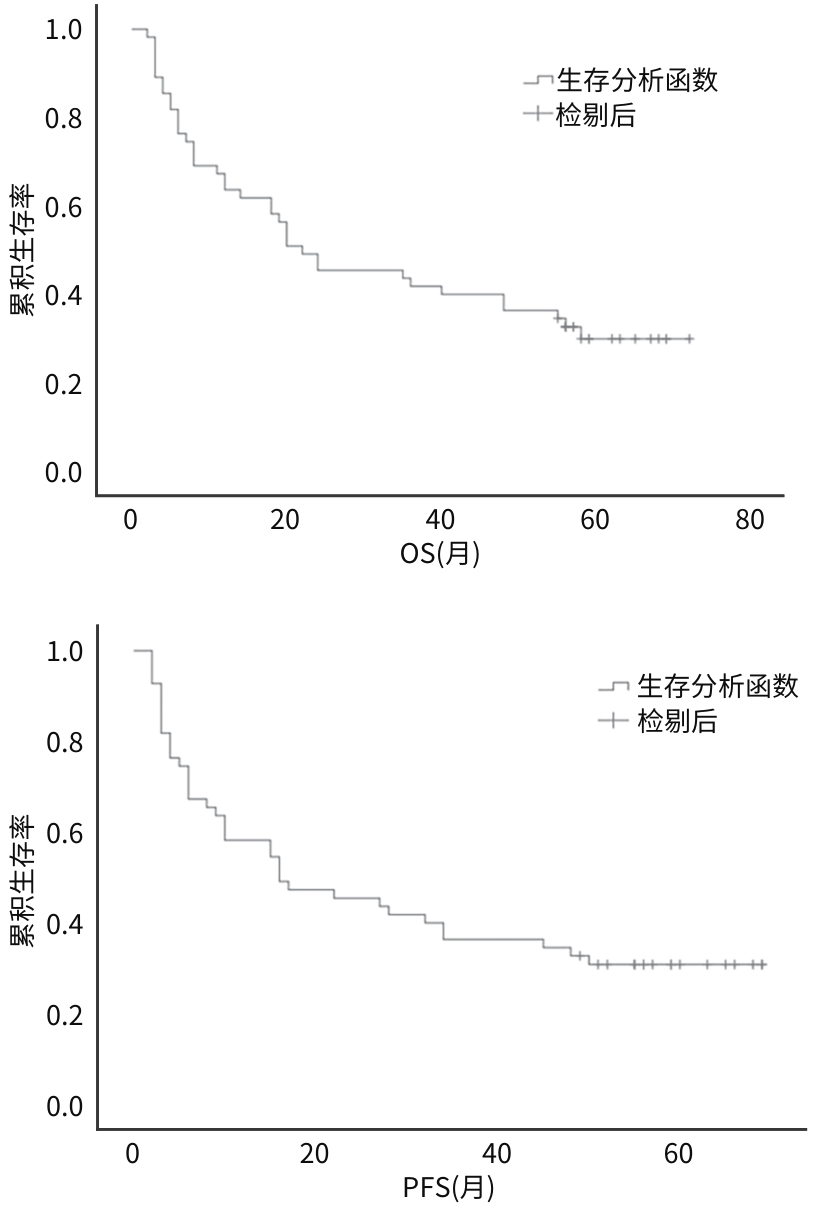
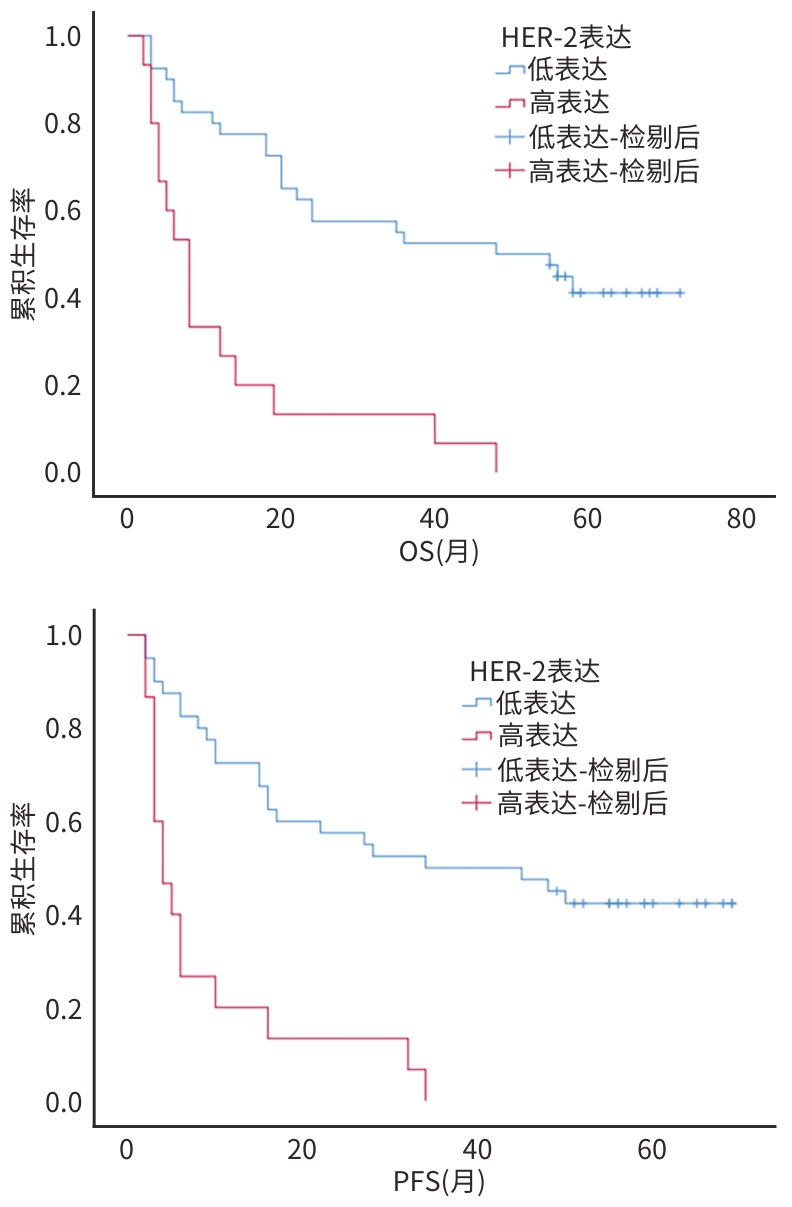
| [1] |
JAVLE M, ZHAO H, ABOU-ALFA GK. Systemic therapy for gallbladder cancer[J]. Chin Clin Oncol, 2019, 8( 4): 44. DOI: 10.21037/cco.2019.08.14. |
| [2] |
HU ZI, LIM KH. Evolving paradigms in the systemic treatment of advanced gallbladder cancer: Updates in year 2022[J]. Cancers(Basel), 2022, 14( 5): 1249. DOI: 10.3390/cancers14051249. |
| [3] |
RUBIN E, SHAN KS, DALAL S, et al. Molecular targeting of the human epidermal growth factor receptor-2(HER2) genes across various cancers[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25( 2): 1064. DOI: 10.3390/ijms25021064. |
| [4] |
KANG Y, LI HT, LIU YP, et al. Regulation of VEGF-A expression and VEGF-A-targeted therapy in malignant tumors[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2024, 150( 5): 221. DOI: 10.1007/s00432-024-05714-5. |
| [5] |
WU ML, HUANG QR, XIE Y, et al. Improvement of the anticancer efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade via combination therapy and PD-L1 regulation[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2022, 15( 1): 24. DOI: 10.1186/s13045-022-01242-2. |
| [6] |
FARHA N, DIMA D, ULLAH F, et al. Precision oncology targets in biliary tract cancer[J]. Cancers(Basel), 2023, 15( 7): 2105. DOI: 10.3390/cancers15072105. |
| [7] |
BRAY F, LAVERSANNE M, SUNG H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024, 74( 3): 229- 263. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21834. |
| [8] |
KRELL RW, WEI AC. Gallbladder cancer: Surgical management[J]. Chin Clin Oncol, 2019, 8( 4): 36. DOI: 10.21037/cco.2019.06.06. |
| [9] |
LI L, LI ML, LIU YB. Progress and prospect of comprehensive treatment of gallbladder cancer[J]. J Hepatobiliary Surg, 2020, 28( 6): 414- 417. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4761.2020.06.006. |
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
ZHU Y, ZHU X, WEI X, et al. HER2-targeted therapies in gastric cancer[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2021, 1876( 1): 188549. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188549. |
| [12] |
QUEIROZ MM, LIMA NF Jr, de CASTRIA TB. Immunotherapy and targeted therapy for advanced biliary tract cancer: Adding new flavors to the pizza[J]. Cancers(Basel), 2023, 15( 7): 1970. DOI: 10.3390/cancers15071970. |
| [13] |
SHUKLA P, MISHRA K, SHUKLA R, et al. Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of VEGF, PDGF-B, and HER2/neu expression in gallbladder cancer[J]. J Cancer Res Ther, 2024, 20( 1): 349- 357. DOI: 10.4103/jcrt.jcrt_1473_22. |
| [14] |
JAVLE M, BORAD MJ, AZAD NS, et al. Pertuzumab and trastuzumab for HER2-positive, metastatic biliary tract cancer(MyPathway): A multicentre, open-label, phase 2a, multiple basket study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2021, 22( 9): 1290- 1300. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00336-3. |
| [15] |
YANG F, QIN SK. Clinical research progress of anti-HER-2 therapy for advanced biliary tract cancer[J]. Chin Clin Oncol, 2023, 28( 9): 842- 848. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0460.2023.09.012. |
| [16] |
APTE RS, CHEN DS, FERRARA N. VEGF in signaling and disease: Beyond discovery and development[J]. Cell, 2019, 176( 6): 1248- 1264. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.01.021. |
| [17] |
SINGH P, JAIN SL, SAKHUJA P, et al. Expression of VEGF-A, HER2/neu, and KRAS in gall bladder carcinoma and their correlation with clinico-pathological parameters[J]. Indian J Pathol Microbiol, 2021, 64( 4): 687- 692. DOI: 10.4103/IJPM.IJPM_248_20. |
| [18] |
YANG Y, WANG WX. Progress in targeted therapy against vascular endothelial growth factors and their receptors for biliary tract cancers[J]. China J Gen Surg, 2024, 33( 2): 265- 272.
杨阳, 王万祥. 血管内皮生长因子及其受体靶向治疗在胆道恶性肿瘤中的研究进展[J]. 中国普通外科杂志, 2024, 33( 2): 265- 272.
|
| [19] |
YI M, ZHENG XL, NIU MK, et al. Combination strategies with PD-1/PD-L1 blockade: Current advances and future directions[J]. Mol Cancer, 2022, 21( 1): 28. DOI: 10.1186/s12943-021-01489-2. |
| [20] |
IBUKIĆ A, RAMIĆ S, ZOVAK M, et al. Expression and prognostic significance of PD-L1 and NY-ESO1 in gallbladder carcinoma[J]. In Vivo, 2023, 37( 4): 1828- 1837. DOI: 10.21873/invivo.13274. |
| [21] |
XU WY, ZHANG HH, YANG XB, et al. Prognostic significance of combined preoperative fibrinogen and CA199 in gallbladder cancer patients[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2018, 24( 13): 1451- 1463. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i13.1451. |
| [22] |
RAWAL N, AWASTHI S, DASH NR, et al. Prognostic relevance of PDL1 and CA19-9 expression in gallbladder cancer vs. inflammatory lesions[J]. Curr Oncol, 2023, 30( 2): 1571- 1584. DOI: 10.3390/curroncol30020121. |
| [23] |
YANG JS, XU RY, WANG CC, et al. Early screening and diagnosis strategies of pancreatic cancer: A comprehensive review[J]. Cancer Commun(Lond), 2021, 41( 12): 1257- 1274. DOI: 10.1002/cac2.12204. |
| [24] |
PEARSON-STUTTARD J, PAPADIMITRIOU N, MARKOZANNES G, et al. Type 2 diabetes and cancer: An umbrella review of observational and mendelian randomization studies[J]. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev, 2021, 30( 6): 1218- 1228. DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.epi-20-1245. |
| [25] |
PÉREZ-MORENO P, RIQUELME I, GARCÍA P, et al. Environmental and lifestyle risk factors in the carcinogenesis of gallbladder cancer[J]. J Pers Med, 2022, 12( 2): 234. DOI: 10.3390/jpm12020234. |
| [26] |
ZHANG R, GENG ZM. Systemic therapy for gallbladder cancer in the era of precision medicine: Coexistence of opportunities and challenges[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 9): 2049- 2056. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.09.005. |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: