肝硬化食管静脉曲张患者门静脉血栓形成的危险因素分析
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.01.013
Risk factors of portal vein thrombosis in cirrhotic patients with esophageal varices
-
摘要:
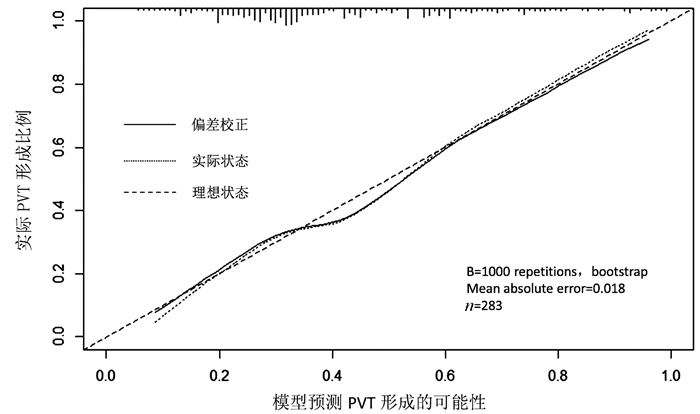
目的 旨在识别肝硬化食管静脉曲张患者中门静脉血栓(PVT)形成的独立危险因素,并建立一个预测PVT发生风险的列线图。 方法 回顾性分析2013年12月—2018年12月于山东大学附属省立医院就诊的283例肝硬化食管静脉曲张患者资料,根据影像学检查将其分为PVT组(n=119)和非PVT组(n=164)。计量资料两组间比较采用t检验或Mann-Whitney U检验,计数资料两组间比较采用χ2检验。利用多因素logistic回归分析筛选独立危险因素,基于多因素回归结果建立并检验列线图,应用C指数(C-index)、校准曲线评价其性能。 结果 单因素分析显示,PVT组在Child-Pugh分级(χ2=9.388,P=0.009)、脾切除史(χ2=26.805,P<0.001)、WBC(Z=-2.248,P=0.025)、PLT(Z=-3.323,P=0.001)、D-二聚体水平(Z=-6.236,P<0.001)及脾脏厚度(Z=-2.432,P=0.015)方面高于非PVT组,而TG水平低于非PVT组(Z=-4.150,P<0.001)。多因素分析显示,TG水平(OR=0.441, 95%CI:0.190~0.889)、D-二聚体水平升高(OR=1.151, 95%CI:1.041~1.272)、PT延长(OR=1.160, 95%CI:1.025~1.313)、有脾切除史(OR=2.933, 95%CI:l.164~7.389)是肝硬化食管静脉曲张患者PVT形成的独立风险因素。基于多因素回归结果,建立了列线图,其C指数值为0.745,校准曲线显示PVT发生的观测值和预测值之间有较好的一致性。 结论 TG水平降低、有脾切除史、D-二聚体水平升高、PT延长是肝硬化食管静脉曲张患者PVT形成的独立危险因素,基于此所建立的列线图,为临床医生评估PVT形成风险提供了一个定量、直观的工具。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the risk factors for portal vein thrombosis (PVT) in cirrhotic patients with esophageal varices, and to establish a nomogram for predicting the risk of PVT. Methods A retrospective analysis was performed for the clinical data of 283 cirrhotic patients with esophageal varices who attended Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University from December 2013 to December 2018, and according to imaging findings, the patients were divided into PVT group with 119 patients and non-PVT group with 164 patients. The t-test or the Mann-Whitney U test was used for comparison of continuous data between two groups, and the chi-square test was used for comparison of categorical data between two groups. A multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to screen out independent risk factors; a nomogram was established and validated based on the results of the multivariate logistic regression analysis, and C-index and calibration curve were used to evaluate its performance. Results The univariate analysis showed that compared with the non-PVT group, the PVT group had significantly higher Child-Pugh class (χ2=9.388, P=0.009), proportion of patients with a history of splenectomy (χ2=26.805, P < 0.001), white blood cell count (Z=-2.248, P=0.025), platelet count (Z=-3.323, P=0.001), D-dimer(Z=-6.236, P < 0.001), and spleen thickness (Z=-2.432, P=0.015) and a significantly lower level of triglyceride (TG) (Z=-4.150, P < 0.001). The multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that a reduction in TG (odds ratio [OR]=0.441, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.190-0.889), an increase in D-dimer (OR=1.151, 95%CI: 1.041-1.272), prolonged prothrombin time (PT) (OR=1.160, 95%CI: 1.025-1.313), and a history of splenectomy (OR=2.933, 95%CI: 1.164-7.389) were independent risk factors for PVT in cirrhotic patients with esophageal varices. In addition, a nomogram was established based on the results of the multivariate regression analysis, with a C-index of 0.745, and the calibration curve showed good consistency between the observed and predicted values for the development of PVT. Conclusion A reduction in TG, an increase in D-dimer, prolonged PT, and a history of splenectomy are independent risk factors for PVT in cirrhotic patients with esophageal varices, and the nomogram developed based on these results can provide a quantitative and intuitive tool for clinicians to assess the risk of PVT. -
Key words:
- Liver Cirrhosis /
- Portal Vein Thrombosis /
- Esophageal and Gastric Varices /
- Risk Factors /
- Nomogram
-
表 1 两组患者一般资料比较
项目 PVT组(n=119) 非PVT组(n=164) 统计值 P值 性别(例) χ2=0.260 0.650 男 75 99 女 44 65 年龄(岁) 55.87±10.80 54.04±10.9 t=-1.395 0.164 脾切除史(例) 53 27 χ2=26.805 <0.001 脾栓塞史(例) 6 4 χ2=1.371 0.242 普萘洛尔应用史(例) 4 7 χ2=0.152 0.697 病因(例) χ2=5.051 0.654 HBV 55 65 酒精性 23 27 HBV+酒精性 4 8 HCV 2 4 HBV+HCV 0 1 HCV+酒精性 0 1 自身免疫性 6 16 其他 29 42 Child-Pugh分级(例) χ2=9.388 0.009 A级 54 90 B级 48 67 C级 17 7 吸烟史(例) 47 57 χ2=0.666 0.414 饮酒史(例) 40 56 χ2=0.009 0.926 高血压史(例) 14 23 χ2=0.310 0.578 糖尿病史(例) 20 23 χ2=0.414 0.520 表 2 两组患者临床资料比较
项目 PVT组(n=119) 非PVT组(n=164) 统计值 P值 WBC(×109/L) 3.88(3.03~5.67) 3.35(2.41~5.13) Z=-2.248 0.025 PLT(×109/L) 124.00(64.00~260.00) 77.00(61.25~124.00) Z=-3.323 0.001 Hb (g/L) 86.00(72.00~107.00) 91.00(74.00~108.00) Z=-0.951 0.341 Alb (g/L) 33.60(28.78~37.63) 33.70(28.86~38.20) Z=-0.359 0.720 AST (U/L) 34.50(24.75~45.25) 37.00(26.00~52.00) Z=-1.319 0.190 ALT (U/L) 22.00(15.00~35.00) 26.00 (17.00~41.00) Z=-1.728 0.110 TG (mmol/L) 0.75(0.59~1.03) 0.94(0.70~1.28) Z=-4.150 <0.001 TC (mmol/L) 3.89(2.97~4.65) 3.73(3.05~4.79) Z=-0.085 0.920 LDL-C (mmol/L) 2.21(1.63~2.80) 2.21(1.68~2.77) Z=-0.056 0.956 HDL-C (mmol/L) 1.03(0.72~1.38) 1.02(0.81~1.29) Z=-0.223 0.824 TBil (μmol/L) 18.35(14.88~26.33) 20.10(14.6~28.3) Z=-0.664 0.520 PT(s) 14.60 (13.60~16.90) 14.30(13.10~15.80) Z=-1.917 0.055 APTT(s) 36.35(30.68~40.35) 34.35(29.75~39.20) Z=-1.345 0.179 INR 1.22(1.15~1.35) 1.20(1.10~1.32) Z=-1.789 0.074 D-二聚体(mg/L) 2.64(1.07~5.70) 0.89(0.40~2.10) Z=-6.236 <0.001 腹水[例(%)] χ2=6.229 0.101 无 57 (47.90) 95 (57.93) 少量 40 (33.61) 48 (29.27) 中量 10 (8.40) 15 (9.15) 大量 12 (10.08) 6 (3.66) 门静脉主干内径(cm) 1.30(1.10~1.50) 1.30(1.20~1.40) Z=-0.286 0.104 脾脏厚度(mm) 5.50(4.80~6.40) 5.00(4.50~6.00) Z=-2.432 0.015 食管静脉曲张程度[例(%)] χ2=2.283 0.319 轻 14 (11.76) 11 (6.71) 中 17 (14.29) 27 (16.46) 重 88 (73.95) 126 (76.83) 肝性脑病[例(%)] 12(10.08) 7(4.27) χ2=5.555 0.135 表 3 多因素logistic回归分析
变量 B值 Wald OR 95%CI P值 TG -0.889 5.101 0.411 0.190~0.889 0.024 D-二聚体 0.141 7.587 1.151 1.041~1.272 0.006 PT 0.149 5.550 1.160 1.025~1.313 0.018 脾切除史 1.076 5.209 2.933 1.164~7.389 0.022 -
[1] ZOCCO MA, DI STASIO E, de CRISTOFARO R, et al. Thrombotic risk factors in patients with liver cirrhosis: Correlation with MELD scoring system and portal vein thrombosis development[J]. J Hepatol, 2009, 51(4): 682-689. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.03.013 [2] RUAN FM, LI BM. Risk factors for the formation of portal vein thrombosis in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(1): 182-185. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.01.043阮芳鸣, 李弼民. 肝硬化门静脉血栓形成的危险因素[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36(1) : 182-185. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.01.043 [3] NORONHA FERREIRA C, MARINHO RT, CORTEZ-PINTO H, et al. Incidence, predictive factors and clinical significance of development of portal vein thrombosis in cirrhosis: A prospective study[J]. Liver Int, 2019, 39(8): 1459-1467. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14121 [4] GUO YL, XU BH, LIU X, et al. Risk factors analysis of early rebleeding after endoscopic treatment of esophageal varices[J]. Chin J Dig Endosc, 2018, 35(2): 89-93. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-5232.2018.02.003郭雅丽, 徐宝宏, 刘贤, 等. 食管静脉曲张内镜治疗术后早期再出血的危险因素分析[J]. 中华消化内镜杂志, 2018, 35(2): 89-93. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-5232.2018.02.003 [5] QI X, SU C, REN W, et al. Association between portal vein thrombosis and risk of bleeding in liver cirrhosis: A systematic review of the literature[J]. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol, 2015, 39(6): 683-691. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinre.2015.02.012 [6] TARZAMNI MK, SOMI MH, FARHANG S, et al. Portal hemodynamics as predictors of high risk esophageal varices in cirrhotic patients[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2008, 14(12): 1898-1902. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.1898 [7] STINE JG, WANG J, SHAH PM, et al. Decreased portal vein velocity is predictive of the development of portal vein thrombosis: A matched case-control study[J]. Liver Int, 2018, 38(1): 94-101. DOI: 10.1111/liv.13500 [8] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Chinese guidelines on the management of liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(11): 2408-2425. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.11.006中华医学会肝病学分会. 肝硬化诊治指南[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(11): 2408-2425. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.11.006 [9] NERY F, CHEVRET S, CONDAT B, et al. Causes and consequences of portal vein thrombosis in 1, 243 patients with cirrhosis: Results of a longitudinal study[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 61(2): 660-667. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27546 [10] OOI K, SHIRAKI K, SAKURAI Y, et al. Clinical significance of abnormal lipoprotein patterns in liver diseases[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2005, 15(4): 655-660. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/15754028 [11] CHEN S, YIN P, ZHAO X, et al. Serum lipid profiling of patients with chronic hepatitis B, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma by ultra fast LC/IT-TOF MS[J]. Electrophoresis, 2013, 34(19): 2848-2856. [12] ZHAO J, ZHAO Y, WANG H, et al. Association between metabolic abnormalities and HBV related hepatocelluar carcinoma in Chinese: A cross-sectional study[J]. Nutr J, 2011, 10: 49. DOI: 10.1186/1475-2891-10-49 [13] FIMOGNARI FL, DE SANTIS A, PICCHERI C, et al. Evaluation of D-dimer and factor Ⅷ in cirrhotic patients with asymptomatic portal venous thrombosis[J]. J Lab Clin Med, 2005, 146(4): 238-243. DOI: 10.1016/j.lab.2005.06.003 [14] WANG Y, SHI Y, DONG Y, et al. Clinical risk factors of asymptomatic deep venous thrombosis in patients with acute stroke[J]. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost, 2019, 25: 1076029619868534. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/335325676_clinical_risk_factors_of_asymptomatic_deep_venous_thrombosis_in_patients_with_acute_stroke [15] ROULEAU P, GUERTIN PA. Early changes in deep vein diameter and biochemical markers associated with thrombi formation after spinal cord injury in mice[J]. J Neurotrauma, 2007, 24(8): 1406-1414. DOI: 10.1089/neu.2006.0260 [16] OKANO K, SHITAMOTO K, ARAKI M, et al. Influencing factors in quantitative measurement using activated platelet levels and platelet-activating capacity for the assessment of thrombosis in pre-metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Nurs Health Sci, 2018, 20(1): 69-78. DOI: 10.1111/nhs.12389 [17] YANG J, ZHOU X, FAN X, et al. mTORC1 promotes aging-related venous thrombosis in mice via elevation of platelet volume and activation[J]. Blood, 2016, 128(5): 615-624. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2015-10-672964 [18] ZHOU J, XU E, SHAO K, et al. Circulating platelet-neutrophil aggregates as risk factor for deep venous thrombosis[J]. Clin Chem Lab Med, 2019, 57(5): 707-715. DOI: 10.1515/cclm-2018-0909 [19] LYU J, DONG SS, GU HT, et al. TCM syndrome characteristics of portal vein thrombosis in patients with liver cirrhosis and related risk factors[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(10): 2210-2213.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.10.016吕靖, 董思思, 顾宏图, 等. 肝硬化并发门静脉血栓的危险因素及中医证候特点[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(10): 2210-2213. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.10.016 [20] LI MX, ZHANG XF, LIU ZW, et al. Risk factors and clinical characteristics of portal vein thrombosis after splenectomy in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2013, 12(5): 512-519. DOI: 10.1016/S1499-3872(13)60081-8 [21] TRIPODI A, PRIMIGNANI M, CHANTARANGKUL V, et al. An imbalance of pro- vs anti-coagulation factors in plasma from patients with cirrhosis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2009, 137(6): 2105-2111. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.08.045 [22] LINARES I, GOLDARACENA N, ROSALES R, et al. Splenectomy as flow modulation strategy and risk factors of de novo portal vein thrombosis in adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation[J]. Liver Transpl, 2018, 24(9): 1209-1220. DOI: 10.1002/lt.25212 [23] IKEDA M, SEKIMOTO M, TAKIGUCHI S, et al. High incidence of thrombosis of the portal venous system after laparoscopic splenectomy: A prospective study with contrast-enhanced CT scan[J]. Ann Surg, 2005, 241(2): 208-216. DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000151794.28392.a6 [24] ABDEL-RAZIK A, MOUSA N, ELHELALY R, et al. De-novo portal vein thrombosis in liver cirrhosis: Risk factors and correlation with the Model for End-stage Liver Disease scoring system[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 27(5): 585-592. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000325 -



 PDF下载 ( 2249 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2249 KB)


 下载:
下载: