| [1] |
ARROYO V, MOREAU R, JALAN R. Acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. N Engl J Med, 2020, 382( 22): 2137- 2145. DOI: 10.1056/nejmra1914900. |
| [2] |
PERRICONE G, ARTZNER T, de MARTIN E, et al. Intensive care management of acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2023, 49( 8): 903- 921. DOI: 10.1007/s00134-023-07149-x. |
| [3] |
ZACCHERINI G, WEISS E, MOREAU R. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: Definitions, pathophysiology and principles of treatment[J]. JHEP Rep, 2021, 3( 1): 100176. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2020.100176. |
| [4] |
SHI K, ZHANG Y, LI YQ, et al. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol as a prognostic marker for 90-day transplant-free mortality in hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2024, 14: 1458818. DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1458818. |
| [5] |
CAI Q, WANG H, ZHU MY, et al. Construction of a novel prognostic scoring model for HBV-ACLF liver failure based on dynamic data[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14( 1): 15198. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-63900-4. |
| [6] |
HUANG ZW, ZHANG G, LIU J, et al. LRFNet: A deep learning model for the assessment of liver reserve function based on Child‐Pugh score and CT image[J]. Comput Meth Programs Biomed, 2022, 223: 106993. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2022.106993. |
| [7] |
RUF A, DIRCHWOLF M, FREEMAN RB. From Child-Pugh to MELD score and beyond: Taking a walk down memory lane[J]. Ann Hepatol, 2022, 27( 1): 100535. DOI: 10.1016/j.aohep.2021.100535. |
| [8] |
JOHNSON PJ, BERHANE S, KAGEBAYASHI C, et al. Assessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A new evidence-based approach-the ALBI grade[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2015, 33( 6): 550- 558. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2014.57.9151. |
| [9] |
LIAO YY, TENG CL, PENG NF, et al. Serum prealbumin is negatively associated with survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients after hepatic resection[J]. J Cancer, 2019, 10( 13): 3006- 3011. DOI: 10.7150/jca.30903. |
| [10] |
HUO RR, LIU HT, DENG ZJ, et al. Dose-response between serum prealbumin and all-cause mortality after hepatectomy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 596691. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.596691. |
| [11] |
YIN Y, CHENG JW, CHEN FY, et al. A novel preoperative predictive model of 90-day mortality after liver resection for huge hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2021, 9( 9): 774. DOI: 10.21037/atm-20-7842. |
| [12] |
DUAN RX, LIU L, WANG Y, et al. Prognostic value of combined detection of alpha-fetoprotein, plasma prothrombin activity, and serum prealbumin in acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. World J Gastrointest Surg, 2025, 17( 2): 99531. DOI: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i2.99531. |
| [13] |
FAN WH, LIAO W, LUO YP, et al. Clinical prediction for outcomes of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure associated with HBV infection: A new model establishment[J]. Open Med, 2020, 15( 1): 714- 722. DOI: 10.1515/med-2020-0207. |
| [14] |
Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Severe Liver Disease and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure(2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 1): 38- 44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007. |
| [15] |
YE QX, HUANG JF, XU ZJ, et al. Short-term prognostic factors for hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. World J Clin Cases, 2022, 10( 23): 8186- 8195. DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i23.8186. |
| [16] |
KIM WR, MANNALITHARA A, HEIMBACH JK, et al. MELD 3.0: The model for end-stage liver disease updated for the modern era[J]. Gastroenterology, 2021, 161( 6): 1887- 1895. e 4. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.08.050. |
| [17] |
ARTRU F, TROVATO F, MORRISON M, et al. Liver transplantation for acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2024, 9( 6): 564- 576. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(23)00363-1. |
| [18] |
LAI M, XU MM, WANG X, et al. Prognostic evaluation of liver transplantation for acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Ogran Transplant, 2025, 16( 3): 482- 488. DOI: 10.12464/j.issn.1674-7445.2025002. |
| [19] |
ZHAO ZY, AN XQ, SHI L, et al. Prognostic value of serum prealbumin/total bilirubin ratio in patients with liver failure[J]. China J Mod Med, 2017, 27( 21): 75- 78. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2017.21.014. |
| [20] |
KURATA Y, MURAKI S, HIROTA T, et al. Effect of liver cirrhosis on theophylline trough concentrations: A comparative analysis of organ impairment using Child-Pugh and MELD scores[J]. Br J Clin Pharmacol, 2022, 88( 8): 3819- 3828. DOI: 10.1111/bcp.15333. |
| [21] |
SHI JD, WANG PH, QI Z, et al. Expression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in acute liver injury and its intervention on cell ferroptosis and inflammation[J]. China Med, 2023, 18( 8): 1200- 1204. DOI: 10.3760/j.issn.1673-4777.2023.08.017. |
| [22] |
GUO GY, YANG WT, LI J, et al. The development and appraisal of MELD 3.0 in liver diseases: Good things never come easy[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2025, 13( 1): 62- 68. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2024.00303. |
| [23] |
CUI DG, XIAO LY, LIU YF, et al. The predictive value of CTP-MELD scores combined with serum M30 and M65 levels for the short-term prognosis of patients with hepatitis B-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2022, 27( 1): 58- 62. DOI: 10.14000/j.cnki.issn.1008-1704.2022.01.016. |
| [24] |
CHEN YQ, LI CY, TANG SH. Value of Δtotal bilirubin-alpha-fetoprotein scoring model in predicting the short-term prognosis of patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2024, 40( 12): 2399- 2405. DOI: 10.12449/JCH241209. 陈雨琪, 李春燕, 汤善宏. Δ总胆红素-甲胎蛋白评分模型对HBV相关慢加急性肝衰竭短期预后的预测价值[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40( 12): 2399- 2405. DOI: 10.12449/JCH241209. |
| [25] |
LI WD, LIU WS, RONG YH, et al. Development and validation of a new prognostic model for predicting survival outcomes in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2024, 12( 10): 834- 844. DOI: 10.14218/jcth.2024.00316. |
| [26] |
GAN YX, OUYANG LY, PAN YX, et al. Predictive value of ICGR15 and ALBI score for post-hepatectomy liver failure and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients after hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy[J/OL]. Chin J Hepat Surg(Electronic Edition), 2025, 14( 3): 395- 401. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3232.2025.03.010. |
| [27] |
ZHANG H, YANG K, WANG Q, et al. Prealbumin as a predictor of short-term prognosis in patients with HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Infect Drug Resist, 2023, 16: 2611- 2623. DOI: 10.2147/idr.s402585. |
| [28] |
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines on acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Hepatol, 2023, 79( 2): 461- 491. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.04.021. |
| [29] |
CHEN XY, GAO FQ, PAN QL, et al. aCCI-HBV-ACLF: A novel predictive model for hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2025, 61( 2): 286- 298. DOI: 10.1111/apt.18347. |
| [30] |
LI C, WANG MD, SUN XD, et al. Development and validation of prealbumin-bilirubin score(preALBI score) for predicting long-term survival after hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma: A multicenter analysis versus ALBI score[J]. Am J Surg, 2024, 232: 87- 94. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2024.01.009. |
| [31] |
TREBICKA J, HERNAEZ R, SHAWCROSS DL, et al. Recent advances in the prevention and treatment of decompensated cirrhosis and acute-on-chronic liver failure(ACLF) and the role of biomarkers[J]. Gut, 2024, 73( 6): 1015- 1024. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-330584. |
| [32] |
CHEN MJ, LI X, TANG SH. Research progress on multidimensional evaluation of liver function in the prognosis of liver failure patients[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2023, 51( 9): 901- 903, 907. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2023.09.05. |



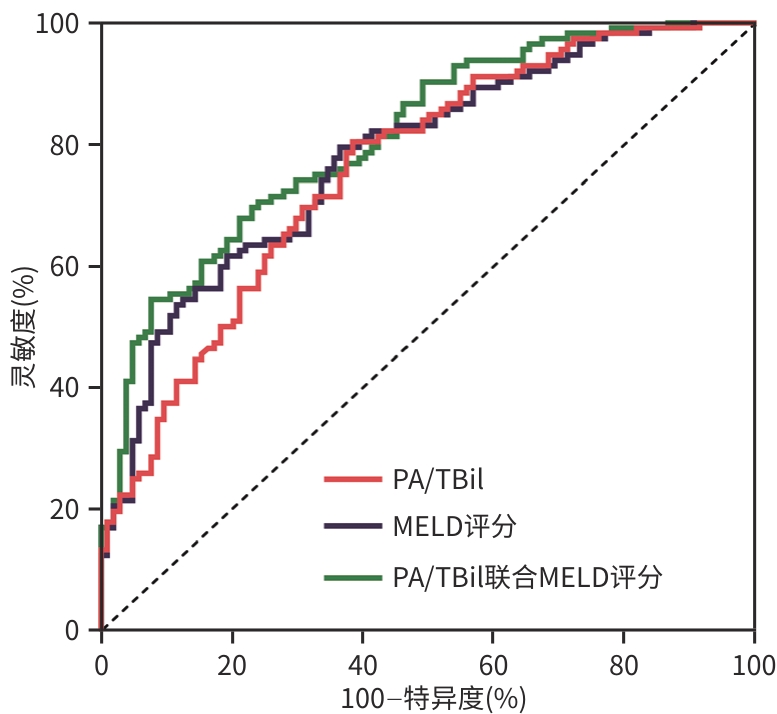




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: