粪菌移植对慢加急性肝衰竭小鼠模型肠道菌群的影响
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.06.031
利益冲突声明:本研究不存在研究者、伦理委员会成员、受试者监护人以及与公开研究成果有关的利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:高安负责课题设计,实施研究,资料分析,撰写论文;徐玉静、陆圣威参与收集及分析数据;孙蔚负责拟定写作思路,修改论文;甘建和负责指导撰写文章并最后定稿。
Effect of fecal microbiota transplantation on intestinal flora in mice with acute-on-chronic liver failure
-
摘要:
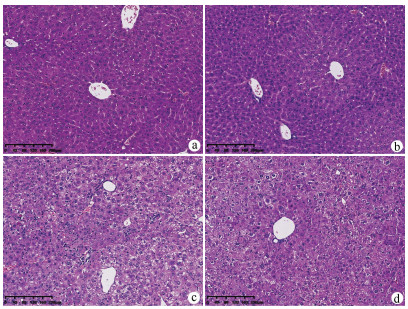
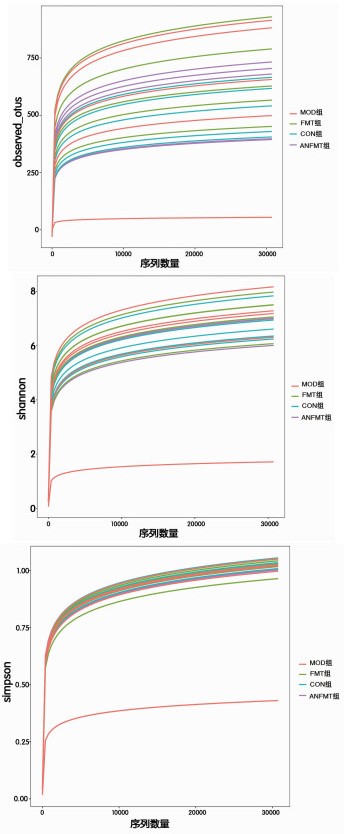
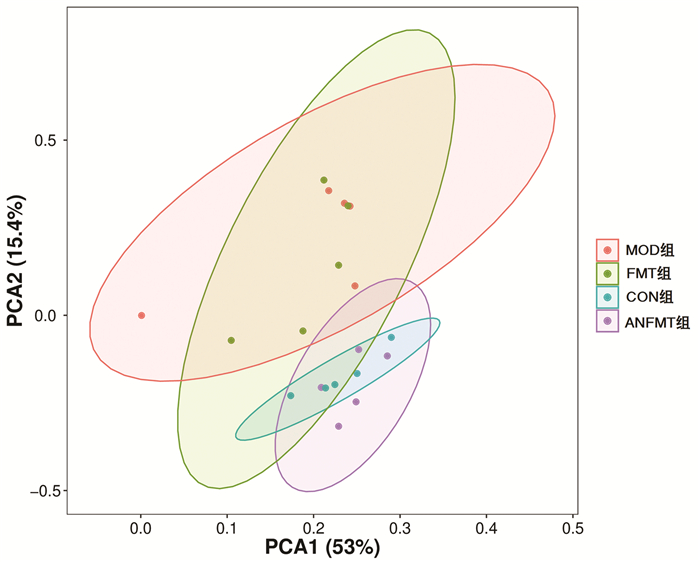
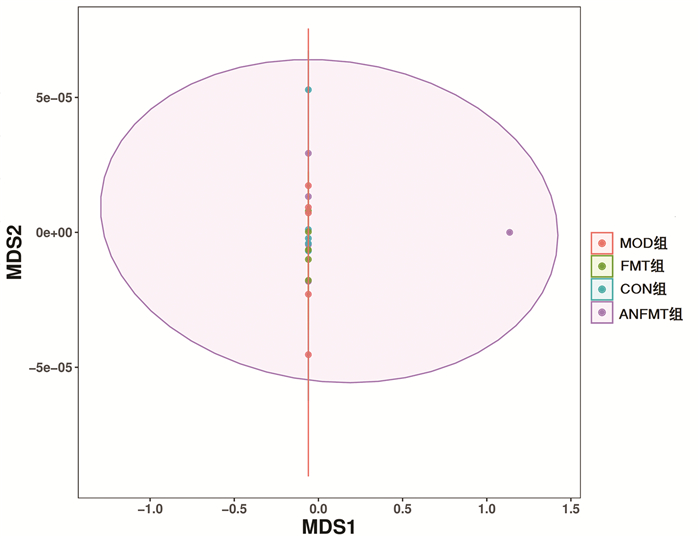
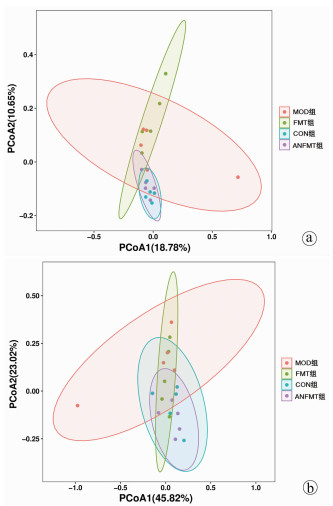
目的 研究粪菌移植(FMT)对慢加急性肝衰竭(ACLF)小鼠的保护作用及其对肠道菌群的影响。方法将40只小鼠按随机数字表法分为正常组(CON组)、模型组(MOD组)、粪菌移植组(FMT组,选取CON组小鼠粪便作为粪菌供体)、模型小鼠粪菌移植组(ANFMT组,选取模型组小鼠粪便作为粪菌供体),每组均10只。观察每组小鼠体质量、死亡情况、肝组织病理、AST、ALT和肠道菌群变化。符合正态分布的计量资料多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,进一步两两比较采用SNK-q检验。 结果 与CON组小鼠相比,MOD组小鼠体质量明显下降,AST、ALT明显升高(P值均<0.05);肝细胞大片状坏死;疣微菌门(Verrucomicrobia)、阿克曼菌属(Akkermansia)、Erysipelatoclostridium显著上升,Dubosiella、Duncaniella显著下降(P值均<0.05)。与CON组小鼠相比,ANFMT组小鼠AST显著升高(P<0.05);肝细胞肿胀,轻微气球样变;未分类(unclassified)、Faecalibaculum显著上升,Patescibacteria、脱铁杆菌门(Deferribacteres)、Muribaculum、Candidatus_Saccharimonas、理研菌属(Rikenella)、Odoribacter、Mucispirillum、Lachnospiraceae_unclassified显著下降(P值均<0.05)。与MOD组小鼠相比,FMT组小鼠AST、ALT显著下降(P值均<0.05);肝细胞明显气球样变,坏死较轻; Paramuribaculum、嗜胆菌属(Bilophila)显著上升,厚壁菌门、Rikenella、Absiella显著下降(P值均<0.05)。 结论 ACLF小鼠肠道菌群紊乱;菌群失调导致肝损伤;FMT能减轻ACLF小鼠肝脏炎症,具有保护作用。 -
关键词:
- 慢加急性肝衰竭 /
- 粪菌移植 /
- 胃肠道微生物组 /
- 小鼠,近交C57BL
Abstract:Objective To investigate the protective effect of fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) on mice with acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) and its effect on intestinal flora. Methods A total of 40 mice were randomly divided into control group (CON group), model group (MOD group), FMT group (feces of the mice in the CON group were used as fecal microbiota donor), and FMT model group (ANFMT group, with feces of the mice in the MOD group as fecal microbiota donor), with 10 mice in each group. All mice were observed in terms of body weight, death, liver histopathology, and changes in aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and intestinal flora. A one-way analysis of variance was used for comparison of normally distributed continuous data between multiple groups, and the SNK-q test was used for further comparison between two groups. Results Compared with the CON group, the MOD group had a significant reduction in body weight and significant increases in AST and ALT (all P < 0.05), as well as large patchy necrosis of hepatocytes, significant increases in Verrucomicrobia, Akkermansia, and Erysipelatoclostridium, and significant reductions in Dubosiella and Duncaniella (all P < 0.05). Compared with the CON group, the ANFMT group had a significant increase in AST (P < 0.05), hepatocyte swelling and mild ballooning degeneration, significant increases in Unclassified and Faecalibaculum, and significant reductions in Patescibacteria, Deferribacteres, Muribaculum, Candidatus_Saccharimonas, Rikenella, Odoribacter, Mucispirillum, and Lachnospiraceae_unclassified (all P < 0.05). Compared with the MOD group, the FMT group had significant reductions in AST and ALT (both P < 0.05), mild hepatocellular necrosis and marked ballooning degeneration, significant increases in Paramuribaculum and Bilophila, and significant reductions in Firmicutes, Rikenella, and Absiella (all P < 0.05). Conclusion Intestinal flora disturbance is observed in ACLF mice, and dysbacteriosis may lead to liver injury. FMT can alleviate liver inflammation in ACLF mice and thus exert a protective effect. -
表 1 4组小鼠体质量与肝功能水平比较
指标 CON组(n=10) ANFMT组(n=10) MOD组(n=6) FMT组(n=8) F值 P值 体质量(g) 27.20±2.63 25.92±1.18 24.26±1.191) 26.16±0.62 2.584 0.075 AST(U/L) 133.34±29.64 201.52±40.651) 427.30±248.761) 265.96±30.271)2) 4.098 0.019 ALT(U/L) 52.81±15.04 67.75±18.37 241.44±180.181) 89.10±46.892) 4.506 0.026 注:1)与CON组相比,P<0.05,2)与MOD组相比,P<0.05。 -
[1] Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Severe Liver Disease and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure(2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(1): 38-44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019. 01.007.中华医学会感染病学分会肝衰竭与人工肝学组, 中华医学会肝病学分会重型肝病与人工肝学组. 肝衰竭诊治指南(2018年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(1): 38-44. DOI: 10.3969/ j.issn.1001-5256.2019. 01.007. [2] CHEN Y, GUO J, QIAN G, et al. Gut dysbiosis in acute-on-chronic liver failure and its predictive value for mortality[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 30(9): 1429-1437. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12932. [3] MINEMURA M, SHIMIZU Y. Gut microbiota and liver diseases[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2015, 21(6): 1691-1702. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i6.1691. [4] CLEMENTE JC, URSELL LK, PARFREY LW, et al. The impact of the gut microbiota on human health: An integrative view[J]. Cell, 2012, 148(6): 1258-1270. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.035. [5] WANG KX, ZHENG C, ZHANG JH, et al. Clinical effect of Qingre Jiedu Liangxue prescription in treatment of mice with acute-on-chronic liver failure and related mechanism[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2765-2771. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.025.王开霞, 郑超, 张景豪, 等. 清热解毒凉血方治疗慢加急性肝衰竭小鼠模型的效果及机制[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(12): 2765-2771. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.025. [6] ZHANG YC, BI YZ, FANG X, et al. Protective effect of probiotics in rats with acute- on- chronic liver failure and related mechanism[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(7): 1570-1575. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.07.张永超, 毕研贞, 方萧, 等. 益生菌对慢加急性肝衰竭大鼠模型的保护作用及其机制[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(7): 1570-1575. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.07. [7] WANG WW, ZHANG Y, HUANG XB, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation prevents hepatic encephalopathy in rats with carbon tetrachloride-induced acute hepatic dysfunction[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2017, 23(38): 6983-6994. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i38.6983. [8] CUI B, FENG Q, WANG H, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation through mid-gut for refractory Crohn's disease: Safety, feasibility, and efficacy trial results[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 30(1): 51-58. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12727. [9] ROUND JL, MAZMANIAN SK. The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2009, 9(5): 313-323. DOI: 10.1038/nri2515. [10] QIN N, YANG F, LI A, et al. Alterations of the human gut microbiome in liver cirrhosis[J]. Nature, 2014, 513(7516): 59-64. DOI: 10.1038/nature13568. [11] MOREAU R, JALAN R, GINES P, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure is a distinct syndrome that develops in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2013, 144(7): 1426-1437, 1437. e1-9. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.02.042. [12] BAJAJ JS, FAGAN A, SIKAROODI M, et al. Liver transplant modulates gut microbial dysbiosis and cognitive function in cirrhosis[J]. Liver Transpl, 2017, 23(7): 907-914. DOI: 10.1002/lt.24754. [13] BAJAJ JS, IDILMAN R, MABUDIAN L, et al. Diet affects gut microbiota and modulates hospitalization risk differentially in an international cirrhosis cohort[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 68(1): 234-247. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29791. [14] ACHARYA C, BAJAJ JS. Gut microbiota and complications of liver disease[J]. Gastroenterol Clin North Am, 2017, 46(1): 155-169. DOI: 10.1016/j.gtc.2016.09.013. [15] DAVIS BC, BAJAJ JS. The human gut microbiome in liver diseases[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2017, 37(2): 128-140. DOI: 10.1055/s-0037-1602763. [16] TILG H, CANI PD, MAYER EA. Gut microbiome and liver diseases[J]. Gut, 2016, 65(12): 2035-2044. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312729. [17] ZHANG W, GU Y, CHEN Y, et al. Intestinal flora imbalance results in altered bacterial translocation and liver function in rats with experimental cirrhosis[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2010, 22(12): 1481-1486. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e32833eb8b0. [18] PENG JH, CUI T, SUN ZL, et al. Effects of puerariae radix extract on endotoxin receptors and TNF-α expression induced by gut-derived endotoxin in chronic alcoholic liver injury[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2012, 2012: 234987. DOI: 10.1155/2012/234987. [19] BILZER M, ROGGEL F, GERBES AL. Role of Kupffer cells in host defense and liver disease[J]. Liver Int, 2006, 26(10): 1175-1186. DOI: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2006.01342.x. [20] TAKEUCHI O, AKIRA S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation[J]. Cell, 2010, 140(6): 805-820. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.022. [21] XU L, KITADE H, NI Y, et al. Roles of chemokines and chemokine receptors in obesity-associated insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Biomolecules, 2015, 5(3): 1563-1579. DOI: 10.3390/biom5031563. [22] WIEST R. Bacterial translocation and alterations of the digestive system[M]//GINÈS P, KAMATH P, ARROYO V. Chronic liver failure. Clinical Gastroenterology. Humana Press, 2011: 189-218. [23] MA HD, WANG YH, CHANG C, et al. The intestinal microbiota and microenvironment in liver[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2015, 14(3): 183-191. DOI: 10.1016/j.autrev.2014.10.013. [24] YANG Y, JOBIN C. Microbial imbalance and intestinal pathologies: connections and contributions[J]. Dis Model Mech, 2014, 7(10): 1131-1142. DOI: 10.1242/dmm.016428. -



 PDF下载 ( 8229 KB)
PDF下载 ( 8229 KB)


 下载:
下载: