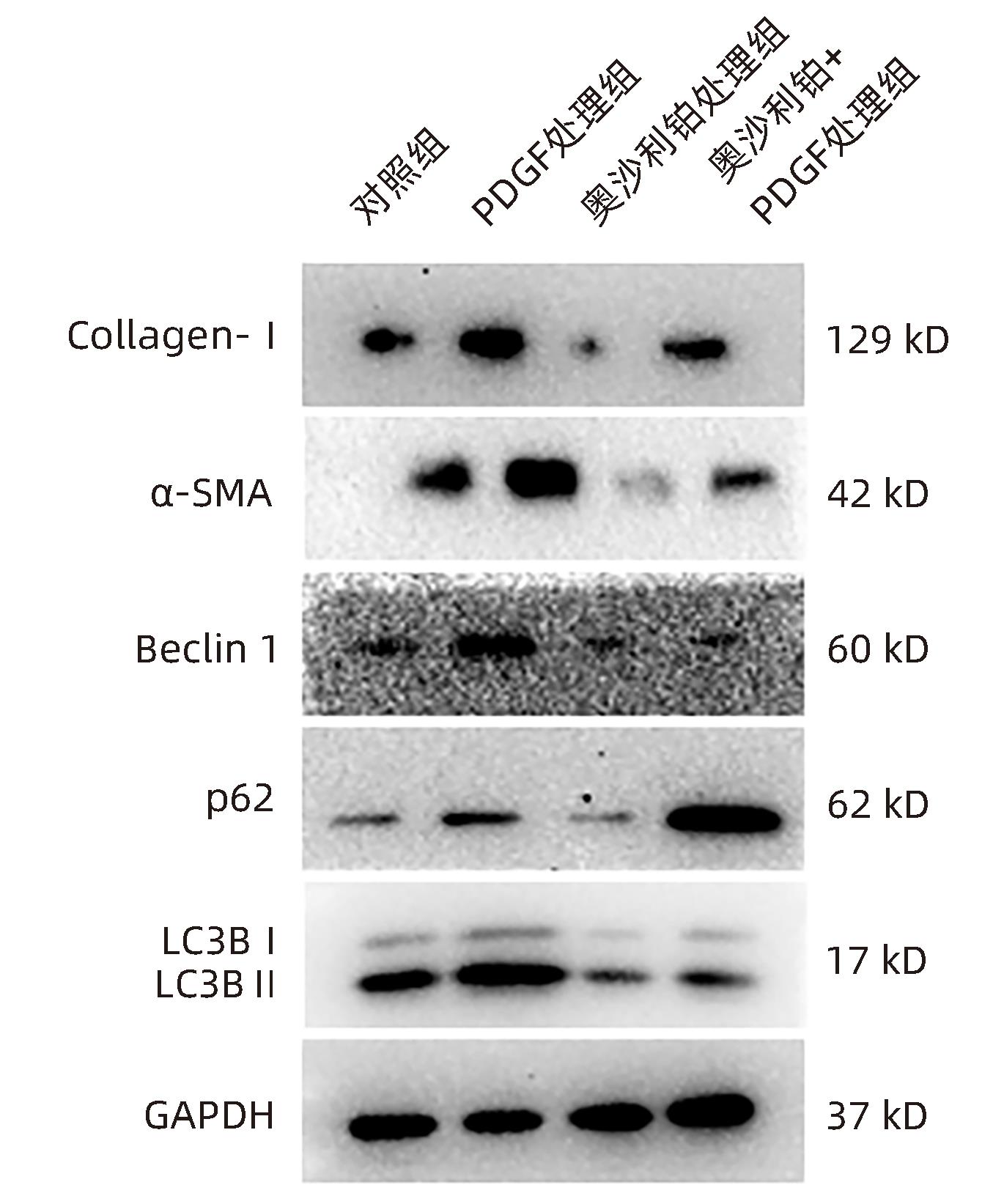
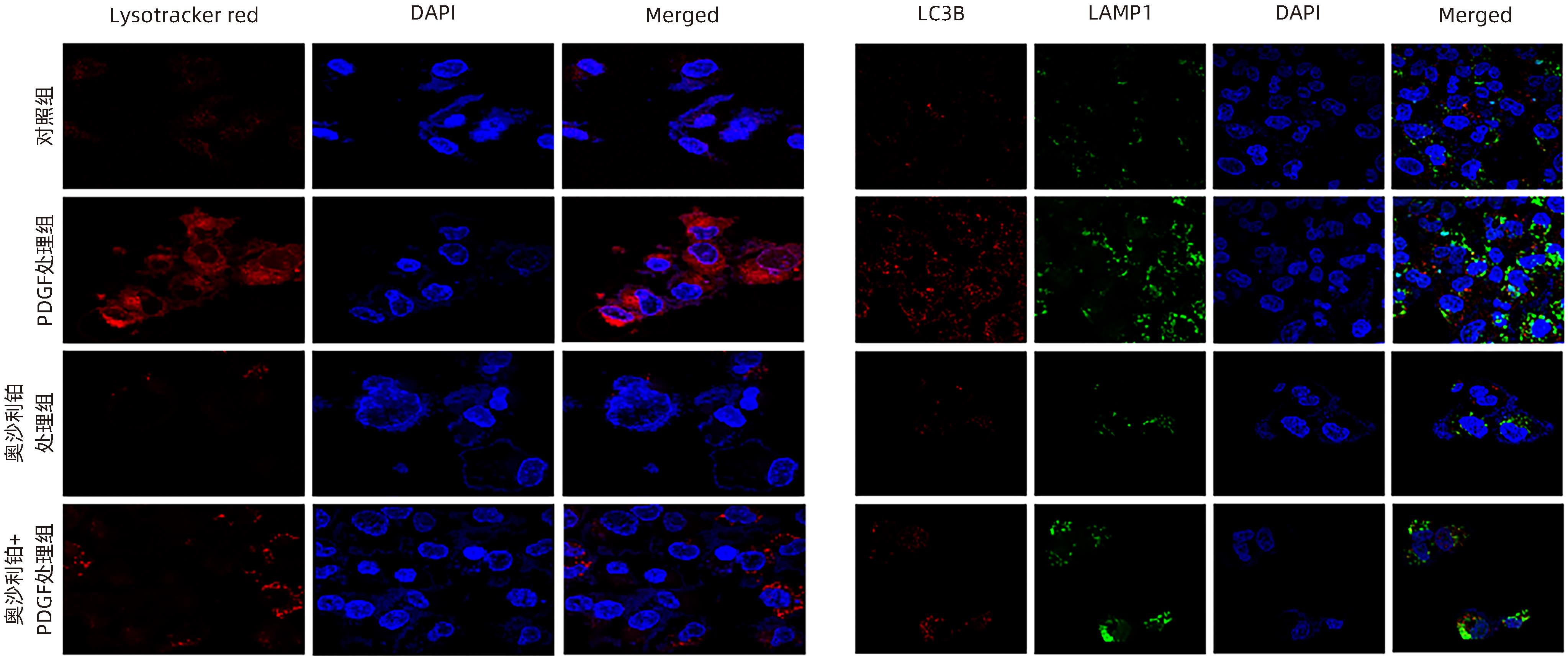
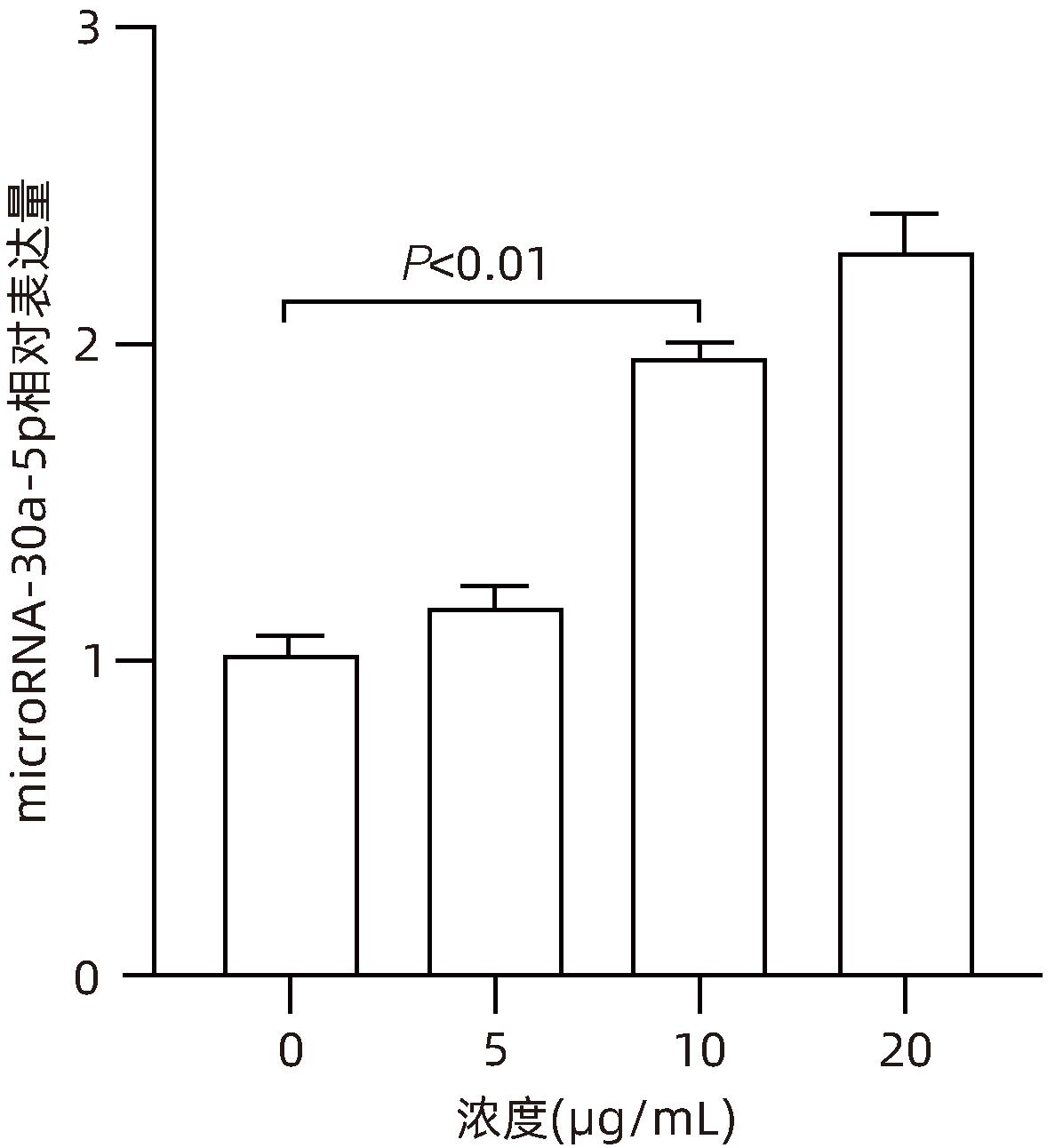
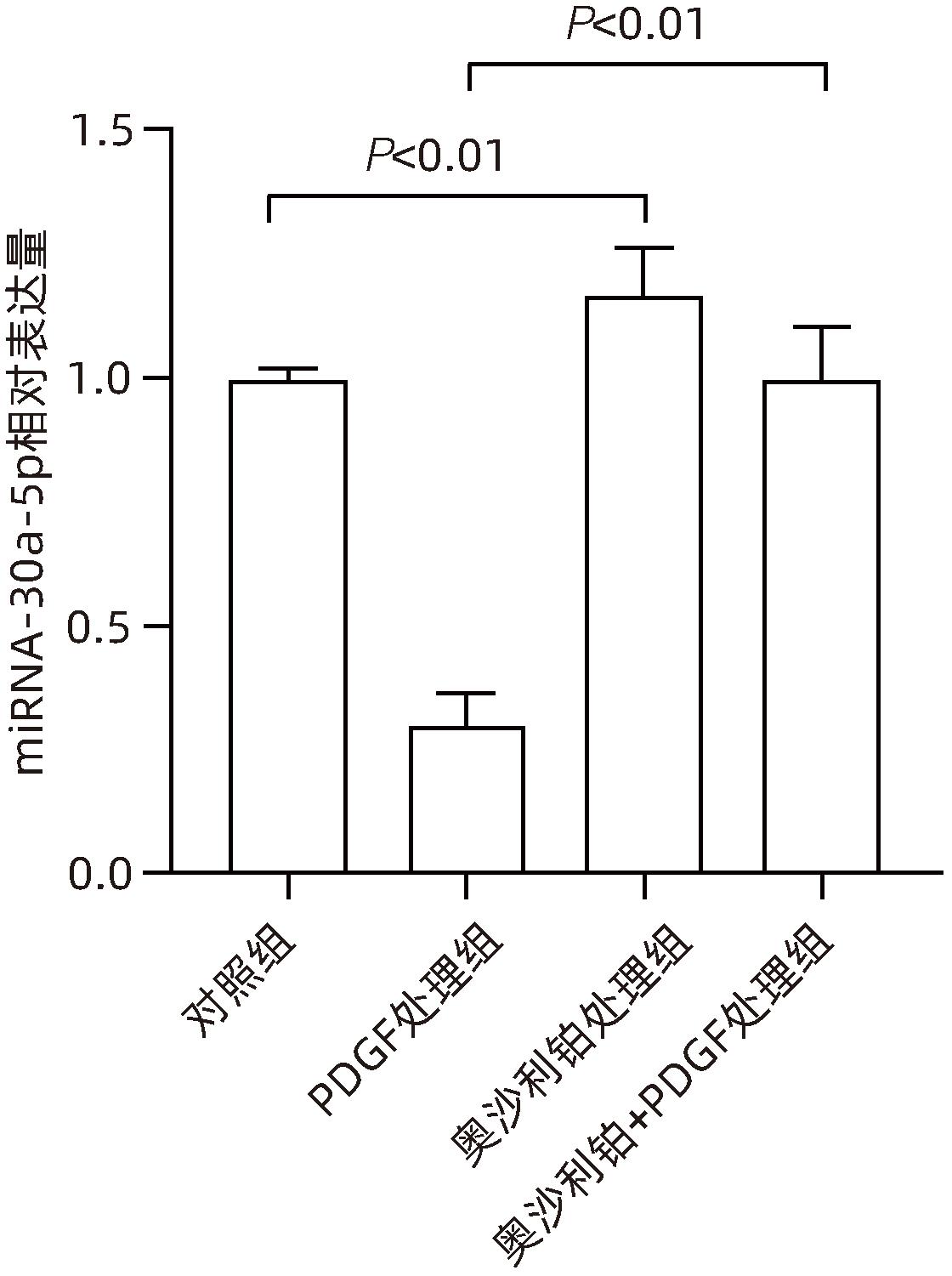
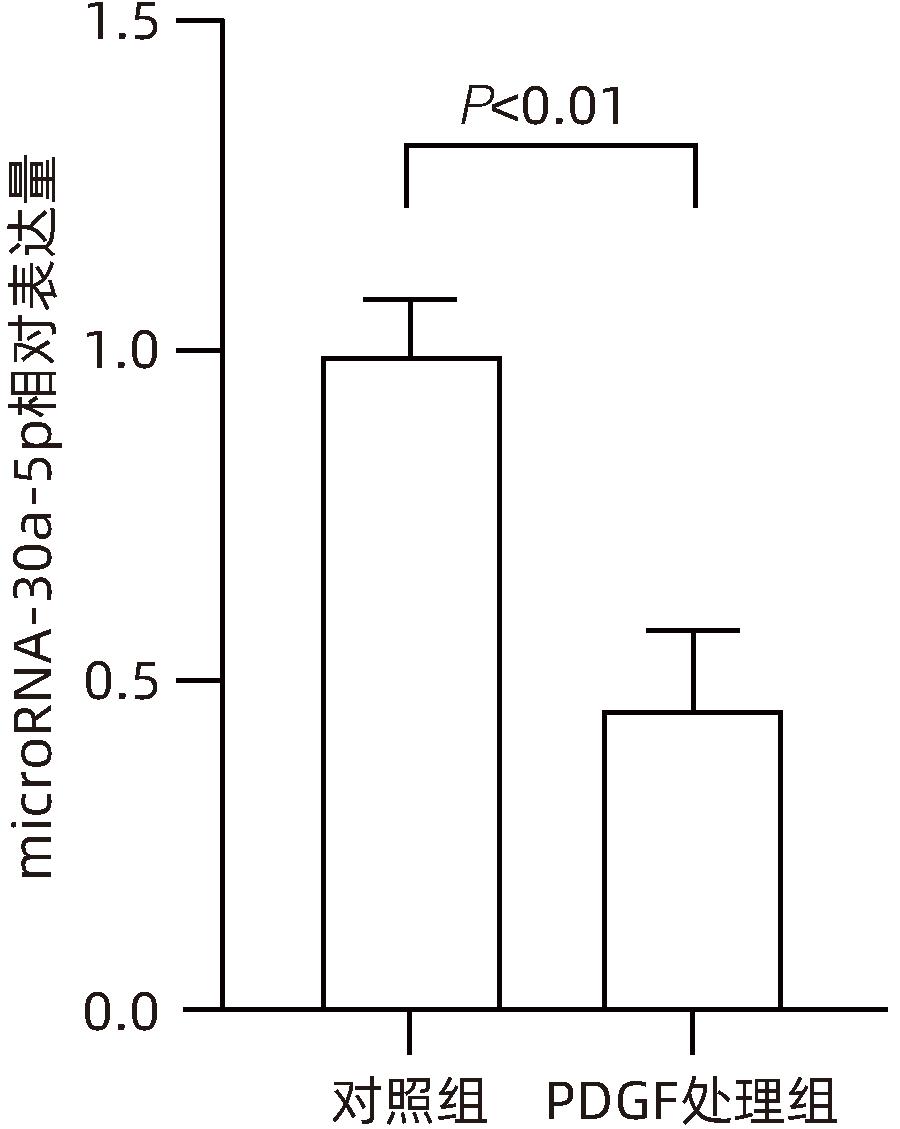
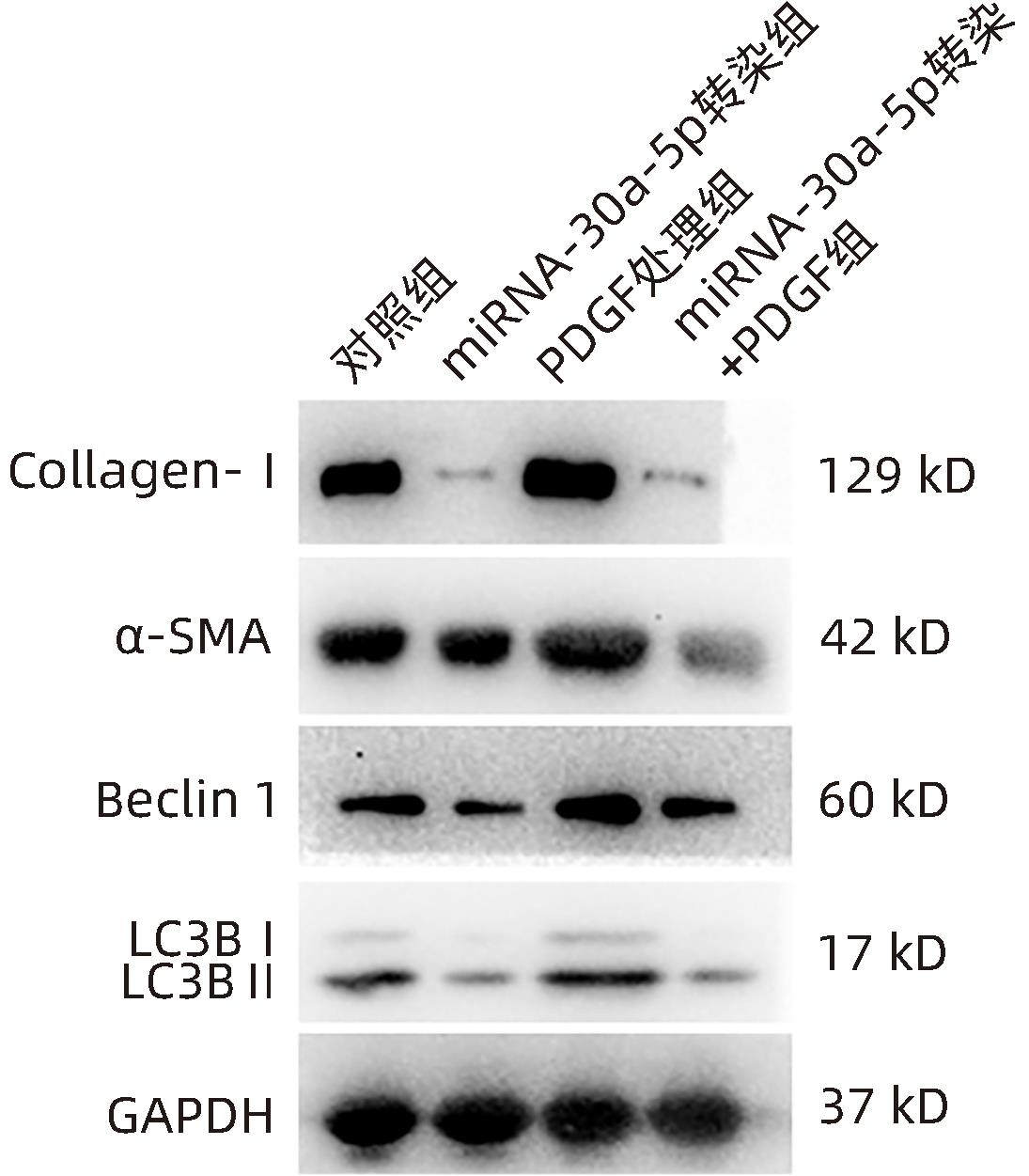
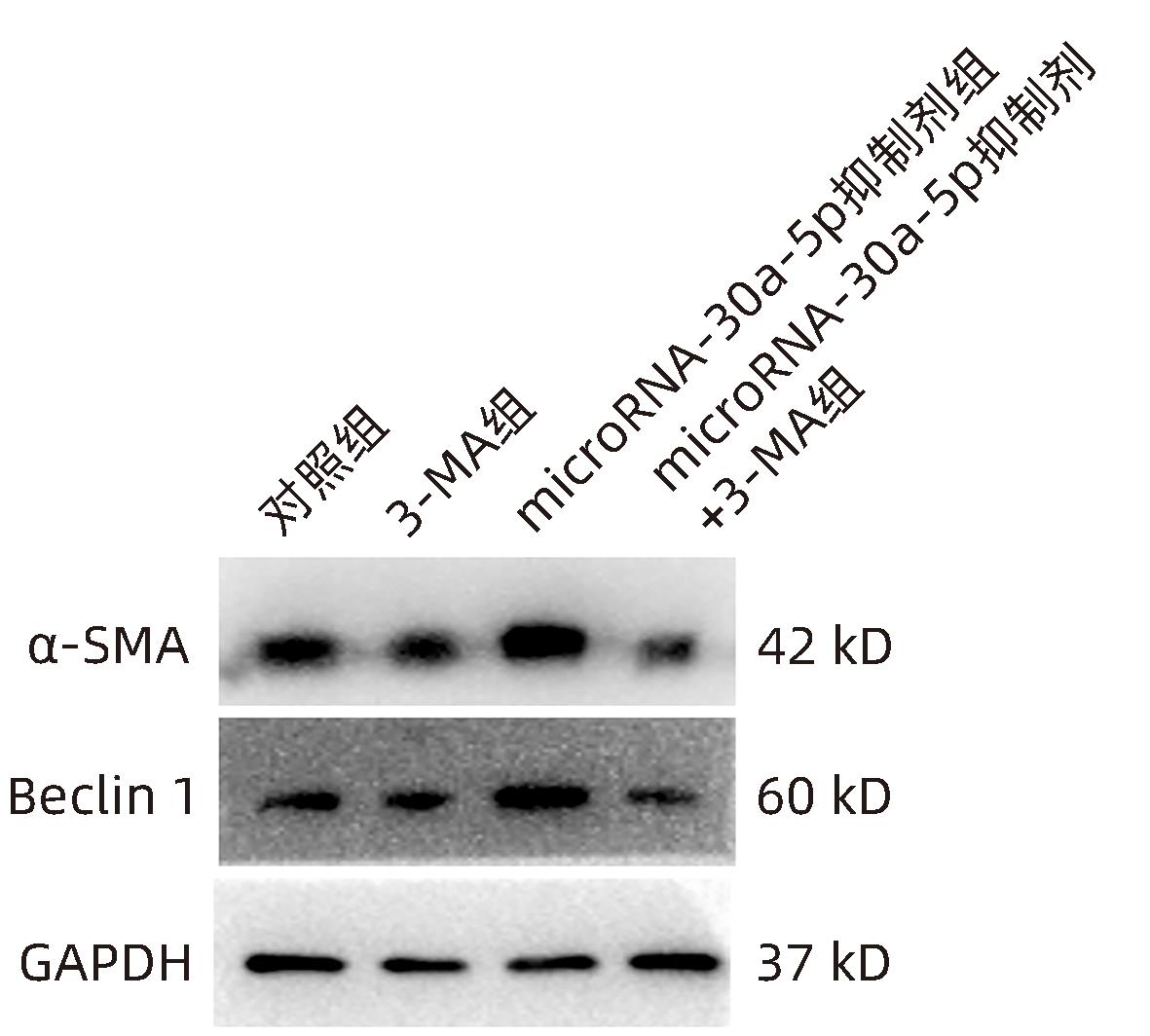
| [1] |
WEISKIRCHEN R, TACKE F. Liver fibrosis: From pathogenesis to novel therapies[J]. Dig Dis, 2016, 34( 4): 410- 422. DOI: 10.1159/000444556. |
| [2] |
AYDIN MM, AKCALI KC. Liver fibrosis[J]. Turk J Gastroenterol, 2018, 29( 1): 14- 21. DOI: 10.5152/tjg.2018.17330. |
| [3] |
BANSAL MB, CHAMROONKUL N. Antifibrotics in liver disease: Are we getting closer to clinical use?[J]. Hepatol Int, 2019, 13( 1): 25- 39. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-018-9897-3. |
| [4] |
History GEERTS A., heterogeneity, biology developmental, and functions of quiescent hepatic stellate cells[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2001, 21( 3): 311- 335. DOI: 10.1055/s-2001-17550. |
| [5] |
ZHANG CY, YUAN WG, HE P, et al. Liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cells: Etiology, pathological hallmarks and therapeutic targets[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2016, 22( 48): 10512- 10522. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i48.10512. |
| [6] |
YAMAGUCHI K, YANG L, MCCALL S, et al. Diacylglycerol acyltranferase 1 anti-sense oligonucleotides reduce hepatic fibrosis in mice with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Hepatology, 2008, 47( 2): 625- 635. DOI: 10.1002/hep.21988. |
| [7] |
HERNÁNDEZ-GEA V, GHIASSI-NEJAD Z, ROZENFELD R, et al. Autophagy releases lipid that promotes fibrogenesis by activated hepatic stellate cells in mice and in human tissues[J]. Gastroenterology, 2012, 142( 4): 938- 946. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.12.044. |
| [8] |
SAITO T, KUMA A, SUGIURA Y, et al. Autophagy regulates lipid metabolism through selective turnover of NCoR1[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10( 1): 1567. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-08829-3. |
| [9] |
TSUKAMOTO H. Cytokine regulation of hepatic stellate cells in liver fibrosis[J]. Alcohol Clin Exp Res, 1999, 23( 5): 911- 916.
|
| [10] |
LI JT, LIAO ZX, PING J, et al. Molecular mechanism of hepatic stellate cell activation and antifibrotic therapeutic strategies[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2008, 43( 6): 419- 428. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-008-2180-y. |
| [11] |
KITANO M, BLOOMSTON PM. Hepatic stellate cells and microRNAs in pathogenesis of liver fibrosis[J]. J Clin Med, 2016, 5( 3): 38. DOI: 10.3390/jcm5030038. |
| [12] |
GRIMSON A, FARH KKH, JOHNSTON WK, et al. MicroRNA targeting specificity in mammals: Determinants beyond seed pairing[J]. Mol Cell, 2007, 27( 1): 91- 105. DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.06.017. |
| [13] |
IORIO MV, CROCE CM. Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation[J]. Cancer J, 2012, 18( 3): 215- 222. DOI: 10.1097/PPO.0b013e318250c001. |
| [14] |
LU RQ, ZHAO G, YANG YL, et al. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIRM1 inhibits cell progression by regulating miR-17-5p/PTEN axis in gastric cancer[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120( 4): 4952- 4965. DOI: 10.1002/jcb.27770. |
| [15] |
FENG MH, LI JW, SUN HT, et al. Sulforaphane inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cell by miRNA-423-5p targeting suppressor of fused[J]. Hum Cell, 2019, 32( 4): 403- 410. DOI: 10.1007/s13577-019-00264-2. |
| [16] |
YU XX, RUAN Y, SHEN T, et al. Dexrazoxane protects cardiomyocyte from doxorubicin-induced apoptosis by modulating miR-17-5p[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020: 5107193. DOI: 10.1155/2020/5107193. |
| [17] |
HAZARI Y, BRAVO-SAN PEDRO JM, HETZ C, et al. Autophagy in hepatic adaptation to stress[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 72( 1): 183- 196. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.08.026. |
| [18] |
APPS MG, CHOI EHY, WHEATE NJ. The state-of-play and future of platinum drugs[J]. Endocr Relat Cancer, 2015, 22( 4): R219- R233. DOI: 10.1530/ERC-15-0237. |
| [19] |
TAN SF, SHI HJ, BA MC, et al. MiR-409-3p sensitizes colon cancer cells to oxaliplatin by inhibiting Beclin-1-mediated autophagy[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2016, 37( 4): 1030- 1038. DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2492. |
| [20] |
ZHU H, WU H, LIU XP, et al. Regulation of autophagy by a beclin 1-targeted microRNA, miR-30a, in cancer cells[J]. Autophagy, 2009, 5( 6): 816- 823. DOI: 10.4161/auto.9064. |
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
POPOV Y, SCHUPPAN D. Targeting liver fibrosis: Strategies for development and validation of antifibrotic therapies[J]. Hepatology, 2009, 50( 4): 1294- 1306. DOI: 10.1002/hep.23123. |
| [23] |
FRIEDMAN SL. Hepatic stellate cells: Protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver[J]. Physiol Rev, 2008, 88( 1): 125- 172. DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00013.2007. |
| [24] |
KISSELEVA T, BRENNER DA. Role of hepatic stellate cells in fibrogenesis and the reversal of fibrosis[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2007, 22( Suppl 1): S73- S78. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04658.x. |
| [25] |
WANG J, CHU ESH, CHEN HY, et al. MicroRNA-29b prevents liver fibrosis by attenuating hepatic stellate cell activation and inducing apoptosis through targeting PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Oncotarget, 2015, 6( 9): 7325- 7338. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.2621. |
| [26] |
OKADA H, HONDA M, CAMPBELL JS, et al. Inhibition of microRNA-214 ameliorates hepatic fibrosis and tumor incidence in platelet-derived growth factor C transgenic mice[J]. Cancer Sci, 2015, 106( 9): 1143- 1152. DOI: 10.1111/cas.12730. |
| [27] |
KLINKHAMMER BM, FLOEGE J, BOOR P. PDGF in organ fibrosis[J]. Mol Aspects Med, 2018, 62: 44- 62. DOI: 10.1016/j.mam.2017.11.008. |



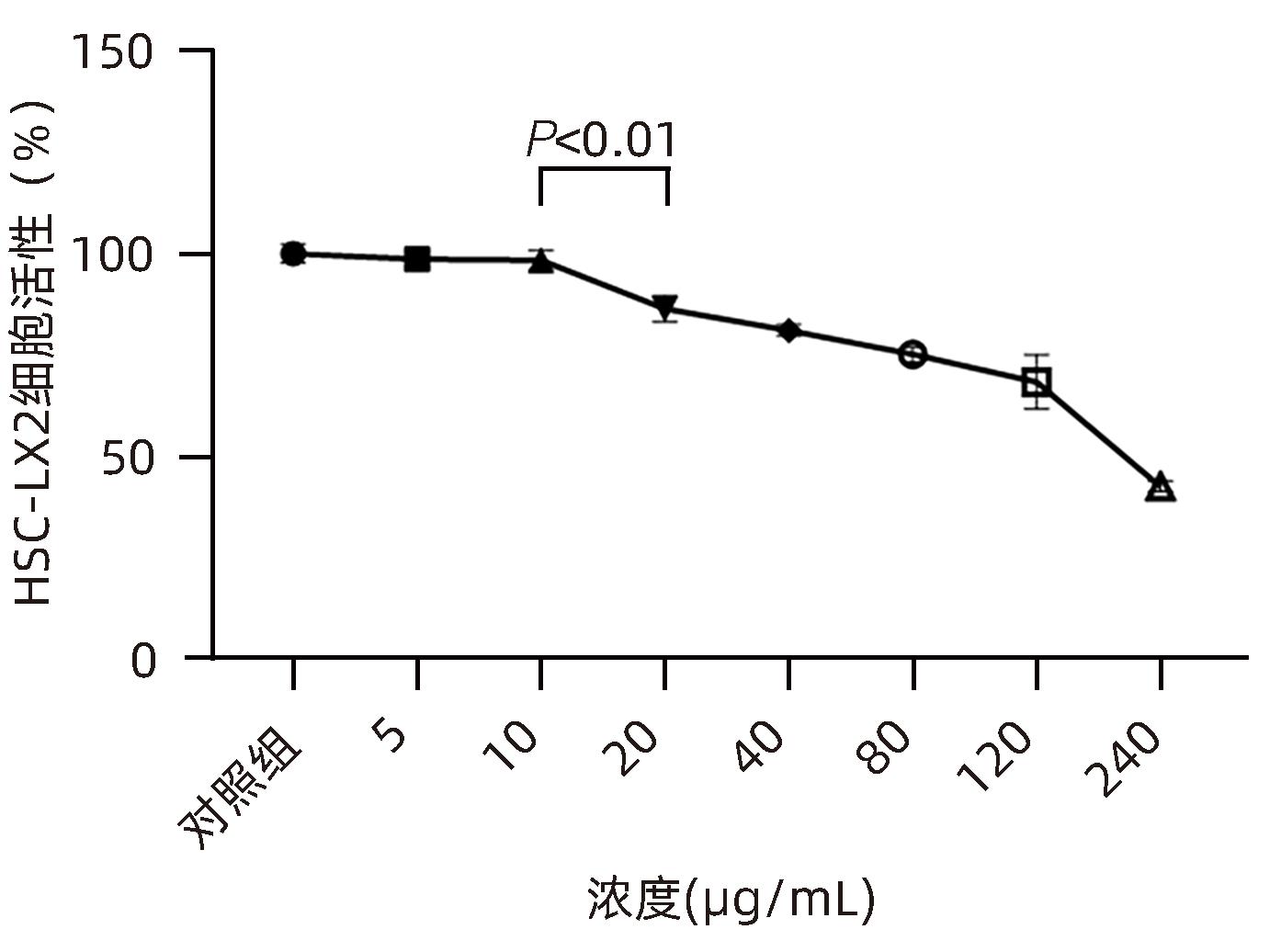




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: