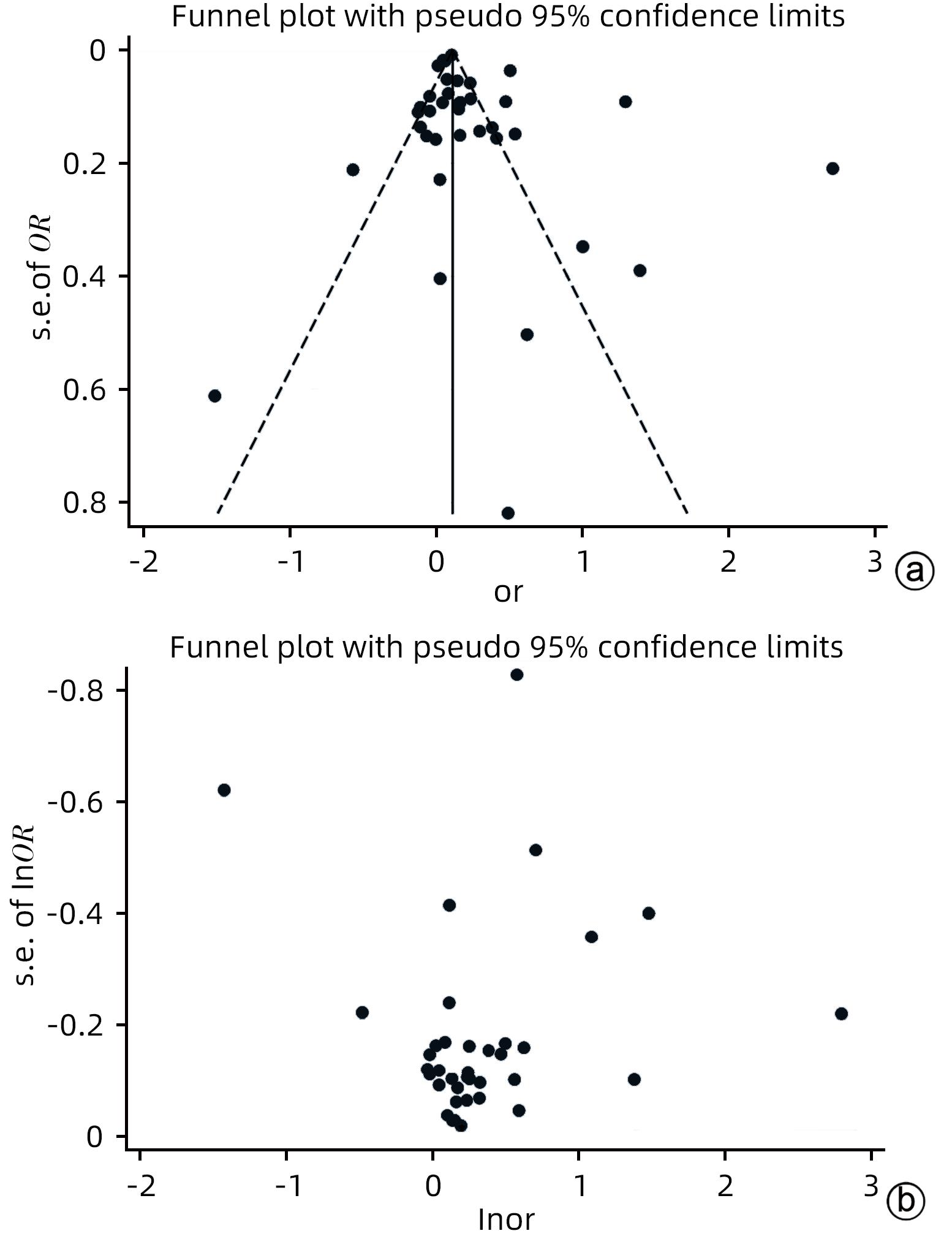
| [1] |
WANG CE, XU WT, GONG J, et al. Research progress in treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Clin J Med Off, 2022, 50( 9): 897- 899, 903. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2022.09.06. |
| [2] |
DIEHL AM, DAY C. Cause, pathogenesis, and treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017, 377( 21): 2063- 2072. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1503519. |
| [3] |
YOUNOSSI ZM, GOLABI P, PAIK JM, et al. The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis(NASH): A systematic review[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 77( 4): 1335- 1347. DOI: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000004. |
| [4] |
GOLABI P, PAIK JM, ALQAHTANI S, et al. Burden of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia, the Middle East and North Africa: Data from Global Burden of Disease 2009-2019[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 75( 4): 795- 809. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.05.022. |
| [5] |
National Workshop on Fatty Liver and Alcoholic Liver Disease, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Fatty Liver Expert Committee, Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Guidelines of prevention and treatment for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a 2018 update[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34( 5): 947- 957. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.05.007. |
| [6] |
ZHU L, SHEN XZ. Role of gut microbiota in progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J/CD]. Chin J Dig Med Imageology Electron Ed, 2014, 4( 6): 29- 32. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-2015.2014.06.010. |
| [7] |
XU XJ, ZHOU Y, LI X. Effects of intestinal microbiota and circadian rhythm on metabolism in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Chem Life, 2021, 41( 11): 2434- 2444. DOI: 10.13488/j.smhx.20210261. |
| [8] |
PARK JY, FORMAN D, WASKITO LA, et al. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori and CagA-positive infections and global variations in gastric cancer[J]. Toxins, 2018, 10( 4): 163. DOI: 10.3390/toxins10040163. |
| [9] |
REN S, CAI PP, LIU YQ, et al. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 37( 3): 464- 470. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.15751. |
| [10] |
FU L, WANG TT, LIU LL, et al. Study on the relationship between carotid atherosclerosis and Helicobacter pylori infection in middle-aged and elderly people[J]. J Clin Exp Med, 2022, 21( 22): 2429- 2433. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2022.22.021. |
| [11] |
RABELO-GONÇALVES EM, ROESLER BM, ZEITUNE JM. Extragastric manifestations of Helicobacter pylori infection: Possible role of bacterium in liver and pancreas diseases[J]. World J Hepatol, 2015, 7( 30): 2968- 2979. DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i30.2968. |
| [12] |
KIM TJ, SINN DH, MIN YW, et al. A cohort study on Helicobacter pylori infection associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2017, 52( 11): 1201- 1210. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-017-1337-y. |
| [13] |
ABDEL-RAZIK A, MOUSA N, SHABANA W, et al. Helicobacter pylori and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A new enigma?[J]. Helicobacter, 2018, 23( 6): e12537. DOI: 10.1111/hel.12537. |
| [14] |
ABO-AMER YEE, SABAL A, AHMED R, et al. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD) in a developing country: A cross-sectional study[J]. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes, 2020, 13: 619- 625. DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S237866. |
| [15] |
WERNLY S, WERNLY B, SEMMLER G, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is not independently associated with Helicobacter pylori in a central European screening cohort[J]. Minerva Med, 2022, 113( 6): 936- 949. DOI: 10.23736/S0026-4806.22.07928-9. |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
ZHENG HB. Cohort study about correlation between Helicobacter pylori infection and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2019.
郑华波. 幽门螺杆菌感染与非酒精性脂肪肝病相关性的队列研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2019.
|
| [18] |
WANG WJ, FAN MK, GONG R, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection is not an independent risk factor of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in China[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2022, 22( 1): 81. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-022-02148-6. |
| [19] |
HIGGINS JPT, THOMPSON SG, DEEKS JJ, et al. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses[J]. BMJ, 2003, 327( 7414): 557- 560. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557. |
| [20] |
GUO YH. Correlation between Helicobacter pylori infection and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[D]. Hefei: Anhui Medical University, 2022.
郭月欢. 幽门螺杆菌感染与非酒精性脂肪性肝病的相关性研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽医科大学, 2022.
|
| [21] |
YAN P, YU BC, LI M, et al. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and Helicobacter pylori infection in Dali City, China[J]. Saudi Med J, 2021, 42( 7): 735- 741. DOI: 10.15537/smj.2021.42.7.20210040. |
| [22] |
YANG W, WANG YJ, ZHANG ZG, et al. Correlation between helicobacter pylori infection and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Chin J Health Care Med, 2020, 22( 2): 212- 213. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3245.2020.02.032. |
| [23] |
XU MY, MA JH, DU J, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with Helicobacter pylori infection in north urban Chinese: A retrospective study[J]. Gastroenterol Res Pract, 2020, 2020: 9797841. DOI: 10.1155/2020/9797841. |
| [24] |
WANG YY, YU QG, LIU XX, et al. Study on association between Helicobacter pylori infection and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Acta Agric Shanghai, 2019, 36( 5): 919- 921. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7171.2019.05.029. |
| [25] |
JIANG T, CHEN X, XIA CM, et al. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in North Chinese: A cross-sectional study[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9( 1): 4874. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-41371-2. |
| [26] |
HOU L, WU Y. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its correlation with Helicobacter pylori infection in Zhenjiang area[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2018, 38( 4): 844- 845. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2018.04.033. |
| [27] |
KANG SJ, KIM HJ, KIM D, et al. Association between cagA negative Helicobacter pylori status and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease among adults in the United States[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13( 8): e0202325. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202325. |
| [28] |
GUO LL, LU MJ, HE M, et al. Research on the correlation between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and Helicobacter pylori[J]. West China Med J, 2016, 31( 10): 1667- 1670. DOI: 10.7507/1002-0179.201600458. |
| [29] |
LIU AN, WANG LL, ZHANG Y, et al. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and Helicobacter pylori[J]. Chin J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2014, 23( 12): 1451- 1454. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5709.2014.12.023. |
| [30] |
ZHU M. Analysis of clinical features and identification of risk factors of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Changchun[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2020.
朱曼. 长春市非酒精性脂肪性肝病患者临床特征分析及危险因素识别研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2020.
|
| [31] |
ZHANG X. Analysis of the correlation between Helicobacter pylori infection and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[D]. Lanzhou: Northwest University for Nationalities, 2020.
张雪. 幽门螺杆菌感染与非酒精性脂肪肝的相关性分析[D]. 兰州: 西北民族大学, 2020.
|
| [32] |
WANG HY. Research on the correlation between serum Helicobacter pylori antibody and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[D]. Yan’an: Yan’an University, 2017.
王海玉. 血清幽门螺旋杆菌抗体与非酒精性脂肪肝病的相关性研究[D]. 延安: 延安大学, 2017.
|
| [33] |
BAI XF. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University, 2015.
柏小芬. 幽门螺杆菌感染与非酒精性脂肪性肝病关系的研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学, 2015.
|
| [34] |
WANG JW, DONG FX, SU H, et al. H. pylori is related to NAFLD but only in female: A Cross-sectional Study[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2021, 18( 11): 2303- 2311. DOI: 10.7150/ijms.50748. |
| [35] |
XU XF, CHEN Y, ZHAO JX, et al. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Fujian Med J, 2022, 44( 4): 8- 11. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2600.2022.04.004. |
| [36] |
PENG C, WANG Y. The role of CagA-positive helicobacter pylori infection in the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Dig, 2019, 27( 6): 461- 465. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2019.06.13. |
| [37] |
YU YY, CAI JT, SONG ZY, et al. The associations among Helicobacter pylori infection, white blood cell count and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a large Chinese population[J]. Medicine, 2018, 97( 46): e13271. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013271. |
| [38] |
ZHANG Y, XU RJ, LI CH, et al. Analysis of the risk factors of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its correlation with helicobacter pylori in Shenzhen physical examination population[J]. Gansu Med J, 2020, 39( 8): 691- 694, 697. DOI: 10.15975/j.cnki.gsyy.2020.08.006. |
| [39] |
HAN YM, LEE J, CHOI JM, et al. The association between Helicobacter pylori with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease assessed by controlled attenuation parameter and other metabolic factors[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16( 12): e0260994. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260994. |
| [40] |
LIU Y, LI DY, LIU YP, et al. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic adipose deposition and stiffness in southwest China[J]. Front Med, 2021, 8: 764472. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.764472. |
| [41] |
FAN NG, PENG L, XIA ZH, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection is not associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study in China[J]. Front Microbiol, 2018, 9: 73. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00073. |
| [42] |
CAI O, HUANG ZP, LI M, et al. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A single-center clinical study[J]. Gastroenterol Res Pract, 2018, 2018: 8040262. DOI: 10.1155/2018/8040262. |
| [43] |
CHEN CX, GUO CY, MAO YS, et al. Relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and Helicobacter pylori infection in middle-aged and elderly people[J]. Chin J Dig, 2016, 36( 12): 839- 842. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1432.2016.12.010. |
| [44] |
LUO C. Expression and correlation analysis of fetuin A in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[D]. Changsha: Hunan Normal University, 2021.
罗超. 胎球蛋白A在非酒精性脂肪性肝病中的表达及相关性分析[D]. 长沙: 湖南师范大学, 2021.
|
| [45] |
PAZIRE SFD. Correlation analysis between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and Helicobacter pylori infection[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Medical University, 2016.
帕孜热·赛福丁. 非酒精性脂肪肝与幽门螺杆菌感染的相关性分析[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆医科大学, 2016.
|
| [46] |
HEYDARI K, YOUSEFI M, ALIZADEH-NAVAEI R, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Turk J Gastroenterol, 2022, 33( 3): 171- 181. DOI: 10.5152/tjg.2022.21467. |
| [47] |
WEI L, DING HG. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: What should we expect from a meta-analysis?[J]. Medicine, 2021, 100( 31): e26706. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000026706. |
| [48] |
LUO YX, SHU XC, LI Q, et al. Advances in research related to Helicobacter pylori and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Chin J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 31( 9): 980- 984. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5709.2022.09.005. |



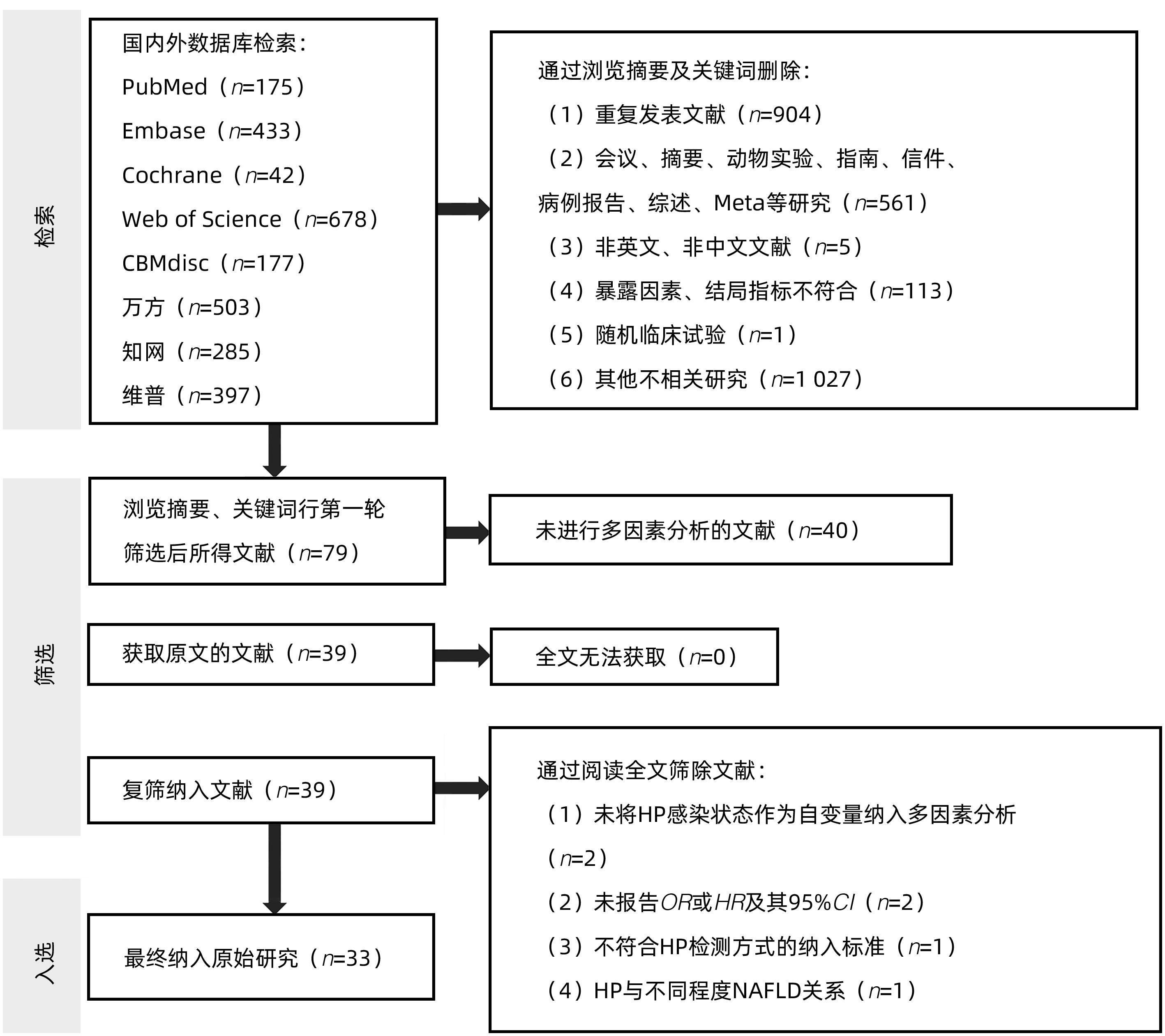




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: