黄芪汤含药血清对血管内皮生长因子诱导的大鼠肝窦内皮细胞增殖、迁移和成管能力的影响及其作用机制
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.10.015
Effect of serum containing Huangqi decoction on the proliferation, migration, and tubulogenesis of rat liver sinusoidal endothelial cells induced by vascular endothelial growth factor and its mechanism of action
-
摘要:
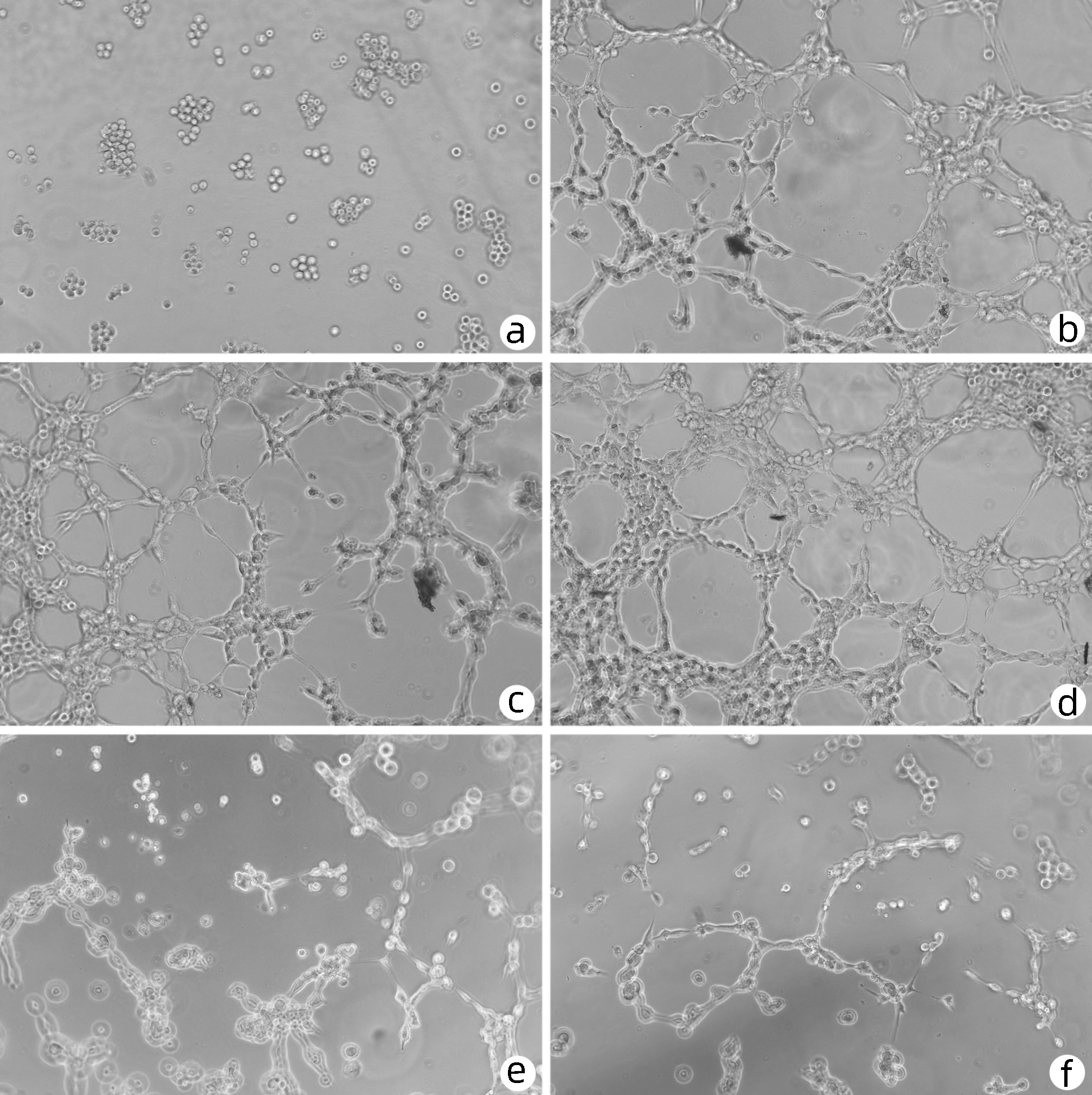
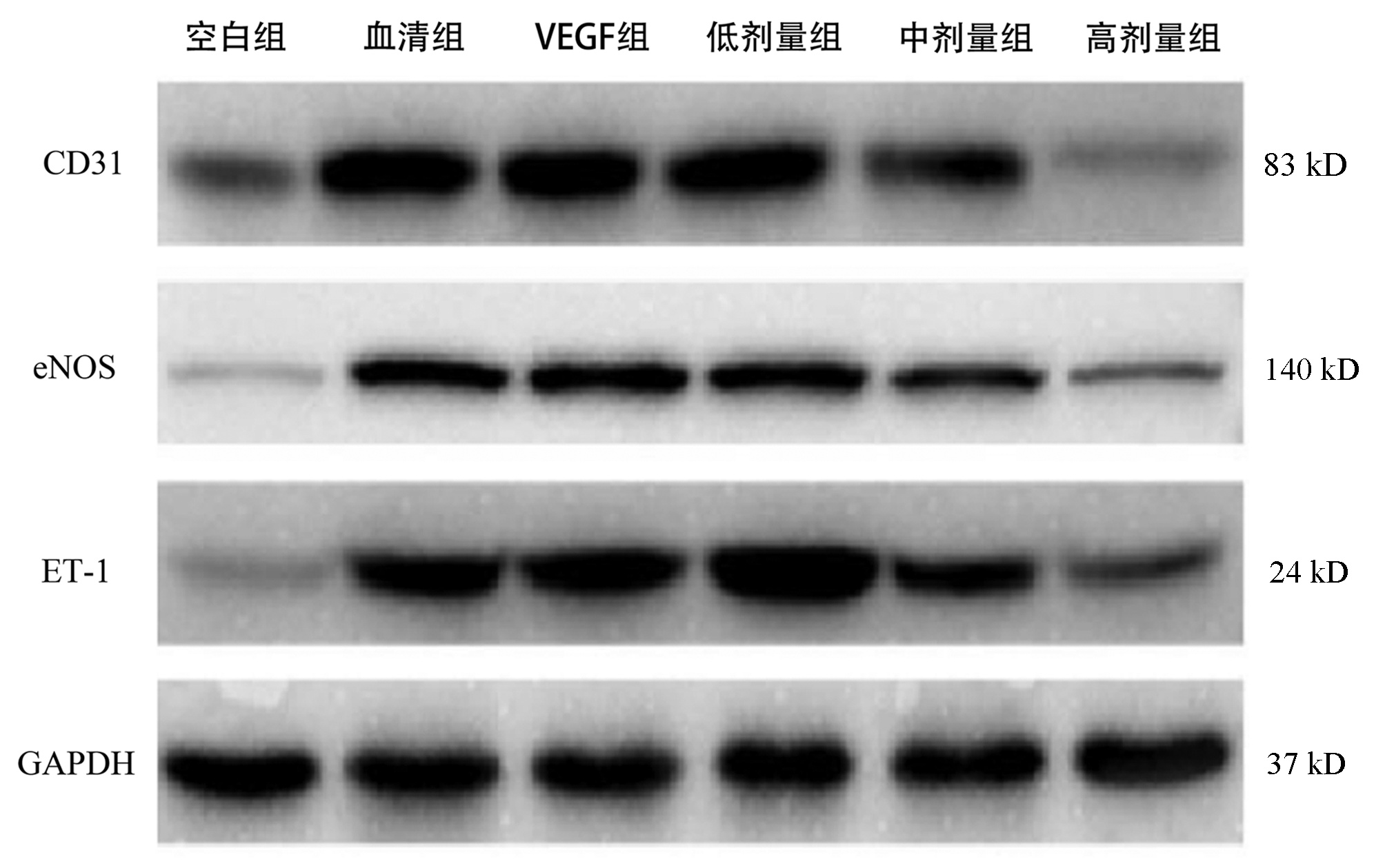
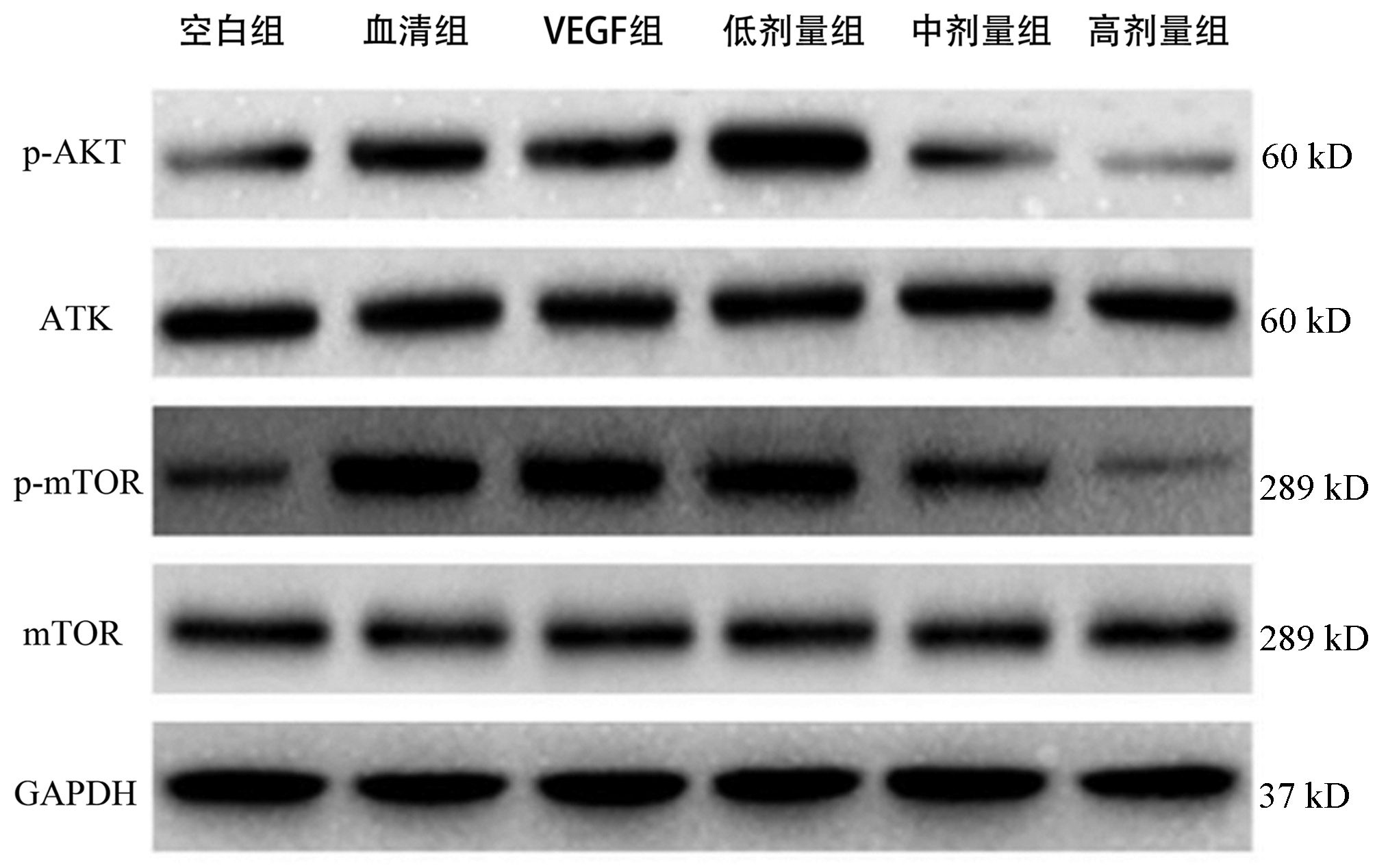
目的 基于蛋白激酶B(AKT)/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mTOR)信号通路探讨黄芪汤含药血清对血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)诱导的大鼠肝窦内皮细胞(LSEC)增殖、迁移和成管能力的影响。 方法 制备黄芪汤含药血清,体外分离、培养SD大鼠LSEC,将大鼠LSEC随机分为空白组,VEGF组,血清对照组,低、中、高剂量黄芪汤含药血清组,利用噻唑蓝(MTT)比色法、Transwell实验、成管实验分别检测各组LSEC增殖、迁移和成管能力,通过Western Blot法检测血小板-内皮细胞黏附分子-1(CD31)、内皮素-1(ET-1)、内皮性一氧化氮合酶(eNOS) 和AKT/mTOR信号通路中AKT、磷酸化(p)-AKT、mTOR、磷酸化(p)-mTOR蛋白表达水平。计量资料多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,进一步两两比较采用Tukey’s检验。 结果 与空白组相比,VEGF组、血清对照组能够促进大鼠LSEC增殖、迁移和血管新生(P值均<0.05);Western Blot结果显示,CD31、ET-1、eNOS和AKT/mTOR信号通路相关蛋白表达显著升高(P值均<0.05)。VEGF组与血清对照组比较,上述指标差异均无统计学意义(P值均>0.05)。与血清组比较,黄芪汤中、高剂量组能显著抑制VEGF诱导的大鼠LSEC增殖、迁移和血管新生(P值均<0.05);Western Blot结果显示,CD31、ET-1、eNOS和AKT/mTOR信号通路相关蛋白表达均显著降低(P值均<0.05)。 结论 较高剂量黄芪汤含药血清能抑制VEGF诱导的大鼠LSEC增殖、迁移和成管能力,其作用机制可能与调控AKT/mTOR信号通路有关。 -
关键词:
- 肝硬化 /
- 黄芪 /
- 肝窦内皮细胞 /
- 大鼠, Sprague-Dawley
Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of serum containing Huangqi decoction on the proliferation, migration, and tubulogenesis of rat liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) induced by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its mechanism of action based on the protein kinase B (AKT)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway. Methods The serum containing Huangqi decoction was prepared, and rat LSECs were isolated and cultured in vitro. Then rat LSECs were randomly divided into blank group, VEGF group, serum control group, and low-, middle-, and high-dose serum containing Huangqi decoction groups. MTT colorimetry, Transwell assay, and tubulogenesis assay were used to measure the proliferation, migration, and tubulogenesis abilities of LSECs in each group, and Western Blot was used to measure the protein expression levels of platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (CD31), endothelin-1 (ET-1), and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), as well as AKT, phosphorylated-AKT (p-AKT), mTOR, and phosphorylated mTOR (p-mTOR) in the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. A one-way analysis of variance was used for comparison of continuous data between multiple groups, and the Tukey's test was used for further comparison between two groups. Results Compared with the blank group, the VEGF group and the serum control group had significantly promoted proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis of rat LSECs (all P < 0.05), and Western Blot showed significant increases in the expression levels of CD31, ET-1, eNOS, and AKT/mTOR signaling pathway-related proteins (all P < 0.05). There were no significant differences in the above indices between the VEGF group and the serum control group (all P > 0.05). Compared with the serum group, the middle- and high-dose serum containing Huangqi decoction groups had significantly inhibited proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis of rat LSECs induced by VEGF (all P < 0.05), and Western Blot showed significant reductions in the expression levels of CD31, ET-1, eNOS, and AKT/mTOR signaling pathway-related proteins (all P < 0.01). Conclusion A relatively high dose of serum containing Huangqi decoction can significantly inhibit the proliferation, migration, and tubulogenesis of rat LSECs induced by VEGF, possibly by regulating the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. -
表 1 各组大鼠LESC活力比较
Table 1. Comparison of LESC cell activity in each group
组别 细胞活力(%) 空白组 100.00±12.05 VEGF组 156.35±16.891) 血清组 165.22±18.521) 低剂量组 173.52±21.561) 中剂量组 131.21±15.672) 高剂量组 111.52±12.362)3) F值 7.317 P值 0.002 注:与空白组比较,1)P<0.05;与血清组比较,2)P<0.05;与中剂量组比较,3)P<0.05。 表 2 各组大鼠LESC迁移细胞数目比较
Table 2. Comparison of LESC migration cell numbers in each group
组别 迁移细胞数(个) 空白组 35.64±3.65 VEGF组 153.63±16.591) 血清组 155.24±15.221) 低剂量组 371.25±41.262) 中剂量组 85.64±10.372) 高剂量组 81.23±9.572) F值 83.199 P值 <0.001 注:与空白组比较,1)P<0.05;与血清组比较,2)P<0.05。 表 3 各组大鼠LESC成管能力比较
Table 3. Comparison of LESC tubulogenesis abilities in each group
组别 节点(个) 交叉点(个) 血管长度(%) 空白组 126.00±11.14 33.33±7.02 100.00±12.63 VEGF组 985.67±93.931) 266.00±26.851) 421.56±68.531) 血清组 922.34±71.011) 263.33±9.291) 475.63±59.671) 低剂量组 1537.67±84.332)3) 431.67±10.502)3) 864.55±124.352)3) 中剂量组 424.34±51.002)3)4) 115.67±9.612)3)4) 225.64±42.362)3)4) 高剂量组 205.34±49.002)3)4)5) 60.00±14.112)3)4)5) 185.66±25.672)3)4) F值 204.507 332.945 46.289 P值 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 注:与空白组比较,1)P<0.05;与VEGF组比较,2)P<0.05;与血清组比较,3)P<0.05;与低剂量组比较,4)P<0.05;与中剂量组比较,5)P<0.05。 表 4 各组大鼠LESC中CD31、eNOS、ET-1蛋白表达比较
Table 4. Comparison of CD31, eNOS and ET-1 protein expression in LESC in each group
组别 CD31 eNOS ET-1 空白组 0.201±0.025 0.053±0.006 0.048±0.005 VEGF组 1.385±0.1391) 0.465±0.0471) 1.052±0.1061) 血清组 1.362±0.1421) 0.452±0.0461) 1.163±0.1161) 低剂量组 1.353±0.136 0.461±0.048 1.583±0.2372)3) 中剂量组 0.575±0.0732)3)4) 0.227±0.0272)3)4) 0.685±0.0692)3)4) 高剂量组 0.067±0.0122)3)4)5) 0.153±0.0152)3)4)5) 0.206±0.0212)3)4)5) F值 89.514 56.273 60.760 P值 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 注:与空白组比较,1)P<0.05;与VEGF组比较,2)P<0.05;与血清组比较,3)P<0.05;与低剂量组比较,4)P<0.05;与中剂量组比较,5)P<0.05。 表 5 各组大鼠LESC中AKT/mTOR信号通路蛋白表达比较
Table 5. Comparison of AKT/mTOR signaling pathway protein expression in LESC in each group
组别 p-AKT/AKT p-mTOR/mTOR 空白组 0.257±0.025 0.852±0.027 VEGF组 0.865±0.1391) 1.229±0.0131) 血清组 0.834±0.1421) 1.227±0.0211) 低剂量组 1.425±0.1361)3) 1.197±0.0121)3) 中剂量组 0.268±0.0732)3)4) 1.065±0.0252)3)4) 高剂量组 0.054±0.0122)3)4)5) 0.696±0.0242)3)4)5) F值 52.884 337.037 P值 <0.001 <0.001 注:与空白组比较,1)P<0.05;与VEGF组比较,2)P<0.05;与血清组比较,3)P<0.05;与低剂量组比较,4)P<0.05;与中剂量组比较,5)P<0.05。 -
[1] DELEVE LD. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in hepatic fibrosis[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 61(5): 1740-1746. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27376. [2] LI H. Angiogenesis in the progression from liver fibrosis to cirrhosis and hepatocelluar carcinoma[J]. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 15(3): 217-233. DOI: 10.1080/17474124.2021.1842732. [3] GRACIA-SANCHO J, MARRONE G, FERNÁNDEZ-IGLESIAS A. Hepatic microcirculation and mechanisms of portal hypertension[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 16(4): 221-234. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-018-0097-3. [4] MARRONE G, SHAH VH, GRACIA-SANCHO J. Sinusoidal communication in liver fibrosis and regeneration[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 65(3): 608-617. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.04.018. [5] ZADOROZHNA M, DI GIOIA S, CONESE M, et al. Neovascularization is a key feature of liver fibrosis progression: anti-angiogenesis as an innovative way of liver fibrosis treatment[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2020, 47(3): 2279-2288. DOI: 10.1007/s11033-020-05290-0. [6] WANG HY, CHEN Y. Research progress on Huangqi Decoction and its single herbs[J]. Shanghai J Tradit Chin Med, 2021, 55(8): 99-103. DOI: 10.16305/j.1007-1334.2021.2009128.王浩艺, 成扬. 黄芪汤及方中单味药研究进展[J]. 上海中医药杂志, 2021, 55(8): 99-103. DOI: 10.16305/j.1007-1334.2021.2009128. [7] CHENG Y, LIU P, HOU TL, et al. Mechanisms of Huangqi Decoction Granules on hepatitis B cirrhosis patients based on RNA-sequencing[J]. Chin J Integr Med, 2019, 25(7): 507-514. DOI: 10.1007/s11655-018-3013-3. [8] WANG HY, HUANG GJ, LIU CJ, et al. Study on effects and mechanism of Huangqi decoction on portal vein pressure in rats with portal hypertension[J]. Chin J Inf Tradit Chin Med, 2022. DOI: 10.19879/j.cnki.1005-5304.202112282.[Onlineaheadofprint]王浩艺, 黄广建, 刘从进, 等. 黄芪汤对肝硬化门静脉高压症大鼠门静脉压力的影响及作用机制研究[J]. 中国中医药信息杂志, 2022. DOI: 10.19879/j.cnki.1005-5304.202112282.[网络首发] [9] ROEHLEN N, CROUCHET E, BAUMERT TF. Liver fibrosis: Mechanistic concepts and therapeutic perspectives[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(4): 875. DOI: 10.3390/cells9040875. [10] FRIEDMAN SL, PINZANI M. Hepatic fibrosis 2022: Unmet needs and a blueprint for the future[J]. Hepatology, 2022, 75(2): 473-488. DOI: 10.1002/hep.32285. [11] LI H. Advances in anti hepatic fibrotic therapy with Traditional Chinese Medicine herbal formula[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2020, 251: 112442. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112442. [12] FU K, WANG C, MA C, et al. The potential application of Chinese medicine in liver diseases: A new opportunity[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 771459. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.771459. [13] Liver Disease Committee, Chinese Association of Integrative Medicine. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of liver fibrosis in integrative medicine practice (2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(7): 1444-1449. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.07.007.中国中西医结合学会肝病专业委员会. 肝纤维化中西医结合诊疗指南(2019年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(7): 1444-1449. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.07.007. [14] POISSON J, LEMOINNE S, BOULANGER C, et al. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells: Physiology and role in liver diseases[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 66(1): 212-227. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.07.009. [15] LI N, LIU C, MA G, et al. Asparaginyl endopeptidase may promote liver sinusoidal endothelial cell angiogenesis via PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. Rev Esp Enferm Dig, 2019, 111(3): 214-222. DOI: 10.17235/reed.2018.5709/2018. [16] RAPOPORT RM, MERKUS D. Endothelin-1 regulation of exercise-induced changes in flow: Dynamic regulation of vascular tone[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2017, 8: 517. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00517. [17] CHENG QN, YANG X, WU JF, et al. Interaction of non-parenchymal hepatocytes in the process of hepatic fibrosis (Review)[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2021, 23(5): 364. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12003. [18] KLINDT C, REICH M, HELLWIG B, et al. The G protein-coupled bile acid receptor TGR5 (Gpbar1) modulates endothelin-1 signaling in liver[J]. Cells, 2019, 8(11): 1467. DOI: 10.3390/cells8111467. [19] GARBUZENKO DV, AREFYEV NO, BELOV DV. Restructuring of the vascular bed in response to hemodynamic disturbances in portal hypertension[J]. World J Hepatol, 2016, 8(36): 1602-1609. DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i36.1602. [20] WU Q, FINLEY SD. Mathematical model predicts effective strategies to inhibit VEGF-eNOS signaling[J]. J Clin Med, 2020, 9(5): 1255. DOI: 10.3390/jcm9051255. [21] WU F, CHEN Z, LIU J, et al. The Akt-mTOR network at the interface of hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis[J]. Exp Hematol, 2021, 103: 15-23. DOI: 10.1016/j.exphem.2021.08.009. -



 PDF下载 ( 3258 KB)
PDF下载 ( 3258 KB)


 下载:
下载: