| [1] |
XIAO AY, TAN MLY, WU LM, et al. Global incidence and mortality of pancreatic diseases: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of population-based cohort studies[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016, 1( 1): 45- 55. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(16)30004-8. |
| [2] |
PETROV MS, BASINA M. DIAGNOSIS OF ENDOCRINE DISEASE: Diagnosing and classifying diabetes in diseases of the exocrine pancreas[J]. Eur J Endocrinol, 2021, 184( 4): R151- R163. DOI: 10.1530/EJE-20-0974. |
| [3] |
HART PA, BELLIN MD, ANDERSEN DK, et al. Type 3c(pancreatogenic) diabetes mellitus secondary to chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016, 1( 3): 226- 237. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(16)30106-6. |
| [4] |
CHO J, SCRAGG R, PETROV MS. Risk of mortality and hospitalization after post-pancreatitis diabetes mellitus vs type 2 diabetes mellitus: A population-based matched cohort study[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2019, 114( 5): 804- 812. DOI: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000225. |
| [5] |
WOODMANSEY C, MCGOVERN AP, MCCULLOUGH KA, et al. Incidence, demographics, and clinical characteristics of diabetes of the exocrine pancreas(type 3c): A retrospective cohort study[J]. Diabetes Care, 2017, 40( 11): 1486- 1493. DOI: 10.2337/dc17-0542. |
| [6] |
SANTOS R, COLEMAN HG, CAIRNDUFF V, et al. Clinical prediction models for pancreatic cancer in general and at-risk populations: A systematic review[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2023, 118( 1): 26- 40. DOI: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002022. |
| [7] |
LIAO WC, CHEN PR, HUANG CC, et al. Relationship between pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes and cachexia[J]. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, 2020, 11( 4): 899- 908. DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.12553. |
| [8] |
DONATH MY. Targeting inflammation in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: Time to start[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2014, 13( 6): 465- 476. DOI: 10.1038/nrd4275. |
| [9] |
LI GQ, SUN JF, ZHANG J, et al. Identification of inflammation-related biomarkers in diabetes of the exocrine pancreas with the use of weighted gene co-expression network analysis[J]. Front Endocrinol(Lausanne), 2022, 13: 839865. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.839865. |
| [10] |
ZHANG Y, ZHANG WQ, LIU XY, et al. Immune cells and immune cell-targeted therapy in chronic pancreatitis[J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1151103. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1151103. |
| [11] |
CASU AN, GRIPPO PJ, WASSERFALL C, et al. Evaluating the immunopathogenesis of diabetes after acute pancreatitis in the diabetes RElated to acute pancreatitis and its mechanisms study: From the type 1 diabetes in acute pancreatitis consortium[J]. Pancreas, 2022, 51( 6): 580- 585. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000002076. |
| [12] |
PONDUGALA PK, SASIKALA M, GUDURU VR, et al. Interferon-γ decreases nuclear localization of pdx-1 and triggers β-cell dysfunction in chronic pancreatitis[J]. J Interferon Cytokine Res, 2015, 35( 7): 523- 529. DOI: 10.1089/jir.2014.0082. |
| [13] |
ELSHARKAWI I, PARAMBATH D, SABER-AYAD M, et al. Exploring the effect of epigenetic modifiers on developing insulin-secreting cells[J]. Hum Cell, 2020, 33( 1): 1- 9. DOI: 10.1007/s13577-019-00292-y. |
| [14] |
QIN WJ, KANG MX, LI C, et al. VNN1 overexpression in pancreatic cancer cells inhibits paraneoplastic islet function by increasing oxidative stress and inducing β-cell dedifferentiation[J]. Oncol Rep, 2023, 49( 6): 120. DOI: 10.3892/or.2023.8557. |
| [15] |
HU FL, LOU N, JIAO JY, et al. Macrophages in pancreatitis: Mechanisms and therapeutic potential[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2020, 131: 110693. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110693. |
| [16] |
ANDERSEN DK, KORC M, PETERSEN GM, et al. Diabetes, pancreatogenic diabetes, and pancreatic cancer[J]. Diabetes, 2017, 66( 5): 1103- 1110. DOI: 10.2337/db16-1477. |
| [17] |
LIAO WC, HUANG BS, YU YH, et al. Galectin-3 and S100A9: Novel diabetogenic factors mediating pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes[J]. Diabetes Care, 2019, 42( 9): 1752- 1759. DOI: 10.2337/dc19-0217. |
| [18] |
HU YF, ZENG N, GE YQ, et al. Identification of the shared gene signatures and biological mechanism in type 2 diabetes and pancreatic cancer[J]. Front Endocrinol(Lausanne), 2022, 13: 847760. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.847760. |
| [19] |
XU TT, XU XX, LIU PC, et al. Transcriptomic analyses and potential therapeutic targets of pancreatic cancer with concomitant diabetes[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 563527. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.563527. |
| [20] |
OLDFIELD L, EVANS A, RAO RG, et al. Blood levels of adiponectin and IL-1Ra distinguish type 3c from type 2 diabetes: Implications for earlier pancreatic cancer detection in new-onset diabetes[J]. EBioMedicine, 2022, 75: 103802. DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103802. |
| [21] |
LEE SH, PARK SY, CHOI CS. Insulin resistance: From mechanisms to therapeutic strategies[J]. Diabetes Metab J, 2022, 46( 1): 15- 37. DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0280. |
| [22] |
GILLIES N, PENDHARKAR SA, ASRANI VM, et al. Interleukin-6 is associated with chronic hyperglycemia and insulin resistance in patients after acute pancreatitis[J]. Pancreatology, 2016, 16( 5): 748- 755. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2016.06.661. |
| [23] |
OLESEN SS, SVANE HML, NICOLAISEN SK, et al. Clinical and biochemical characteristics of postpancreatitis diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional study from the Danish nationwide DD2 cohort[J]. J Diabetes, 2021, 13( 12): 960- 974. DOI: 10.1111/1753-0407.13210. |
| [24] |
ASLAM M, VIJAYASARATHY K, TALUKDAR R, et al. Reduced pancreatic polypeptide response is associated with early alteration of glycemic control in chronic pancreatitis[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2020, 160: 107993. DOI: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107993. |
| [25] |
HENNIG R, KEKIS PB, FRIESS H, et al. Pancreatic polypeptide in pancreatitis[J]. Peptides, 2002, 23( 2): 331- 338. DOI: 10.1016/s0196-9781(01)00605-2. |
| [26] |
CAI DS, YUAN MS, FRANTZ DF, et al. Local and systemic insulin resistance resulting from hepatic activation of IKK-beta and NF-kappaB[J]. Nat Med, 2005, 11( 2): 183- 190. DOI: 10.1038/nm1166. |
| [27] |
HEO YJ, CHOI SE, JEON JY, et al. Visfatin induces inflammation and insulin resistance via the NF-κB and STAT3 signaling pathways in hepatocytes[J]. J Diabetes Res, 2019, 2019: 4021623. DOI: 10.1155/2019/4021623. |
| [28] |
CHEANG JY, MOYLE PM. Glucagon-like peptide-1(GLP-1)-based therapeutics: Current status and future opportunities beyond type 2 diabetes[J]. ChemMedChem, 2018, 13( 7): 662- 671. DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201700781. |
| [29] |
TUDURÍ E, LÓPEZ M, DIÉGUEZ C, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 analogs and their effects on pancreatic islets[J]. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 2016, 27( 5): 304- 318. DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2016.03.004. |
| [30] |
DRUCKER DJ. Mechanisms of action and therapeutic application of glucagon-like peptide-1[J]. Cell Metab, 2018, 27( 4): 740- 756. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.03.001. |
| [31] |
SALGAÇO MK, OLIVEIRA LGS, COSTA GN, et al. Relationship between gut microbiota, probiotics, and type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2019, 103( 23-24): 9229- 9238. DOI: 10.1007/s00253-019-10156-y. |
| [32] |
TILG H, ZMORA N, ADOLPH TE, et al. The intestinal microbiota fuelling metabolic inflammation[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2020, 20( 1): 40- 54. DOI: 10.1038/s41577-019-0198-4. |
| [33] |
TAO J, CHEEMA H, KESH K, et al. Chronic pancreatitis in a caerulein-induced mouse model is associated with an altered gut microbiome[J]. Pancreatology, 2022, 22( 1): 30- 42. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2021.12.003. |
| [34] |
TALUKDAR R, SARKAR P, JAKKAMPUDI A, et al. The gut microbiome in pancreatogenic diabetes differs from that of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11( 1): 10978. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-90024-w. |
| [35] |
JANDHYALA SM, MADHULIKA A, DEEPIKA G, et al. Altered intestinal microbiota in patients with chronic pancreatitis: Implications in diabetes and metabolic abnormalities[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 43640. DOI: 10.1038/srep43640. |
| [36] |
ZOU WB, TANG XY, ZHOU DZ, et al. SPINK1, PRSS1, CTRC, and CFTR genotypes influence disease onset and clinical outcomes in chronic pancreatitis[J]. Clin Transl Gastroenterol, 2018, 9( 11): 204. DOI: 10.1038/s41424-018-0069-5. |
| [37] |
LIU QC, ZHUANG ZH, ZENG K, et al. Prevalence of pancreatic diabetes in patients carrying mutations or polymorphisms of the PRSS1 gene in the Han population[J]. Diabetes Technol Ther, 2009, 11( 12): 799- 804. DOI: 10.1089/dia.2009.0051. |
| [38] |
KIMURA H, KLEIN AP, HRUBAN RH, et al. The role of inherited pathogenic CDKN2A variants in susceptibility to pancreatic cancer[J]. Pancreas, 2021, 50( 8): 1123- 1130. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001888. |
| [39] |
YIN LD, WEI JS, LU ZP, et al. Prevalence of germline sequence variations among patients with pancreatic cancer in China[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2022, 5( 2): e2148721. DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.48721. |
| [40] |
MCWILLIAMS R, HIGHSMITH WE, RABE KG, et al. Cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator gene carrier status is a risk factor for young onset pancreatic adenocarcinoma[J]. Gut, 2005, 54( 11): 1661- 1662. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2005.074534. |
| [41] |
ABE K, KITAGO M, KITAGAWA Y, et al. Hereditary pancreatic cancer[J]. Int J Clin Oncol, 2021, 26( 10): 1784- 1792. DOI: 10.1007/s10147-021-02015-6. |
| [42] |
ASSOCIATION AD. 2. classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes-2021[J]. Diabetes Care, 2021, 44( Suppl 1): S15- S33. DOI: 10.2337/dc21-S002. |
| [43] |
LÖHR JM, DOMINGUEZ-MUNOZ E, ROSENDAHL J, et al. United European Gastroenterology evidence-based guidelines for the diagnosis and therapy of chronic pancreatitis(HaPanEU)[J]. United European Gastroenterol J, 2017, 5( 2): 153- 199. DOI: 10.1177/2050640616684695. |
| [44] |
UC A, ANDERSEN DK, BELLIN MD, et al. Chronic pancreatitis in the 21st century-research challenges and opportunities: Summary of a national institute of diabetes and digestive and kidney diseases workshop[J]. Pancreas, 2016, 45( 10): 1365- 1375. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000713. |
| [45] |
CUI YF, ANDERSEN DK. Pancreatogenic diabetes: Special considerations for management[J]. Pancreatology, 2011, 11( 3): 279- 294. DOI: 10.1159/000329188. |
| [46] |
BELLIN MD. Pancreatogenic diabetes in children with recurrent acute and chronic pancreatitis: Risks, screening, and treatment(mini-review)[J]. Front Pediatr, 2022, 10: 884668. DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.884668. |
| [47] |
WU K, WANG WL, CHEN H, et al. Insulin promotes proliferation of pancreatic ductal epithelial cells by increasing expression of PLK1 through PI3K/AKT and NF-κB pathway[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2019, 509( 4): 925- 930. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.12.182. |
| [48] |
YANG X, XU ZP, ZHANG CL, et al. Metformin, beyond an insulin sensitizer, targeting heart and pancreatic β cells[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2017, 1863( 8): 1984- 1990. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.09.019. |
| [49] |
WANG CC, ZHANG TP, LIAO Q, et al. Metformin inhibits pancreatic cancer metastasis caused by SMAD4 deficiency and consequent HNF4G upregulation[J]. Protein Cell, 2021, 12( 2): 128- 144. DOI: 10.1007/s13238-020-00760-4. |
| [50] |
CHEN K, QIAN WK, JIANG ZD, et al. Metformin suppresses cancer initiation and progression in genetic mouse models of pancreatic cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2017, 16( 1): 131. DOI: 10.1186/s12943-017-0701-0. |
| [51] |
MAIDA A, LAMONT BJ, CAO X, et al. Metformin regulates the incretin receptor axis via a pathway dependent on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α in mice[J]. Diabetologia, 2011, 54( 2): 339- 349. DOI: 10.1007/s00125-010-1937-z. |
| [52] |
GOODARZI MO, PETROV MS. Diabetes of the exocrine pancreas: Implications for pharmacological management[J]. Drugs, 2023, 83( 12): 1077- 1090. DOI: 10.1007/s40265-023-01913-5. |
| [53] |
CAMPAGNOLA P, de PRETIS N, ZORZI A, et al. Chronic pancreatitis and nutritional support[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol, 2023, 62-63: 101823. DOI: 10.1016/j.bpg.2023.101823. |
| [54] |
DUGGAN SN, SMYTH ND, MURPHY A, et al. High prevalence of osteoporosis in patients with chronic pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2014, 12( 2): 219- 228. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.06.016. |
| [55] |
DYTZ MG, MARCELINO PAH, de CASTRO SANTOS O, et al. Clinical aspects of pancreatogenic diabetes secondary to hereditary pancreatitis[J]. Diabetol Metab Syndr, 2017, 9: 4. DOI: 10.1186/s13098-017-0203-7. |
| [56] |
DUGGAN SN, EWALD N, KELLEHER L, et al. The nutritional management of type 3c(pancreatogenic) diabetes in chronic pancreatitis[J]. Eur J Clin Nutr, 2017, 71( 1): 3- 8. DOI: 10.1038/ejcn.2016.127. |



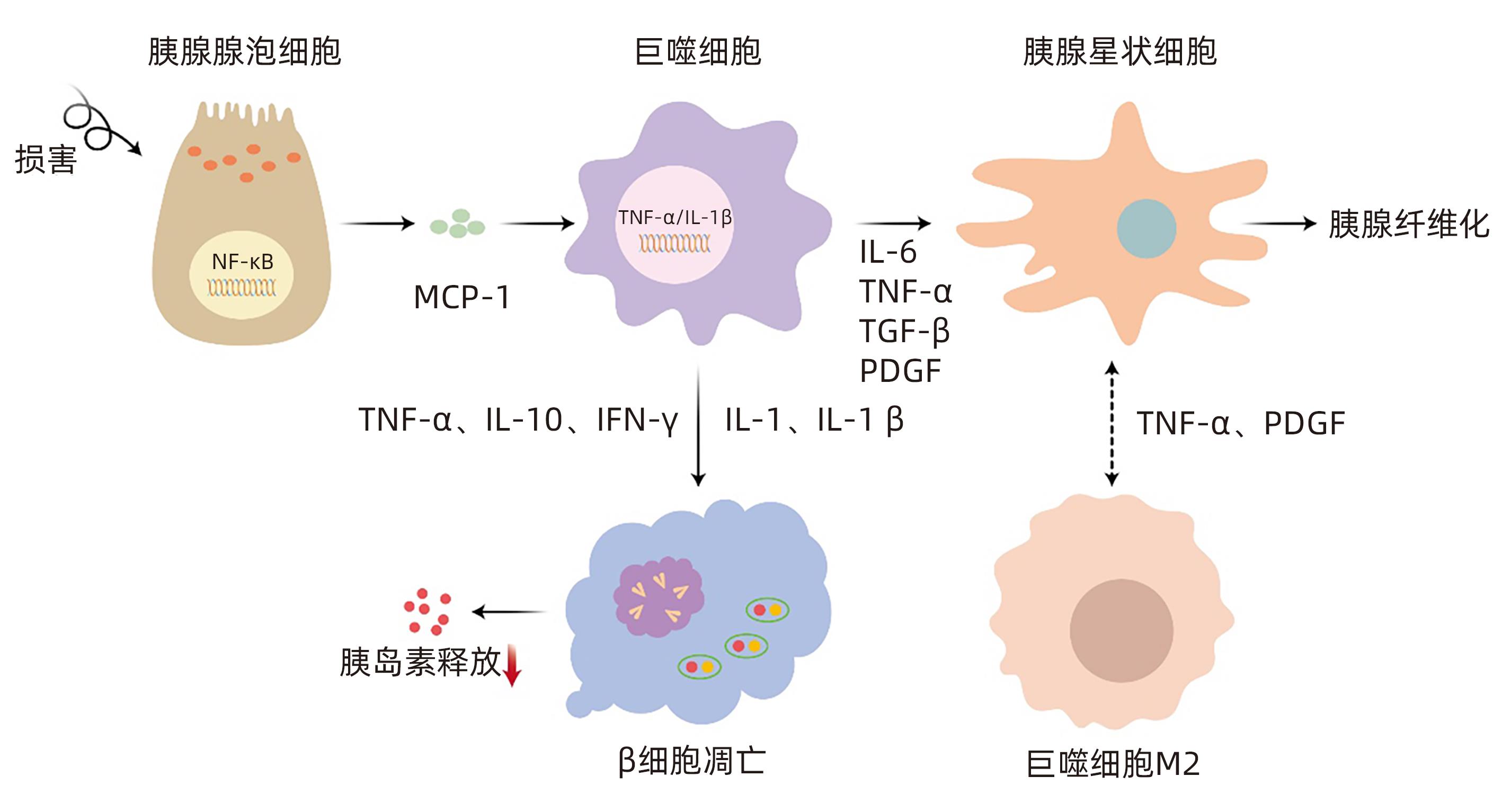




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: