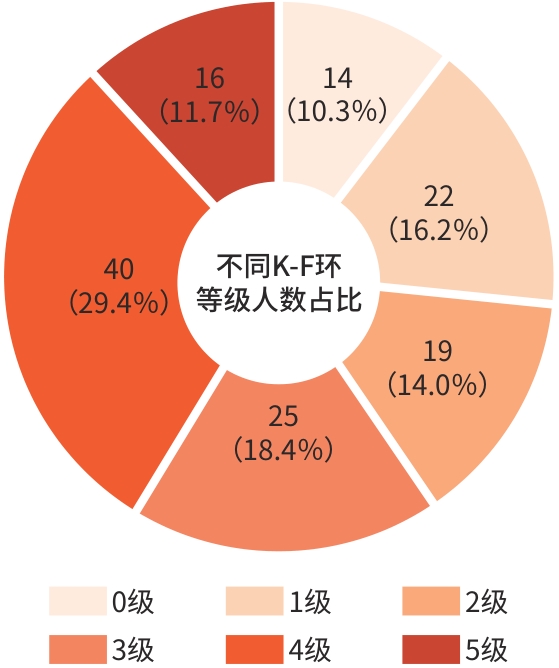
| [1] |
CZŁONKOWSKA A, LITWIN T, DUSEK P, et al. Wilson disease[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2018, 4( 1): 21. DOI: 10.1038/s41572-018-0018-3. |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
GAO WS, LIU YW, CHEN J. Analysis of 128 Wilson’s disease[J]. Acta Acad Med Sin, 2001, 23( 5): 506- 508.
高维生, 刘跃武, 陈杰. 128例肝豆状核变性分析[J]. 中国医学科学院学报, 2001, 23( 5): 506- 508.
|
| [4] |
DEGUTI MM, TIETGE UJF, BARBOSA ER, et al. The eye in Wilson’s disease: Sunflower cataract associated with Kayser-fleischer ring[J]. J Hepatol, 2002, 37( 5): 700. DOI: 10.1016/s0168-8278(02)00179-4. |
| [5] |
ZHOU ZH, HU JY, HAN YZ, et al. Analysis on Kayser-Fleischer ring in hepatolenticular degeneration[J/OL]. Chin J Clin(Electronic Edition), 2014, 8( 12): 2271- 2274. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-0785.2014.12.019. |
| [6] |
XU LH. Correlation between corneal K-F ring classification and clinic in 320 patients with hepatolenticular degeneration[D]. Hefei: Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, 2020.
徐柳慧. 320例肝豆状核变性患者角膜K-F环分级与临床相关性研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽中医药大学, 2020.
|
| [7] |
LANGWIŃSKA-WOŚKO E, LITWIN T, SZULBORSKI K, et al. Optical coherence tomography and electrophysiology of retinal and visual pathways in Wilson’s disease[J]. Metab Brain Dis, 2016, 31( 2): 405- 415. DOI: 10.1007/s11011-015-9776-8. |
| [8] |
Inherited Metabolic Liver Disease Collaboration Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of hepatolenticular degeneration(2022 edition)[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2022, 30( 1): 9- 20. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20211217-00603. |
| [9] |
CZŁONKOWSKA A, TARNACKA B, MÖLLER JC, et al. Unified Wilson’s Disease Rating Scale- a proposal for the neurological scoring of Wilson’s disease patients[J]. Neurol Neurochir Pol, 2007, 41( 1): 1- 12.
|
| [10] |
NASREDDINE ZS, PHILLIPS NA, BÉDIRIAN V, et al. The Montreal cognitive assessment, MoCA: A brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment[J]. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2005, 53( 4): 695- 699. DOI: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2005.53221.x. |
| [11] |
WOUTERS H, van GOOL WA, SCHMAND B, et al. Three sides of the same coin: Measuring global cognitive impairment with the MMSE, ADAS-cog and CAMCOG[J]. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry, 2010, 25( 8): 770- 779. DOI: 10.1002/gps.2402. |
| [12] |
WO HY, KANG CW, ZHAN L, et al. Clinical features of patients with hepatolenticular degeneration aged above 35 years[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2024, 40( 1): 116- 120. DOI: 10.12449/JCH240120. 沃洪云, 康成为, 詹蕾, 等. 35岁以上肝豆状核变性患者的临床特征分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40( 1): 116- 120. DOI: 10.12449/JCH240120. |
| [13] |
LIU MM, COHEN EJ, BREWER GJ, et al. Kayser-Fleischer ring as the presenting sign of Wilson disease[J]. Am J Ophthalmol, 2002, 133( 6): 832- 834. DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9394(02)01408-3. |
| [14] |
XIA B. A case of hepatolenticular degeneration with ocular symptoms as the first symptom[J]. Chin J Ophthalmol Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 19( 5): 361- 362. DOI: 10.14166/j.issn.1671-2420.2019.05.018. |
| [15] |
KANG LL, ZONG ZF, DONG K, et al. Effects of resveratrol on mental symptoms and corneal K-F ring in patients with Wilson’s disease[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2024, 52( 6): 627- 630. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2024.06.21. |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
FENU M, LIGGI M, DEMELIA E, et al. Kayser-fleischer ring in Wilson’s disease: A cohort study[J]. Eur J Intern Med, 2012, 23( 6): e150- e156. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejim.2012.04.005. |
| [19] |
CHEN FF, HU FY, CAO XL, et al. Response to D-penicillamine treatment in patients with Wi1son’s disease and different degree of Kayser-Fleischer ring[J]. J Pract Hepatol, 2024, 27( 1): 145- 147. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2024.01.037. |
| [20] |
WANG GQ, ZHANG L, MA XF, et al. Analysis on related factors of Kayser-fleischer ring in patients with Wilson’s disease[J]. J Med Res, 2013, 42( 7): 98- 101. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-548X.2013.07.030. |
| [21] |
HU JY, ZHOU ZH, WANG X, et al. The effect of long-term copper removal therapy on the grading changes of K-F ring in the cornea of patients with hepatic steatosis[C]. The 18th National Neurology Academic Conference of the Chinese Medical Association. Chengdu, 2015.
胡纪源, 周志华, 王训, 等. 长期驱铜治疗对肝豆状核变性角膜K-F环分级变化的影响[C]. 中华医学会第十八次全国神经病学学术会议. 成都, 2015.
|
| [22] |
JIA FF, ZHOU H, YANG X, et al. Hepatolenticular degeneration with mental disorder as first symptom: A case report and literature review[J]. J Jilin Univ(Med Edit), 2023, 49( 6): 1620- 1624. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230629. |
| [23] |
HAN YS, WANG X, HAN YZ, et al. Study of reliability and validity of Chinese version of united Wilson’s disease rating scale[J]. J Clin Neurol, 2013, 26( 4): 241- 243.
韩永升, 王训, 韩咏竹, 等. 中文版统一肝豆状核变性评分量表的信度和效度的研究[J]. 临床神经病学杂志, 2013, 26( 4): 241- 243.
|
| [24] |
YANG YL, YANG WM, WANG H, et al. Based on the digital muscle function evaluation system Myoton PRO, this paper discusses the correlation between muscle tension and clinical characteristics and TCM syndromes in patients with hepatolenticular degeneration.[J/OL]. China Ind Econ, 2024: 1- 8.
杨玉龙, 杨文明, 汪瀚, 等. 基于数字化肌肉功能评估系统Myoton PRO探讨肝豆状核变性患者肌张力与临床特征及中医证型的相关性[J/OL]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2024: 1- 8.
|



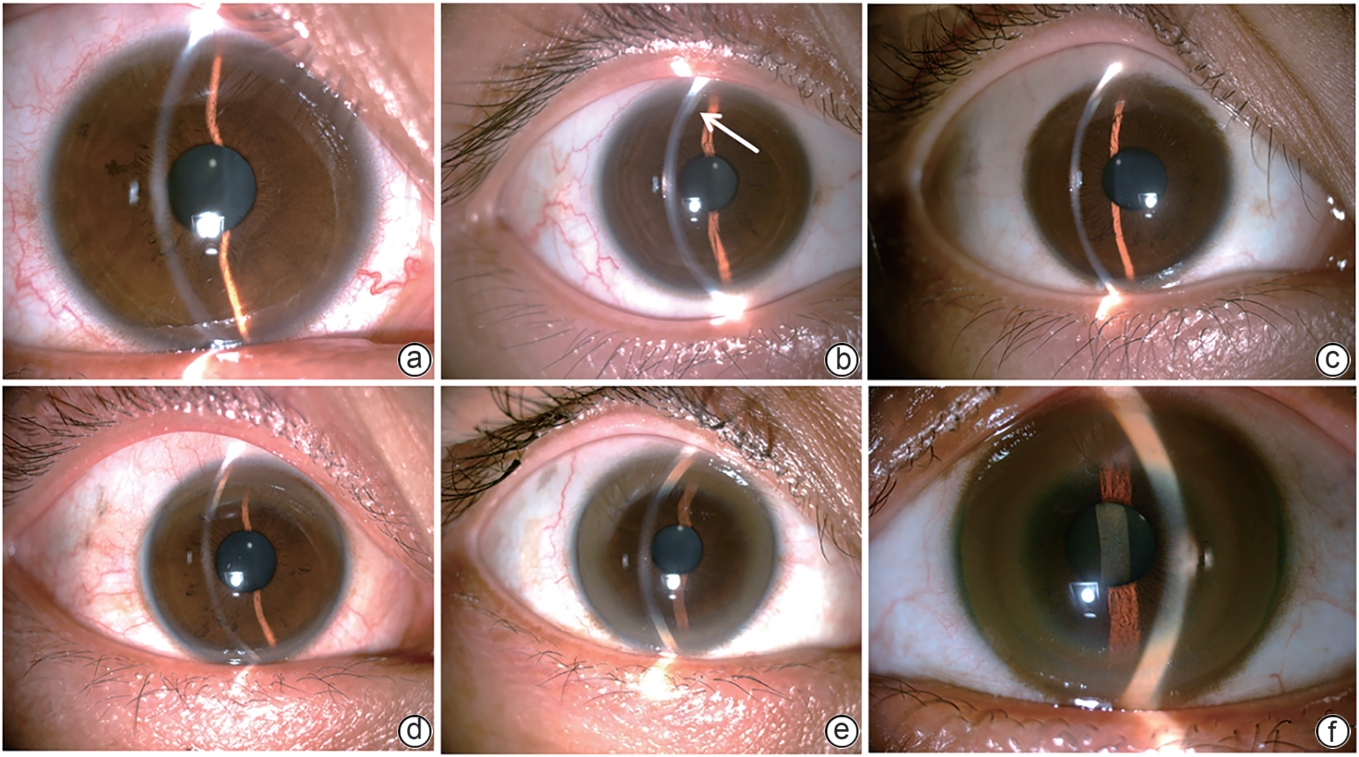




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: