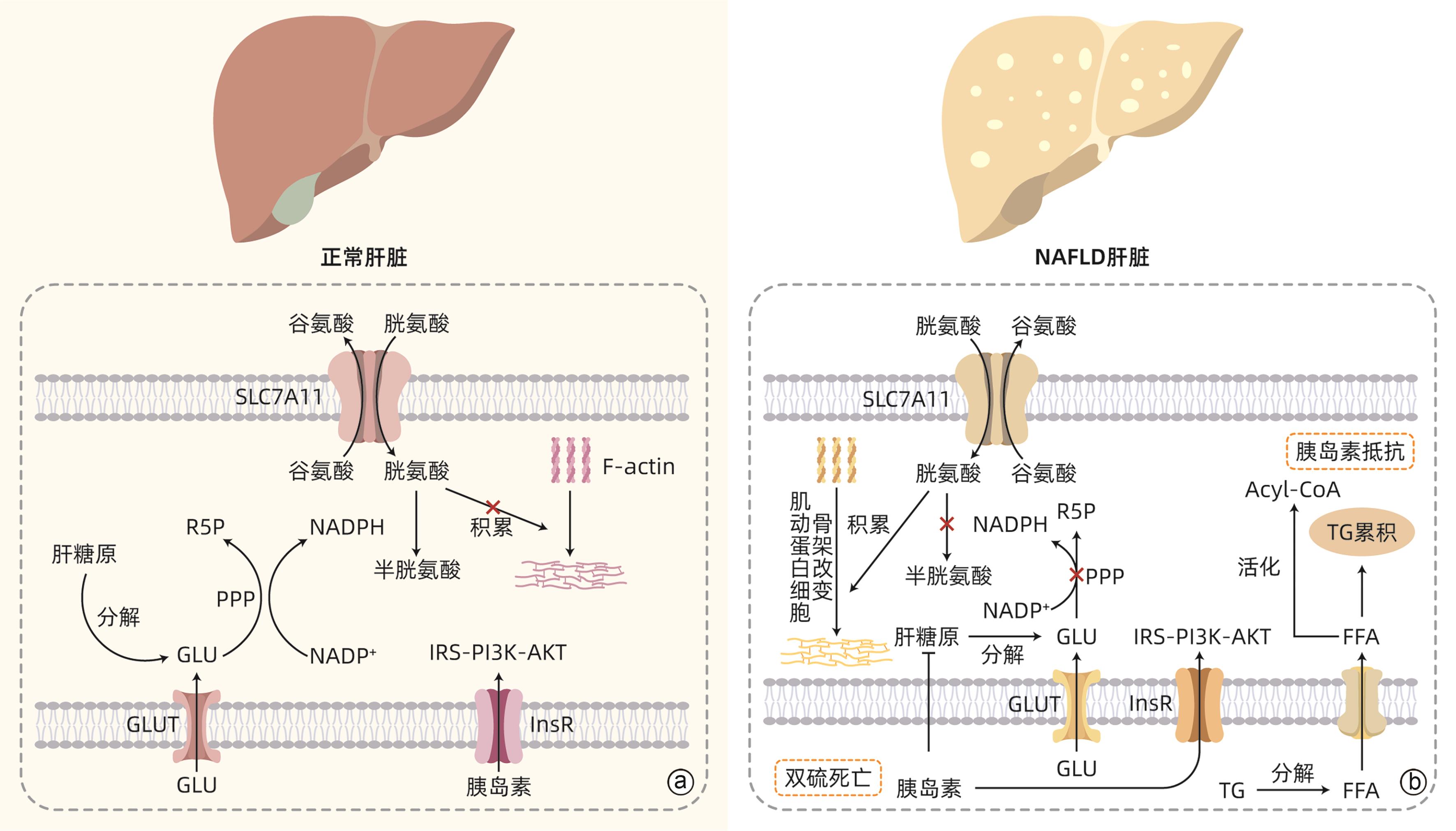
| [1] |
AMORIM R, SOARES P, CHAVARRIA D, et al. Decreasing the burden of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: From therapeutic targets to drug discovery opportunities[J]. Eur J Med Chem, 2024, 277: 116723. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116723. |
| [2] |
YANG BM, TANG GM, WANG MT, et al. Trimethylamine N-oxide induces non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by activating the PERK[J]. Toxicol Lett, 2024, 400: 93- 103. DOI: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2024.08.009. |
| [3] |
YOUNOSSI ZM, GOLABI P, PAIK JM, et al. The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis(NASH): A systematic review[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 77( 4): 1335- 1347. DOI: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000004. |
| [4] |
LUO XH, GUO JJ, DENG HB, et al. Unveiling the role of disulfidptosis-related genes in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 15: 1386905. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1386905. |
| [5] |
LIU XG, NIE LT, ZHANG YL, et al. Actin cytoskeleton vulnerability to disulfide stress mediates disulfidptosis[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2023, 25( 3): 404- 414. DOI: 10.1038/s41556-023-01091-2. |
| [6] |
ZHENG TJ, LIU QB, XING FY, et al. Disulfidptosis: A new form of programmed cell death[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2023, 42( 1): 137. DOI: 10.1186/s13046-023-02712-2. |
| [7] |
SARMIENTO-SALINAS FL, PEREZ-GONZALEZ A, ACOSTA-CASIQUE A, et al. Reactive oxygen species: Role in carcinogenesis, cancer cell signaling and tumor progression[J]. Life Sci, 2021, 284: 119942. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119942. |
| [8] |
NJEIM R, ALKHANSA S, FORNONI A. Unraveling the crosstalk between lipids and NADPH oxidases in diabetic kidney disease[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2023, 15( 5): 1360. DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051360. |
| [9] |
MUSAOGULLARI A, CHAI YC. Redox regulation by protein S-glutathionylation: From molecular mechanisms to implications in health and disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21( 21): 8113. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21218113. |
| [10] |
SHUAI Y, MA ZH, YUAN P. Disulfidptosis: Disulfide stress-induced novel cell death pathway[J]. MedComm(2020), 2024, 5( 7): e579. DOI: 10.1002/mco2.579. |
| [11] |
YUE JD, YIN YK, FENG XJ, et al. Discovery of the inhibitor targeting the SLC7A11/xCT axis through in silico and in vitro experiments[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25( 15): 8284. DOI: 10.3390/ijms25158284. |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
SHUBHRASMITA SAHU S, SARKAR P, CHATTOPADHYAY A. Quantitation of F-actin in cytoskeletal reorganization: Context, methodology and implications[J]. Methods, 2024, 230: 44- 58. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2024.07.009. |
| [14] |
YANG GN, KOPECKI Z, COWIN AJ. Role of actin cytoskeleton in the regulation of epithelial cutaneous stem cells[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2016, 25( 10): 749- 759. DOI: 10.1089/scd.2016.0051. |
| [15] |
DEWANE G, SALVI AM, DEMALI KA. Fueling the cytoskeleton-links between cell metabolism and actin remodeling[J]. J Cell Sci, 2021, 134( 3): jcs248385. DOI: 10.1242/jcs.248385. |
| [16] |
JYOTSANA N, TA KT, DELGIORNO KE. The role of cystine/glutamate antiporter SLC7A11/xCT in the pathophysiology of cancer[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 858462. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.858462. |
| [17] |
XU ZC, WANG YP, YANG WL, et al. Total extracts from Abelmoschus manihot(L.) alleviate radiation-induced cardiomyocyte ferroptosis via regulating redox imbalances mediated by the NOX4/xCT/GPX4 axis[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2024, 334: 118582. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118582. |
| [18] |
COSTA I, BARBOSA DJ, BENFEITO S, et al. Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and their involvement in brain diseases[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2023, 244: 108373. DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108373. |
| [19] |
KOPPULA P, ZHUANG L, GAN BY. Cystine transporter SLC7A11/xCT in cancer: Ferroptosis, nutrient dependency, and cancer therapy[J]. Protein Cell, 2021, 12( 8): 599- 620. DOI: 10.1007/s13238-020-00789-5. |
| [20] |
MURRAY TV, DONG X, SAWYER GJ, et al. NADPH oxidase 4 regulates homocysteine metabolism and protects against acetaminophen-induced liver damage in mice[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2015, 89: 918- 930. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.09.015. |
| [21] |
COLLET JF, CHO SH, IORGA BI, et al. How the assembly and protection of the bacterial cell envelope depend on cysteine residues[J]. J Biol Chem, 2020, 295( 34): 11984- 11994. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.011201. |
| [22] |
ADEVA-ANDANY MM, PÉREZ-FELPETE N, FERNÁNDEZ-FERNÁNDEZ C, et al. Liver glucose metabolism in humans[J]. Biosci Rep, 2016, 36( 6): e00416. DOI: 10.1042/BSR20160385. |
| [23] |
GARCÍA-DOMÍNGUEZ E, CARRETERO A, VIÑA-ALMUNIA A, et al. Glucose 6-P dehydrogenase-an antioxidant enzyme with regulatory functions in skeletal muscle during exercise[J]. Cells, 2022, 11( 19): 3041. DOI: 10.3390/cells11193041. |
| [24] |
SONG WX, LI DY, TAO L, et al. Solute carrier transporters: The metabolic gatekeepers of immune cells[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2020, 10( 1): 61- 78. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2019.12.006. |
| [25] |
YU XX, GUO ZH, FANG ZH, et al. Identification and validation of disulfidptosis-associated molecular clusters in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Front Genet, 2023, 14: 1251999. DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1251999. |
| [26] |
AHMED B, SULTANA R, GREENE MW. Adipose tissue and insulin resistance in obese[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2021, 137: 111315. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111315. |
| [27] |
AMINI-SALEHI E, LETAFATKAR N, NOROUZI N, et al. Global prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: An updated review meta-analysis comprising a population of 78 million from 38 countries[J]. Arch Med Res, 2024, 55( 6): 103043. DOI: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2024.103043. |
| [28] |
OH AR, JEONG Y, YU JJ, et al. Hepatocyte Kctd17 inhibition ameliorates glucose intolerance and hepatic steatosis caused by obesity-induced chrebp stabilization[J]. Gastroenterology, 2023, 164( 3): 439- 453. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2022.11.019. |
| [29] |
ATORRASAGASTI C, ONORATO AM, MAZZOLINI G. The role of SPARC(secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine) in the pathogenesis of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Physiol Biochem, 2023, 79( 4): 815- 831. DOI: 10.1007/s13105-022-00913-5. |
| [30] |
AJOOLABADY A, KAPLOWITZ N, LEBEAUPIN C, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in liver diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 77( 2): 619- 639. DOI: 10.1002/hep.32562. |
| [31] |
CELIK C, LEE SYT, YAP WS, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and lipids in health and diseases[J]. Prog Lipid Res, 2023, 89: 101198. DOI: 10.1016/j.plipres.2022.101198. |
| [32] |
LIANG YC, KAUSHAL D, WILSON RB. Cellular senescence and extracellular vesicles in the pathogenesis and treatment of obesity-A narrative review[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25( 14): 7943. DOI: 10.3390/ijms25147943. |
| [33] |
de ALMEIDA CHUFFA LG, SEIVA FRF, SILVEIRA HS, et al. Melatonin regulates endoplasmic reticulum stress in diverse pathophysiological contexts: A comprehensive mechanistic review[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2024: e31383. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.31383. |
| [34] |
ZHANG J, GUO JF, YANG NN, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated cell death in liver injury[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13( 12): 1051. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-022-05444-x. |
| [35] |
SIMÕES ICM, AMORIM R, TEIXEIRA J, et al. The alterations of mitochondrial function during NAFLD progression-an independent effect of mitochondrial ROS production[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22( 13): 6848. DOI: 10.3390/ijms22136848. |
| [36] |
KARKUCINSKA-WIECKOWSKA A, SIMOES ICM, KALINOWSKI P, et al. Mitochondria, oxidative stress and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A complex relationship[J]. Eur J Clin Invest, 2022, 52( 3): e13622. DOI: 10.1111/eci.13622. |
| [37] |
LIU XG, ZHUANG L, GAN BY. Disulfidptosis: Disulfide stress-induced cell death[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2024, 34( 4): 327- 337. DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2023.07.009. |
| [38] |
JOLY JH, DELFARAH A, PHUNG PS, et al. A synthetic lethal drug combination mimics glucose deprivation-induced cancer cell death in the presence of glucose[J]. J Biol Chem, 2020, 295( 5): 1350- 1365. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011471. |
| [39] |
HORNA-TERRÓN E, PRADILLA-DIESTE A, SÁNCHEZ-DE-DIEGO C, et al. TXNDC5, a newly discovered disulfide isomerase with a key role in cell physiology and pathology[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2014, 15( 12): 23501- 23518. DOI: 10.3390/ijms151223501. |
| [40] |
NATH B, SZABO G. Hypoxia and hypoxia inducible factors: Diverse roles in liver diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2012, 55( 2): 622- 633. DOI: 10.1002/hep.25497. |
| [41] |
GONG H, HE QD, ZHU LL, et al. Associations between systemic inflammation indicators and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Evidence from a prospective study[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 15: 1389967. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1389967. |
| [42] |
LIU Q, BENGMARK S, QU S. The role of hepatic fat accumulation in pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD)[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2010, 9: 42. DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-9-42. |
| [43] |
BURGER D, FICKENTSCHER C, de MOERLOOSE P, et al. F-actin dampens NLRP3 inflammasome activity via Flightless-I and LRRFIP2[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 29834. DOI: 10.1038/srep29834. |
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
YU LL, HONG W, LU S, et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and steatohepatitis: Therapeutic targets and treatment[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 780496. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.780496. |
| [46] |
LEE PP, LOBATO-MÁRQUEZ D, PRAMANIK N, et al. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein regulates autophagy and inflammasome activity in innate immune cells[J]. Nat Commun, 2017, 8( 1): 1576. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-01676-0. |
| [47] |
ELMORSY EA, SABER S, HAMAD RS, et al. Modulating the HSP90 control over NFκB/NLRP3/caspase-1 axis is a new therapeutic target in the management of liver fibrosis: Insights into the role of TAS-116(pimitespib)[J]. Life Sci, 2024, 354: 122966. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122966. |
| [48] |
RAMOS-TOVAR E, MURIEL P. NLRP3 inflammasome in hepatic diseases: A pharmacological target[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2023, 217: 115861. DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115861. |
| [49] |
SATHEESAN A, KUMAR J, LEELA KV, et al. Review on the role of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3(NLRP3) inflammasome pathway in diabetes: Mechanistic insights and therapeutic implications[J]. Inflammopharmacology, 2024, 32( 5): 2753- 2779. DOI: 10.1007/s10787-024-01556-2. |
| [50] |
BARROW ER, VALIONYTE E, BAXTER CR, et al. Discovery of SQSTM1/p62-dependent P-bodies that regulate the NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. Cell Rep, 2024, 43( 3): 113935. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.113935. |



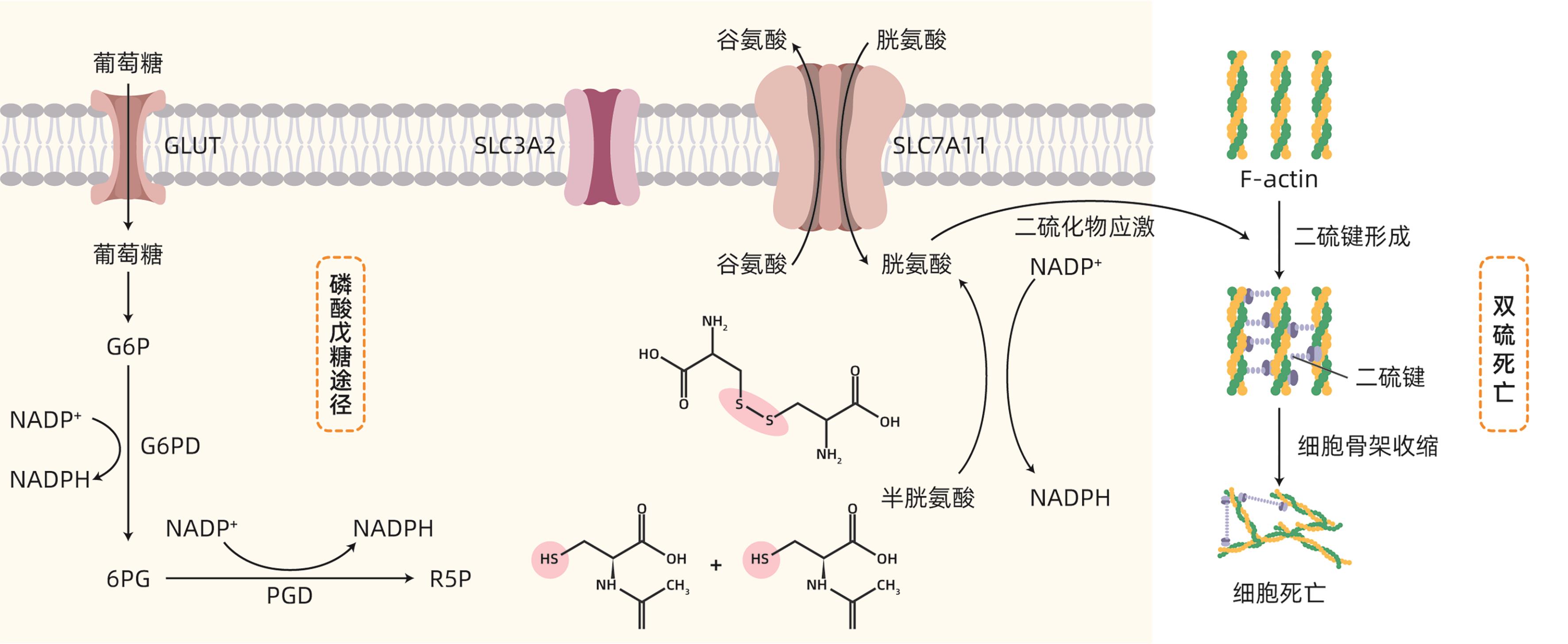




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: