miR-21靶向调控PTEN/PI3K/Akt通路对胆管癌细胞恶性生物学行为的影响
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.09.026
Effect of micro-ribonucleic acid-21 on the malignant biological behavior of cholangiocarcinoma cells by targeting the PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway
-
摘要:
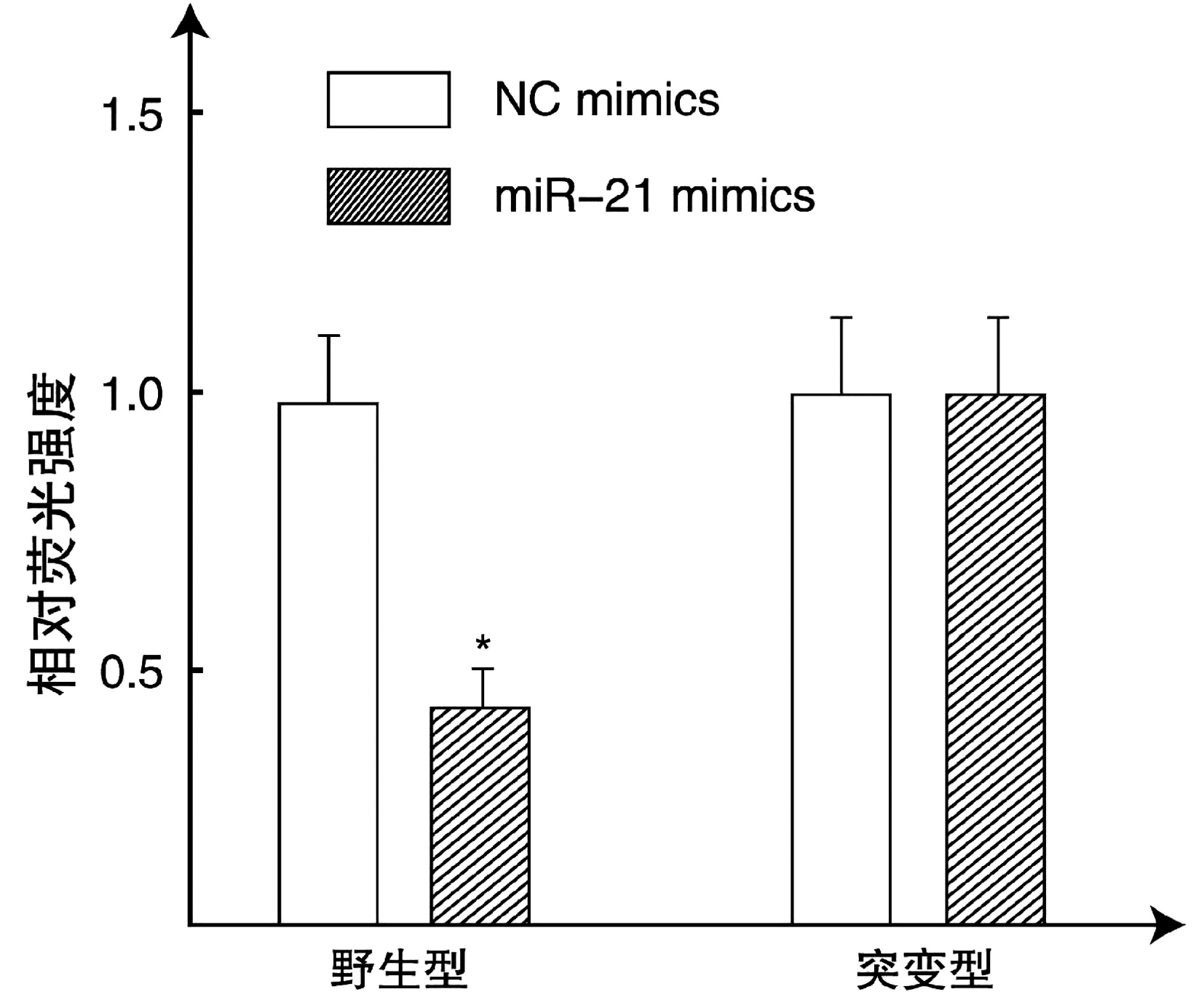
目的 探讨微小核糖核酸-21(miR-21)靶向蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶(PTEN)/磷酸肌醇-3-激酶(PI3K)/蛋白激酶B (Akt)通路对人胆管癌细胞株QBC939恶性生物学行为的影响。 方法 将对数期生长的胆管癌细胞株QBC939分为4组: 空载组、空白对照组、过表达组、沉默组。倒置荧光显微镜检测转染效率; 四甲基偶氮唑蓝法、流式细胞仪、Transwell小室实验、划痕实验检测细胞增殖活性、凋亡率、侵袭活性和迁移活性。实时逆转录聚合酶链反应(RT-qPCR)检测miR-21、PTEN、PI3K、Akt、哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mTOR) mRNA的表达; 免疫印迹法检测PTEN、PI3K、Akt、磷酸化Akt (p-Akt)和mTOR蛋白表达; 双荧光素酶报告基因实验验证miR-21对PTEN的作用。计量资料多组间比较采用单因素方差分析, 进一步两两差异比较采用SNK-q检验。 结果 过表达组、沉默组、空载组转染效率分别为(90.27±18.03)%、(91.43±18.26)%和(92.16±18.41)%。与空白对照组和空载组比较, 过表达组QBC939细胞增殖活性明显提高(P值均 < 0.05), 凋亡率显著下降(P值均 < 0.01);与空白对照组、空载组和过表达组比较, 沉默组细胞增殖活性显著降低(P值均 < 0.01), 而凋亡率显著上升(P值均 < 0.01)。与空白对照组和空载组比较, 过表达组QBC939细胞迁移率和穿膜数目均显著增高(P值均 < 0.01);与空白对照组、空载组和过表达组比较, 沉默组迁移率和穿膜数目均显著下降(P值均 < 0.01)。与空白对照组和空载组比较, 过表达组miR-21、PI3K、Akt和mTOR mRNA表达均升高, PTEN mRNA表达下降, 差异均有统计学意义(P值均 < 0.05);与空白对照组、空载组和过表达组比较, 沉默组miR-21、PI3K、Akt和mTOR mRNA表达均下降, PTEN mRNA表达升高, 差异均有统计学意义(P值均 < 0.05)。与空白对照组和空载组比较, 过表达组PI3K、Akt、p-Akt和mTOR蛋白表达均显著升高, PTEN蛋白表达显著下降(P值均 < 0.01);与空白对照组、空载组和过表达组比较, 沉默组PI3K、Akt、p-Akt和mTOR蛋白表达均显著下降, PTEN蛋白表达显著升高(P值均 < 0.01)。miR-21可靶向调控PTEN的表达。 结论 miR-21沉默可靶向PTEN/PI3K/Akt通路, 上调PTEN表达, 下调PI3K、Akt、mTOR表达及p-Akt水平, 抑制人胆管癌细胞株QBC939的恶性行为。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of micro-ribonucleic acid-21(miR-21) on the malignant biological behavior of human cholangiocarcinoma cell line QBC939 by targeting the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTEN)/inositol phosphate 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) pathway. Methods The cholangiocarcinoma cell line QBC939 in the logarithmic growth phase was divided into empty vector group, blank control group, overexpression group, and silencing group.An inverted fluorescence microscope was used to observe transfection efficiency; MTT assay, flow cytometry, Transwell assay, and wound healing assay were used to measure cell proliferative activity, apoptosis rate, invasion activity, and migration activity.Quantitative reverse transcription PCR was used to measure the mRNA expression levels of miR-21, PTEN, PI3K, Akt, and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR); Western blotting was used to measure the protein expression levels of PTEN, PI3K, Akt, phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt), and mTOR; dual-luciferase reporter assay was used to verify the effect of miR-21 on PTEN.A one-way analysis of variance was used for comparison of continuous data between multiple groups, and the SNK-q test was used for further comparison between two groups. Results Transfection efficiency was 90.27%±18.03% in the overexpression group, 91.43%±18.26% in the silencing group, and 92.16%±18.41% in the empty vector group.Compared with the blank control group and the empty vector group, the overexpression group had a significant increase in the proliferative activity of QBC939 cells (both P < 0.05) and a significant reduction in apoptosis rate (both P < 0.01);compared with the blank control group, the empty vector group, and the overexpression group, the silencing group had a significant reduction in proliferative activity (P < 0.01) and a significant increase in apoptosis rate (P < 0.01).Compared with the blank control group and the empty vector group, the overexpression group had significant increases in the migration rate of QBC939 cells and number of cells penetrating the membrane (all P < 0.01);compared with the blank control group, the empty vector group, and the overexpression group, the silencing group had significant reductions in migration rate and number of cells penetrating the membrane (all P < 0.01).Compared with the blank control group and the empty vector group, the overexpression group had significant increases in the mRNA expression levels of miR-21, PI3K, Akt, and mTOR and a significant reduction in the mRNA expression level of PTEN (all P < 0.05);compared with the blank control group, the empty vector group, and the overexpression group, the silencing group had significant reductions in the mRNA expression levels of miR-21, PI3K, Akt, and mTOR and a significant increase in the mRNA expression level of PTEN (all P < 0.05).Compared with the blank control group and the empty vector group, the overexpression group had significant increases in the protein expression levels of PI3K, Akt, p-Akt, and mTOR and a significant reduction in the protein expression level of PTEN (all P < 0.01);compared with the blank control group, the empty vector group, and the overexpression group, the silencing group had significant reductions in the protein expression levels of PI3K, Akt, p-Akt, and mTOR and a significant increase in the protein expression level of PTEN (all P < 0.01).Furthermore, miR-21 showed targeted regulation of PTEN expression. Conclusion MiR-21 silencing may inhibit the malignant biological behavior of human cholangiocarcinoma cell line QBC939 by targeting the PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway to upregulate the expression of PTEN and downregulate the expression of PI3K, Akt, mTOR, and p-Akt. -
Key words:
- MicroRNAs /
- Signal Transduction /
- Cell Proliferation /
- Apoptosis
-
表 1 PCR反应引物序列
Table 1. The primer sequences of PCR reaction
基因 引物序列 扩增产物长度(bp) miR-21 上游引物5′-GTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT-3′ 72 下游引物5′-GCCGCTAGCTTATCAGACTGATGT-3′ PI3K 上游引物5′-CAAAGCCGAGAACCTATTGC-3′ 384 下游引物5′-TTGAGGGAGTCATTGTGCTG-3′ Akt 上游引物5′-TGGACTACTTGCACTCCGAG-3′ 175 下游引物5′-CGCAGAACGTCTTCATGGTG-3′ mTOR 上游引物5′-ATGACGAGACCCAGGCTAAG-3′ 225 下游引物5′-GCCAGTCCATGCCATCAG-3′ PTEN 上游引物5′-TTATTGCTATGGGATTTCCTGC-3′ 198 下游引物5′-GCTGTGGTGGGTTATGGTCTTC-3′ β-actin 上游引物5′-TGACGTGGACATCCGCAAAG-3′ 443 下游引物5′-CTGGAAGGTGGACAGCGAGG-3′ 表 2 各组QBC939细胞凋亡率
Table 2. The apoptosis rates of QBC939 cells in each group
组别 细胞凋亡率(%) 空白对照组 5.74±1.13 空载组 6.08±1.20 过表达组 3.49±0.651)2) 沉默组 29.87±5.891)2)3) F值 81.767 P值 <0.001 注:与空白对照组比较,1)P<0.01;与空载组比较,2)P<0.01;与过表达组比较,3)P<0.01。 表 3 各组QBC939细胞体外侵袭实验结果
Table 3. Results of in vitro invasion experiments of QBC939 cells in each group
组别 迁移率(%) 穿膜数目(个) 空白对照组 49.21±9.81 253.53±50.61 空载组 49.03±9.78 251.49±50.25 过表达组 80.17±16.021)2) 413.01±82.561)2) 沉默组 28.64±5.711)2)3) 137.96±27.571)2)3) F值 18.784 20.194 P值 <0.001 <0.001 注:与空白对照组比较,1)P<0.01;与空载组比较,2)P<0.01;与过表达组比较,3)P<0.01。 表 4 各组细胞PI3K、Akt、p-Akt、mTOR和PTEN蛋白相对表达量
Table 4. Relative expression levels of PI3K, Akt, p-Akt, mTOR, and PTEN proteins in each group
组别 PI3K Akt p-Akt mTOR PTEN 空白对照组 1.35±0.26 0.45±0.09 0.51±0.09 0.79±0.15 0.43±0.08 空载组 1.33±0.24 0.44±0.07 0.49±0.08 0.78±0.14 0.42±0.06 过表达组 2.21±0.411)2) 0.84±0.161)2) 0.95±0.181)2) 1.81±0.361)2) 0.23±0.041)2) 沉默组 0.72±0.131)2)3) 0.19±0.031)2)3) 0.11±0.021)2)3) 0.41±0.081)2)3) 0.71±0.141)2)3) F值 24.197 36.489 43.880 40.639 25.059 P值 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 注:与空白对照组比较,1)P<0.01;与空载组比较,2)P<0.01;与过表达组比较,3)P<0.01。 -
[1] CARPINO G, CARDINALE V, FOLSERAAS T, et al. Neoplastic transformation of the peribiliary stem cell niche in cholangiocarcinoma arisen in primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 69(2): 622-638. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30210. [2] KHAN SA, TAVOLARI S, BRANDI G. Cholangiocarcinoma: Epidemiology and risk factors[J]. Liver Int, 2019, 39(Suppl 1): 19-31. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14095. [3] WANG M, CHEN Z, GUO P, et al. Therapy for advanced cholangiocarcinoma: Current knowledge and future potential[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2021, 25(2): 618-628. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.16151. [4] CILLO U, FONDEVILA C, DONADON M, et al. Surgery for cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Liver Int, 2019, 39 (Suppl 1): 143-155. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14089. [5] KONTOMANOLIS EN, KOUTRAS A, SYLLAIOS A, et al. Role of oncogenes and tumor-suppressor genes in carcinogenesis: A review[J]. Anticancer Res, 2020, 40(11): 6009-6015. DOI: 10.21873/anticanres.14622. [6] CARNEIRO BA, EL-DEIRY WS. Targeting apoptosis in cancer therapy[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2020, 17(7): 395-417. DOI: 10.1038/s41571-020-0341-y. [7] JIANG N, DAI Q, SU X, et al. Role of PI3K/AKT pathway in cancer: the framework of malignant behavior[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2020, 47(6): 4587-4629. DOI: 10.1007/s11033-020-05435-1. [8] ZHU B, WEI Y. Antitumor activity of celastrol by inhibition of proliferation, invasion, and migration in cholangiocarcinoma via PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. Cancer Med, 2020, 9(2): 783-796. DOI: 10.1002/cam4.2719. [9] CHEN L, YANG ZS, ZHOU YZ, et al. Dihydromyricetin inhibits cell proliferation, migration, invasion and promotes apoptosis via regulating miR-21 in human cholangiocarcinoma cells[J]. J Cancer, 2020, 11(19): 5689-5699. DOI: 10.7150/jca.45970. [10] LIU H, WANG J, TAO Y, et al. Curcumol inhibits colorectal cancer proliferation by targeting miR-21 and modulated PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathways[J]. Life Sci, 2019, 221: 354-361. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.02.049. [11] SCHMITTGEN TD, LIVAK KJ. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method[J]. Nat Protoc, 2008, 3(6): 1101-1108. DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2008.73. [12] MCGEARY SE, LIN KS, SHI CY, et al. The biochemical basis of microRNA targeting efficacy[J]. Science, 2019, 366(6472): eaav1741. DOI: 10.1126/science.aav1741. [13] ZOU Y, LI R, KUANG D, et al. Galangin inhibits cholangiocarcinoma cell growth and metastasis through downregulation of MicroRNA-21 expression[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020: 5846938. DOI: 10.1155/2020/5846938. [14] NARAYANAN S, CAI CY, ASSARAF YG, et al. Targeting the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway to overcome anti-cancer drug resistance[J]. Drug Resist Updat, 2020, 48: 100663. DOI: 10.1016/j.drup.2019.100663. [15] MOLLAEI H, SAFARALIZADEH R, ROSTAMI Z. MicroRNA replacement therapy in cancer[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(8): 12369-12384. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.28058. [16] SALIMINEJAD K, KHORRAM KHORSHID HR, SOLEYMANI FARD S, et al. An overview of microRNAs: Biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(5): 5451-5465. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.27486. [17] ROSSI M, ALTOMARE E, BOTTA C, et al. miR-21 antagonism abrogates Th17 tumor promoting functions in multiple myeloma[J]. Leukemia, 2021, 35(3): 823-834. DOI: 10.1038/s41375-020-0947-1. [18] WANG H, TAN Z, HU H, et al. microRNA-21 promotes breast cancer proliferation and metastasis by targeting LZTFL1[J]. BMC Cancer, 2019, 19(1): 738. DOI: 10.1186/s12885-019-5951-3. [19] WANG B, HUA P, ZHANG L, et al. LncRNA-IUR up-regulates PTEN by sponging miR-21 to regulate cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Esophagus, 2020, 17(3): 298-304. DOI: 10.1007/s10388-020-00724-x. [20] TAN AC. Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2020, 11(3): 511-518. DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.13328. [21] JANG DK, LEE YG, CHAN CHAE Y, et al. GDC-0980 (apitolisib) treatment with gemcitabine and/or cisplatin synergistically reduces cholangiocarcinoma cell growth by suppressing the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2020, 529(4): 1242-1248. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.06.011. [22] ZHANG XM, LIU ZL, QIU B, et al. Downregulation of EVI1 expression inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in hilar cholangiocarcinoma via the PTEN/AKT signalling pathway[J]. J Cancer, 2020, 11(6): 1412-1423. DOI: 10.7150/jca.31903. [23] LI G, ZHANG C, LIANG W, et al. Berberine regulates the Notch1/PTEN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and acts synergistically with 17-AAG and SAHA in SW480 colon cancer cells[J]. Pharm Biol, 2021, 59(1): 21-30. DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2020.1865407. [24] LIU HY, ZHANG YY, ZHU BL, et al. miR-21 regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells through PTEN/PI3K/AKT[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2019, 23(10): 4149-4155. DOI: 10.26355/eurrev_201905_17917. -



 PDF下载 ( 5240 KB)
PDF下载 ( 5240 KB)


 下载:
下载: