静脉期图像注:患者,男,58岁,胰头导管腺癌(与图 1同一患者),超声造影显示胰头病变静脉期呈低增强(箭头)。a,常规超声;b,超声造影静脉期。Figure 4. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in venous phase
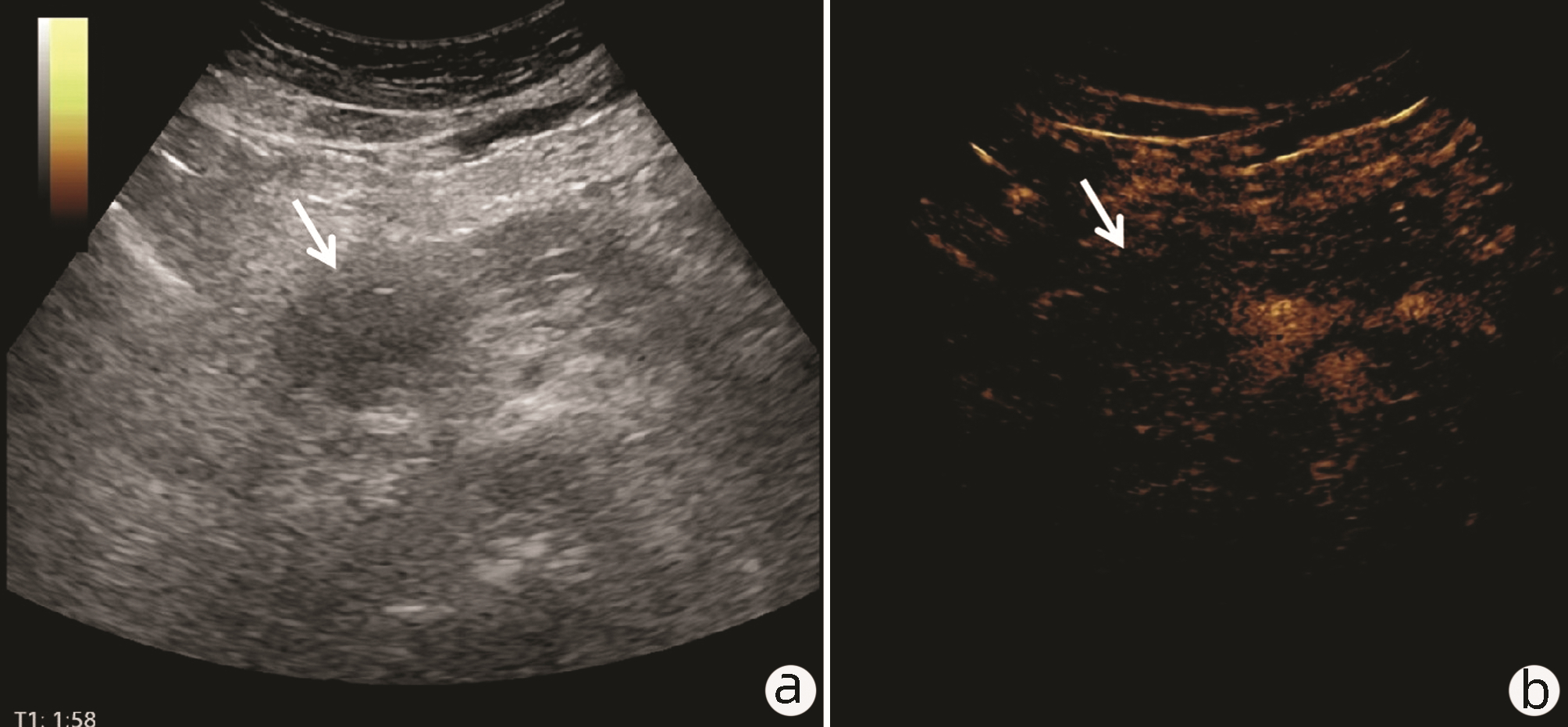
图 4 PDAC超声造影静脉期图像注:患者,男,58岁,胰头导管腺癌(与图 1同一患者),超声造影显示胰头病变静脉期呈低增强(箭头)。a,常规超声;b,超声造影静脉期。Figure 4. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in venous phase 图 5 AIP超声造影动脉期图像注:患者,男,36岁,AIP(与图 2同一患者),超声显示胰腺整体弥漫性肿大,动脉期造影呈均匀性等增强表现(箭头)。a,常规超声;b,超声造影动脉期。Figure 5. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of autoimmune pancreatitis in arterial phase
图 5 AIP超声造影动脉期图像注:患者,男,36岁,AIP(与图 2同一患者),超声显示胰腺整体弥漫性肿大,动脉期造影呈均匀性等增强表现(箭头)。a,常规超声;b,超声造影动脉期。Figure 5. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of autoimmune pancreatitis in arterial phase 图 6 AIP超声造影静脉期图像注:患者,男,36岁,AIP(与图 2同一患者),超声显示胰腺整体弥漫性肿大,静脉期造影呈均匀性等增强表现(箭头)。a,常规超声;b,超声造影静脉期。Figure 6. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of autoimmune pancreatitis in venous phase
图 6 AIP超声造影静脉期图像注:患者,男,36岁,AIP(与图 2同一患者),超声显示胰腺整体弥漫性肿大,静脉期造影呈均匀性等增强表现(箭头)。a,常规超声;b,超声造影静脉期。Figure 6. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of autoimmune pancreatitis in venous phase2.4 两者联合应用的诊断效能
18F-FDG PET/CT和超声造影联合应用共诊断83例恶性病灶中75例,诊断25例良性病灶中21例,其诊断的灵敏度、特异度、准确度、阳性预测值及阴性预测值分别为90.36%、84.00%、88.89%、94.94%及72.41%。18F-FDG PET/CT显像的诊断灵敏度、准确度均高于超声造影(P值均<0.05);两者联合应用时诊断效能与18F-FDG PET/CT显像统计学比较时差异均无统计学意义(P值均>0.05)(表 1、2)。
3. 讨论
18F-FDG PET/CT显像能从分子水平反映病变生理生化信息,其异常改变要早于形态结构变化,18F-FDG摄取程度与病变的类型及肿瘤恶性程度相关,肿瘤恶性程度越高,18F-FDG摄取越多,在图像上表现为放射性摄取越明显,所以,18F-FDG PET/CT有助于诊断肿瘤的良恶性、肿瘤分期及评估治疗效果等,其中也包括胰腺癌[7-9]。
以往研究[10]表明,18F-FDG PET/CT显像对胰腺癌的诊断灵敏度及特异度分别为90%和85%,具有较高的诊断效能,本研究18F-FDG PET/CT显像对胰腺良恶性病变的诊断灵敏度、特异度、准确度、阳性预测值及阴性预测值分别为86.75%、80.00%、85.19%、93.51%及64.52%,与以往的研究结论一致。
18F-FDG为葡萄糖类似物,其在体内反映组织病变的葡萄糖代谢情况,恶性病变其增殖能力强,所需能量来源多,良性病变则反之,本研究得出恶性病变的SUVmax均值为5.1±2.5,明显高于良性病变SUVmax均值2.3±1.2,两者的差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),但两组间个别病变的SUVmax存在交叉的现象,这也与病变病理特征有关,如本组病例中被漏诊的2例PNET均为G1级别,肿瘤细胞密度较低,恶性程度较低,18F-FDG摄取较少,从而SUVmax较低,均<3.0;交界性肿瘤存在恶性潜能,其肿瘤代谢水平均较低,本研究中的黏液性囊腺瘤及ITPN代谢均不高,SUVmax较低,相反,AIP病变中存在大量的炎性细胞,其增殖能力较旺盛,需要大量的18F-FDG作为能量来源,从而SUVmax较高[11-13]。由于18F-FDG的这种特性,不能仅依据SUVmax高低诊断良恶性,研究者试图研发其他分子探针进行PET/CT或PET/MR显像,以期更准确的诊断胰腺病变[14-17]。而在超声造影中,具有较高的空间分辨率,与PET/CT相比,不仅较好的显示病灶本身的结构形态信息,在显示胰管受累情况也具有优势,而胰管受累则是鉴别良恶性的指征之一,对于一些直径<2 cm的小胰腺癌、低度恶性或交界性肿瘤,超声造影则显示出了较好的诊断效能,这也是导致本研究中两者特异度、阳性预测值及阴性预测值无统计学差异的原因之一。
PET/CT检查为全身显像,不仅可以显示胰腺病变本身情况,还可以显示其他远处部位是否存在转移性病变[18],大大提高对胰腺恶性病变诊断的信心,本研究中83例恶性病变中有32例存在周围及远处淋巴结转移,29例存在远处脏器转移;AIP往往是IgG4相关性疾病的一部分表现,其通常可累及胰腺、胆管、淋巴结、唾液腺、肾脏、前列腺等器官,PET/CT可显示全身其他受累器官,本组7例AIP病例中有5例伴有胆管、纵隔淋巴结、唾液腺及前列腺等器官不同程度受累。而超声造影为局部检查,只对靶器官及邻近周围组织器官进行检查,无法观察存在远处器官转移的情况,这也是导致超声造影灵敏度及准确度低于PET/CT的原因之一。另PET/CT为功能代谢显像,其细胞功能代谢改变要早于解剖形态学的改变,而胰腺本身又位于腹膜后,受周围肠道气体干扰,超声检查有时效果不佳,虽然超声造影能够提供病灶血供方面的信息帮助诊断,如上述图像中典型的PDAC血供为乏血供可明确诊断,但有些不典型的PDAC或部分形态较规则、边界清楚且不伴有胰管受累肿瘤可能会出现漏诊的现象,这些因素均是导致诊断灵敏度及准确度不如18F-FDG PET/CT检查的原因之一。
超声造影检查不仅可以显示胰腺病变的常规超声特征,还可以实时显示胰腺病变的血供情况,由于造影剂无过敏现象及在体内清除快,可对病变进行多次重复观察,临床中得到越来越广泛的应用[19-22],尤其适用于患有幽闭恐惧症及对CT、MR增强检查存在禁忌证的患者。本研究结果表明,超声造影对胰腺良恶性病变的鉴别诊断也具有较高的价值,其诊断的灵敏度、特异度、准确度、阳性预测值及阴性预测值分别为69.88%、76.00%、71.30%、90.63%及43.18%,与18F-FDG PET/CT显像比较,其中灵敏度及准确度差异有统计学意义,而特异度、阳性预测值及阴性预测值比较差异无统计学意义。
18F-FDG PET/CT可进行延迟显像来增加鉴别良恶性的诊断效能,但本课题组前期研究[4]结果显示延迟显像诊断效能与SUVmax相当。18F-FDG PET/CT显示胰腺病变功能代谢情况,但无法显示病变血供情况,临床中常常需要结合增强CT、MR图像进行综合诊断,尤其对于一些有特征性血供表现的肿瘤鉴别[18, 23],尤其是胰腺癌,其好发于老年人,而这部分患者可能由于造影剂过敏或体内存在金属物品等原因无法进行CT、MR增强检查时,通过超声造影检查可提供病变的血供情况,这也推动了临床中超声造影也是越来越普及。本研究通过18F-FDG PET/CT结合超声造影,可提高胰腺病变的良恶性诊断价值,如体积较小的PDAC在18F-FDG PET/CT中可出现假阴性,在超声造影中可表现为动脉期及静脉期为低增强的典型表现,可作出补充诊断;肿块型胰腺炎往往由于炎性细胞的浸润,在18F-FDG PET/CT中表现为高摄取,可造成假阳性,在超声造影中表现为动脉期及静脉期均呈高增强,可与PDAC进行鉴别。
本研究尚存在不足,仅将18F-FDG PET/CT常规显像与超声造影进行分析,未将延迟显像指标纳入,亦未将CT、MR增强结果进行综合对比分析,本课题组将在以后的研究中进一步深入讨论。
综上所述,18F-FDG PET/CT对胰腺病变良恶性鉴别具有较高诊断价值,并高于超声造影,两者联合应用时可显示病变血供情况,实用性强,诊断效能较单独应用时有所提高,临床中可将18F-FDG PET/CT与超声造影联合应用鉴别诊断胰腺良恶性病变。
-
注:患者,男,58岁,胰头导管腺癌(与图 1同一患者),超声造影显示胰头病变动脉期呈低增强(箭头)。a,常规超声;b,超声造影动脉期。
图 3 PDAC超声造影动脉期图像
Figure 3. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in arterial phase
注:患者,男,58岁,胰头导管腺癌(与图 1同一患者),超声造影显示胰头病变静脉期呈低增强(箭头)。a,常规超声;b,超声造影静脉期。
图 4 PDAC超声造影静脉期图像
Figure 4. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in venous phase
注:患者,男,36岁,AIP(与图 2同一患者),超声显示胰腺整体弥漫性肿大,动脉期造影呈均匀性等增强表现(箭头)。a,常规超声;b,超声造影动脉期。
图 5 AIP超声造影动脉期图像
Figure 5. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of autoimmune pancreatitis in arterial phase
注:患者,男,36岁,AIP(与图 2同一患者),超声显示胰腺整体弥漫性肿大,静脉期造影呈均匀性等增强表现(箭头)。a,常规超声;b,超声造影静脉期。
图 6 AIP超声造影静脉期图像
Figure 6. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of autoimmune pancreatitis in venous phase
表 1 3种诊断方法分别对胰腺良恶性病变检出的数目比较
Table 1. Comparison of 3 diagnostic results with the number of benign and malignant pancreatic lesions
病理 例数 PET/CT(例) 超声造影(例) PET/CT+超声造影(例) + - + - + - 恶性 83 72 11 58 25 75 8 良性 25 5 20 6 19 4 21 表 2 3种诊断方法对胰腺良恶性病变诊断指标比较
Table 2. Comparison of 3 diagnostic indexes of benign and malignant pancreatic lesions
组别 灵敏度 特异度 准确度 阳性预测值 阴性预测值 PET/CT 86.75%1) 80.00% 85.19%1) 93.51% 64.52% 超声造影 69.88% 76.00% 71.30% 90.63% 43.18% PET/CT+超声造影 90.36%1) 84.00% 88.89%1) 94.94% 72.41% χ2值 6.952 0.117 6.119 0.403 3.316 P值 0.008 0.733 0.013 0.546 0.069 注:与超声造影比,1)P<0.05。 -
[1] Chinese Pancreatic Surgery Association, Chinese Society of Surgery, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer in China(2021)[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2021, 20(7): 713-729. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20210618-00289.中华医学会外科学分会胰腺外科学组. 中国胰腺癌诊治指南(2021)[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2021, 20(7): 713-729. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20210618-00289. [2] CAI J, CHEN HD, LU M, et al. Trend analysis on morbidity and mortality of pancreatic cancer in China, 2005-2015[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2021, 42(5): 794-800. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20201115-01328.蔡洁, 陈宏达, 卢明, 等. 2005-2015年中国胰腺癌发病与死亡趋势分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2021, 42(5): 794-800. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20201115-01328. [3] YANG H, WANG XK, FAN JH. Present status of epidemiology, risk factors and screening of pancreatic cancer in China[J]. Cancer Res Prev Treat, 2021, 48(10): 909-915. DOI: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2021.21.0789.杨欢, 王晓坤, 范金虎. 中国胰腺癌流行病学、危险因素及筛查现况[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2021, 48(10): 909-915. DOI: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2021.21.0789. [4] ZHENG LC, LIU GC, OUYANG XL, et al. Diagnosis of 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging in benign and malignant pancreatic lesions[J]. Chin J Med Imaging, 2018, 26(9): 680-684. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5185.2018.09.010.郑立春, 刘桂超, 欧阳向柳, 等. ~(18)F-FDG PET/CT显像对胰腺良恶性病变的诊断价值[J]. 中国医学影像学杂志, 2018, 26(9): 680-684. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5185.2018.09.010. [5] PU Y, WANG C, ZHAO S, et al. The clinical application of 18F-FDG PET/CT in pancreatic cancer: a narrative review[J]. Transl Cancer Res, 2021, 10(7): 3560-3575. DOI: 10.21037/tcr-21-169. [6] GAO B, OUYANG XL, ZHANG HL, et al. Diagnostic value of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in aged patients with pancreatic tumors[J]. Chin J Ultrasound in Med, 2018, 34(8): 706-709. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0101.2018.08.010.高蓓, 欧阳向柳, 张浩良, 等. 超声造影对于老年胰腺肿瘤患者的诊断价值分析[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2018, 34(8): 706-709. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0101.2018.08.010. [7] LI S, JIANG H, WANG Z, et al. An effective computer aided diagnosis model for pancreas cancer on PET/CT images[J]. Comput Methods Programs Biomed, 2018, 165: 205-214. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.09.001. [8] MYSSAYEV A, MYSSAYEV A, IDEGUCHI R, et al. Usefulness of FDG PET/CT derived parameters in prediction of histopathological finding during the surgery in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(1): e0210178. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210178. [9] YAMASHITA YI, OKABE H, HAYASHI H, et al. Usefulness of 18-FDG PET/CT in detecting malignancy in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas[J]. Anticancer Res, 2019, 39(5): 2493-2499. DOI: 10.21873/anticanres.13369. [10] REN SN, LI DN, PAN GX, et al. Research progress in diagnosis and prognosis evaluation of pancreatic cancer by~(18)F-FDG PET/CT[J]. Chin J Pancreatol, 2019, 19(4): 307-310. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-1935.2019.04.018.任胜男, 李丹妮, 潘桂霞, 等. 胰腺癌~(18)F-FDG PET/CT诊断及预后评估的研究进展[J]. 中华胰腺病杂志, 2019, 19(4): 307-310. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-1935.2019.04.018. [11] SRINIVASAN N, KOH YX, GOH B. Systematic review of the utility of 18-FDG PET in the preoperative evaluation of IPMNs and cystic lesions of the pancreas[J]. Surgery, 2019, 165(5): 929-937. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2018.11.006. [12] DUNET V, HALKIC N, SEMPOUX C, et al. Use of PET and MRI imaging features to predict grade and survival of resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. Inter J Med Rad, 2021, 44(2): 247. DOI: 10.19300/j.2021.e0211.DUNET V, HALKIC N, SEMPOUX C, 等. 应用PET和MRI影像学特征预测可切除的胰腺导管腺癌肿瘤分级及生存率[J]. 国际医学放射学杂志, 2021, 44(2): 247. DOI: 10.19300/j.2021.e0211. [13] WANG PP, HUO L, LIU Y, et al. Clinical value of 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging in non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms[J]. Chin J Nuclear Med Mol Imaging, 2022, 42(3): 139-143. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn321828-20200721-00288.王佩佩, 霍力, 刘宇, 等. 无功能胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤~(18)F-FDG PET/CT显像的临床应用价值[J]. 中华核医学与分子影像杂志, 2022, 42(3): 139-143. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn321828-20200721-00288. [14] YAMANE T, AIKAWA M, YASUDA M, et al. [18F]FMISO PET/CT as a preoperative prognostic factor in patients with pancreatic cancer[J]. EJNMMI Res, 2019, 9(1): 39. DOI: 10.1186/s13550-019-0507-8. [15] LIERMANN J, SYED M, BEN-JOSEF E, et al. Impact of FAPI-PET/CT on target volume definition in radiation therapy of locally recurrent pancreatic cancer[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2021, 13(4). DOI: 10.3390/cancers13040796. [16] BONACINA M, GHIRARDELLI P, SETTI L, et al. 68Ga-PSMA and 68Ga-DOTATOC PET/CT imaging mismatch of primary pancreatic adenocarcinoma in prostate cancer patient[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2022, 49(2): 781-782. DOI: 10.1007/s00259-021-05523-9. [17] ZHANG Z, JIA G, PAN G, et al. Comparison of the diagnostic efficacy of 68 Ga-FAPI-04 PET/MR and 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with pancreatic cancer[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2022, 49(8): 2877-2888. DOI: 10.1007/s00259-022-05729-5. [18] JIA W, YIN LL, JI B, et al. Comparison of 18F-FDG PET/CT and enhanced CT to assess the tumor stage, vascular invasion, distant metastasis and surgical indications of pancreatic cancer[J]. Chin J Gen Surg, 2019, 28(3): 360-365. DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2019.03.017.贾维, 印隆林, 季冰, 等. ~(18)F-FDG PET/CT显像与增强CT评估胰腺癌分期、血管侵犯、远处转移和手术指征的比较[J]. 中国普通外科杂志, 2019, 28(3): 360-365. DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2019.03.017. [19] LIN ZM, PAN MQ, XU YY, et al. Contrast enhanced ultrasonography vs. contrast enhanced computed tomography for the diagnosis of focal lesions of the pancreas[J]. Chin J Gen Surg, 2018, 33(10): 849-852. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-631X.2018.10.013.林子梅, 潘敏强, 徐永远, 等. 胰腺实性局灶性病变的超声造影与增强CT对照研究[J]. 中华普通外科杂志, 2018, 33(10): 849-852. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-631X.2018.10.013. [20] LIN ZM, WEN Q, XU YY, et al. Application of contrast enhanced ultrasound in TN staging of pancreas cancer: comparsion with contrast enhanced computed tomography[J]. China J Ultrasonography, 2018, 27(7): 614-617. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1004-4477.2018.07.014.林子梅, 闻卿, 徐永远, 等. 超声造影在胰腺癌T、N分期中的应用价值[J]. 中华超声影像学杂志, 2018, 27(7): 614-617. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1004-4477.2018.07.014. [21] WU LQ, LIU XH, LUAN ZY, et al. Meta-analysis on the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant pancreatic masses by contrast-enhanced ultrasound[J]. J Clin Ultrasound Med, 2018, 20(6): 383-387. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-6978.2018.06.009.吴亮群, 刘雪红, 栾智勇, 等. 超声造影鉴别诊断胰腺良恶性病变的Meta分析[J]. 临床超声医学杂志, 2018, 20(6): 383-387. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-6978.2018.06.009. [22] LI Y, XU Y, SONG YF, et al. Clinical value of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in differentiating focal pancreatitis from pancreatic cancer: a comparative study with conventional ultrasound[J]. J Chin Med Imaging, 2021, 32(10): 729-732. DOI: 10.12117/jccmi.2021.10.011.李煜, 许芸, 宋一凡. 超声造影增强模式鉴别局灶性胰腺炎与胰腺癌的临床价值: 与常规超声的对照研究[J]. 中国临床医学影像杂志, 2021, 32(10): 729-732. DOI: 10.12117/jccmi.2021.10.011. [23] XU J, CHEN YL, WANG XW. Comparison on Clinical Value of 18F-FDG PET/CT, Enhanced CT, and MRI in Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Pancreas Cystic Lesions[J]. Chin J CT and MRI, 2022, 20(2): 99-101. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5131.2022.02.033.徐杰, 陈艳林, 王雪伟. ~(18)F-FDG PET/CT与增强CT、MRI在诊断鉴别胰腺囊性良恶性病变的临床价值比较[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2022, 20(2): 99-101. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5131.2022.02.033. 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 邓明民,王奇峰. F-脱氧葡萄糖PET显像技术对结直肠癌肝转移灶G-与原发性肝癌的鉴别诊断价值. 长春中医药大学学报. 2024(01): 87-90 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 秦小雪,张文,高红,胡宇霞. 高分辨率磁共振成像与正电子发射计算机体层显像仪在直肠癌周围转移性小淋巴结检出及术前T分期诊断中的应用价值. 中国医药导报. 2023(16): 145-148+153 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-




 PDF下载 ( 3391 KB)
PDF下载 ( 3391 KB)

 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:



 百度学术
百度学术







