| [1] |
RUMGAY H, ARNOLD M, FERLAY J, et al. Global burden of primary liver cancer in 2020 and predictions to 2040[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 77( 6): 1598- 1606. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.08.021. |
| [2] |
YANG T, WANG MD, XU XF, et al. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma in China: Seeking common grounds while reserving differences[J]. Clin Mol Hepatol, 2023, 29( 2): 342- 344. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2023.0106. |
| [3] |
YANG T, ZHANG H, LAU WY, et al. Liver disease in China: A long way to go[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 62( 5): 1640. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27769. |
| [4] |
VILLANUEVA A. Hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2019, 380( 15): 1450- 1462. DOI: 10.1056/nejmra1713263. |
| [5] |
WANG MD, DIAO YK, YAO LQ, et al. Emerging role of molecular diagnosis and personalized therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. iLIVER, 2024, 3( 1): 100083. DOI: 10.1016/j.iliver.2024.100083. |
| [6] |
YANG C, ZHANG HL, ZHANG LM, et al. Evolving therapeutic landscape of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 20( 4): 203- 222. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-022-00704-9. |
| [7] |
ZHU AX, DUDA DG, SAHANI DV, et al. HCC and angiogenesis: Possible targets and future directions[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2011, 8( 5): 292- 301. DOI: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2011.30. |
| [8] |
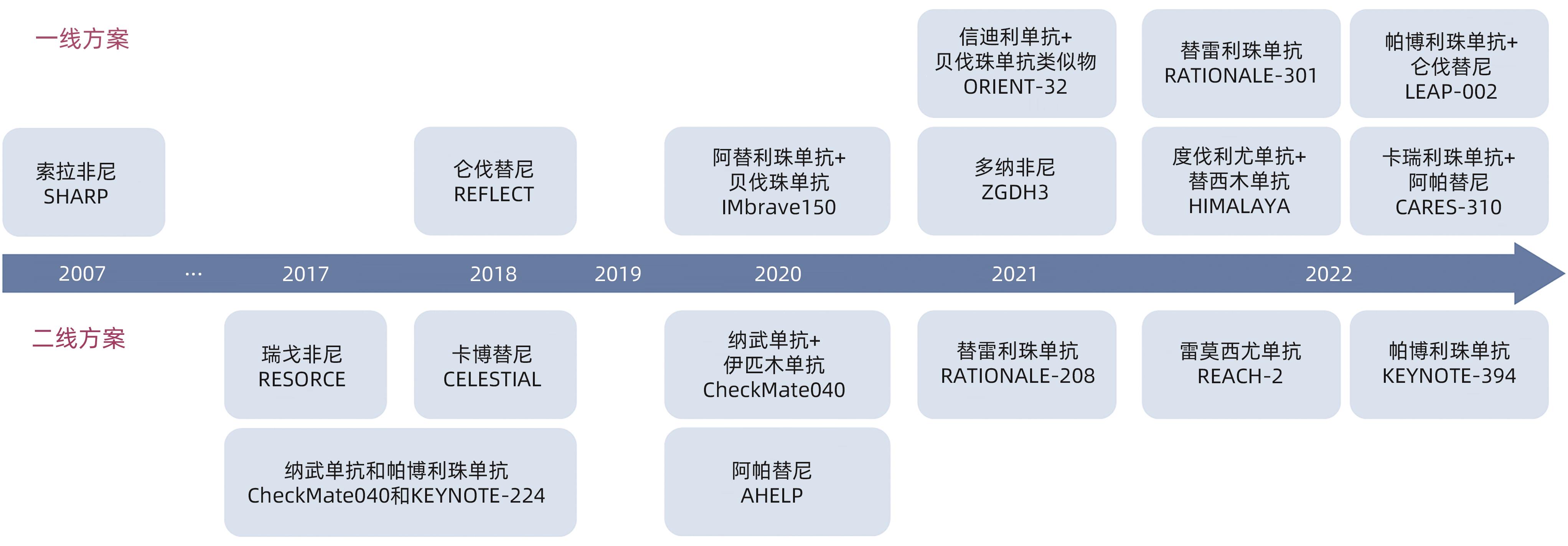
LLOVET JM, RICCI S, MAZZAFERRO V, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2008, 359( 4): 378- 390. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa0708857. |
| [9] |
CHENG AL, KANG YK, CHEN ZD, et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2009, 10( 1): 25- 34. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70285-7. |
| [10] |
KUDO M, FINN RS, QIN SK, et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial[J]. Lancet, 2018, 391( 10126): 1163- 1173. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30207-1. |
| [11] |
ABOU-ALFA GK, MEYER T, CHENG AL, et al. Cabozantinib in patients with advanced and progressing hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2018, 379( 1): 54- 63. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1717002. |
| [12] |
BRUIX J, QIN SK, MERLE P, et al. Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment(RESORCE): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet, 2017, 389( 10064): 56- 66. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32453-9. |
| [13] |
QIN SK, LI Q, GU SZ, et al. Apatinib as second-line or later therapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma(AHELP): A multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 6( 7): 559- 568. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00109-6. |
| [14] |
QIN SK, BI F, GU SZ, et al. Donafenib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of unresectable or metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomized, open-label, parallel-controlled phase II-III trial[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2021, 39( 27): 3002- 3011. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.21.00163. |
| [15] |
PINTER M, SCHEINER B, PECK-RADOSAVLJEVIC M. Immunotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A focus on special subgroups[J]. Gut, 2021, 70( 1): 204- 214. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-321702. |
| [16] |
LLOVET JM, MONTAL R, SIA D, et al. Molecular therapies and precision medicine for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2018, 15( 10): 599- 616. DOI: 10.1038/s41571-018-0073-4. |
| [17] |
EL-KHOUEIRY AB, SANGRO B, YAU T, et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma(CheckMate 040): An open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial[J]. Lancet, 2017, 389( 10088): 2492- 2502. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31046-2. |
| [18] |
KUDO M, MATILLA A, SANTORO A, et al. Checkmate-040: Nivolumab(NIVO) in patients(pts) with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma(aHCC) and Child-Pugh B(CPB) status[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2019, 37( 4_suppl): 327. DOI: 10.1200/jco.2019.37.4_suppl.327. |
| [19] |
QIN SK, KUDO M, MEYER T, et al. Tislelizumab vs sorafenib as first-line treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase 3 randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2023, 9( 12): 1651- 1659. DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2023.4003. |
| [20] |
ZHU AX, FINN RS, EDELINE J, et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with sorafenib(KEYNOTE-224): A non-randomised, open-label phase 2 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2018, 19( 7): 940- 952. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30351-6. |
| [21] |
FINN RS, RYOO BY, MERLE P, et al. Pembrolizumab As second-line therapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in KEYNOTE-240: A randomized, double-blind, phase III trial[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2020, 38( 3): 193- 202. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.19.01307. |
| [22] |
QIN SK, CHEN ZD, LIU Y, et al. A phase II study of anti-PD-1 antibody camrelizumab plus FOLFOX4 or GEMOX systemic chemotherapy as first-line therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma or biliary tract cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2019, 37( 15_suppl): 4074. DOI: 10.1200/jco.2019.37.15_suppl.4074. |
| [23] |
FINN RS, IKEDA M, ZHU AX, et al. Phase Ⅰb study of lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2020, 38( 26): 2960- 2970. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.20.00808. |
| [24] |
FINN RS, QIN SK, IKEDA M, et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2020, 382( 20): 1894- 1905. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1915745. |
| [25] |
National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer(2024 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2024, 40( 5): 893- 918. DOI: 10.12449/JCH240508. 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. 原发性肝癌诊疗指南(2024年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40( 5): 893- 918. DOI: 10.12449/JCH240508. |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
SINGAL AG, LLOVET JM, YARCHOAN M, et al. AASLD Practice Guidance on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 78( 6): 1922- 1965. DOI: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000466. |
| [28] |
HUANG DX, CHEN Y, ZENG QL, et al. Blood supply characteristics of pedunculated hepatocellular carcinoma prior to and following transcatheter arterial chemoembolization treatment: An angiographic demonstration[J]. Oncol Lett, 2018, 15( 3): 3383- 3389. DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.7844. |
| [29] |
REN ZG, XU JM, BAI YX, et al. Sintilimab plus a bevacizumab biosimilar(IBI 305) versus sorafenib in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma(ORIENT-32): A randomised, open-label, phase 2-3 study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2021, 22( 7): 977- 990. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00252-7. |
| [30] |
QIN SK, CHAN SL, GU SZ, et al. Camrelizumab plus rivoceranib versus sorafenib as first-line therapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma(CARES-310): A randomised, open-label, international phase 3 study[J]. Lancet, 2023, 402( 10408): 1133- 1146. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00961-3. |
| [31] |
LLOVET JM, KUDO M, MERLE P, et al. Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab versus lenvatinib plus placebo for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma(LEAP-002): A randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2023, 24( 12): 1399- 1410. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00469-2. |
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
KELLEY RK, RIMASSA L, CHENG AL, et al. Cabozantinib plus atezolizumab versus sorafenib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma(COSMIC-312): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2022, 23( 8): 995- 1008. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(22)00326-6. |
| [34] |
YAU T, KANG YK, KIM TY, et al. Efficacy and safety of nivolumab plus ipilimumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with sorafenib: The CheckMate 040 randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2020, 6( 11): e204564. DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.4564. |
| [35] |
GALLE PR, DECAENS T, KUDO M, et al. Nivolumab(NIVO) plus ipilimumab(IPI) vs lenvatinib(LEN) or sorafenib(SOR) as first-line treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma(uHCC): First results from CheckMate 9DW[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2024, 42( 17_suppl): LBA4008. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2024.42.17_suppl.LBA4008. |
| [36] |
KELLEY RK, SANGRO B, HARRIS W, et al. Safety, efficacy, and pharmacodynamics of tremelimumab plus durvalumab for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Randomized expansion of a phase I/II study[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2021, 39( 27): 2991- 3001. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.20.03555. |
| [37] |
ABOU-ALFA GK, LAU G, KUDO M, et al. Tremelimumab plus durvalumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. NEJM Evid, 2022, 1( 8): EVIDoa2100070. DOI: 10.1056/EVIDoa2100070. |
| [38] |
KUDO M, UESHIMA K, IKEDA M, et al. Randomised, multicentre prospective trial of transarterial chemoembolisation(TACE) plus sorafenib as compared with TACE alone in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: TACTICS trial[J]. Gut, 2020, 69( 8): 1492- 1501. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318934. |
| [39] |
PENG Z, FAN W, ZHU B, et al. Lenvatinib combined with transarterial chemoembolization as first-line treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase Ⅲ, randomized clinical trial(LAUNCH)[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2023, 41( 1): 117- 127. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.22.00392. |
| [40] |
ZHAO M, LYU N, ZHONG S, et al. 983P Safety and efficacy of durvalumab plus hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy in HCC with severe portal vein tumor thrombosis(Vp3/4)-the DurHope study[J]. Ann Oncol, 2023, 34: S608. DOI: 10.1016/j.annonc.2023.09.2128. |
| [41] |
DAWSON LA, WINTER KA, KNOX JJ, et al. NRG/RTOG 1112: Randomized phase III study of sorafenib vs. stereotactic body radiation therapy(SBRT) followed by sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC)[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2023, 41( 4_suppl): 489. DOI: 10.1200/jco.2023.41.4_suppl.489. |
| [42] |
YANG X, HU Y, YANG KY, et al. Cell-free DNA copy number variations predict efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitor-based therapy in hepatobiliary cancers[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2021, 9( 5): e001942. DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001942. |
| [43] |
ZAPPASODI R, WOLCHOK JD, MERGHOUB T. Strategies for predicting response to checkpoint inhibitors[J]. Curr Hematol Malig Rep, 2018, 13( 5): 383- 395. DOI: 10.1007/s11899-018-0471-9. |
| [44] |
REN ZG, GUO YB, BAI YX, et al. Tebotelimab, a PD-1/LAG-3 bispecific antibody, in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma who had failed prior targeted therapy and/or immunotherapy: An open-label, single-arm, phase 1/2 dose-escalation and expansion study[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2023, 41( 4_suppl): 578. DOI: 10.1200/jco.2023.41.4_suppl.578. |
| [45] |
XING BC, DA X, ZHANG YQ, et al. A phase II study combining KN046(an anti-PD-L1/CTLA-4 bispecific antibody) and lenvatinib in the treatment for advanced unresectable or metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC): Updated efficacy and safety results[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2022, 40( 16_suppl): 4115. DOI: 10.1200/jco.2022.40.16_suppl.4115. |
| [46] |
FINN RS, RYOO BY, HSU CH, et al. Results from the MORPHEUS-liver study: Phase Ib/II randomized evaluation of tiragolumab(tira) in combination with atezolizumab(atezo) and bevacizumab(bev) in patients with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma(uHCC)[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2023, 41( 16_suppl): 4010. DOI: 10.1200/jco.2023.41.16_suppl.4010. |
| [47] |
REN Z, HUANG Y, GUO Y, et al. 945MO AdvanTIG-206: Phase II randomized open-label study of ociperlimab(OCI)+tislelizumab(TIS)+BAT1706(bevacizumab biosimilar) versus TIS+BAT1706 in patients(pts) with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC)[J]. Ann Oncol, 2023, 34: S594. DOI: 10.1016/j.annonc.2023.09.2091. |
| [48] |
LU MY, WILLIAMSON DFK, CHEN TY, et al. Data-efficient and weakly supervised computational pathology on whole-slide images[J]. Nat Biomed Eng, 2021, 5( 6): 555- 570. DOI: 10.1038/s41551-020-00682-w. |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: