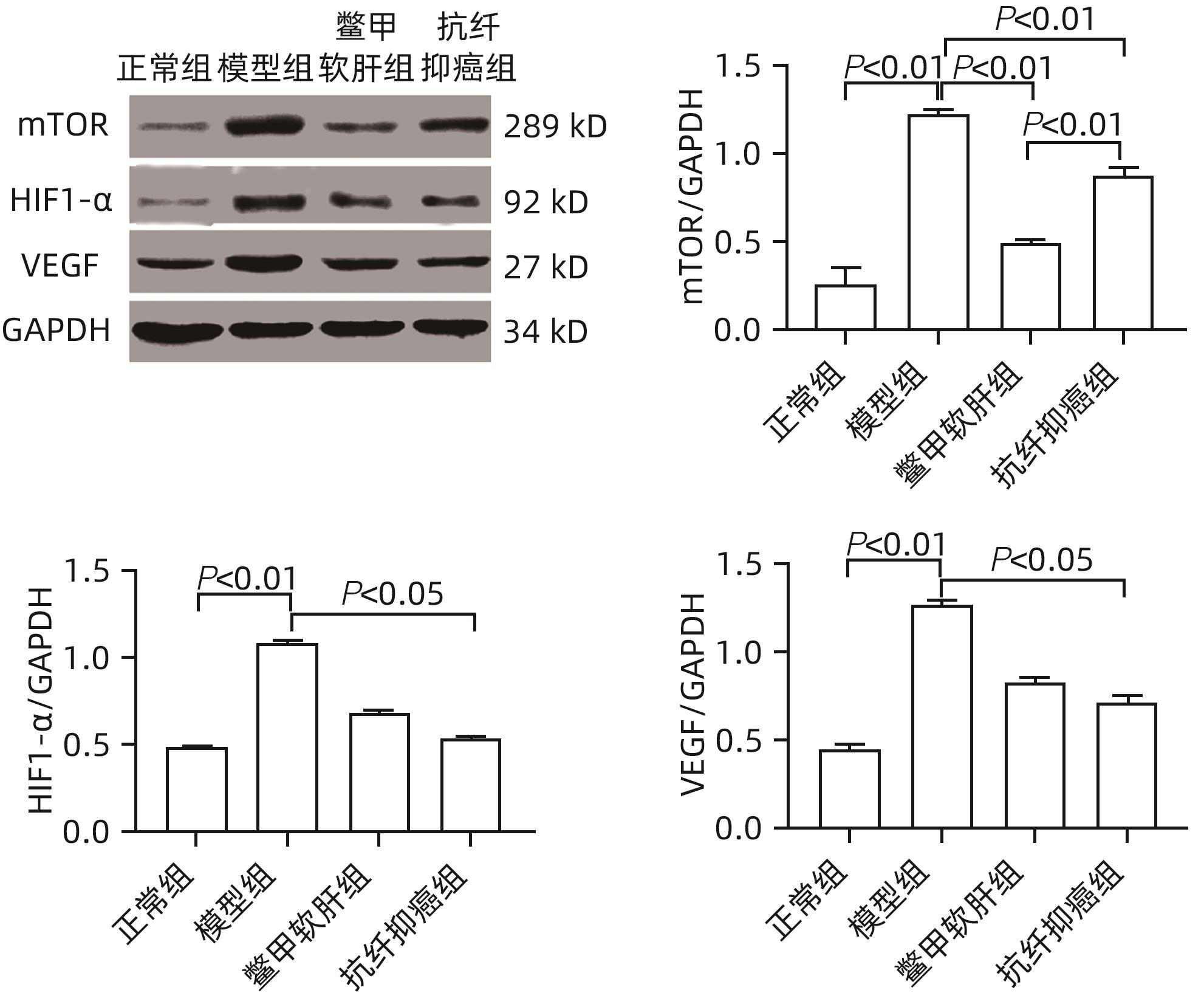
| [1] |
VILLANUEVA A. Hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2019, 380( 15): 1450- 1462. DOI: 10.1056/nejmra1713263. |
| [2] |
General Office of National Health Commission. Standard for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer(2022 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 2): 288- 303. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.02.009. |
| [3] |
Chinese Journal of Hepatology; Liver Cancer Study Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Expert consensus on multidisciplinary diagnosis and treatment of precancerous lesions of hepatocellular carcinoma(2020 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36( 3): 514- 518. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.03.007. |
| [4] |
LIU H, CHEN XT, WANG PF, et al. PRMT1-mediated PGK1 arginine methylation promotes colorectal cancer glycolysis and tumorigenesis[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2024, 15( 2): 170. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-024-06544-6. |
| [5] |
LI ZG, YANG XZ, LI XK, et al. Association of hypoxic microenvironment with the development and progression of liver diseases[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36( 8): 1891- 1895. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.08.047. |
| [6] |
LAPLANTE M, SABATINI DM. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease[J]. Cell, 2012, 149( 2): 274- 293. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.017. |
| [7] |
SAXTON RA, SABATINI DM. mTOR signaling in growth, metabolism, and disease[J]. Cell, 2017, 169( 2): 361- 371. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.03.035. |
| [8] |
YANG XG, LU Y, HANG JJ, et al. Lactate-modulated immunosuppression of myeloid-derived suppressor cells contributes to the radioresistance of pancreatic cancer[J]. Cancer Immunol Res, 2020, 8( 11): 1440- 1451. DOI: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-20-0111. |
| [9] |
MUSLEH UD DIN S, STREIT SG, HUYNH BT, et al. Therapeutic targeting of hypoxia-inducible factors in cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25( 4): 2060. DOI: 10.3390/ijms25042060. |
| [10] |
SCHITO L, SEMENZA GL. Hypoxia-inducible factors: Master regulators of cancer progression[J]. Trends Cancer, 2016, 2( 12): 758- 770. DOI: 10.1016/j.trecan.2016.10.016. |
| [11] |
GIANNITRAPANI L, DI GAUDIO F, CERVELLO M, et al. Genetic biomarkers of sorafenib response in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25( 4): 2197. DOI: 10.3390/ijms25042197. |
| [12] |
FAIVRE S, RIMASSA L, FINN RS. Molecular therapies for HCC: Looking outside the box[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 72( 2): 342- 352. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.09.010. |
| [13] |
LIU RJ, YANG XZ, ZHANG P, et al. Efficacy observation on Kangxian yi’ai formula in rats with liver precancerous lesions[J]. World Chin Med, 2015, 10( 9): 1309- 1312. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2015.09.004. |
| [14] |
LI Y, YE YA, LI ZG, et al. Study on the mechanism of kangxianyiai formula delay the occurrence of hepatic precancerous lesions by regulating the signal pathway of PI3K-akt[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Liver Dis, 2019, 29( 3): 240- 243, 289. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2019.03.014. |
| [15] |
LIU LP, HO RL, CHEN GG, et al. Sorafenib inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1α synthesis: Implications for antiangiogenic activity in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2012, 18( 20): 5662- 5671. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0552. |
| [16] |
WANG XB, WANG N, CHEUNG F, et al. Chinese medicines for prevention and treatment of human hepatocellular carcinoma: Current progress on pharmacological actions and mechanisms[J]. J Integr Med, 2015, 13( 3): 142- 164. DOI: 10.1016/S2095-4964(15)60171-6. |
| [17] |
HU B, AN HM, WANG SS, et al. Preventive and therapeutic effects of Chinese herbal compounds against hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Molecules, 2016, 21( 2): 142. DOI: 10.3390/molecules21020142. |
| [18] |
XU F, ZENG YL, LI J, et al. Mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine compound in preventing and treating hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae, 2019, 25( 24): 196- 204. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20191921. |
| [19] |
LI Y, YE YA, ZHANG LD, et al. Effects of Kangxian Yi’ai Formula on integrin α5β1/FAK signaling pathway in rats with hepatic precancerous lesions[J]. China J Tradit Chin Med Pharm, 2019, 34( 2): 759- 762.
李莹, 叶永安, 张露丹, 等. 抗纤抑癌方对肝癌前病变大鼠整合素α5β1/FAK信号通路的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2019, 34( 2): 759- 762.
|
| [20] |
PAKRAVAN K, BABASHAH S, SADEGHIZADEH M, et al. MicroRNA-100 shuttled by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes suppresses in vitro angiogenesis through modulating the mTOR/HIF-1α/VEGF signaling axis in breast cancer cells[J]. Cell Oncol, 2017, 40( 5): 457- 470. DOI: 10.1007/s13402-017-0335-7. |
| [21] |
MIYAZAWA M, YASUDA M, FUJITA M, et al. Therapeutic strategy targeting the mTOR-HIF-1alpha-VEGF pathway in ovarian clear cell adenocarcinoma[J]. Pathol Int, 2009, 59( 1): 19- 27. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2008.02320.x. |
| [22] |
WAN XL, SHEN N, MENDOZA A, et al. CCI-779 inhibits rhabdomyosarcoma xenograft growth by an antiangiogenic mechanism linked to the targeting of mTOR/Hif-1alpha/VEGF signaling[J]. Neoplasia, 2006, 8( 5): 394- 401. DOI: 10.1593/neo.05820. |



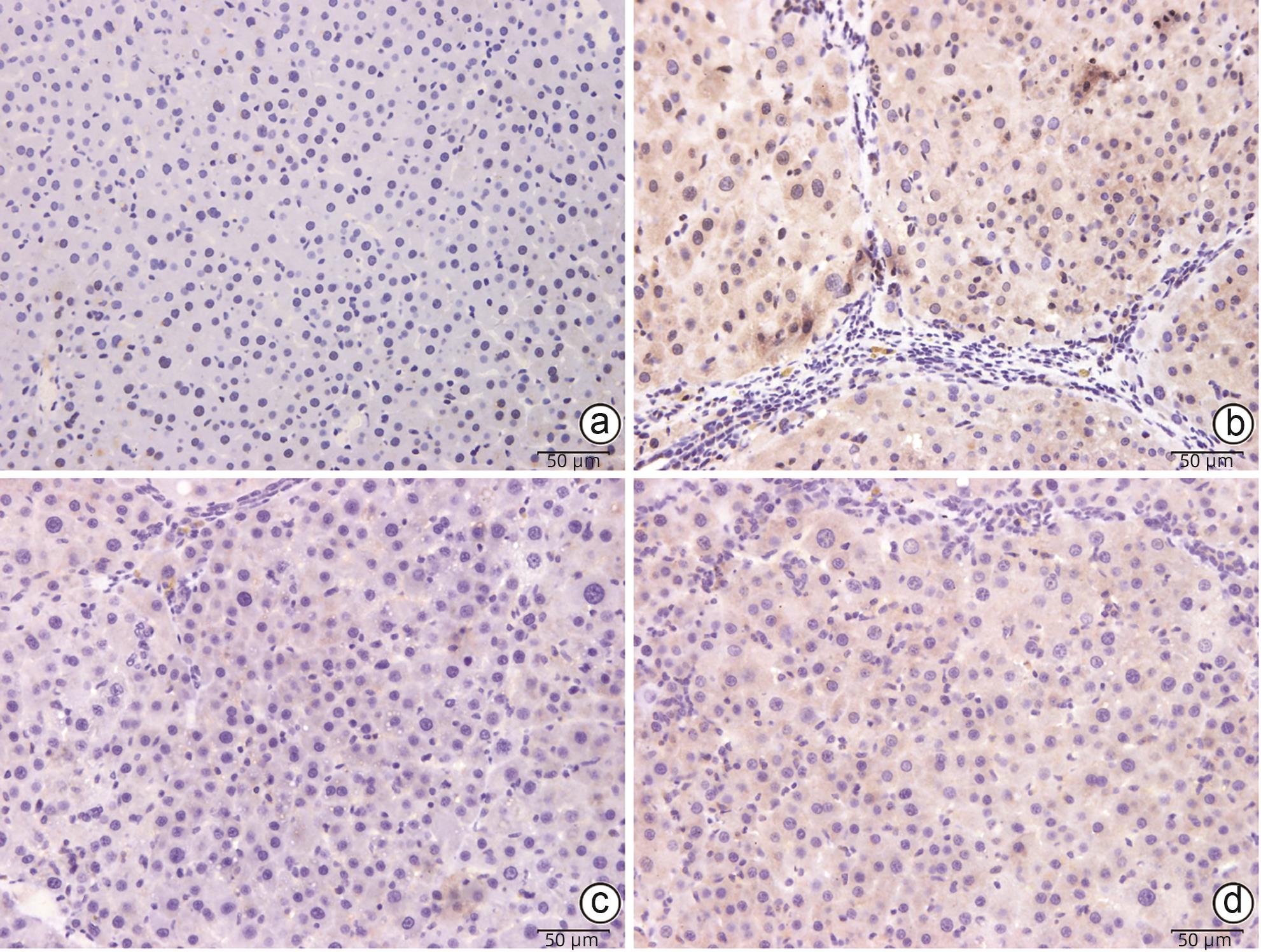




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: