养血柔肝丸对多因素诱导的肝纤维化大鼠模型TGFβ1/Smad信号通路的影响
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.09.018
Effect of Yangxue Rougan pills on the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway in a rat model of liver fibrosis induced by multiple factors
-
摘要:
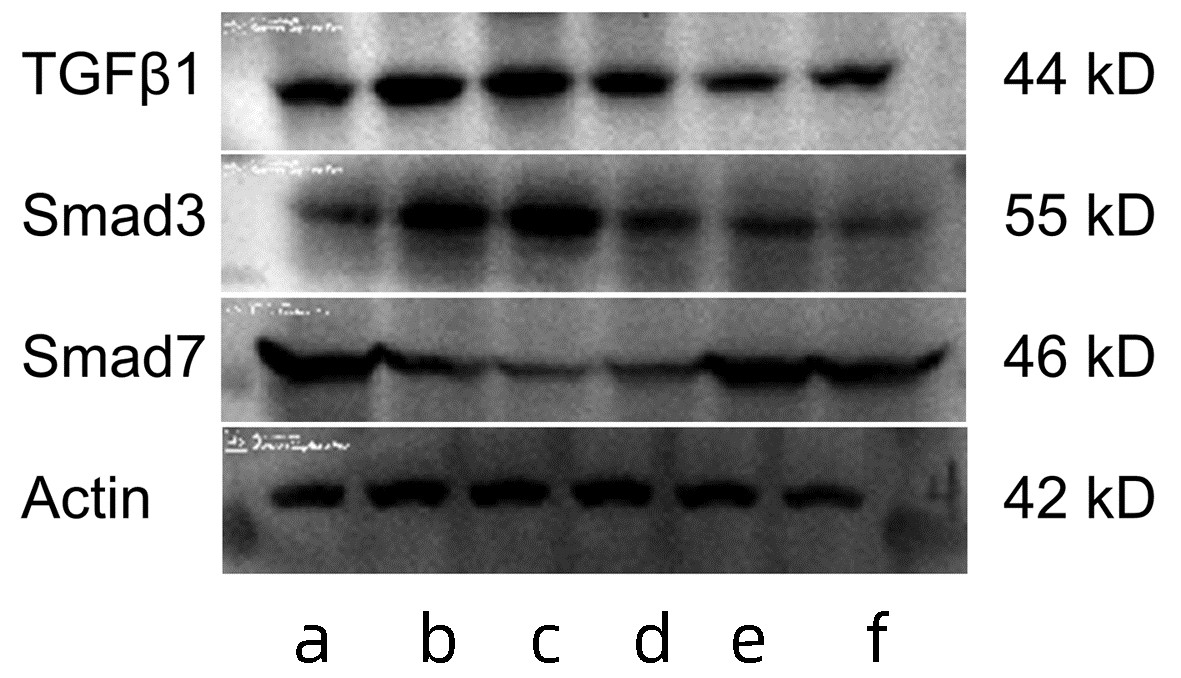
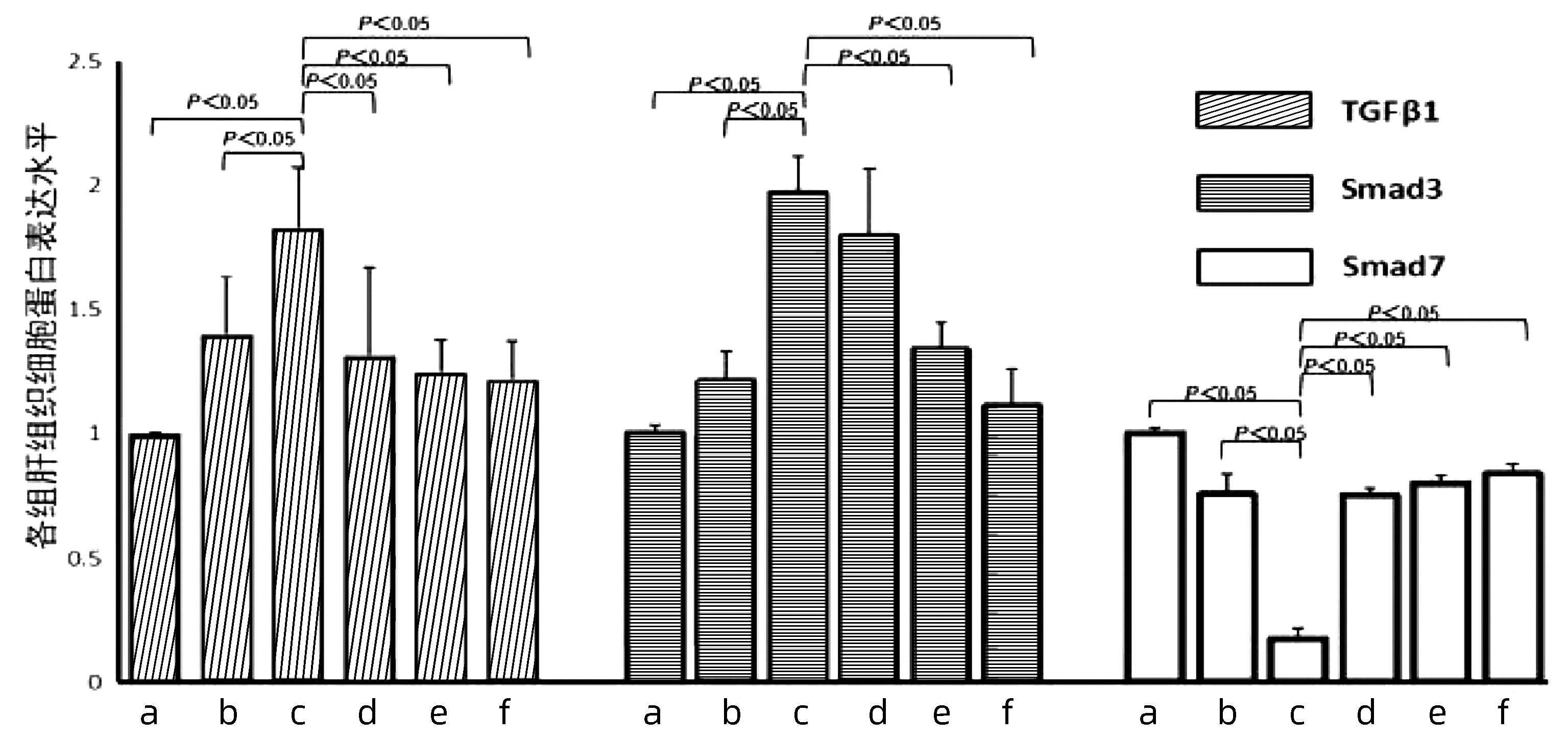
目的 观察养血柔肝丸对多因素诱导所致的大鼠肝纤维化的影响, 探讨养血柔肝丸治疗肝纤维化的作用机制。 方法 50只雄性大鼠随机分成空白对照组、多因素模型组、养血柔肝丸高剂量组、养血柔肝丸中剂量组、养血柔肝丸低剂量组和扶正化瘀胶囊组,共6组。空白对照组给予正常饮水和正常饲料。剩余各组大鼠给予改良高脂低蛋白饲料,5%食用酒精,并且大鼠皮下注射含有40%四氯化碳的橄榄油溶液和腹腔注射猪血清0.5 mL/只,2次/周,连续12周。从第7周开始,给予养血柔肝丸,分为高剂量组(9.5 g/kg)、中剂量组(4.75 g/kg)、低剂量组(2.38 g/kg),扶正化瘀胶囊组(0.75 g/kg),空白对照组、多因素模型组每日灌胃等体积量蒸馏水,连续6周,于第12周处理大鼠。采用HE染色及Masson染色病理观察大鼠肝纤维化程度; PCR和Western blot检测大鼠肝TGFβ1、Smad3、Smad7的表达情况。计量资料多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,进一步两两比较采用Dunnett-t检验法。 结果 多因素模型组与空白对照组相比可见肝小叶结构严重破坏,纤维化明显增强,形成不同大小的假小叶; 而养血柔肝丸各剂量组较多因素模型组肝纤维化程度明显好转,以养血柔肝丸高、中剂量组治疗趋势最显著。多因素模型组大鼠肝组织TGFβ1、Smad3的表达与空白对照组比较有明显提升(P值均<0.05),Smad7的表达则明显下降(P<0.05),而养血柔肝丸各剂量组TGFβ1的表达与多因素模型组比较有所降低(P值均<0.05),Smad7的表达则明显升高(P值均<0.05);养血柔肝丸高、中剂量组Smad3的表达与多因素模型组比较有所降低, 差异有统计学意义(P值均<0.05)。 结论 养血柔肝丸可明显抑制大鼠肝纤维化,使大鼠肝组织中TGFβ1、Smad3的表达下调,Smad7的表达上调,TGFβ1/Smad信号通路是养血柔肝丸改善肝纤维化的作用机制之一。 -
关键词:
- 肝硬化 /
- 转化生长因子β1 /
- Smad蛋白质类 /
- 药理作用分子作用机制
Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of Yangxue Rougan pills on a rat model of liver fibrosis induced by multiple factors and the mechanism of action of Yangxue Rougan pills in the treatment of liver fibrosis. Methods A total of 50 male rats were randomly divided into blank control group, multi-factor model group, Fuzheng Huayu capsule group, and high-, middle-, and low-dose Yangxue Rougan pill groups. The rats in the blank control group were given normal water and feed, and those in the other groups were given modified high-fat low-protein diet and 5% alcohol, as well as subcutaneous injection of olive oil solution containing 40% carbon tetrachloride and intraperitoneal injection of pig serum 0.5 mL per rat, twice a week for 12 consecutive weeks. Since week 7, the rats in the high-, middle-, and low-dose Yangxue Rougan pill groups were given Yangxue Rougan pills at a dose of 9.5, 4.75, and 2.38 g/kg, respectively, those in the Fuzheng Huayu capsule group were given Fuzheng Huayu capsules at a dose of 0.75 g/kg, and those in the blank control group and the multi-factor model group were given an equal volume of distilled water by gavage every day for 6 consecutive weeks. The rats were treated at week 12. HE staining and Masson staining were used to observe the degree of liver fibrosis in rats, and PCR and Western blot were used to measure the expression of TGF-β1, Smad3, and Smad7 in the liver. A one-way analysis of variance was used for comparison of continuous data between multiple groups, and the Dunnett's t-test was used for further comparison between two groups. Results Compared with the blank control group, the multi-factor model group had a severely damaged lobular structure and a significantly higher degree of liver fibrosis, with the formation of pseudolobules with different sizes; compared with the multi-factor model group, the Yangxue Rougan pill groups had a significant improvement in the degree of liver fibrosis, with the most significant therapeutic effect in the high- and middle-dose Yangxue Rougan pill groups. Compared with the blank control group, the multi-factor model group had significant increases in the expression of TGF-β1 and Smad3 and a significant reduction in the expression of Smad7 in liver tissue (all P < 0.05); compared with the multi-factor model group, the Yangxue Rougan pill groups had a significant reduction in the expression of TGF-β1 and a significant increase in the expression of Smad7 (all P < 0.05); compared with the multi-factor model group, the high- and middle-dose Yangxue Rougan pill groups had a significant reduction in the expression of Smad3 (both P < 0.05). Conclusion Yangxue Rougan pills can significantly inhibit liver fibrosis in rats by downregulating the expression of TGF-β1 and Smad3 and upregulating the expression of Smad7, and therefore, the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway is one of the mechanisms of action of Yangxue Rougan pills in improving liver fibrosis. -
表 1 引物序列
Table 1. Primer sequence
基因 引物序列(5′-3′) 扩增片段长度(bp) β-actin F: CCCATCTATGAGGGTTACGC 150 R: TTTAATGTCACGCACGATTTC TGFβ1 F: ATTCCTGGCGTTACCTTGG 120 R: AGCCCTGTATTCCGTCTCCT Smad3 F: GAGACATTCCACGCTTCACA 110 R: GCTGCATTCCGGTTAACATT Smad7 F: AAGTCAAGAGGCTGTGTTGCTGTG 128 R: CATCGGGTATCTGGAGTAAGGAGGAG -
[1] DONGIOVANNI P, ROMEO S, VALENTI L. Hepatocellular carcinoma in nonalcoholic fatty liver: role of environmental and genetic factors[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(36): 12945-12955. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i36.12945. [2] LEE JH, JANG EJ, SEO HL, et al. Sauchinone attenuates liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cell activation through TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2014, 224: 58-67. DOI: 10.1016/j.cbi.2014.10.005. [3] HAMZAVI J, EHNERT S, GODOY P, et al. Disruption of the Smad7 gene enhances CCI4-dependent liver damage and fibrogenesis in mice[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2008, 12(5B): 2130-2144. DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00262.x. [4] ATTA HM. Reversibility and heritability of liver fibrosis: Implications for research and therapy[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2015, 21(17): 5138-5148. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i17.5138. [5] ELPEK GÖ. Cellular and molecular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis: An update[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(23): 7260-7276. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7260. [6] OAKLEY F, MESO M, IREDALE JP, et al. Inhibition of inhibitor of kappaB kinases stimulates hepatic stellate cell apoptosis and accelerated recovery from rat liver fibrosis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2005, 128(1): 108-120. DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00541-10. [7] DOOLEY S, TEN DIJKE P. TGF-β in progression of liver disease[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2012, 347(1): 245-256. DOI: 10.1007/s00441-011-1246-y. [8] YANG AT, LI WY, YAN XZ, et al. Hepcidin decreased hepatic stellate cells activation[J]. J Clin Exp Med, 2020, 19(10): 1037-1040. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2020.010.009.杨爱婷, 李为雨, 严旭禛, 等. 铁调素在肝纤维化中的表达特点及对肝星状细胞的作用[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2020, 19(10): 1037-1040. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2020.010.009. [9] CUI W, JIN HB, LI ZW. Mechanism of the transforming growth factor-beta induction of fibronectin expression in hepatic stem-like cells[J]. Braz J Med Biol Res, 2010, 43(1): 36-42. DOI: 10.1002/hep.23354. [10] LATELLA G, VETUSCHI A, SFERRA R, et al. Targeted disruption of Smad3 confers resistance to the development of dimethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic fibrosis in mice[J]. Liver Int, 2009, 29(7): 997-1009. DOI: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2009.02011.x. [11] YANG XY, YANG Y, ZHENG Y, et al. Effect of exogenous Smad7 gene transfected hepatic stellate cells on mRNA expression of transforming growth factor beta 1, collagen Ⅰ and collagen Ⅲ [J]. J Clin Rehabil Tissue Eng Res, 2009, 13(50): 9887-9891. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8225.2009.50.018.杨小艳, 杨勇, 郑勇, 等. 外源Smad7转染肝星状细胞及对转化生长因子β1和Ⅰ、Ⅲ型胶原mRNA表达的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009, 13(50): 9887-9891. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8225.2009.50.018. -



 PDF下载 ( 4844 KB)
PDF下载 ( 4844 KB)


 下载:
下载: