A preliminary study on percutaneous transhepatic drainage combined with sequential percutaneous nephroscopy in treatment of refractory liver abscess
-
摘要:
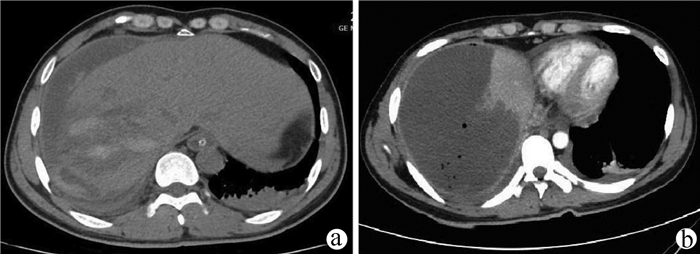
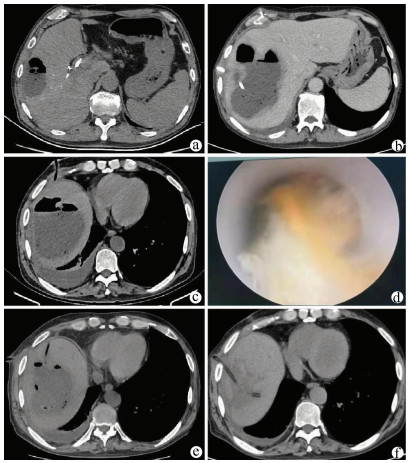
目的 探讨肝动脉介入栓塞术后形成的复杂性肝脓肿行经皮经肝穿刺引流序贯经皮肾镜坏死组织清除引流治疗的效果。 方法 回顾性分析2018年1月—2020年12月西安交通大学医学院附属汉中三二〇一医院肝胆胰脾外科收治的3例肝动脉介入栓塞术后形成难治性肝脓肿患者(胰十二指肠切除术后肝转移瘤行介入形成肝脓肿1例、巨块型肝癌反复行介入治疗后肝脓肿1例、外伤性肝破裂行肝动脉介入栓塞术后继发肝脓肿1例),3例患者均采用经皮经肝穿刺引流序贯经皮肾镜治疗难治性肝脓肿,对其具体治疗过程进行总结。 结果 3例患者均经CT检查、血常规、降钙素原、血培养及临床表现诊断为难治性肝脓肿,采用常规超声或CT引导下经皮经肝穿刺置管、敏感抗生素治疗疗效欠佳,后序贯经皮肾镜行肝脓肿坏死组织清除引流后肝脓肿均治愈,预后良好。 结论 针对介入术后形成的难治性肝脓肿,常规穿刺治疗效果欠佳,且无法或患者难以耐受外科手术时,采用经皮经肝穿刺引流序贯经皮肾镜治疗复杂性肝脓肿是安全、有效的。 -
关键词:
- 肝脓肿 /
- 引流术 /
- 内窥镜检查, 消化系统
Abstract:Objective To investigate the clinical effect of percutaneous transhepatic drainage combined with sequential percutaneous nephroscopy for necrosectomy and drainage in the treatment of refractory liver abscess after transcatheter arterial embolization (TACE). Methods A retrospective analysis was performed for three patients with refractory liver abscess after TACE in The Affiliated 3201 Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University School of Medicine from January 2018 to December 2020, and among the three patients, one had the formation of liver abscess after TACE for hepatic metastases after pancreaticoduodenectomy, one had liver abscess after repeated TACE for massive hepatocellular carcinoma, and one had secondary liver abscess after TACE for traumatic hepatic rupture. All three patients received percutaneous transhepatic drainage and sequential percutaneous nephroscopy for the treatment of refractory liver abscess, and their specific treatment process was summarized. Results All three patients were diagnosed with refractory liver abscess based on CT, routine blood test, procalcitonin, blood culture, and clinical manifestation. Percutaneous transhepatic catheterization under the guidance of conventional ultrasonography or CT and effective antibiotics had an unsatisfactory therapeutic effect, and after sequential percutaneous nephroscopy was performed for necrosectomy and drainage, liver abscess was cured and the patients had good prognosis. Conclusion For refractory liver abscess after TACE, when routine puncture treatment has an unsatisfactory therapeutic effect or a patient cannot tolerate surgical operation, percutaneous transhepatic drainage combined with sequential percutaneous nephroscopy is safe and effective in the treatment of refractory liver abscess. -
Key words:
- Liver Abscess /
- Drainage /
- Endoscopy, Digestive System
-
表 1 3例难治性肝脓肿患者一般资料
患者 年龄(岁) 性别 原发疾病 基础疾病 手术史 肝脓肿大小 WBC(×109/L) 高热时间 Child-Pugh分级 A 57 男 胰腺癌伴肝转移瘤 原发性高血压 Whipple术后、TACE 14 cm×9 cm×12 cm 28.5 介入后4 d A级 B 65 男 巨块型肝癌 2型糖尿病 TACE(3次) 8 cm×6 cm×6 cm 26.8 介入后6 d B级 C 23 女 重度复合、肝破裂 创伤性湿肺 TACE 12 cm×10 cm×8 cm 32.6 介入后2 d A级 -
[1] BROWN DB, GESCHWIND JF, SOULEN MC, et al. Society of Interventional Radiology position statement on chemoembolization of hepatic malignancies[J]. J Vasc Interv Radiol, 2009, 20(7 Suppl): s317-323. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvir.2009.04.015. [2] NAULT JC, SUTTER O, NAHON P, et al. Percutaneous treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: State of the art and innovations[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 68(4): 783-797. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.10.004. [3] LI M, LU YY, DONG JH, et al. Clinical effect of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization combined with microwave ablation in treatment of advanced primary liver cancer[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(12): 2720-2724. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.12.016.李猛, 陆荫英, 董景辉, 等. 经肝动脉化疗栓塞术联合微波消融治疗中晚期原发性肝癌的效果分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36(12): 2720-2724. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.12.016. [4] LI JH, YAO RR, SHEN HJ, et al. Clostridium perfringens infection after transarterial chemoembolization for large hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2015, 21(14): 4397-4401. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4397. [5] HUANG Y, ZHANG WH. Research advances in diagnosis and treatment of bacterial liver abscess[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34(3): 641-644. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.03.045.黄洋, 张伟辉. 细菌性肝脓肿的诊治进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2018, 34(3): 641-644. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.03.045. [6] WI JW, CHO EA, JUN CH, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of pyogenic liver abscess in elderly Korean patients[J]. Korean J Gastroenterol, 2015, 66(1): 27-32. DOI: 10.4166/kjg.2015.66.1.27. [7] CAI MT, LIANG LC. Pathogen distribution and drug resistance in liver cancer patients with liver abscess after transarterial chemoembolization or ablation[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(1): 118-122. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.01.026.蔡妙甜, 梁连春. 原发性/转移性肝癌患者经肝动脉化疗栓塞术或消融术后发生肝脓肿的病原菌分布及耐药性分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36(1): 118-122. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.01.026. [8] ZHU QL, XIANG XX, YUAN LY, et al. Clinical effect of ultrasound-guided percutaneous drainage in treatment of liver abscess[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(6): 1318-1321. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.06.027.朱沁玲, 向晓星, 袁乐瑶, 等. 超声引导下经皮穿刺引流治疗肝脓肿的效果观察[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(6): 1318-1321. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.06.027. [9] PICKENS RC, JENSEN S, SULZER JK, et al. Minimally invasive surgical management as effective first-line treatment of large pyogenic hepatic abscesses[J]. Am Surg, 2019, 85(8): 813-820. [10] BEI YF. Clinical effect and feasibility of laparoscopic catheter drainage versus incision and drainage in treatment of liver abscess[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2015, 20(6): 499. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2015.06.025.贝云枫. 腹腔镜下行肝脓肿置管引流和切开引流的疗效及可行性分析[J]. 肝脏, 2015, 20(6): 499. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2015.06.025. [11] SHIN JU, KIM KM, SHIN SW, et al. A prediction model for liver abscess developing after transarterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2014, 46(9): 813-817. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2014.05.003. [12] JIA Z, TU J, CAO C, et al. Liver abscess following transarterial chemoembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective analysis of 23 cases[J]. J Cancer Res Ther, 2018, 14(Supplement): S628-S633. DOI: 10.4103/0973-1482.199385. -



 PDF下载 ( 2925 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2925 KB)

 下载:
下载: