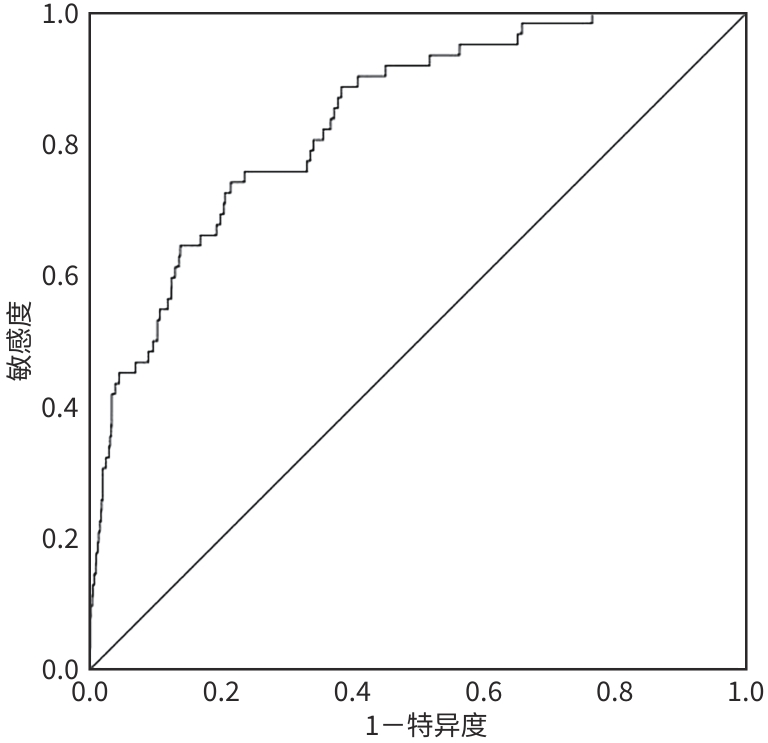
| [1] |
GOBEZIE MY, HASSEN M, TESFAYE NA, et al. Prevalence of meropenem-resistant Pseudomonas Aeruginosa in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control, 2024, 13( 1): 37. DOI: 10.1186/S13756-024-01389-2. |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
WEBER S, GERBES AL. Challenges and future of drug-induced liver injury research-laboratory tests[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23( 11): 6049. DOI: 10.3390/ijms23116049. |
| [4] |
Technical Committee of Prevention and Treatment of Drug-induced Liver Injury, Chinese Medical Biotechnology Association, Drug Hepatology Group, Branch Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Chinese guideline for diagnosis and management of drug-induced liver injury(2023 version)[J]. Chin J Gastroenterol, 2023, 28( 7): 397- 431. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20230419-00176. |
| [5] |
HAN J, LIU J, YU Z, et al. Risk factors for irinotecan-induced liver injury: a retrospective multicentre cross-sectional study in China[J]. BMJ Open, 2023, 13( 6): e069794. DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-069794. |
| [6] |
HAYASHI PH, LUCENA MI, FONTANA RJ, et al. A revised electronic version of RUCAM for the diagnosis of DILI[J]. Hepatology, 2022, 76( 1): 18- 31. DOI: 10.1002/hep.32327. |
| [7] |
WANG SM, JIN S, LI JR, et al. Influencing factors for the prognosis of patients with drug-induced liver injury and establishment of a nomogram model[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2024, 40( 3): 562- 567. DOI: 10.12449/JCH240320. 王诗美, 靳帅, 李俊儒, 等. 药物性肝损伤患者预后影响因素分析及列线图模型的建立[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40( 3): 562- 567. DOI: 10.12449/JCH240320. |
| [8] |
LIN LM, HONG MH, WU DN, et al. Incidence and risk factors of voriconazole-induced liver injury in the context of therapeutic drug monitoring[J]. Chin J Infect Chemotherapy, 2023, 23( 6): 709- 714. DOI: 10.16718/j.1009-7708.2023.06.007. |
| [9] |
YANG XM, SHEN BR, LIU PY, et al. Logistic regression analysis of risk factors of antituberculosis drug-induced liver injury[J]. Chin J Hosp Pharm, 2019 39( 1): 67- 71. DOI: 10.13286/j.cnki.Chinhosppharmacyj.2019.01.15.
|
| [10] |
ZHONG T, FAN YZ, DONG XL, et al. An Investigation of the risk factors associated with anti-tuberculosis drug-induced liver injury or abnormal liver functioning in 757 patients with pulmonary tuberculosis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 708522. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.708522. |
| [11] |
LIN YX, LI PP, ZHANG YP, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of acute liver injury in hospitalized adults with acute kidney injury: a large multicenter study[J]. Hepatol Int, 2024, 18( 6): 1756- 1769. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-023-10627-5. |
| [12] |
YU ZW, ZHAO YH, JIN JY, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of tigecycline-induced liver injury: A multicenter retrospective study[J]. Int J Infect Dis, 2022, 120: 59- 64. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2022.04.024. |
| [13] |
LIU XZ, LIU JJ, FANG X, et al. A real-world study of azivudine tablets for drug-induced liver injury caused by novel coronavirus pneumonia[J]. Chin J Hosp Pharm, 2024, 44( 9): 1082- 1087. DOI: 10.13286/j.1001-5213.2024.09.12. |
| [14] |
EDER P, PERMODA-OSIP A, MAJEWSKI P, et al. Agomelatine-induced liver injury in a patient with choledocholithiasis[J]. Acta Neuropsychiatr, 2014, 27( 1): 56- 59. DOI: 10.1017/neu.2014.28. |
| [15] |
WEI Q, LI L, ZENG XQ, et al. Analysis of clinical features and prognostic risk factors in patients with drug-induced liver injury[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2024, 32( 3): 214- 221. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j. cn501113-20240201-00072.
|
| [16] |
PAPP-WALLACE KM, ENDIMIANI A, TARACILA MA, et al. Carbapenems: Past, present, and future[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2011, 55( 11): 4943- 4960. DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00296-11. |
| [17] |
DENG XY, HUANG JJ, SUN J, et al. Incidence and risk factors of drug-induced liver injury in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia[J]. ADRJ, 2020, 22( 6): 360- 365. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn114015-20200331-00322. |
| [18] |
TATTERSALL T, WRIGHT H, REDMOND A. Meropenem-induced liver injury and beta-lactam cross-reactivity[J]. BMJ Case Rep, 2018, 11( 1): e227124. DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2018-227124. |
| [19] |
CHEUNG S, BULOVIC J, PILLAI A, et al. A case of meropenem-induced liver injury and jaundice[J]. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect, 2021, 11( 1): 143- 144. DOI: 10.1080/20009666.2020.1845929. |
| [20] |
YANG JQ, ZHAO WX, ZHOU C, et al. Risk factors for the development of advanced liver fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and establishment of a nomogram model[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2024, 40( 8): 1579- 1584. DOI: 10.12449/JCH240812. 杨金秋, 赵文霞, 周铖, 等. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病发生进展期肝纤维化的危险因素及列线图预测模型构建[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40( 8): 1579- 1584. DOI: 10.12449/JCH240812. |
| [21] |
WU XJ, PENG JL, FAN H, et al. Clinical features and prognostic factors of 310 patients with antituberculosis drug-induced liver injury[J]. J Kunming Med Univ, 2024, 45( 3): 157- 165. DOI: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X. S20240324.
|
| [22] |
LV BB, LIU LS, LIU XM, et al. Incidence, clinical features and risk factors of tacrolimus induced idiosyncratic liver injury in renal transplant recipients: A nested case-control study[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14: 1126765. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1126765. |
| [23] |
ZHU YH, WANG XS, SONG MF, et al. Characteristies of acute liver injury in elderly patients with sepsis in intensive care unit and its influencing factors[J]. Chin J Mult Organ Dis Elderly, 2023, 22( 5): 362- 366. DOI: 10.11915/j.issn.1671-5403.2023.05.74. |
| [24] |
HE Y, LI BL, LI H. Analysis of influencing factors on drug-induced liver injury induced by antituberculosis therapy in patients with newly treated pulmonary tuberculosis combined with hepatitis B virus infection[J]. J Changchun Univ Chin Med, 2024, 40( 4): 450- 454. DOI: 10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2024.04.023. |
| [25] |
WANG JF, ZHAO L, WANG JJ, et al. The study of serum TBA, ALP and coagulation function in sepsis patients with liver injury[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2022, 27( 5): 593- 595. DOI: 10.14000/j.cnki.issn.1008-1704.2022.05.024. 王俊峰, 赵亮, 王俊杰, 等. 脓毒血症肝损伤患者血清TBA、ALP水平与凝血功能特征观察[J]. 肝脏, 2022, 27( 5): 593- 595. DOI: 10.14000/j. cnki.issn.1008-1704.2022.05.024.
|
| [26] |
DAI XY, ZHENG YY, TANG JN, et al. Alkaline phosphatase-to-albumin ratio as a novel predictor of long-term adverse outcomes in coronary artery disease patients who underwent PCI[J]. Biosci Rep, 2021, 41( 7): BSR20203904. DOI: 10.1042/BSR20203904. |
| [27] |
VILLANUEVAPAZ M, MORAN L, LOPEZALCANTARA N, et al. Oxidative stress in drug-induced liver injury(DILI): From mechanisms to biomarkers for use in clinical practice[J]. Antioxidants(Basel), 2021, 10( 3): 390. DOI: 10.3390/antiox10030390. |
| [28] |
JIANG YY, SHI L, LIU Y. Correlation between gamma-glutamyl transferase and coronary heart disease[J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2021, 24( 2): 176- 182. DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2020.00.422. |
| [29] |
DENG Y, WANG CY, TAN WH, et al. High risk factors associated with relapse of chronic drug-induced liver injury[J]. Med J Chine PLA, 2021, 46( 9): 928- 934. DOI 10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2021.09.14. DOI: 10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2021.09.14 |
| [30] |
ZHANG ZJ, LIU Y. Analysis of influencing factors of acute liver failure in 147 patients with liver injury induced by antituberculosis drugs[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2024, 29( 5): 552- 556. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2024.05.017. |
| [31] |
WANG QL, LIANG QS, HUANG A, et al. Influencing factors for the prognosis of biopsy proven patients with chronic drug-induced liver injury: An analysis of 255 cases[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 6): 1334- 1340. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.06.022. |
| [32] |
GENG JL, ZHANG YN, PAN HQ. Establishment and validation of a risk prediction model for drug-induced liver injury in patients with tuberculosis[J]. Chin J Antituberc, 2024, 46( 6): 699- 706. DOI: 10.19982/j.issn.1000-6621.20240030. |
| [33] |
Committee of Neoplastic Supportive-care(CONS), China Anti Cancer Association. Chinese expert consensus on management of thrombocytopenia in cancer patients with liver injury(2022 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 6): 1287- 1294. DOI: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2023.23.0156. 中国抗癌协会肿瘤支持治疗专业委员会.. 肿瘤合并肝损伤患者血小板减少症管理中国专家共识(2022版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023, 39( 6): 1287- 1294. DOI: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2023. 23.0156.
|
| [34] |
CHRISTOPHE L, JEAN-LOUIS V. Mechanisms and treatment of organ failure in sepsis[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2018, 14( 7): 417- 427. DOI: 10.1038/s41581-018- 0005-7.
|
| [35] |
JIANG F, YAN H, LIANG L, et al. Incidence and risk factors of anti‐tuberculosis drug induced liver injury(DILI): Large cohort study involving 4652 Chinese adult tuberculosis patients[J]. Liver Int, 2021, 41( 7): 1565- 1575. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14896. |
| [36] |
LI XY, TANG JT, MAO YM. Incidence and risk factors of drug‐induced liver injury[J]. Liver Int, 2022, 42( 9): 1999- 2014. DOI: 10.1111/liv.15262. |



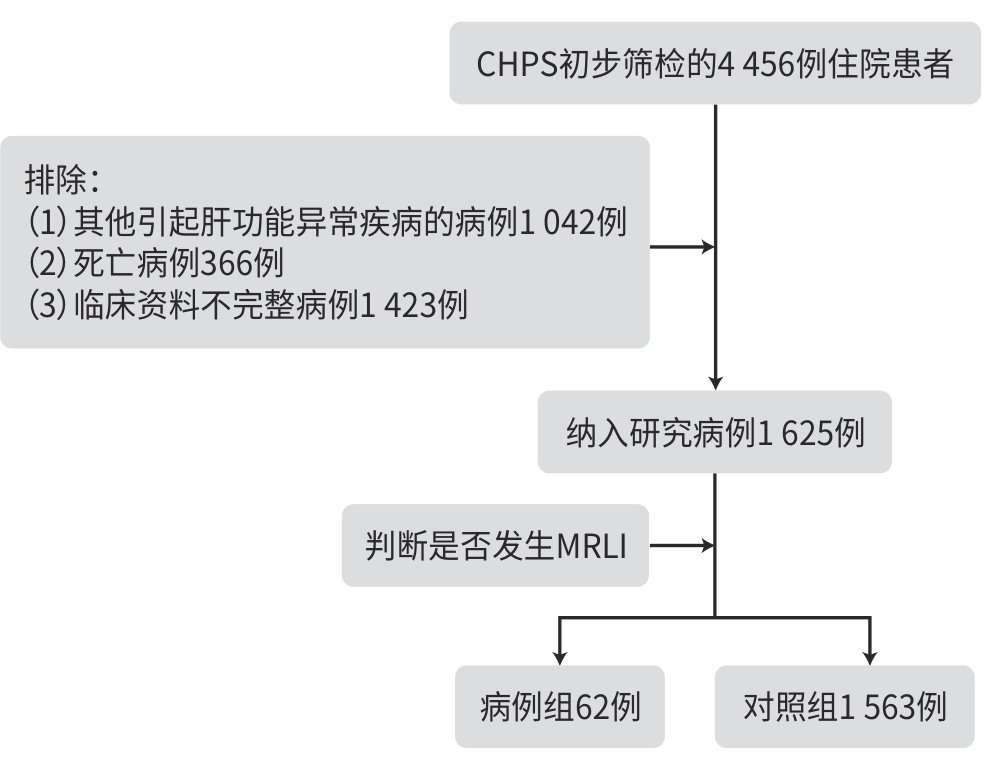




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: