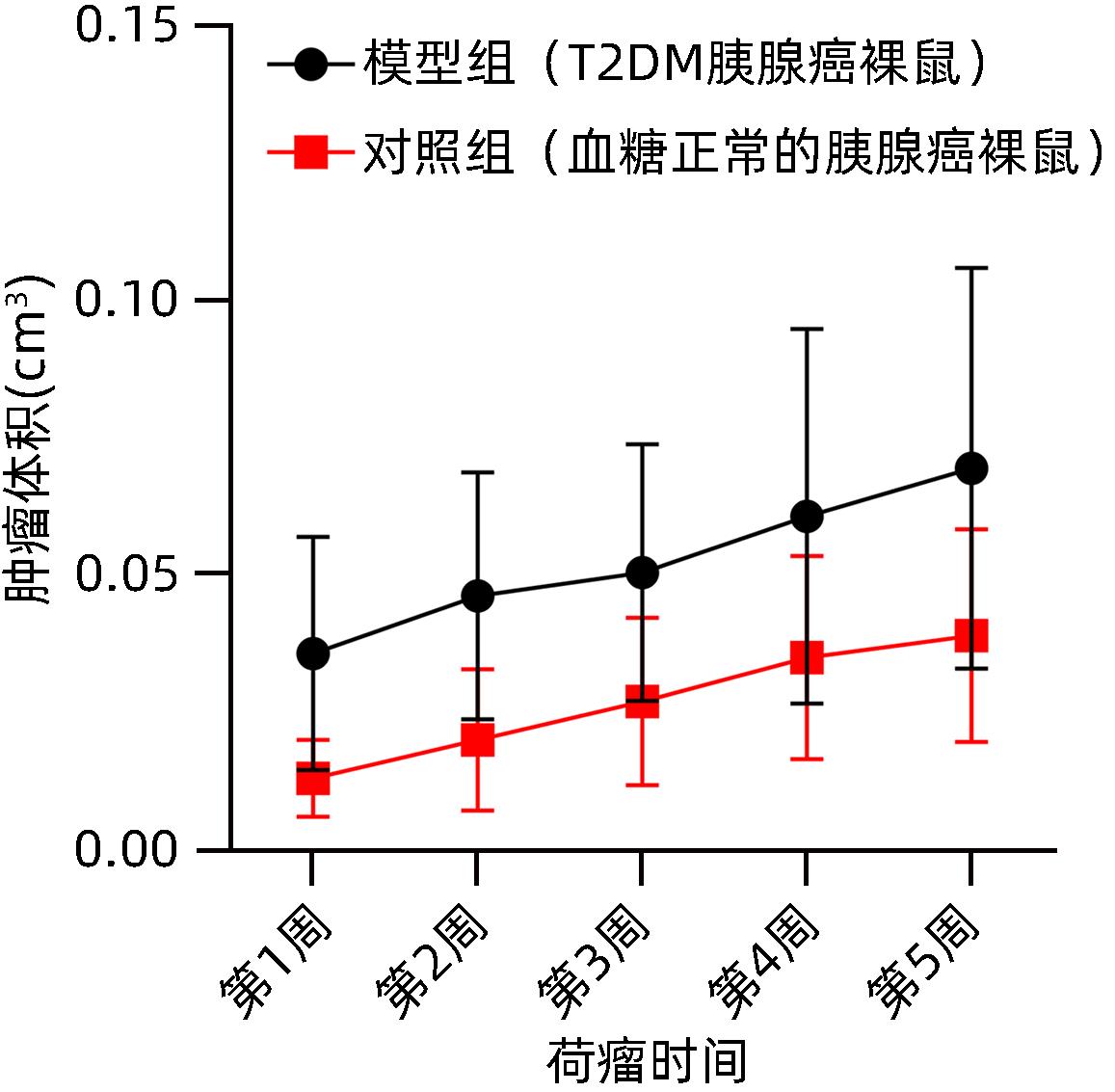
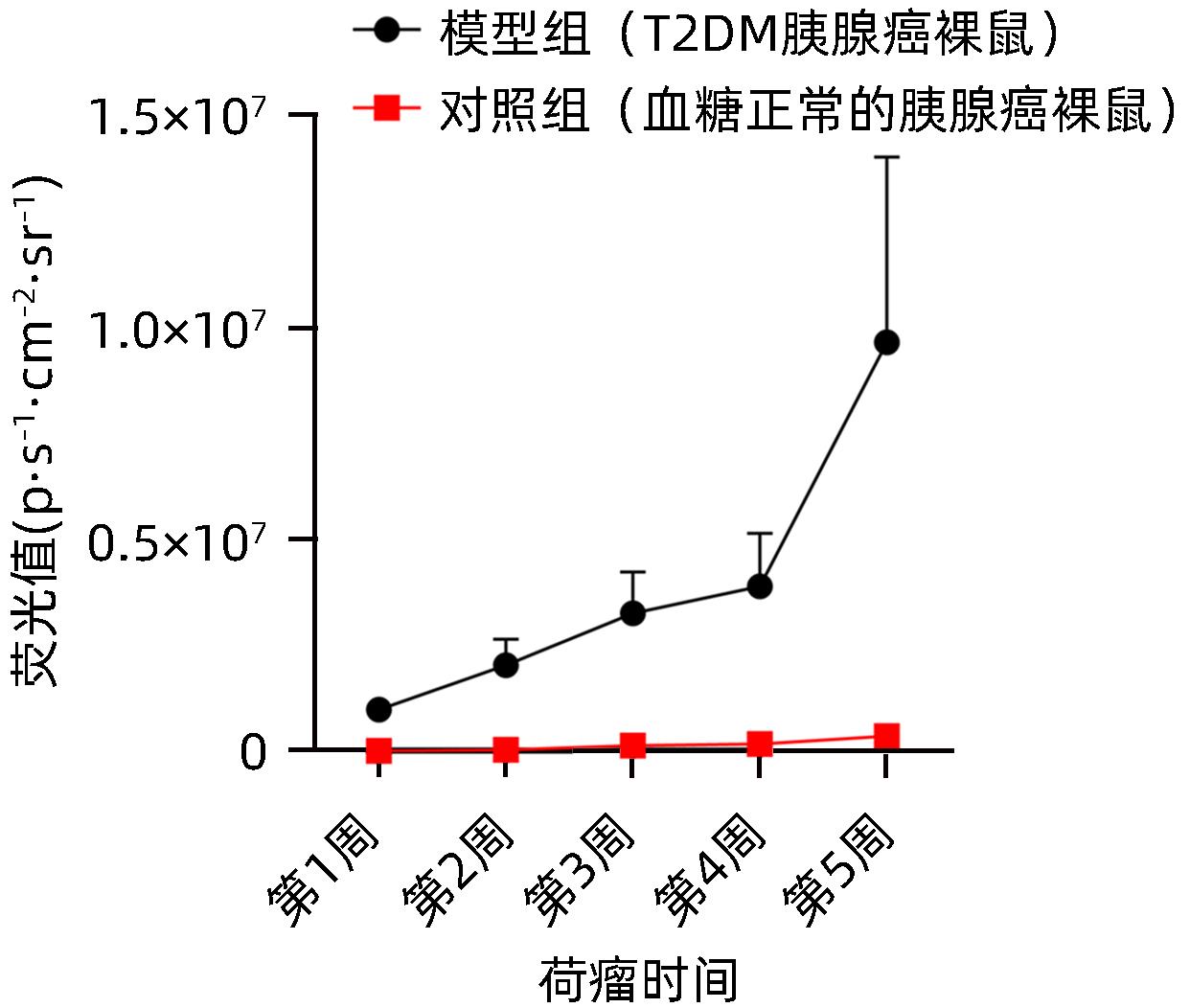
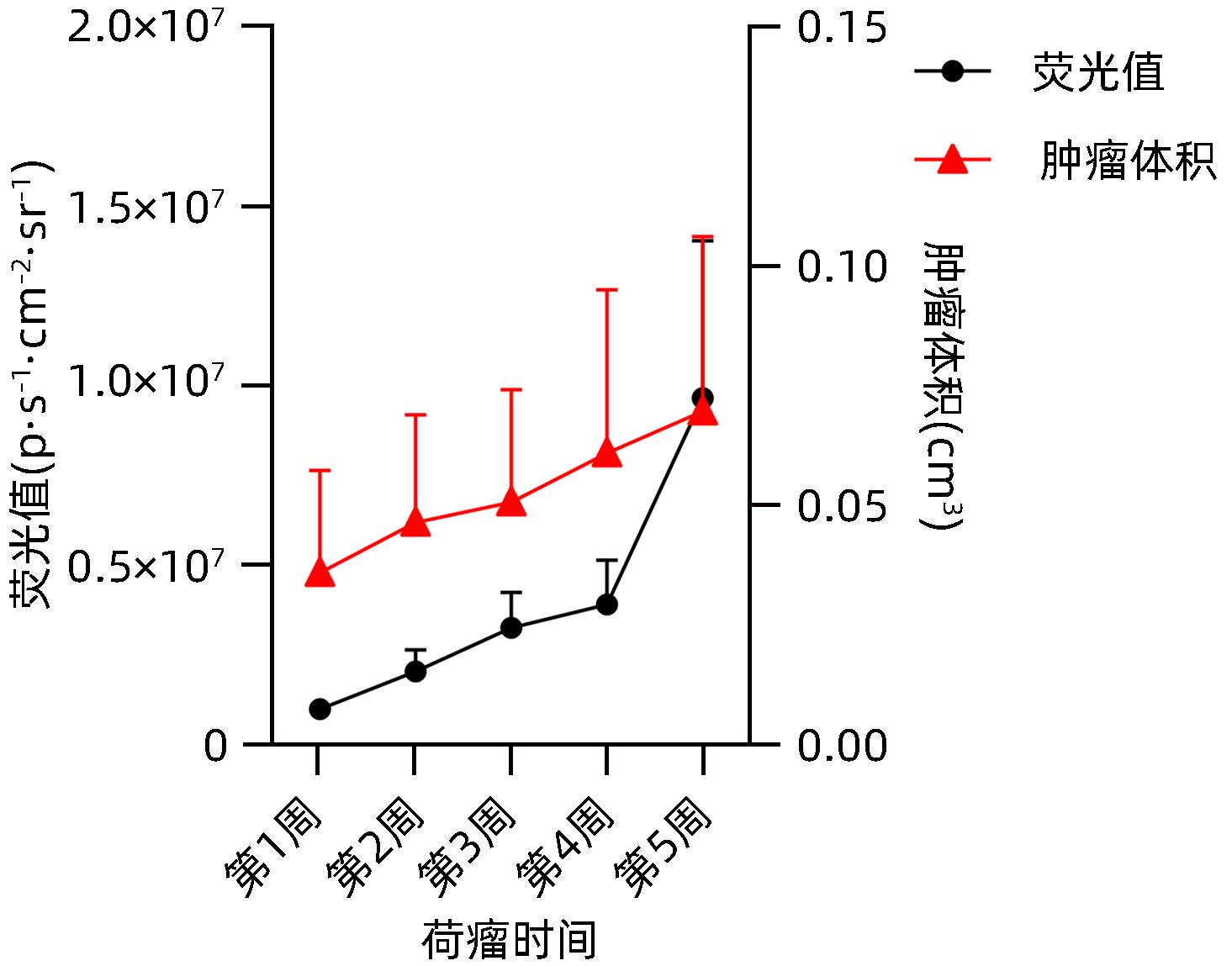
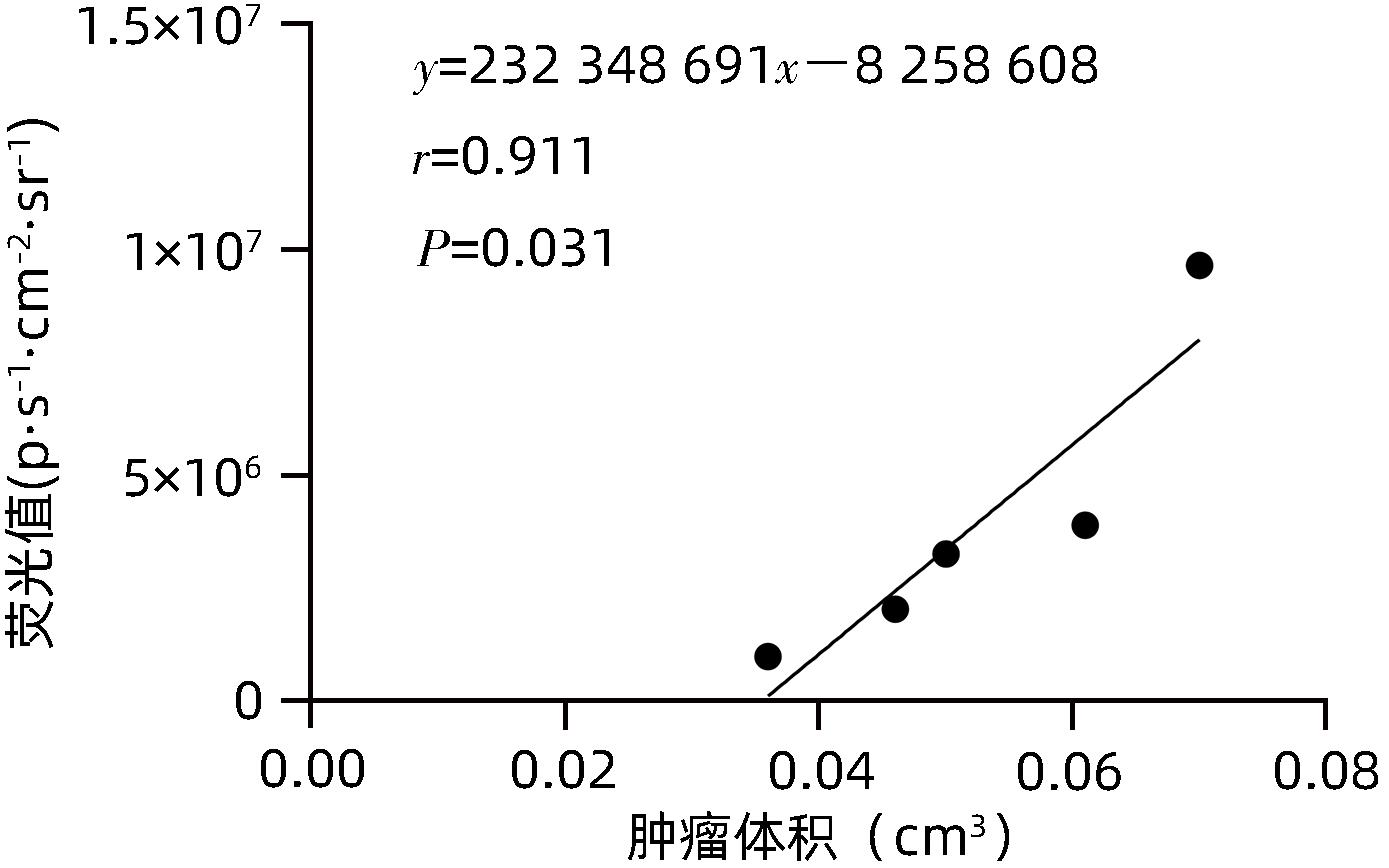
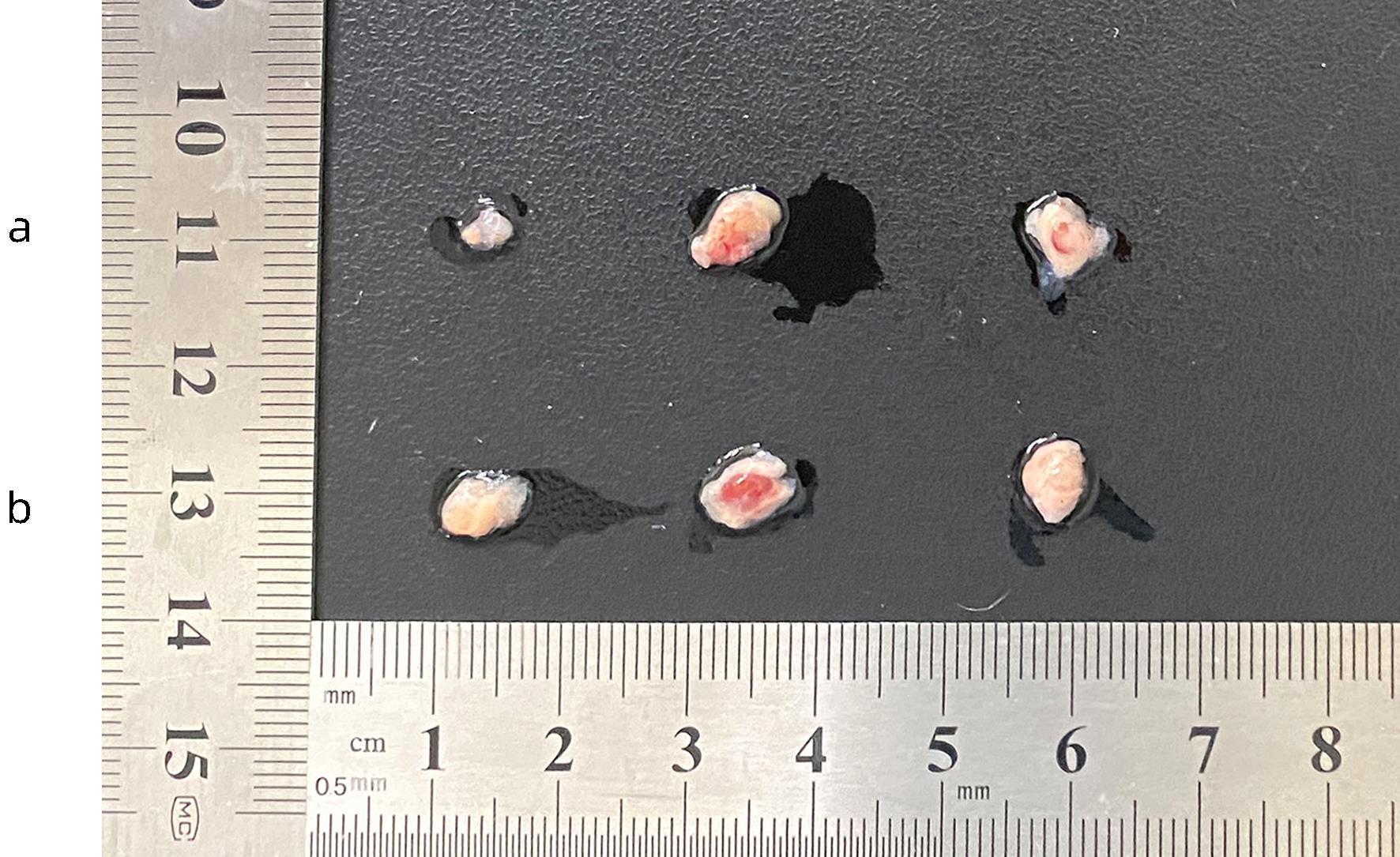
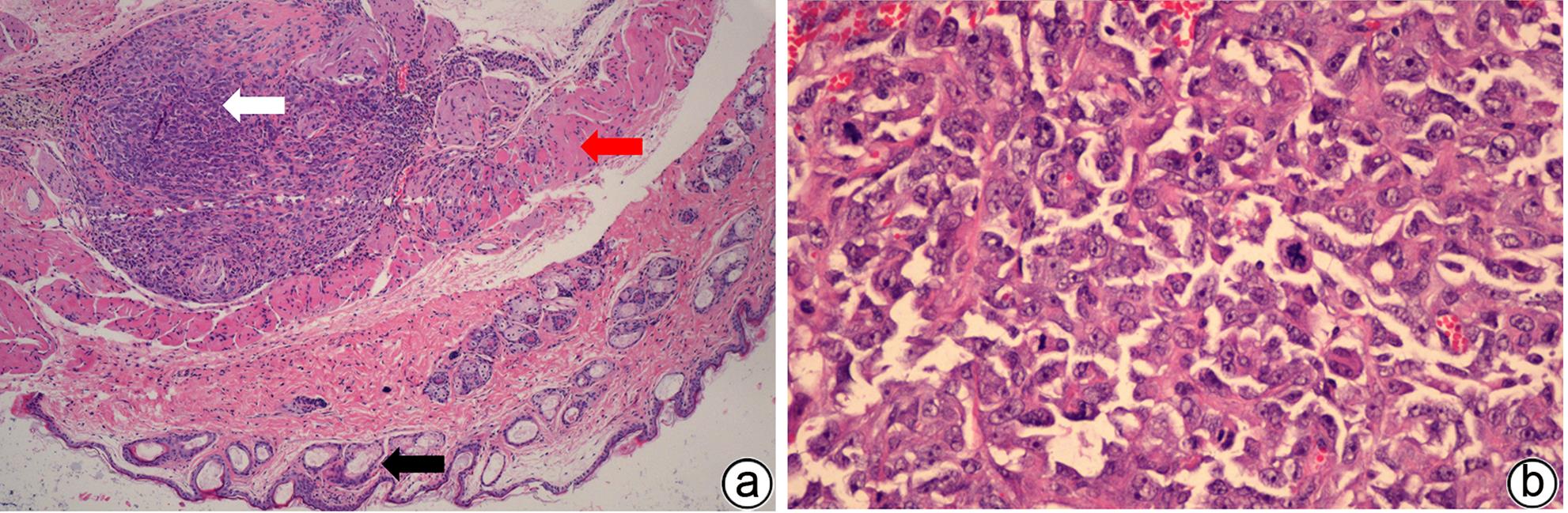
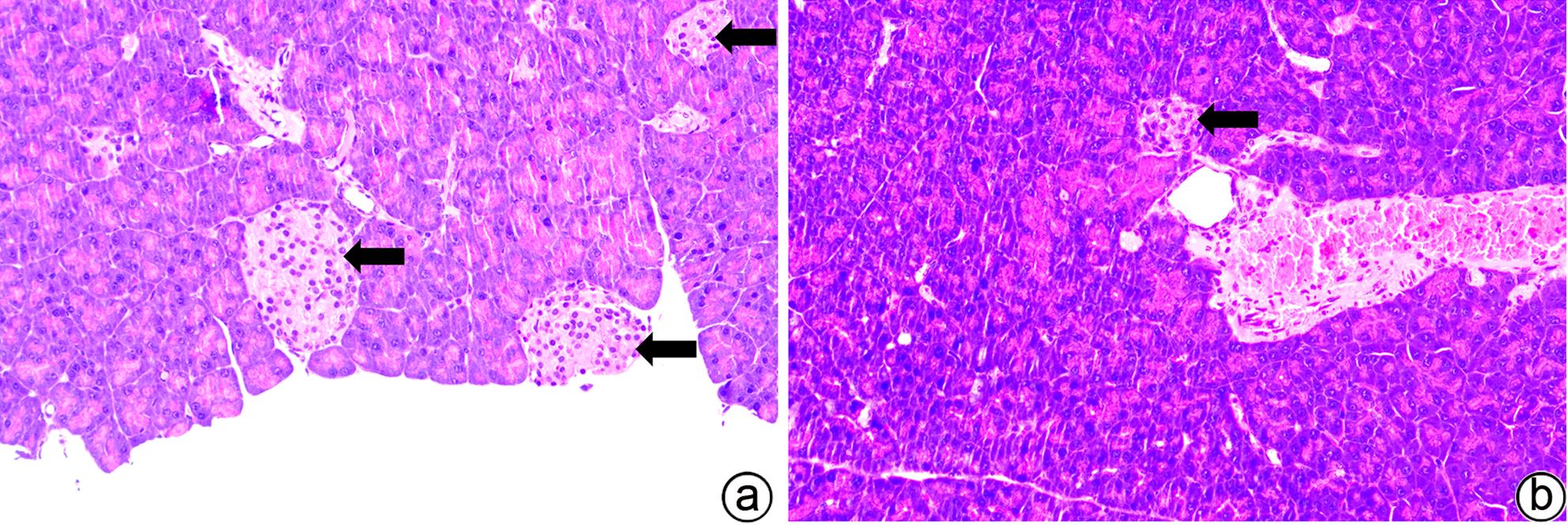
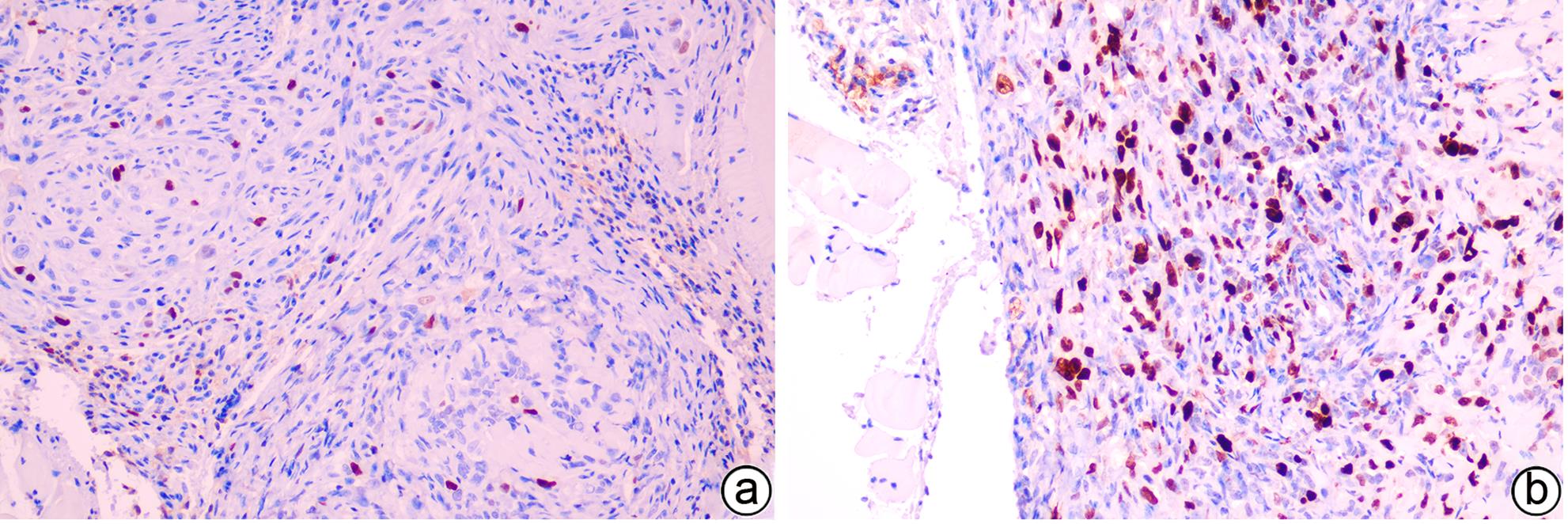
| [1] |
SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71( 3): 209- 249. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21660. |
| [2] |
XIE ZB, GAO Y, HO C, et al. Exosome-delivered CD44v6/C1QBP complex drives pancreatic cancer liver metastasis by promoting fibrotic liver microenvironment[J]. Gut, 2022, 71( 3): 568- 579. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323014. |
| [3] |
BOSETTI C, ROSATO V, LI D, et al. Diabetes, antidiabetic medications, and pancreatic cancer risk: An analysis from the International Pancreatic Cancer Case-Control Consortium[J]. Ann Oncol, 2014, 25( 10): 2065- 2072. DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdu276. |
| [4] |
LI WJ, ZHANG XH, SANG H, et al. Effects of hyperglycemia on the progression of tumor diseases[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38( 1): 327. DOI: 10.1186/s13046-019-1309-6. |
| [5] |
NOH Y, JEON SM, SHIN S. Association between glucose-lowering treatment and cancer metastasis among patients with preexisting type 2 diabetes and incident malignancy[J]. Int J Cancer, 2019, 144( 7): 1530- 1539. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.31870. |
| [6] |
OVERBEEK JA, van HERK-SUKEL MPP, VISSERS PAJ, et al. Type 2 diabetes, but not insulin(analog) treatment, is associated with more advanced stages of breast cancer: A national linkage of cancer and pharmacy registries[J]. Diabetes Care, 2019, 42( 3): 434- 442. DOI: 10.2337/dc18-2146. |
| [7] |
POPOVIC K, SMOLOVIĆ B, MARTINOVIĆ M, et al. The relationship between diabetes mellitus and pancreatic cancer-diabetes mellitus as a red flag for pancreatic cancer[J]. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2023, 32( 3): 298- 305. DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-22-0951. |
| [8] |
LI JH, MA JG, HAN L, et al. Hyperglycemic tumor microenvironment induces perineural invasion in pancreatic cancer[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2015, 16( 6): 912- 921. DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2015.1040952. |
| [9] |
LI W, ZHANG L, CHEN X, et al. Hyperglycemia promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic cancer via hydrogen peroxide[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2016, 2016: 5190314. DOI: 10.1155/2016/5190314. |
| [10] |
CHENG L, QIN T, MA JG, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α mediates hyperglycemia-induced pancreatic cancer glycolysis[J]. Anticancer Agents Med Chem, 2019, 19( 12): 1503- 1512. DOI: 10.2174/1871520619666190626120359. |
| [11] |
ZHANG L, ZHANG WN, ZHANG X, et al. High-glucose microenvironment promotes perineural invasion of pancreatic cancer via activation of hypoxia inducible factor 1α[J]. Oncol Rep, 2022, 47( 4): 64. DOI: 10.3892/or.2022.8275. |
| [12] |
LI W, LIU H, QIAN WK, et al. Hyperglycemia aggravates microenvironment hypoxia and promotes the metastatic ability of pancreatic cancer[J]. Comput Struct Biotechnol J, 2018, 16: 479- 487. DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2018.10.006. |
| [13] |
DEL PUERTO-NEVADO L, MINGUEZ P, CORTON M, et al. Molecular evidence of field cancerization initiated by diabetes in colon cancer patients[J]. Mol Oncol, 2019, 13( 4): 857- 872. DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.12438. |
| [14] |
KANG J, LI CQ, GAO XH, et al. Metformin inhibits tumor growth and affects intestinal flora in diabetic tumor-bearing mice[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2021, 912: 174605. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174605. |
| [15] |
JIANG YG, FENG CX, SHI YH, et al. Eugenol improves high-fat diet/streptomycin-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus(T2DM) mice muscle dysfunction by alleviating inflammation and increasing muscle glucose uptake[J]. Front Nutr, 2022, 9: 1039753. DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1039753. |
| [16] |
CUI XN, FENG J, WEI TJ, et al. Pancreatic alpha cell glucagon-liver FGF21 axis regulates beta cell regeneration in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetologia, 2023, 66( 3): 535- 550. DOI: 10.1007/s00125-022-05822-2. |
| [17] |
ELSNER M, GULDBAKKE B, TIEDGE M, et al. Relative importance of transport and alkylation for pancreatic beta-cell toxicity of streptozotocin[J]. Diabetologia, 2000, 43( 12): 1528- 1533. DOI: 10.1007/s001250051564. |
| [18] |
HE CX, WANG K, XIA J, et al. Natural exosomes-like nanoparticles in mung bean sprouts possesses anti-diabetic effects via activation of PI3K/Akt/GLUT4/GSK-3β signaling pathway[J]. J Nanobiotechnology, 2023, 21( 1): 349. DOI: 10.1186/s12951-023-02120-w. |
| [19] |
MCNEILLY AD, GALLAGHER JR, EVANS ML, et al. Chronic hyperglycaemia increases the vulnerability of the hippocampus to oxidative damage induced during post-hypoglycaemic hyperglycaemia in a mouse model of chemically induced type 1 diabetes[J]. Diabetologia, 2023, 66( 7): 1340- 1352. DOI: 10.1007/s00125-023-05907-6. |
| [20] |
ENTENBERG D, OKTAY MH, CONDEELIS JS. Intravital imaging to study cancer progression and metastasis[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2023, 23( 1): 25- 42. DOI: 10.1038/s41568-022-00527-5. |
| [21] |
SYED AJ, ANDERSON JC. Applications of bioluminescence in biotechnology and beyond[J]. Chem Soc Rev, 2021, 50( 9): 5668- 5705. DOI: 10.1039/d0cs01492c. |
| [22] |
LIU S, SU YC, LIN MZ, et al. Brightening up biology: Advances in luciferase systems for in vivo imaging[J]. ACS Chem Biol, 2021, 16( 12): 2707- 2718. DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.1c00549. |
| [23] |
YAN YC, SHI PF, SONG WL, et al. Chemiluminescence and bioluminescence imaging for biosensing and therapy: in vivo and in vivo perspectives[J]. Theranostics, 2019, 9( 14): 4047- 4065. DOI: 10.7150/thno.33228. |
| [24] |
MERLE N, ELMSHÄUSER S, STRASSHEIMER F, et al. Monitoring autochthonous lung tumors induced by somatic CRISPR gene editing in mice using a secreted luciferase[J]. Mol Cancer, 2022, 21( 1): 191. DOI: 10.1186/s12943-022-01661-2. |
| [25] |
LI SF, RUAN ZY, ZHANG H, et al. Recent achievements of bioluminescence imaging based on firefly luciferin-luciferase system[J]. Eur J Med Chem, 2021, 211: 113111. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.113111. |
| [26] |
DEROOSE CM, REUMERS V, GIJSBERS R, et al. Noninvasive monitoring of long-term lentiviral vector-mediated gene expression in rodent brain with bioluminescence imaging[J]. Mol Ther, 2006, 14( 3): 423- 431. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2006.05.007. |
| [27] |
TAO ZN, LI T, MA HW, et al. Autophagy suppresses self-renewal ability and tumorigenicity of glioma-initiating cells and promotes Notch1 degradation[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9( 11): 1063. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-018-0957-3. |
| [28] |
YOU K, WANG DJ, WANG L, et al. Effect of NOR1 gene knockout on nude mice xenograft tumor of human liver cancer and its mechanism of action[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36( 2): 381- 386. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.02.030. |
| [29] |
LI XY, YANG YF, CHEN Y, et al. Expression and significance of response gene to complement 32 in liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in mice[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 10): 2396- 2405. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.10.018. |
| [30] |
JANG SJ, KANG JH, KIM KI, et al. Application of bioluminescence imaging to therapeutic intervention of herpes simplex virus type I-Thymidine kinase/ganciclovir in glioma[J]. Cancer Lett, 2010, 297( 1): 84- 90. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2010.04.028. |
| [31] |
WANG XL, ROSOL M, GE SD, et al. Dynamic tracking of human hematopoietic stem cell engraftment using in vivo bioluminescence imaging[J]. Blood, 2003, 102( 10): 3478- 3482. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2003-05-1432. |



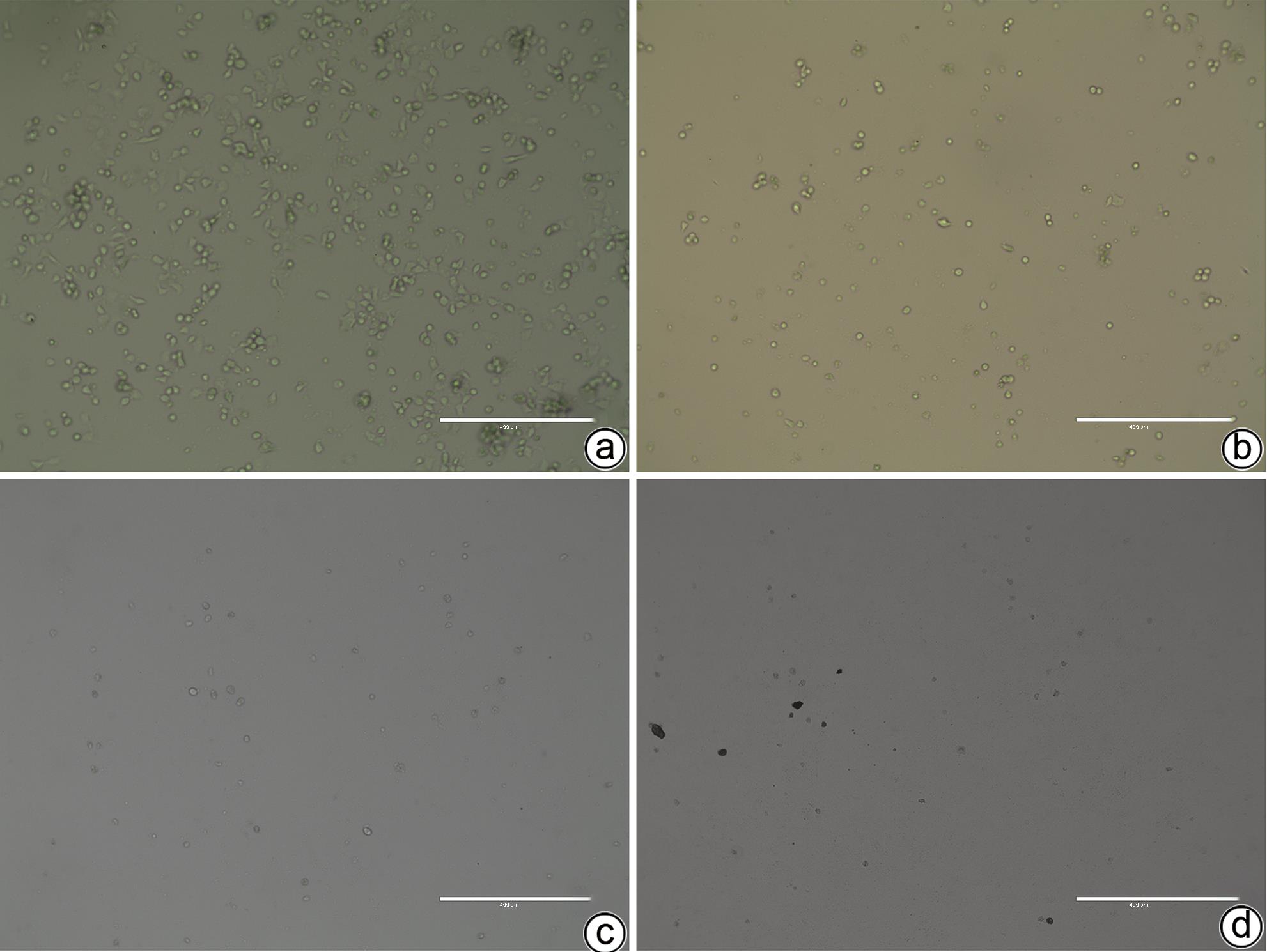




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: