细胞焦亡在肝纤维化中的作用及研究进展
DOI: 10.12449/JCH260125
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:金泳帆负责设计论文框架,起草论文;赵春梅负责论文修改;邰文琳负责拟定写作思路,指导撰写文章并最后定稿。
-
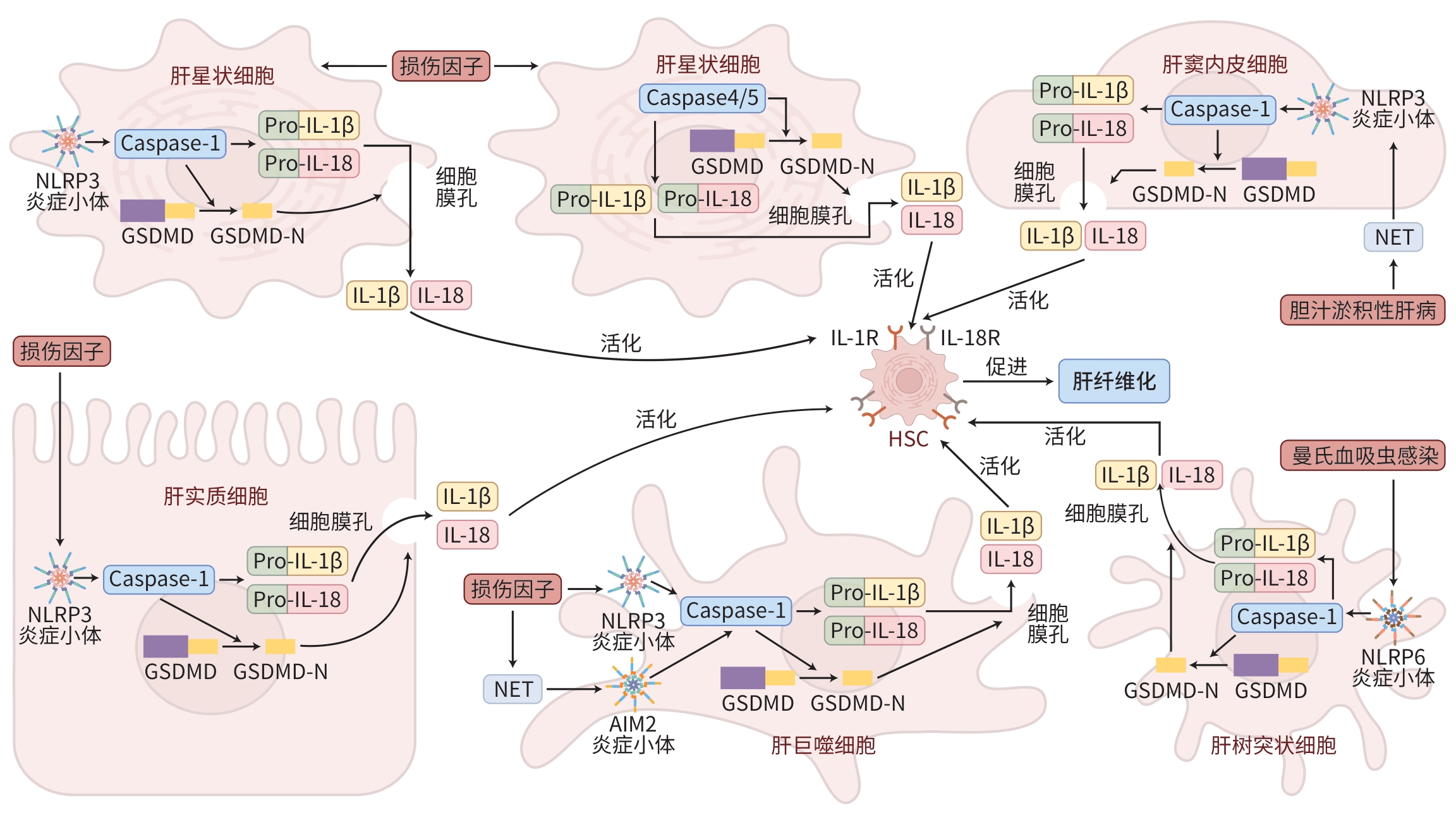
摘要: 肝纤维化既是慢性肝损伤后肝脏自我修复的病理过程,也是慢性肝病进展至肝硬化的关键环节。细胞焦亡作为一种促炎性程序性细胞死亡方式,已被证明在多种疾病中发挥重要作用,也被视为肝纤维化治疗的一个潜在靶点。本文系统阐述了肝实质细胞、肝星状细胞及肝巨噬细胞焦亡与肝纤维化的关联,并针对细胞焦亡介导的抗纤维化治疗策略进行了探讨。Abstract: Hepatic fibrosis is not only a pathological process of hepatic self-repair after chronic liver injury, but also a critical stage in the progression of chronic liver disease to liver cirrhosis. Studies have shown that as a pro-inflammatory form of programmed cell death, pyroptosis plays an important role in various diseases and is also considered a potential therapeutic target for hepatic fibrosis. This article systematically reviews the association of pyroptosis in hepatocytes, hepatic stellate cells, and hepatic macrophages with hepatic fibrosis and discusses pyroptosis-mediated therapeutic strategies targeting hepatic fibrosis.
-
Key words:
- Pyroptosis /
- Hepatic Fibrosis /
- Inflammasome
-
[1] MARRONE G, SHAH VH, GRACIA-SANCHO J. Sinusoidal communication in liver fibrosis and regeneration[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 65( 3): 608- 617. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.04.018. [2] ROEHLEN N, CROUCHET E, BAUMERT TF. Liver fibrosis: Mechanistic concepts and therapeutic perspectives[J]. Cells, 2020, 9( 4): 875. DOI: 10.3390/cells9040875. [3] ASRANI SK, DEVARBHAVI H, EATON J, et al. Burden of liver diseases in the world[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 70( 1): 151- 171. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.09.014. [4] RAO ZP, ZHU YT, YANG P, et al. Pyroptosis in inflammatory diseases and cancer[J]. Theranostics, 2022, 12( 9): 4310- 4329. DOI: 10.7150/thno.71086. [5] ROSS C, CHAN AH, von PEIN JB, et al. Inflammatory caspases: Toward a unified model for caspase activation by inflammasomes[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2022, 40: 249- 269. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-101220-030653. [6] SHI JJ, GAO WQ, SHAO F. Pyroptosis: Gasdermin-mediated programmed necrotic cell death[J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 2017, 42( 4): 245- 254. DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2016.10.004. [7] EVAVOLD CL, KAGAN JC. How inflammasomes inform adaptive immunity[J]. J Mol Biol, 2018, 430( 2): 217- 237. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2017.09.019. [8] BIBO-VERDUGO B, SALVESEN GS. Caspase mechanisms in the regulation of inflammation[J]. Mol Aspects Med, 2022, 88: 101085. DOI: 10.1016/j.mam.2022.101085. [9] de CARVALHO RIBEIRO M, SZABO G. Role of the inflammasome in liver disease[J]. Annu Rev Pathol, 2022, 17: 345- 365. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-032521-102529. [10] WU JR, CAI JJ, TANG YT, et al. The noncanonical inflammasome-induced pyroptosis and septic shock[J]. Semin Immunol, 2023, 70: 101844. DOI: 10.1016/j.smim.2023.101844. [11] WAN Y, LI JY, PU JL, et al. Role of caspase-11 non-canonical inflammasomes in retinal ischemia/reperfusion injury[J]. Mol Med, 2024, 30( 1): 159. DOI: 10.1186/s10020-024-00938-0. [12] KONG Q, ZHANG ZB. Cancer-associated pyroptosis: A new license to kill tumor[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1082165. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1082165. [13] ZOU J, ZHENG YX, HUANG Y, et al. The versatile gasdermin family: Their function and roles in diseases[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 751533. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.751533. [14] RATHINAM VAK, FITZGERALD KA. Inflammasome complexes: Emerging mechanisms and effector functions[J]. Cell, 2016, 165( 4): 792- 800. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.03.046. [15] WANG JX, SUN ZW, XIE JR, et al. Inflammasome and pyroptosis in autoimmune liver diseases[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1150879. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1150879. [16] ZHAO HJ, LIU HY, YANG YH, et al. The role of autophagy and pyroptosis in liver disorders[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23( 11): 6208. DOI: 10.3390/ijms23116208. [17] DAN X, OUYANG S. The role and mechanisms of macrophage polarization and hepatocyte pyroptosis in acute liver failure[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1279264. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1279264. [18] ZHU LJ, TONG HJ, REN C, et al. Inflammation unleashed: The role of pyroptosis in chronic liver diseases[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 141: 113006. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113006. [19] RAMOS-TOVAR E, MURIEL P. NLRP3 inflammasome in hepatic diseases: A pharmacological target[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2023, 217: 115861. DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115861. [20] MRIDHA AR, WREE A, ROBERTSON AAB, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome blockade reduces liver inflammation and fibrosis in experimental NASH in mice[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 66( 5): 1037- 1046. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.01.022. [21] ZHANG Y, WU R, ZHAN X, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps facilitate liver inflammation/fibrosis progression by entering macrophages and triggering AIM2 inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2024, 22( 1): 556. DOI: 10.1186/s12964-024-01944-9. [22] SANCHES RCO, SOUZA C, MARINHO FV, et al. NLRP6 plays an important role in early hepatic immunopathology caused by Schistosoma mansoni infection[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 795. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00795. [23] ZHU JH, OUYANG SX, ZHANG GY, et al. GSDME promotes MASLD by regulating pyroptosis, Drp1 citrullination-dependent mitochondrial dynamic, and energy balance in intestine and liver[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2024, 31( 11): 1467- 1486. DOI: 10.1038/s41418-024-01343-0. [24] CHARAN HV, DWIVEDI DK, KHAN S, et al. Mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated hepatic stellate cell activation: Therapeutic potential for liver fibrosis[J]. Genes Dis, 2023, 10( 2): 480- 494. DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2021.12.006. [25] INZAUGARAT ME, JOHNSON CD, HOLTMANN TM, et al. NLR family pyrin domain-containing 3 inflammasome activation in hepatic stellate cells induces liver fibrosis in mice[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 69( 2): 845- 859. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30252. [26] LI Y, ZHANG YJ, CHEN TT, et al. Role of aldosterone in the activation of primary mice hepatic stellate cell and liver fibrosis via NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 35( 6): 1069- 1077. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.14961. [27] FENG S, XIE XM, LI JC, et al. Bile acids induce liver fibrosis through the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway and the mechanism of FXR inhibition of NLRP3 activation[J]. Hepatol Int, 2024, 18( 3): 1040- 1052. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-023-10610-0. [28] TANG N, ZHANG YP, YING W, et al. Interleukin-1β upregulates matrix metalloproteinase-13 gene expression via c-Jun N-terminal kinase and p38 MAPK pathways in rat hepatic stellate cells[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2013, 8( 6): 1861- 1865. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2013.1719. [29] KNORR J, KAUFMANN B, INZAUGARAT ME, et al. Interleukin-18 signaling promotes activation of hepatic stellate cells in mouse liver fibrosis[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 77( 6): 1968- 1982. DOI: 10.1002/hep.32776. [30] XIE ZY, XU YX, YAO L. Angiotensin II can trigger HSC-LX2 pyroptosis through both classical and non-classical pathways[J]. Life Sci, 2022, 307: 120878. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120878. [31] WREE A, EGUCHI A, MCGEOUGH MD, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation results in hepatocyte pyroptosis, liver inflammation, and fibrosis in mice[J]. Hepatology, 2014, 59( 3): 898- 910. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26592. [32] GAUL S, LESZCZYNSKA A, ALEGRE F, et al. Hepatocyte pyroptosis and release of inflammasome particles induce stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 74( 1): 156- 167. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.07.041. [33] LANG ZC, ZHANG RR, LI XM, et al. GAS5-inhibited hepatocyte pyroptosis contributes to hepatic stellate cell inactivation via microRNA-684 and AHR[J]. iScience, 2023, 26( 8): 107326. DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107326. [34] XIAO Y, ZHAO C, TAI Y, et al. STING mediates hepatocyte pyroptosis in liver fibrosis by Epigenetically activating the NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. Redox Biol, 2023, 62: 102691. DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102691. [35] DOU L, SHI XM, HE XS, et al. Macrophage phenotype and function in liver disorder[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 3112. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03112. [36] TACKE F. Targeting hepatic macrophages to treat liver diseases[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 66( 6): 1300- 1312. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.02.026. [37] CHENG D, CHAI J, WANG HW, et al. Hepatic macrophages: Key players in the development and progression of liver fibrosis[J]. Liver Int, 2021, 41( 10): 2279- 2294. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14940. [38] SHU B, ZHOU YX, LI H, et al. The METTL3/MALAT1/PTBP1/USP8/TAK1 axis promotes pyroptosis and M1 polarization of macrophages and contributes to liver fibrosis[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2021, 7( 1): 368. DOI: 10.1038/s41420-021-00756-x. [39] WAN YP, ZHANG W, HUANG CK, et al. Ursolic acid alleviates Kupffer cells pyroptosis in liver fibrosis by the NOX2/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2022, 113( Pt A): 109321. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109321. [40] LIU Y, KONG XH, YOU Y, et al. S100A8-mediated NLRP3 inflamma‑some-dependent pyroptosis in macrophages facilitates liver fibrosis progression[J]. Cells, 2022, 11( 22): 3579. DOI: 10.3390/cells-11223-579. [41] WANG BY, YANG LX, YUAN XX, et al. Roles and therapeutic targeting of dendritic cells in liver fibrosis[J]. J Drug Target, 2024, 32( 6): 647- 654. DOI: 10.1080/1061186X.2024.2347365. [42] XIANG M, LIU TT, TIAN C, et al. Kinsenoside attenuates liver fibro-inflammation by suppressing dendritic cells via the PI3K-AKT-FoxO1 pathway[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2022, 177: 106092. DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106092. [43] MÉNDEZ-SÁNCHEZ N, CÓRDOVA-GALLARDO J, BARRANCO-FRAGOSO B, et al. Hepatic dendritic cells in the development and progression of metabolic steatohepatitis[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 641240. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.641240. [44] YU MX, ZHENG CW, LI XW, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps-induced pyroptosis of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells exacerbates intrahepatic coagulation in cholestatic mice[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2025, 1871( 3): 167700. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2025.167700. -



 PDF下载 ( 726 KB)
PDF下载 ( 726 KB)

 下载:
下载:


