1990—2021年中国15~39岁人群肝胆胰良性疾病负担变化趋势分析
DOI: 10.12449/JCH260119
Changing trend of benign hepatobiliary and pancreatic diseases among people aged 15—39 years in China in 1990—2021
-
摘要:
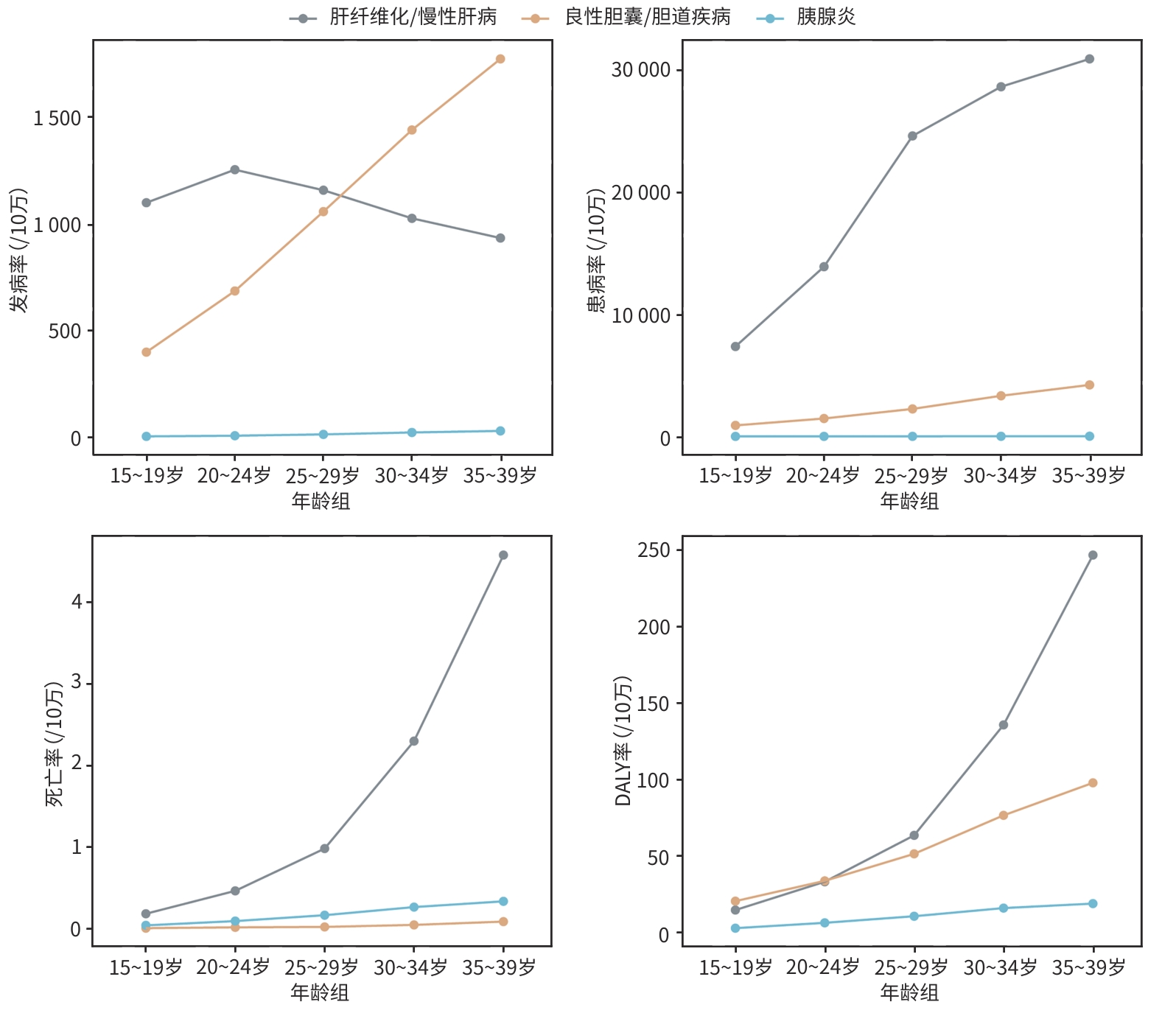
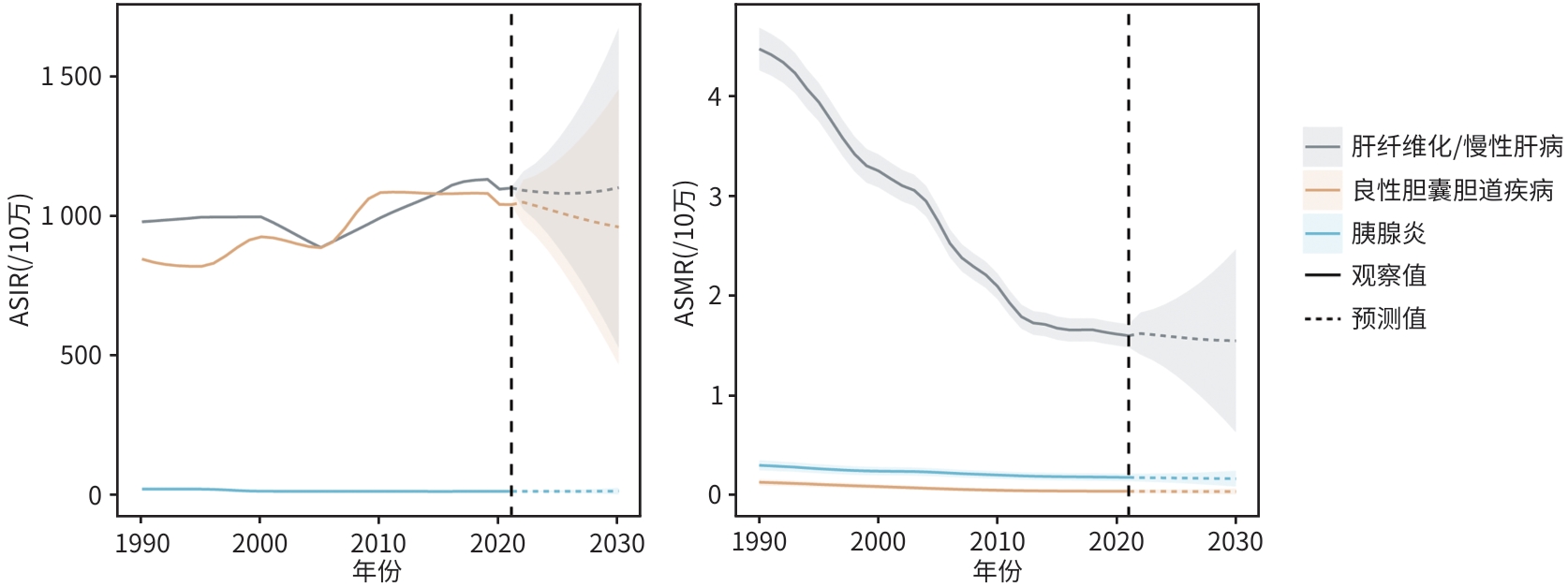
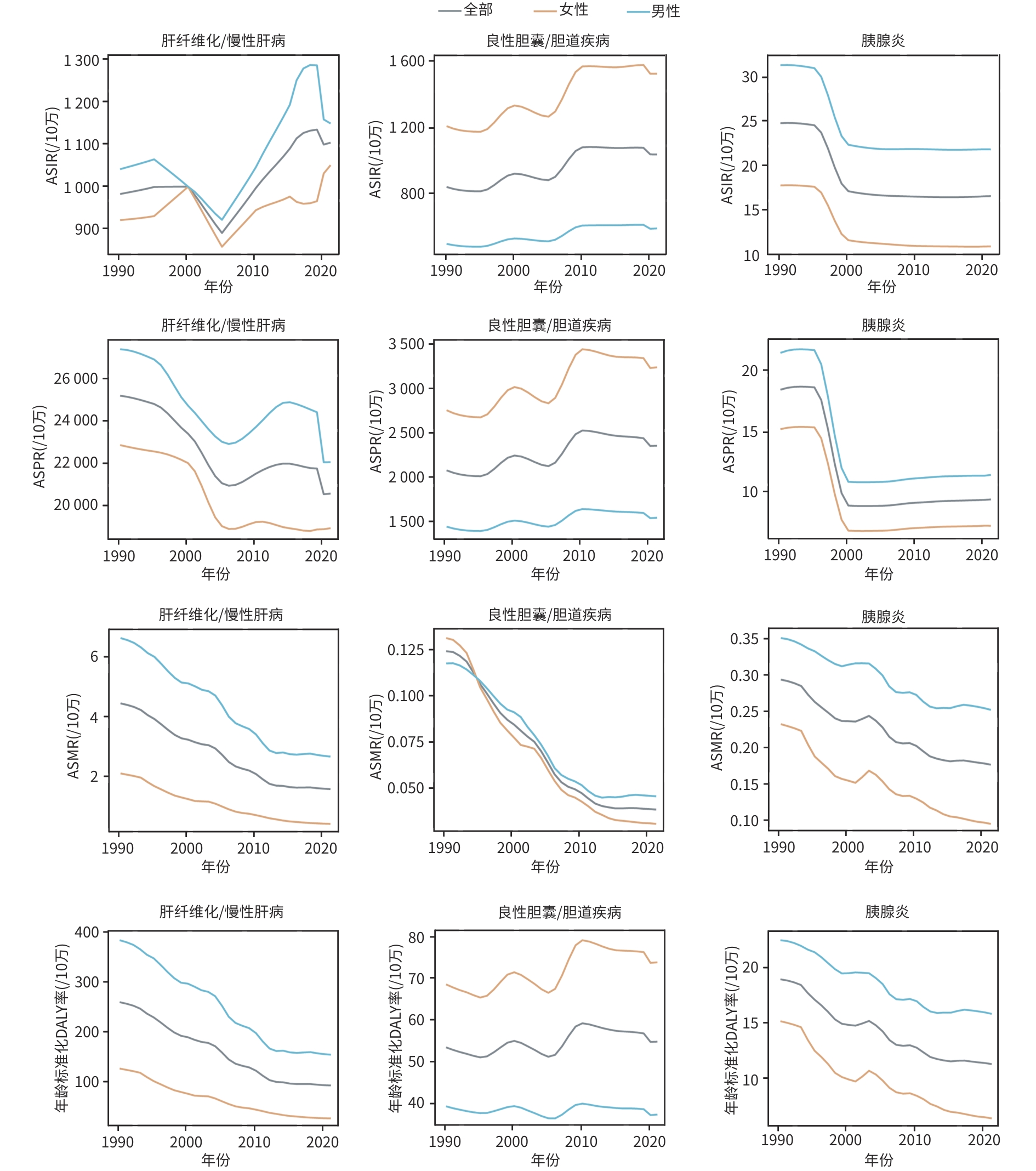
目的 分析1990—2021年我国15~39岁人群肝胆胰良性疾病的发病、患病、死亡和伤残调整寿命年(DALY)变化趋势。 方法 基于全球疾病负担研究(GBD)2021年数据,获取我国15~39岁人群肝纤维化/慢性肝病、良性胆囊/胆道疾病与胰腺炎的流行病学数据,计算估计年度百分比变化(EAPC)评估发病率、患病率、死亡率和DALY的变化趋势。利用贝叶斯年龄-时期-队列模型预测2022—2030年的发病率和死亡率。 结果 2021年,我国15~39岁人群中肝胆胰良性疾病新发共10 448 778例,相比于1990年增加3.8%;患病数、死亡数和DALY数相比于1990年分别减少20.4%、59.6%和50.2%。2021年,我国15~39岁人群中肝纤维化/慢性肝病、良性胆囊/胆道疾病与胰腺炎的年龄标准化发病率分别为1 104.4/10万、1 045.05/10万和16.64/10万,年龄标准化患病率分别为20 592.37/10万、2 364.85/10万和9.43/10万,年龄标准化死亡率分别为1.61/10万、0.04/10万和0.18/10万。1990—2021年,我国15~39岁人群中肝纤维化/慢性肝病的年龄标准化发病率(EAPC=0.43,95%CI: 0.23~0.63)呈上升趋势,良性胆囊胆道疾病的年龄标准化发病率(EAPC=1.07,95%CI: 0.91~1.24)和年龄标准化患病率(EAPC=0.75,95% CI:0.59~0.89)呈上升趋势;三类疾病的年龄标准化死亡率均呈下降趋势。预计2022—2030年,良性胆囊/胆道疾病发病率有所下降,胰腺炎发病率有所上升。 结论 我国15~39岁人群肝纤维化/慢性肝病与胆囊/胆道疾病发病率在过去30年间整体呈升高趋势,需进一步关注我国15~39岁人群的肝胆良性疾病的疾病负担。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the changing trends of the incidence rate, prevalence rate, mortality rate, and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) of benign hepatobiliary and pancreatic diseases among people aged 15 — 39 years in China in 1990 — 2021. Methods The data of 2021 Global Burden of Disease Study were downloaded to obtain the epidemiological data of liver fibrosis/chronic liver disease, benign gallbladder/biliary tract diseases, and pancreatitis among people aged 15 — 39 years in China, and estimated annual percentage change (EAPC) was calculated to assess the changing trends of incidence, prevalence, mortality, and DALY rates. The Bayesian age-period-cohort model was used to predict the incidence and mortality rates from 2022 to 2030. Results In 2021, there were 10 448 778 new cases of benign hepatobiliary and pancreatic diseases among the individuals aged 15 — 39 years in China, which was increased by 3.8% compared with the data in 1990, while the numbers of prevalent cases, deaths, and DALYs were reduced by 20.4%, 59.6%, and 50.2%, respectively. In 2021, the age-standardized incidence rates of liver fibrosis/chronic liver disease, benign gallbladder/biliary tract diseases, and pancreatitis were 1 104.40/100 000, 1 045.05/100 000, and 16.64/100 000, respectively; the age-standardized prevalence rates were 20 592.37/100 000, 2 364.85/100 000, and 9.43/100 000, respectively; the age-standardized mortality rates were 1.61/100 000, 0.04/100 000, and 0.18/100 000, respectively. From 1990 to 2021, there was a tendency of increase in the age-standardized incidence rate of liver fibrosis/chronic liver disease (EAPC=0.43, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.23 — 0.63), and there was also a tendency of increase in the age-standardized incidence and prevalence rates of benign gallbladder/biliary tract diseases (incidence rate: EAPC=1.07, 95%CI: 0.91 — 1.24; prevalence rate: EAPC=0.75, 95%CI: 0.59 — 0.89), while there was a tendency of reduction in the age-standardized mortality rate of all three disease categories. Predictions for 2022 — 2030 indicated a potential reduction in the incidence rate of benign gallbladder/biliary tract diseases and an increase in the incidence rate of pancreatitis. Conclusion There has been an overall upward trend in the incidence rate of liver fibrosis/chronic liver disease and gallbladder/biliary tract diseases over the past three decades, and it is needed to pay attention to the disease burden of benign hepatobiliary diseases among the people aged 15 — 39 years in China. -
Key words:
- Liver Diseases /
- Gallbladder Diseases /
- Biliary Tract Diseases /
- Pancreatitis /
- Global Burden of Disease
-
表 1 我国2021年15~39岁人群肝胆胰良性疾病的ASIR、ASPR、ASMR和年龄标准化DALY率
Table 1. Age-standardized incidence, prevalence, mortality and DALY rates of benign hepatobiliary and pancreatic diseases among people aged 15 to 39 years in China, 2021
疾病 ASIR(/10万) ASPR(/10万) ASMR(/10万) 年龄标准化DALY率(/10万) 肝纤维化/慢性肝病 总体 1 104.40 20 592.37 1.61 94.16 男性 1 149.81 22 087.22 2.69 155.98 女性 1 051.16 18 946.28 0.44 27.91 良性胆囊/胆道疾病 总体 1 045.05 2 364.85 0.04 54.95 男性 600.17 1 551.03 0.05 37.48 女性 1 530.86 3 250.72 0.03 73.98 胰腺炎 总体 16.64 9.43 0.18 11.41 男性 21.91 11.45 0.25 15.96 女性 10.98 7.26 0.09 6.49 -
[1] MURRAY CJL. The global burden of disease study at 30 years[J]. Nat Med, 2022, 28( 10): 2019- 2026. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-022-01990-1. [2] GBD 2021 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability(YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years(DALYs), and healthy life expectancy(HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021[J]. Lancet, 2024, 403( 10440): 2133- 2161. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00757-8. [3] THAM EKJ, TAN DJH, DANPANICHKUL P, et al. The global burden of cirrhosis and other chronic liver diseases in 2021[J]. Liver Int, 2025, 45( 3): e70001. DOI: 10.1111/liv.70001. [4] DAI FY, CAI YZ, YANG SJ, et al. Global burden of gallbladder and biliary diseases(1990-2021) with healthcare workforce analysis and projections to 2035[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2025, 25( 1): 249. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-025-03842-x. [5] JIANG WK, DU Y, XIANG CF, et al. Age-period-cohort analysis of pancreatitis epidemiological trends from 1990 to 2019 and forecasts for 2044: A systematic analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. Front Public Health, 2023, 11: 1118888. DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1118888. [6] CHEN X, ZHANG LY, CHEN W. Global, regional, and national burdens of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus in adolescents from 1990 to 2021, with forecasts to 2030: A systematic analysis of the global burden of disease study 2021[J]. BMC Med, 2025, 23( 1): 48. DOI: 10.1186/s12916-025-03890-w. [7] LUO ZY, SHAN SY, CAO J, et al. Temporal trends in cross-country inequalities of stroke and subtypes burden from 1990 to 2021: A secondary analysis of the global burden of disease study 2021[J]. E Clinical Medicine, 2024, 76: 102829. DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102829. [8] DENG YJ, WEI BJ, ZHAI Z, et al. Dietary risk-related colorectal cancer burden: Estimates from 1990 to 2019[J]. Front Nutr, 2021, 8: 690663. DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2021.690663. [9] LI TY, ZHANG HX, LIAN MY, et al. Global status and attributable risk factors of breast, cervical, ovarian, and uterine cancers from 1990 to 2021[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2025, 18( 1): 5. DOI: 10.1186/s13045-025-01660-y. [10] YUAN QH, WANG LJ, SUN BJ, et al. Global, regional, and national differences in the burden of refraction disorders among children, adolescents, and older adults: Current trends and future projections[J]. BMC Public Health, 2025, 25( 1): 2653. DOI: 10.1186/s12889-025-23887-7. [11] WANG YF, LU HL, HU MR, et al. Alcohol consumption in China before and during COVID-19: Preliminary results from an online retrospective survey[J]. Front Psychiatry, 2020, 11: 597826. DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.597826. [12] YUE TT, ZHANG QQ, CAI T, et al. Trends in the disease burden of HBV and HCV infection in China from 1990-2019[J]. Int J Infect Dis, 2022, 122: 476- 485. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.017. [13] ZHUANG Q, DONG ZX, WAN XJ. Research progress of effect of estrogen and its receptors on cholesterol gallstone disease[J]. J Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ Med Sci, 2021, 41( 10): 1394- 1396. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2021.10.020.庄谦, 董志霞, 宛新建. 雌激素及其受体影响胆固醇结石形成的研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2021, 41( 10): 1394- 1396. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2021.10.020. [14] JIANG MK, LU ZQ, ZHOU WM, et al. Analysis of the disease burden of pancreatitis in China from 1990 to 2019[J]. Chin J Evid Based Med, 2022, 22( 8): 869- 875.蒋梦可, 陆宗庆, 周伍明, 等. 1990—2019年中国胰腺炎疾病负担分析[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2022, 22( 8): 869- 875. [15] QI Y, YAN Q, SUN LJ, et al. Trends of smoking and drinking behaviors among adolescents in Shanghai from 2004 to 2019[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2022, 43( 7): 1003- 1006, 1010. DOI: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2022.07.011.祁月, 严琼, 孙力菁, 等. 上海市2004—2019年青少年吸烟饮酒行为变化趋势[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2022, 43( 7): 1003- 1006, 1010. DOI: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2022.07.011. [16] QU YB, SHEN SJ, YUAN HH, et al. Trends of substance abuse behavior among adolescents in Guangdong Province, 2007-2016[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2020, 41( 11): 1650- 1653. DOI: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2020.11.014.曲亚斌, 沈少君, 袁华晖, 等. 广东省2007—2016年青少年物质滥用行为变化趋势[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2020, 41( 11): 1650- 1653. DOI: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2020.11.014. [17] PAIK JM, KABBARA K, EBERLY KE, et al. Global burden of NAFLD and chronic liver disease among adolescents and young adults[J]. Hepatology, 2022, 75( 5): 1204- 1217. DOI: 10.1002/hep.32228. [18] ZHAO ZH, WEI TH, QIAN NN, et al. Disease burden of cirrhosis caused by non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in China, 1990-2021: a comparative analysis with global trends[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2025, 29( 7): 782- 789. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2025.07.006.赵自豪, 魏涛华, 钱南南, 等. 1990―2021年中国非酒精性脂肪性肝病疾病负担:与全球的对比分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2025, 29( 7): 782- 789. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2025.07.006. [19] PAN XF, WANG LM, PAN A. Epidemiology and determinants of obesity in China[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2021, 9( 6): 373- 392. DOI: 10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00045-0. [20] CHEN XT, WEN XS, ZHANG Y, et al. 7-year longitudinal prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents in Shanghai Minhang District: A cross-sectional survey from 2014 to 2020[J]. Chin J Evid Based Pediatr, 2022, 17( 2): 109- 115. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5501.2022.02.005.陈逍天, 温晓飒, 张羿, 等. 上海市闵行区儿童青少年非酒精性脂肪肝病7年患病率横断面调查[J]. 中国循证儿科杂志, 2022, 17( 2): 109- 115. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5501.2022.02.005. [21] WANG K, LIU ZG, TANG RM, et al. Gallstones in the era of metabolic syndrome: Pathophysiology, risk prediction, and management[J]. Cureus, 2025, 17( 3): e80541. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.80541. [22] ALIMUJIANG YMT TEK, MA YF, LI CY, et al. Growth and development of Chinese adolescents and the trend of overweight[J/OL]. Acta Anthropol Sin, 2025: 1- 11.( 2025-04-23). https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2025.0020. DOI: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2025.0020阿力木江·依米提·塔尔肯, 马云飞, 李成跃, 等. 中国青少年的生长发育及超重趋势[J/OL]. 人类学学报, 2025: 1- 11.( 2025-04-23). https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2025.0020. DOI: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2025.0020 [23] YANG JT, DENG SW, ZHAO HY, et al. The burden of type 2 diabetes in adolescents and young adults in China: A secondary analysis from the global burden of disease study 2021[J]. Health Data Sci, 2024, 4: 0210. DOI: 10.34133/hds.0210. [24] BEYER G, HABTEZION A, WERNER J, et al. Chronic pancreatitis[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396( 10249): 499- 512. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31318-0. [25] HU LH, JIN ZD. Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of dyspepsia in chronic pancreatitis patients[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 12): 2757- 2762. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.12.002.胡良皞, 金震东. 慢性胰腺炎患者消化不良的诊治进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023, 39( 12): 2757- 2762. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.12.002. -



 PDF下载 ( 115020 KB)
PDF下载 ( 115020 KB)

 下载:
下载: