| [1] |
MURATORI L, LOHSE AW, LENZI M. Diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis[J]. BMJ, 2023, 380: e070201. DOI: 10.1136/bmj-2022-070201. |
| [2] |
HAN B, TU CT. Diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis in specific clinical phenotypes and patient populations: Current concepts[J/CD]. Chin J Liver Dis(Electronic Version), 2023, 15( 4): 16- 21.
韩冰, 涂传涛. 特殊临床表型及特殊人群自身免疫性肝炎诊治现状[J/CD]. 中国肝脏病杂志(电子版), 2023, 15( 4): 16- 21.
|
| [3] |
FORSYTH KS, JIWRAJKA N, LOVELL CD, et al. The conneXion between sex and immune responses[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2024, 24( 7): 487- 502. DOI: 10.1038/s41577-024-00996-9. |
| [4] |
MA X, WANG Q, XIAO X, et al. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis(2021)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 1): 42- 49. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20211112-00796. |
| [5] |
LAMBA M, NGU JH, STEDMAN CAM. Trends in incidence of autoimmune liver diseases and increasing incidence of autoimmune hepatitis[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 19( 3): 573- 579. e 1. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.05.061. |
| [6] |
TRIVEDI PJ, HIRSCHFIELD GM. Recent advances in clinical practice: Epidemiology of autoimmune liver diseases[J]. Gut, 2021, 70( 10): 1989- 2003. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322362. |
| [7] |
TRIVEDI PJ, HIRSCHFIELD GM, ADAMS DH, et al. Immunopathogenesis of primary biliary cholangitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis and autoimmune hepatitis: Themes and concepts[J]. Gastroenterology, 2024, 166( 6): 995- 1019. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2024.01.049. |
| [8] |
COLAPIETRO F, MAISONNEUVE P, LYTVYAK E, et al. Incidence and predictors of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with autoimmune hepatitis[J]. J Hepatol, 2024, 80( 1): 53- 61. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.09.010. |
| [9] |
LIBERT C, DEJAGER L, PINHEIRO I. The X chromosome in immune functions: When a chromosome makes the difference[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2010, 10( 8): 594- 604. DOI: 10.1038/nri2815. |
| [10] |
HEYMANN F, TACKE F. Immunology in the liver: From homeostasis to disease[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016, 13( 2): 88- 110. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2015.200. |
| [11] |
VUERICH M, WANG N, KALBASI A, et al. Dysfunctional immune regulation in autoimmune hepatitis: From pathogenesis to novel therapies[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 746436. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.746436. |
| [12] |
STARK JM, TIBBITT CA, COQUET JM. The metabolic requirements of Th2 cell differentiation[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 2318. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02318. |
| [13] |
CHEN HR, HAN ZY, FAN YY, et al. CD4 + T-cell subsets in autoimmune hepatitis: A review[J]. Hepatol Commun, 2023, 7( 10): e0269. DOI: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000269. |
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
TAUBERT R, HARDTKE-WOLENSKI M, NOYAN F, et al. Intrahepatic regulatory T cells in autoimmune hepatitis are associated with treatment response and depleted with current therapies[J]. J Hepatol, 2014, 61( 5): 1106- 1114. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.05.034. |
| [16] |
BEHFARJAM F, SANATI MH, NASSERI MOGHADDAM S, et al. Role of Th1/Th2 cells and related cytokines in autoimmune hepatitis[J]. Turk J Gastroenterol, 2017, 28( 2): 110- 114. DOI: 10.5152/tjg.2017.17501. |
| [17] |
AKKOÇ T. Re: The role of Th1/Th2 cells and associated cytokines in autoimmune hepatitis[J]. Turk J Gastroenterol, 2017, 28( 2): 115- 116. DOI: 10.5152/tjg.2017.14021. |
| [18] |
ZHU JX, CHEN HX, CUI JJ, et al. Oroxylin A inhibited autoimmune hepatitis-induced liver injury and shifted Treg/Th17 balance to Treg differentiation[J]. Exp Anim, 2023, 72( 3): 367- 378. DOI: 10.1538/expanim.22-0171. |
| [19] |
SONG JG, DAI J, CHEN XP, et al. Bifidobacterium mitigates autoimmune hepatitis by regulating IL-33-induced Treg/Th17 imbalance via the TLR2/4 signaling pathway[J]. Histol Histopathol, 2024, 39( 5): 623- 632. DOI: 10.14670/HH-18-669. |
| [20] |
JI WW, PENG X, LOU TL, et al. Total flavonoids from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum ameliorates inflammatory stress in concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis mice by regulating Treg/Th17 immune homeostasis[J]. Inflammopharmacology, 2019, 27( 6): 1297- 1307. DOI: 10.1007/s10787-019-00599-0. |
| [21] |
MA L, ZHANG LW, ZHUANG Y, et al. The imbalance between Foxp3 +Tregs and Th1/Th17/Th22 cells in patients with newly diagnosed autoimmune hepatitis[J]. J Immunol Res, 2018, 2018: 3753081. DOI: 10.1155/2018/3753081. |
| [22] |
AI G, YAN WM, YU HJ, et al. Soluble Fgl2 restricts autoimmune hepatitis progression via suppressing Tc17 and conventional CD8 + T cell function[J]. J Gene Med, 2018, 20( 7-8): e3023. DOI: 10.1002/jgm.3023. |
| [23] |
MOULTON VR. Sex hormones in acquired immunity and autoimmune disease[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 2279. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02279. |
| [24] |
XING EZ, BILLI AC, GUDJONSSON JE. Sex bias and autoimmune diseases[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2022, 142( 3 Pt B): 857- 866. DOI: 10.1016/j.jid.2021.06.008. |
| [25] |
BROWN MA, SU MA. An inconvenient variable: Sex hormones and their impact on T cell responses[J]. J Immunol, 2019, 202( 7): 1927- 1933. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1801403. |
| [26] |
CHAKRABORTY B, BYEMERWA J, KREBS T, et al. Estrogen receptor signaling in the immune system[J]. Endocr Rev, 2023, 44( 1): 117- 141. DOI: 10.1210/endrev/bnac017. |
| [27] |
THOMAS P, PANG Y, FILARDO EJ, et al. Identity of an estrogen membrane receptor coupled to a G protein in human breast cancer cells[J]. Endocrinology, 2005, 146( 2): 624- 632. DOI: 10.1210/en.2004-1064. |
| [28] |
SINGH RP, HAHN BH, BISCHOFF DS. Interferon genes are influenced by 17β-estradiol in SLE[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 725325. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.725325. |
| [29] |
ADURTHI S, KUMAR MM, VINODKUMAR HS, et al. Oestrogen Receptor-α binds the FOXP3 promoter and modulates regulatory T-cell function in human cervical cancer[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7( 1): 17289. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-17102-w. |
| [30] |
MOHAMMAD I, STARSKAIA I, NAGY T, et al. Estrogen receptor α contributes to T cell-mediated autoimmune inflammation by promoting T cell activation and proliferation[J]. Sci Signal, 2018, 11( 526): eaap9415. DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.aap9415. |
| [31] |
McNEER SK, KOCINSKI AD, GOODMAN WA. Murine CD4 + T cells exhibit sexually dimorphic responses to estrogen signaling[J]. J Immunol, 2023, 210( 1_Supplement): 64. 13. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.210.supp.64.13. |
| [32] |
GOODMAN WA, BEDOYAN SM, HAVRAN HL, et al. Impaired estrogen signaling underlies regulatory T cell loss-of-function in the chronically inflamed intestine[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2020, 117( 29): 17166- 17176. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2002266117. |
| [33] |
MCMURRAY RW, SUWANNAROJ S, NDEBELE K, et al. Differential effects of sex steroids on T and B cells: Modulation of cell cycle phase distribution, apoptosis and bcl-2 protein levels[J]. Pathobiology, 2001, 69( 1): 44- 58. DOI: 10.1159/000048757. |
| [34] |
KWON H, SCHAFER JM, SONG NJ, et al. Androgen conspires with the CD8 + T cell exhaustion program and contributes to sex bias in cancer[J]. Sci Immunol, 2022, 7( 73): eabq2630. DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abq2630. |
| [35] |
HOFFMANN JP, LIU JA, SEDDU K, et al. Sex hormone signaling and regulation of immune function[J]. Immunity, 2023, 56( 11): 2472- 2491. DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.10.008. |
| [36] |
WALECKI M, EISEL F, KLUG J, et al. Androgen receptor modulates Foxp3 expression in CD4 +CD25 +Foxp3 + regulatory T-cells[J]. Mol Biol Cell, 2015, 26( 15): 2845- 2857. DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E14-08-1323. |
| [37] |
ZHU ML, BAKHRU P, CONLEY B, et al. Sex bias in CNS autoimmune disease mediated by androgen control of autoimmune regulator[J]. Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 11350. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11350. |
| [38] |
LYU TT. Diethylstilbestrol inhibits acute autoimmune hepatitis induced by concanavalin A in mice[D]. Guangzhou: Southern Medical University, 2013.
吕廷廷. 己烯雌酚抑制刀豆蛋白A诱导的小鼠急性自身免疫性肝炎[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2013.
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
LIBERAL R, GRANT CR, MA Y, et al. CD39 mediated regulation of Th17-cell effector function is impaired in juvenile autoimmune liver disease[J]. J Autoimmun, 2016, 72: 102- 112. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaut.2016.05.005. |
| [41] |
VUERICH M, HARSHE R, FRANK LA, et al. Altered aryl-hydrocarbon-receptor signalling affects regulatory and effector cell immunity in autoimmune hepatitis[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 74( 1): 48- 57. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.06.044. |
| [42] |
GUAN XN, POLESSO F, WANG CJ, et al. Androgen receptor activity in T cells limits checkpoint blockade efficacy[J]. Nature, 2022, 606( 7915): 791- 796. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04522-6. |
| [43] |
ZHANG MA, AHN JJ, ZHAO FL, et al. Antagonizing peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α activity selectively enhances Th1 immunity in male mice[J]. J Immunol, 2015, 195( 11): 5189- 5202. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500449. |
| [44] |
BEN-BATALLA I, VARGAS-DELGADO ME, von AMSBERG G, et al. Influence of androgens on immunity to self and foreign: Effects on immunity and cancer[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 1184. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01184. |
| [45] |
MARTINELLI S, NANNINI G, CIANCHI F, et al. The impact of microbiota-immunity-hormone interactions on autoimmune diseases and infection[J]. Biomedicines, 2024, 12( 3): 616. DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12030616. |
| [46] |
SUN C, ZHU DZ, ZHU Q, et al. The significance of gut microbiota in the etiology of autoimmune hepatitis: A narrative review[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2024, 14: 1337223. DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1337223. |
| [47] |
CHENG ZL, YANG L, CHU HK. The gut microbiota: A novel player in autoimmune hepatitis[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2022, 12: 947382. DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.947382. |



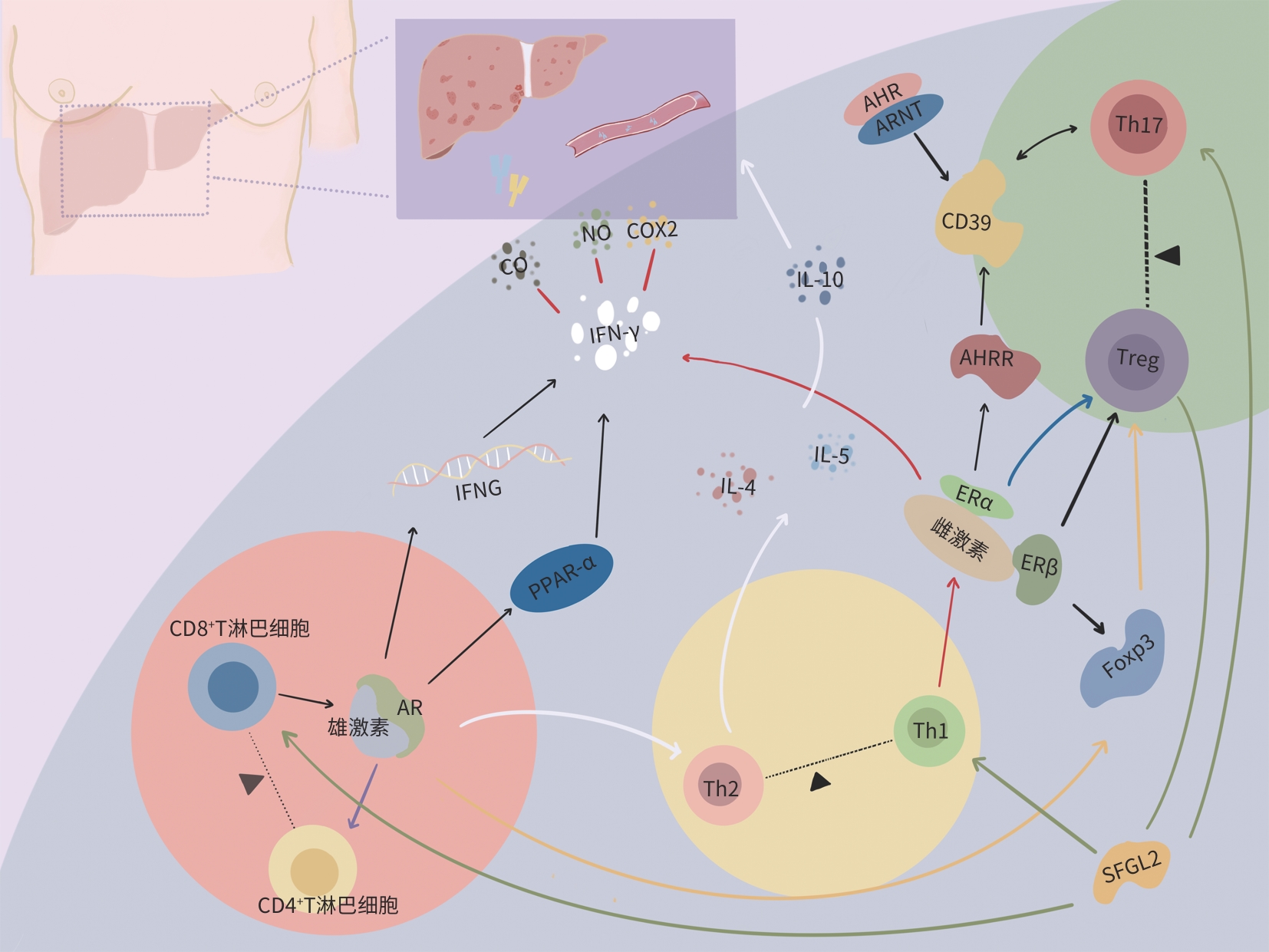




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: