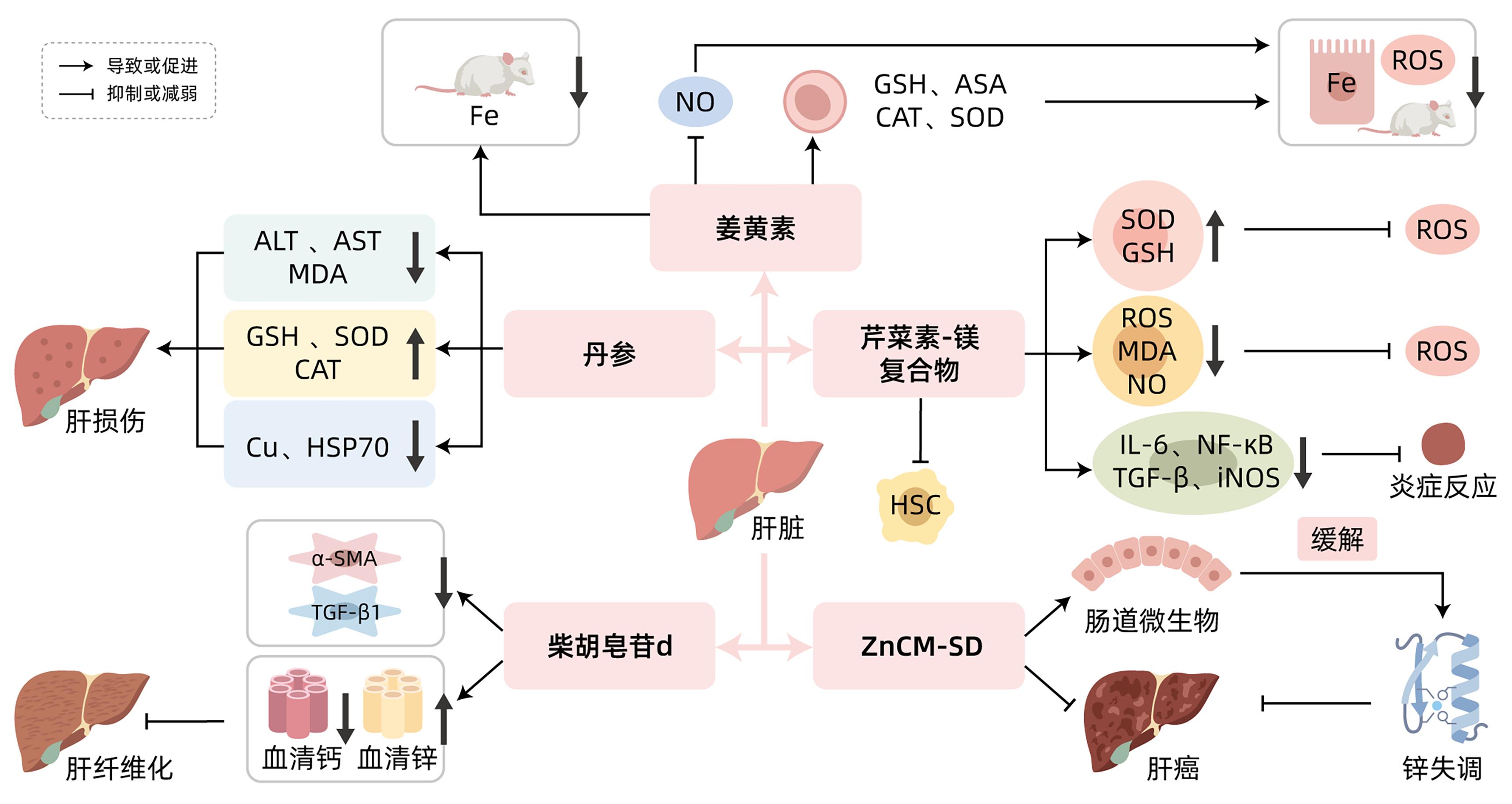
| [1] |
RODRÍGUEZ MJ, SABAJ M, TOLOSA G, et al. Maresin-1 prevents liver fibrosis by targeting Nrf2 and NF-κB, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation[J]. Cells, 2021, 10( 12): 3406. DOI: 10.3390/cells10123406. |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
LIU T, LIU YL, ZHANG FY, et al. Association of copper metabolism disorder with cell damage and liver diseases[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 9): 2244- 2251. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.09.032. |
| [4] |
HIMOTO T, MASAKI T. Associations between zinc deficiency and metabolic abnormalities in patients with chronic liver disease[J]. Nutrients, 2018, 10( 1): 88. DOI: 10.3390/nu10010088. |
| [5] |
TIAN H, XIANG P, ZHOU WH, et al. Correlation between the physiological characteristics of magnesium and cirrhosis[J]. Hebei Med J, 2021, 43( 8): 1246- 1251. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2021.08.029. |
| [6] |
OLIVA-VILARNAU N, HANKEOVA S, VORRINK SU, et al. Calcium signaling in liver injury and regeneration[J]. Front Med(Lausanne), 2018, 5: 192. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00192. |
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
ZHAO JY, LI YW, LI L. The role of iron and hepcidin in hepatic fibrosis[J]. Prog Physiol Sci, 2010, 41( 3): 183- 188.
赵晋英, 李艳伟, 李琳. 铁和铁调素在肝纤维化中的作用[J]. 生理科学进展, 2010, 41( 3): 183- 188.
|
| [9] |
SIKORSKA K, BERNAT A, WROBLEWSKA A. Molecular pathogenesis and clinical consequences of iron overload in liver cirrhosis[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2016, 15( 5): 461- 479. DOI: 10.1016/s1499-3872(16)60135-2. |
| [10] |
KEITH B, JOHNSON RS, SIMON MC. HIF1α and HIF2α: Sibling rivalry in hypoxic tumour growth and progression[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2011, 12( 1): 9- 22. DOI: 10.1038/nrc3183. |
| [11] |
ZHANG LJ, DAI XZ, WANG L, et al. Iron overload accelerated lipid metabolism disorder and liver injury in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Front Nutr, 2022, 9: 961892. DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.961892. |
| [12] |
ZHANG LL, CHENG N, WANG X. Metabolic mechanism of copper and its toxic effect on liver[J]. Chin J Gastroenterol, 2016, 21( 12): 762- 764. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7125.2016.12.016. |
| [13] |
LI YW, WAN XH, NING Q, et al. Excessive copper induces hepatocyte apoptosis and affects Bax and Bcl-2 expression in rat liver[J]. Chin J Contemp Pediatr, 2008, 10( 1): 42- 46.
李毓雯, 万小华, 宁琴, 等. 铜过量负荷导致肝细胞凋亡及其对Bax Bcl-2基因表达的影响[J]. 中国当代儿科杂志, 2008, 10( 1): 42- 46.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
GOU Y, ZHANG Y, QI JX, et al. Enhancing the copper(II) complexes cytotoxicity to cancer cells through bound to human serum albumin[J]. J Inorg Biochem, 2015, 144: 47- 55. DOI: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2014.12.012. |
| [16] |
AIGNER E, STRASSER M, HAUFE H, et al. A role for low hepatic copper concentrations in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2010, 105( 9): 1978- 1985. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2010.170. |
| [17] |
GRÜNGREIFF K, REINHOLD D, WEDEMEYER H. The role of zinc in liver cirrhosis[J]. Ann Hepatol, 2016, 15( 1): 7- 16. DOI: 10.5604/16652681.1184191. |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
KOHGO Y, IKUTA K, OHTAKE T, et al. Iron overload and cofactors with special reference to alcohol, hepatitis C virus infection and steatosis/insulin resistance[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2007, 13( 35): 4699- 4706. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i35.4699. |
| [20] |
GRÜNGREIFF K, GOTTSTEIN T, REINHOLD D, et al. Albumin substitution in decompensated liver cirrhosis: Don’t forget zinc[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13( 11): 4011. DOI: 10.3390/nu13114011. |
| [21] |
WEAVER BP, ZHANG YX, HISCOX S, et al. Zip4(Slc39a4) expression is activated in hepatocellular carcinomas and functions to repress apoptosis, enhance cell cycle and increase migration[J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5( 10): e13158. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013158. |
| [22] |
LIN CC, HUANG JF, TSAI LY, et al. Selenium, iron, copper, and zinc levels and copper-to-zinc ratios in serum of patients at different stages of viral hepatic diseases[J]. Biol Trace Elem Res, 2006, 109( 1): 15- 24. DOI: 10.1385/BTER:109:1:015. |
| [23] |
KODAMA H, TANAKA M, NAITO Y, et al. Japan’s practical guidelines for zinc deficiency with a particular focus on taste disorders, inflammatory bowel disease, and liver cirrhosis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21( 8): 2941. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21082941. |
| [24] |
ROMANI AM. Magnesium homeostasis and alcohol consumption[J]. Magnes Res, 2008, 21( 4): 197- 204.
|
| [25] |
KABE Y, ANDO K, HIRAO S, et al. Redox regulation of NF-kappaB activation: Distinct redox regulation between the cytoplasm and the nucleus[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2005, 7( 3-4): 395- 403. DOI: 10.1089/ars.2005.7.395. |
| [26] |
LIU SJ, ZHANG HW, GU CY, et al. Associations between hepatitis B virus mutations and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2009, 101( 15): 1066- 1082. DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djp180. |
| [27] |
LI Z, ZHENG YM. Effects of magnesium ions on the growth and proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and its mechanism[J]. Chin J Curr Adv Gen Surg, 2022, 25( 8): 608- 611, 617. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9905.2022.08.004. |
| [28] |
CUI JW, ZHANG J, CHENG WZ, et al. Clinical observation on the serum vitamin D level of the patients with chronic hepatitis B infection[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Liver Dis, 2017, 27( 5): 269- 271, 275. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2017.05.004. |
| [29] |
XU XY, XIA SW, HUANG XJ, et al. Relationship between disease severity and serum calcium level in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. Chin J Lab Diagn, 2019, 23( 11): 1929- 1931. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4287.2019.11.016. |
| [30] |
BIVER E, CALMY A, RIZZOLI R. Bone health in HIV and hepatitis B or C infections[J]. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis, 2017, 9( 1): 22- 34. DOI: 10.1177/1759720X16671927. |
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
ZHANG YG, ZHANG G. The relationship between cell calcium and hepatic fibrosis[J]. Chin J N Clin Med, 2019, 12( 6): 683- 687.
张英耿, 张国. 细胞钙与肝纤维化的关系[J]. 中国临床新医学, 2019, 12( 6): 683- 687.
|
| [33] |
WU WJ, YANG MF, ZHU RM. Research progress on molecular biological mechanism of hepatic stellate cell activation[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2009, 12( 4): 308- 311. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2009.04.028. |
| [34] |
GUERRA MT, FLORENTINO RM, FRANCA A, et al. Expression of the type 3 InsP 3 receptor is a final common event in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Gut, 2019, 68( 9): 1676- 1687. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317811. |
| [35] |
YU ZY, WANG KS, REN YX, et al. Mechanism of action of curcumin in treatment of pancreatic cancer[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34( 4): 900- 904. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.04.044. |
| [36] |
RAINEY NE, MOUSTAPHA A, SARIC A, et al. Iron chelation by curcumin suppresses both curcumin-induced autophagy and cell death together with iron overload neoplastic transformation[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2019, 5: 150. DOI: 10.1038/s41420-019-0234-y. |
| [37] |
SWAMY AV, GULLIAYA S, THIPPESWAMY A, et al. Cardioprotective effect of curcumin against doxorubicin-induced myocardial toxicity in albino rats[J]. Indian J Pharmacol, 2012, 44( 1): 73- 77. DOI: 10.4103/0253-7613.91871. |
| [38] |
BADRIA FA, IBRAHIM AS, BADRIA AF, et al. Curcumin attenuates iron accumulation and oxidative stress in the liver and spleen of chronic iron-overloaded rats[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10( 7): e0134156. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134156. |
| [39] |
UEDA S, MASUTANI H, NAKAMURA H, et al. Redox control of cell death[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2002, 4( 3): 405- 414. DOI: 10.1089/15230860260196209. |
| [40] |
HUANG LL, SU J. Research progress on the mechanism of action and clinical application of Danshen[J]. Chin J Drug Abuse Prev Treat, 2023, 29( 6): 1002- 1006. DOI: 10.15900/j.cnki.zylf1995.2023.06.022. |
| [41] |
YANG CL, WU J, CHEN YK. Protective effect of Salvia miltiorrhiza on high-copper diet-induced liver injury in rats[J]. J Tradit Chin Vet Med, 2016, 35( 6): 13- 16. DOI: 10.13823/j.cnki.jtcvm.2016.06.003. |
| [42] |
FANG AP, CHEN PY, WANG XY, et al. Serum copper and zinc levels at diagnosis and hepatocellular carcinoma survival in the Guangdong Liver Cancer Cohort[J]. Int J Cancer, 2019, 144( 11): 2823- 2832. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.31991. |
| [43] |
ALEXANDER JL, WILSON ID, TEARE J, et al. Gut microbiota modulation of chemotherapy efficacy and toxicity[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 14( 6): 356- 365. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.20. |
| [44] |
SHEN L, JI HF. Bidirectional interactions between dietary curcumin and gut microbiota[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2019, 59( 18): 2896- 2902. DOI: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1478388. |
| [45] |
VINOD BS, ANTONY J, NAIR HH, et al. Mechanistic evaluation of the signaling events regulating curcumin-mediated chemosensitization of breast cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2013, 4( 2): e505. DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2013.26. |
| [46] |
WU RH, MEI XT, YE YB, et al. Zn(II)-curcumin solid dispersion impairs hepatocellular carcinoma growth and enhances chemotherapy by modulating gut microbiota-mediated zinc homeostasis[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2019, 150: 104454. DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104454. |
| [47] |
MENG ZQ. Study on the mechanism of apigenin alleviates liver injury induced by high fat diet through activating autophagy[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2023.
孟卓群. 芹菜素激活自噬缓解高脂饮食所致肝损伤的作用机制研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2023.
|
| [48] |
XU XR, LI M, CHEN WW, et al. Apigenin attenuates oxidative injury in ARPE-19 cells thorough activation of Nrf2 pathway[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2016, 2016: 4378461. DOI: 10.1155/2016/4378461. |
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
PAN XW, SHAO YD, WANG FG, et al. Protective effect of apigenin magnesium complex on H 2O 2-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in rat hepatic stellate cells[J]. Pharm Biol, 2020, 58( 1): 553- 560. DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2020.1772840. |
| [51] |
GUO JZ, WAN F, LI X, et al. Study of the influence about the lipoperoxidation and zine, calcium content on Saikosaponin-d against liver fibrosis in rats[J]. Pharmacol Clin Chin Mater Med, 2009, 25( 3): 11- 14.
郭景珍, 万方, 李忻, 等. 柴胡皂苷d对肝纤维化大鼠脂质过氧化与微量元素锌、钙的影响[J]. 中药药理与临床, 2009, 25( 3): 11- 14.
|
| [52] |
ZHAO JL, MA LJ, QU M, et al. Effect of traditional Chinese medicine treatment on serum trace elements in rats with schistosomiasis hepatic fibrosis[J]. Shandong Med J, 2008, 48( 19): 38- 39. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2008.19.015. |
| [53] |
HU Y, WANG XL, LI DG, et al. Experimental study on the effects of Ca2+ antagonists on rat model of cirrhosis with portal hypertension[J]. Chin J Dig, 1995, 15( 2): 89- 91.
胡颖, 王秀玲, 李定国, 等. 钙拮抗剂对大鼠肝硬化模型门脉高压的实验研究[J]. 中华消化杂志, 1995, 15( 2): 89- 91.
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
SEKI E, SCHWABE RF. Hepatic inflammation and fibrosis: Functional links and key pathways[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 61( 3): 1066- 1079. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27332. |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: