| [1] |
SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71( 3): 209- 249. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21660. |
| [2] |
SIEGEL RL, MILLER KD, JEMAL A. Cancer statistics, 2020[J]. CA A Cancer J Clinicians, 2020, 70( 1): 7- 30. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21590. |
| [3] |
General Office of National Health Commission. Standard for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer(2022 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 2): 288- 303. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.02.009. |
| [4] |
HE J, CHEN WQ, SHEN HB, et al. China guideline for liver cancer screening(2022, Beijing)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 8): 1739- 1758, 1954- 1967. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.08.007. |
| [5] |
LIEBMAN HA, FURIE BC, TONG MJ, et al. Des-gamma-carboxy(abnormal) prothrombin as a serum marker of primary hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 1984, 310( 22): 1427- 1431. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM198405313102204. |
| [6] |
DING CM, HOU JF, TAO GW, et al. Early diagnosis and screening of hepatocellular carcinoma[J/OL]. Chin J Hepatic Surg(Electronic Edition), 2023, 12( 1): 22- 28. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3232.2023.01.005. |
| [7] |
YUAN LW, TANG W, ZHOU JP, et al. Quantitative measurement of des-γ-carboxy-prothrombin in cancerous and non-cancerous liver tissue and its role in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. World Chin J Dig, 2006, 14( 1): 45- 49. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3079.2006.01.009. |
| [8] |
SHIMADA M, YAMASHITA Y, HAMATSU T, et al. The role of des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin levels in hepatocellular carcinoma and liver tissues[J]. Cancer Lett, 2000, 159( 1): 87- 94. DOI: 10.1016/s0304-3835(00)00539-5. |
| [9] |
YUEN MF, LAI CL. Serological markers of liver cancer[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol, 2005, 19( 1): 91- 99. DOI: 10.1016/j.bpg.2004.10.003. |
| [10] |
FUJIYAMA S, MORISHITA T, SAGARA K, et al. Clinical evaluation of plasma abnormal prothrombin(PIVKA-II) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepato-gastroenterology, 1986, 33( 5): 201- 205. DOI: 10.1007/BF02560343. |
| [11] |
UEHARA S, GOTOH K, HANDA H, et al. Distribution of the heterogeneity of des-γ-carboxyprothrombin in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Gastro And Hepatol, 2005, 20( 10): 1545- 1552. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2005.03899.x. |
| [12] |
SEKIYA C, KOHDA H, HASEBE C, et al. Characteristics of the PIVKA-II found in hepatocellular carcinoma, investigation using monoclonal antibodies MU-3 and 19B7[J]. Int Hepatol Commun, 1994, 2( 5): 277- 284. DOI: 10.1016/0928-4346(94)90063-9. |
| [13] |
OHHIRA M, OHTAKE T, SAITO H, et al. Increase of serum des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin in alcoholic liver disease without hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Alcohol Clin Exp Res, 1999, 23( 4 Suppl): 67S- 70S. DOI: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1999.tb04537.x. |
| [14] |
MURATA K, SUZUKI H, OKANO H, et al. Hypoxia-induced des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin production in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Oncol, 2010, 36( 1): 161- 170.
|
| [15] |
SUZUKI H, MURATA K, GOTOH T, et al. Phenotype-dependent production of des-γ-carboxy prothrombin in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2011, 46( 10): 1219- 1229. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-011-0432-8. |
| [16] |
HAO X, FAN R, HOU JL. Early warning and accurate screening for the high-risk population of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 3): 499- 504. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.03.002. |
| [17] |
BEST J, BECHMANN LP, SOWA JP, et al. GALAD score detects early hepatocellular carcinoma in an international cohort of patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 18( 3): 728- 735. e 4. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.11.012. |
| [18] |
NAN Y, GARAY OU, LU X, et al. Early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma screening in patients with chronic hepatitis B in China: a cost-effectiveness analysis[J]. J Comp Eff Res, 2024, 13( 4): e230146. DOI: 10.57264/cer-2023-0146. |
| [19] |
LOGLIO A, IAVARONE M, FACCHETTI F, et al. The combination of PIVKA-II and AFP improves the detection accuracy for HCC in HBV Caucasian cirrhotics on long-term oral therapy[J]. Liver Int, 2020, 40( 8): 1987- 1996. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14475. |
| [20] |
KIM HS, PARK JW, JANG JS, et al. Prognostic values of alpha-fetoprotein and protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective study[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2009, 43( 5): 482- 488. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e318182015a. |
| [21] |
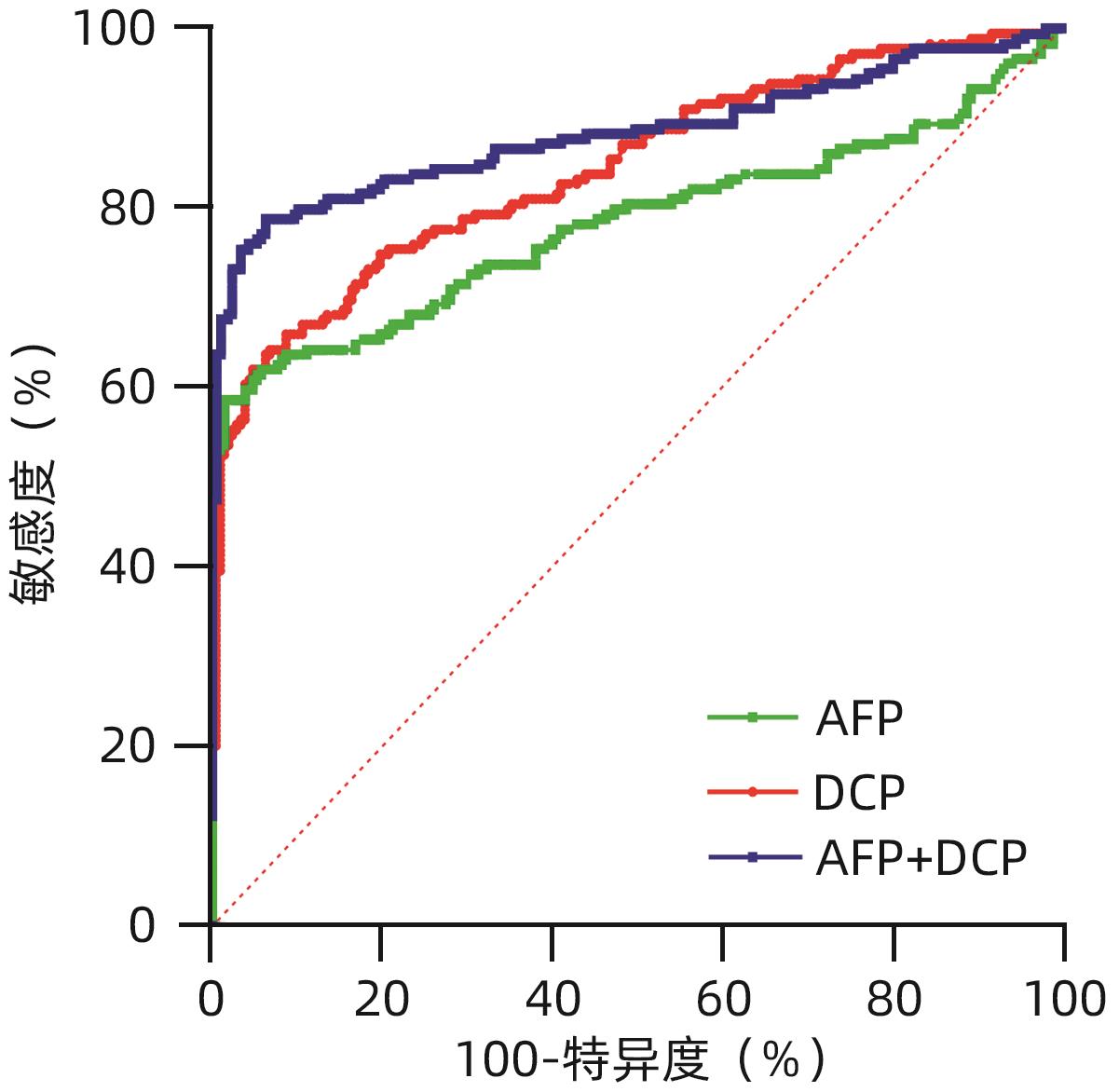
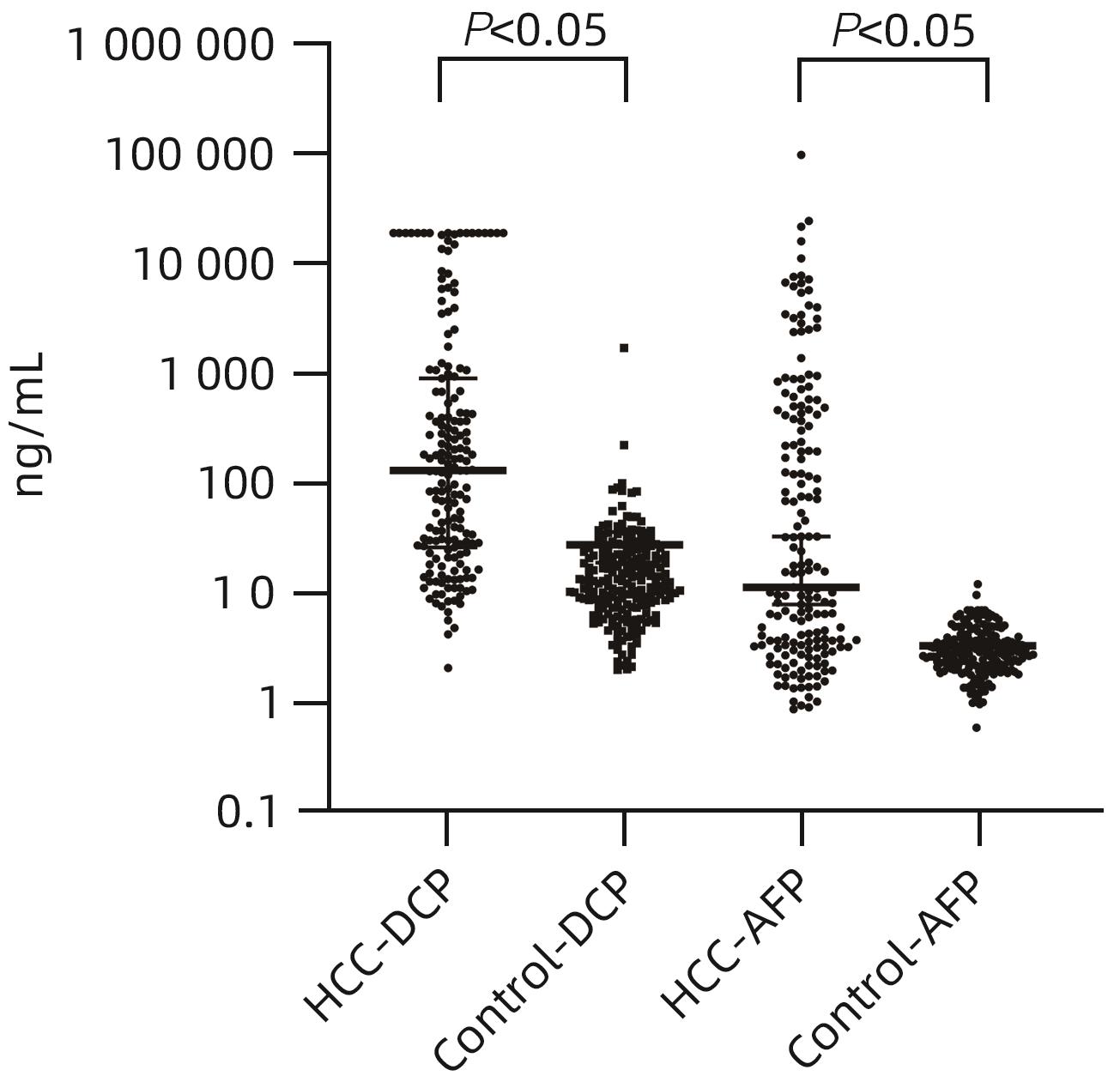
FENG HL, LI BL, LI Z, et al. PIVKA-II serves as a potential biomarker that complements AFP for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. BMC Cancer, 2021, 21( 1): 401. DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08138-3. |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: