转录因子阴阳1在肝细胞癌中的作用
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.08.039
利益冲突声明:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:周洁负责资料搜集,资料分析与总结,撰写论文;华芸豪参与搜集资料,修改论文;王晓美负责拟定写作思路,指导撰写文章;牛俊奇负责论文写作方向设计并最后定稿。
-
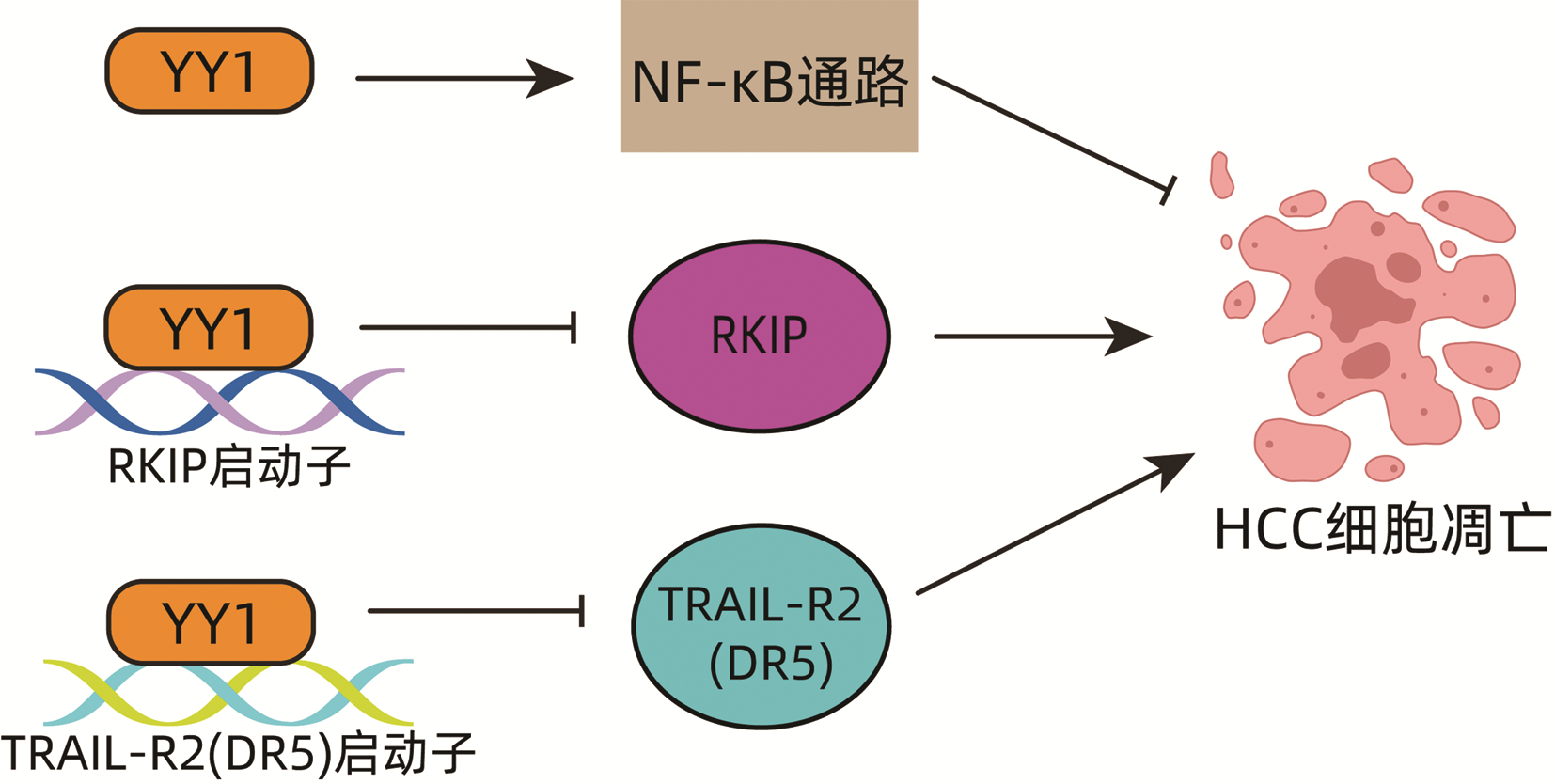
摘要: 肝细胞癌(HCC)起病隐匿,大多数患者确诊时进展至中晚期,错过了最佳治疗时机,往往预后不良。转录因子阴阳1(YY1)是一种多功能转录因子,可调节多种重要基因的转录,在多种肿瘤中发挥重要作用。既往研究显示,YY1影响HCC许多生物学行为,如增殖、凋亡、迁移和血管生成,还与HCC的耐药性及不良预后密切相关。本文系统总结了YY1在HCC发生发展中的作用相关研究进展,为HCC的治疗提供一定的理论依据。Abstract: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) often has an insidious onset, and most patients are in the advanced stage and have lost the best opportunity for treatment at the time of diagnosis, resulting in a poor prognosis. As a multifunctional transcription factor, Yin Yang 1 (YY1) regulates the transcription of a variety of important genes and plays a key role in various tumors. Previous studies have shown that YY1 affects many biological behaviors such as proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and angiogenesis and is closely associated with drug resistance and poor prognosis of HCC. This article reviews the research advances in the role of YY1 in the development and progression of HCC, so as to provide a theoretical basis for the treatment of HCC.
-
Key words:
- Carcinoma, Hepatocellular /
- Transcription Factors /
- Zinc Fingers
-
[1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21660. [2] MELIALA I, HOSEA R, KASIM V, et al. The biological implications of Yin Yang 1 in the hallmarks of cancer[J]. Theranostics, 2020, 10(9): 4183-4200. DOI: 10.7150/thno.43481. [3] SARVAGALLA S, KOLAPALLI SP, VALLABHAPURAPU S. The two sides of YY1 in cancer: A friend and a foe[J]. Front Oncol, 2019, 9: 1230. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01230. [4] MARTINEZ-RUIZ GU, MORALES-SANCHEZ A, PACHECO-HERNANDEZ AF. Roles played by YY1 in embryonic, adult and cancer stem cells[J]. Stem Cell Rev Rep, 2021, 17(5): 1590-1606. DOI: 10.1007/s12015-021-10151-9. [5] LEE JS, SEE RH, GALVIN KM, et al. Functional interactions between YY1 and adenovirus E1A[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 1995, 23(6): 925-931. DOI: 10.1093/nar/23.6.925. [6] LIU D, ZHANG J, WU Y, et al. YY1 suppresses proliferation and migration of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by regulating the CDKN3/MdM2/P53/P21 signaling pathway[J]. Int J Cancer, 2018, 142(7): 1392-1404. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.31173. [7] SHEN B, LI Y, YE Q, et al. YY1-mediated long non-coding RNA Kcnq1ot1 promotes the tumor progression by regulating PTEN via DNMT1 in triple negative breast cancer[J]. Cancer Gene Ther, 2021, 28(10-11): 1099-1112. DOI: 10.1038/s41417-020-00254-9. [8] WANG L, GAO Y, ZHAO X, et al. HOXD3 was negatively regulated by YY1 recruiting HDAC1 to suppress progression of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via ITGA2 pathway[J]. Cell Prolif, 2020, 53(8): e12835. DOI: 10.1111/cpr.12835. [9] ZHANG L, CAI X, CHEN K, et al. Hepatitis B virus protein up-regulated HLJ1 expression via the transcription factor YY1 in human hepatocarcinoma cells[J]. Virus Res, 2011, 157(1): 76-81. DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2011.02.009. [10] YANG W, LI Z, QIN R, et al. YY1 Promotes endothelial cell-dependent tumor angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma by transcriptionally activating VEGFA[J]. Front Oncol, 2019, 9: 1187. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01187. [11] XUAN W, ZHOU C, YOU G. LncRNA LINC00668 promotes cell proliferation, migration, invasion ability and EMT process in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting miR-532-5p/YY1 axis[J]. Biosci Rep, 2020, 40(5): BSR20192697. DOI: 10.1042/BSR20192697. [12] XU XP, PENG XQ, YIN XM, et al. miR-34a-5p suppresses the invasion and metastasis of liver cancer by targeting the transcription factor YY1 to mediate MYCT1 upregulation[J]. Acta Histochem, 2020, 122(6): 151576. DOI: 10.1016/j.acthis.2020.151576. [13] ZHANG S, JIANG T, FENG L, et al. Yin Yang-1 suppresses differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the downregulation of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha[J]. J Mol Med (Berl), 2012, 90(9): 1069-1077. DOI: 10.1007/s00109-012-0879-y. [14] LUO YD, FANG L, YU HQ, et al. p53 haploinsufficiency and increased mTOR signalling define a subset of aggressive hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 74(1): 96-108. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.07.036. [15] GRÖNROOS E, TERENTIEV AA, PUNGA T, et al. YY1 inhibits the activation of the p53 tumor suppressor in response to genotoxic stress[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2004, 101(33): 12165-12170. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0402283101. [16] NOTARBARTOLO M, GIANNITRAPANI L, VIVONA N, et al. Frequent alteration of the Yin Yang 1/Raf-1 kinase inhibitory protein ratio in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. OMICS, 2011, 15(5): 267-272. DOI: 10.1089/omi.2010.0096. [17] MEI C, JIANG X, GU Y, et al. YY1-mediated reticulocalbin-2 upregulation promotes the hepatocellular carcinoma progression via activating MYC signaling[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2021, 11(5): 2238-2251. [18] DING D, HUANG H, JIANG W, et al. Reticulocalbin-2 enhances hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation via modulating the EGFR-ERK pathway[J]. Oncogene, 2017, 36(48): 6691-6700. DOI: 10.1038/onc.2017.230. [19] WANG Y, DOU L, QIN Y, et al. OIP5-AS1 contributes to tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma by miR-300/YY1-activated WNT pathway[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2020, 20: 440. DOI: 10.1186/s12935-020-01467-6. [20] PETKOVA V, ROMANOWSKI MJ, SULIJOADIKUSUMO I, et al. Interaction between YY1 and the retinoblastoma protein. Regulation of cell cycle progression in differentiated cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2001, 276(11): 7932-7936. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M007411200. [21] WANG X, FENG Y, XU L, et al. YY1 restrained cell senescence through repressing the transcription of p16[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2008, 1783(10): 1876-1883. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.05.015. [22] TSANG DP, WU WK, KANG W, et al. Yin Yang 1-mediated epigenetic silencing of tumour-suppressive microRNAs activates nuclear factor-κB in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Pathol, 2016, 238(5): 651-664. DOI: 10.1002/path.4688. [23] ODABAEI G, CHATTERJEE D, JAZIREHI AR, et al. Raf-1 kinase inhibitor protein: structure, function, regulation of cell signaling, and pivotal role in apoptosis[J]. Adv Cancer Res, 2004, 91: 169-200. DOI: 10.1016/S0065-230X(04)91005-6. [24] E CY. The research of the DR4 and DR5 expressions in hepatocellular carcinoma apoptosis induced by TRAIL[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2008.鄂长勇. 死亡受体DR4和DR5的表达在TRAIL诱导肝癌细胞凋亡中的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2008. [25] BARITAKI S, HUERTA-YEPEZ S, SAKAI T, et al. Chemotherapeutic drugs sensitize cancer cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis: up-regulation of DR5 and inhibition of Yin Yang 1[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2007, 6(4): 1387-1399. DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0521. [26] ALLOUCHE A, NOLENS G, TANCREDI A, et al. The combined immunodetection of AP-2alpha and YY1 transcription factors is associated with ERBB2 gene overexpression in primary breast tumors[J]. Breast Cancer Res, 2008, 10(1): R9. DOI: 10.1186/bcr1851. [27] HAN J, MENG J, CHEN S, et al. YY1 complex promotes quaking expression via super-enhancer binding during EMT of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Res, 2019, 79(7): 1451-1464. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-2238. [28] CHO AA, BONAVIDA B. Targeting the overexpressed YY1 in cancer inhibits EMT and metastasis[J]. Crit Rev Oncog, 2017, 22(1-2): 49-61. DOI: 10.1615/CritRevOncog.2017020473. [29] KALLURI R, WEINBERG RA. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. J Clin Invest, 2009, 119(6): 1420-1428. DOI: 10.1172/JCI39104. [30] PALMER MB, MAJUMDER P, COOPER JC, et al. Yin yang 1 regulates the expression of snail through a distal enhancer[J]. Mol Cancer Res, 2009, 7(2): 221-229. DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0229. [31] CANO A, PÉREZ-MORENO MA, RODRIGO I, et al. The transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2000, 2(2): 76-83. DOI: 10.1038/35000025. [32] MARTÍNEZ-ESTRADA OM, CULLERÉS A, SORIANO FX, et al. The transcription factors Slug and Snail act as repressors of Claudin-1 expression in epithelial cells[J]. Biochem J, 2006, 394(Pt 2): 449-457. DOI: 10.1042/BJ20050591. [33] MYONG NH. Loss of E-cadherin and acquisition of vimentin in epithelial-mesenchymal transition are noble indicators of uterine cervix cancer progression[J]. Korean J Pathol, 2012, 46(4): 341-348. DOI: 10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.4.341. [34] HAO L, HA JR, KUZEL P, et al. Cadherin switch from E- to N-cadherin in melanoma progression is regulated by the PI3K/PTEN pathway through Twist and Snail[J]. Br J Dermatol, 2012, 166(6): 1184-1197. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2012.10824.x. [35] STANISAVLJEVIC J, PORTA-de-la-RIVA M, BATLLE R, et al. The p65 subunit of NF-κB and PARP1 assist Snail1 in activating fibronectin transcription[J]. J Cell Sci, 2011, 124(Pt 24): 4161-4171. DOI: 10.1242/jcs.078824. [36] SEMENZA GL. Angiogenesis in ischemic and neoplastic disorders[J]. Annu Rev Med, 2003, 54: 17-28. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.med.54.101601.152418. [37] WU S, KASIM V, KANO MR, et al. Transcription factor YY1 contributes to tumor growth by stabilizing hypoxia factor HIF-1α in a p53-independent manner[J]. Cancer Res, 2013, 73(6): 1787-1799. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-0366. [38] de NIGRIS F, CRUDELE V, GIOVANE A, et al. CXCR4/YY1 inhibition impairs VEGF network and angiogenesis during malignancy[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2010, 107(32): 14484-14489. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1008256107. [39] SITWALA KV, ADAMS K, MARKOVITZ DM. YY1 and NF-Y binding sites regulate the transcriptional activity of the dek and dek-can promoter[J]. Oncogene, 2002, 21(57): 8862-8870. DOI: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206041. [40] ZHANG Y, LIU J, WANG S, et al. The DEK oncogene activates VEGF expression and promotes tumor angiogenesis and growth in HIF-1α-dependent and -independent manners[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(17): 23740-23756. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.8060. [41] CHEN MS, HU ZL. Research progress of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy in the conversion therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2021, 20(2): 171-177. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20201230-00813.陈敏山, 胡自力. 肝动脉灌注化疗在肝癌转化治疗中的研究进展[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2021, 20(2): 171-177. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20201230-00813. [42] DONG S, MA X, WANG Z, et al. YY1 promotes HDAC1 expression and decreases sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to HDAC inhibitor[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(25): 40583-40593. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17196. [43] WEI JY, SUN W, LIU XM, et al. Advances in targated therapy and immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(10): 2320-2324. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.10.035.魏建莹, 孙巍, 刘晓民, 等. 肝细胞癌的靶向及免疫治疗进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36(10): 2320-2324. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.10.035. [44] ZOU W, WOLCHOK JD, CHEN L. PD-L1 (B7-H1) and PD-1 pathway blockade for cancer therapy: Mechanisms, response biomarkers, and combinations[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2016, 8(328): 328rv4. DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aad7118. [45] HAYS E, BONAVIDA B. YY1 regulates cancer cell immune resistance by modulating PD-L1 expression[J]. Drug Resist Updat, 2019, 43: 10-28. DOI: 10.1016/j.drup.2019.04.001. [46] CORTEZ MA, IVAN C, VALDECANAS D, et al. PDL1 regulation by p53 via miR-34[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2016, 108(1): djv303. DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djv303. [47] KIM JS, SON SH, KIM MY, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic relevance of CP2c and YY1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(15): 24389-24400. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15462. [48] HUANG YP, LUO WX, XU LB. Expression and function of transcription factor YY1 in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Lingnan Mod Clin Surg, 2021, 21(1): 44-52, 58. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-976X.2021.01.008.黄贻培, 罗伟鑫, 许磊波. 转录因子YY1在肝细胞癌中的表达和功能研究[J]. 岭南现代临床外科, 2021, 21(1): 44-52, 58. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-976X.2021.01.008. -



 PDF下载 ( 3288 KB)
PDF下载 ( 3288 KB)


 下载:
下载: