消除乙型肝炎病毒感染危害的关键科学问题与突破路径
DOI: 10.12449/JCH260101
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:王怡雪负责归纳文献并撰写论文;彭博负责查阅并归纳文献;魏磊、龙泉鑫、夏宇尘负责修改论文;孙银燕负责撰写并修改论文;李文辉负责指导撰写并修改论文。
Key scientific issues and breakthrough paths to eliminate the harm of hepatitis B virus infection
-
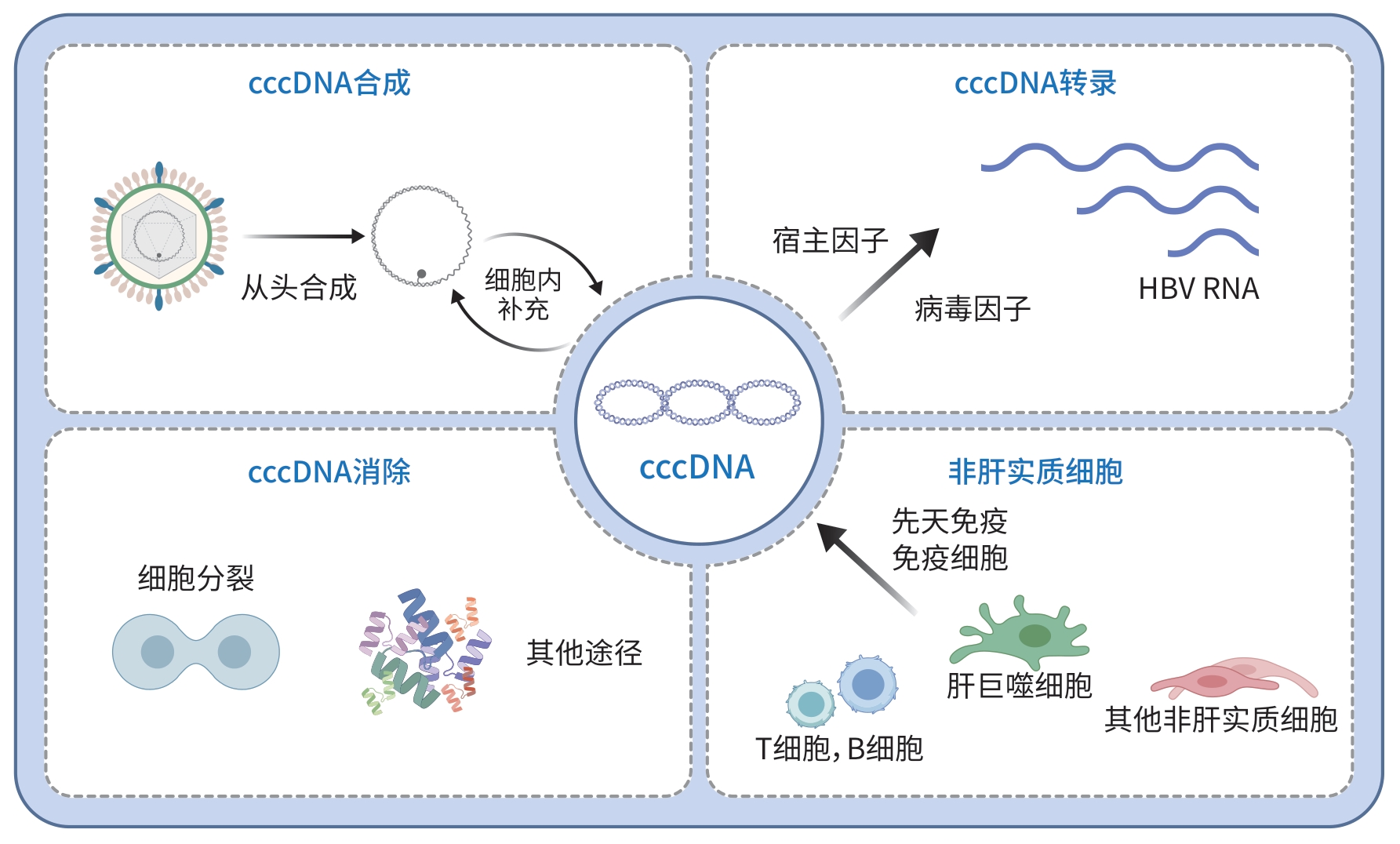
摘要: 乙型肝炎病毒(HBV)仅感染肝实质细胞,并在肝实质细胞核内形成共价闭合环状DNA(cccDNA)。HBV cccDNA是病毒基因转录的关键模板、子代病毒产生的唯一来源和病毒抗原表达的起始原因,是HBV持续感染的分子基础。因此,根治HBV慢性感染的关键在于清除和/或功能沉默cccDNA。本文从cccDNA合成、转录、清除及非实质细胞对cccDNA影响的全生命周期角度,讨论消除HBV感染危害所需要解决的科学问题,为未来根治HBV感染提供参考思路。Abstract: Hepatitis B virus (HBV) exclusively infects liver parenchymal cells and forms covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) within their nuclei. HBV cccDNA serves as the essential template for viral gene transcription, the sole source of progeny virus production, and the key driver of viral antigen expression, and it is the molecular basis for the persistence of HBV infection. Therefore, elimination and/or functional silencing of cccDNA is the key to eradicate chronic HBV infection. This article discusses the critical scientific issues that need to be solved during elimination of the harm of HBV infection from the perspectives of the synthesis, transcription, and clearance of cccDNA, as well as the impact of nonparenchymal cells on cccDNA, in order to provide a reference for eradicating HBV infection in the future.
-
Key words:
- Hepatitis B Virus /
- Covalently Closed Circular DNA /
- Molecular Mechanisms
-
[1] World Health Organization. Global hepatitis report 2024: Action for access in low- and middle-income countries[EB/OL].( 2024-04-09)[ 2025-10-30]. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240091672. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240091672 [2] WERLE-LAPOSTOLLE B, BOWDEN S, LOCARNINI S, et al. Persistence of cccDNA during the natural history of chronic hepatitis B and decline during adefovir dipivoxil therapy[J]. Gastroenterology, 2004, 126( 7): 1750- 1758. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2004.03.018. [3] KRAMVIS A, CHANG KM, DANDRI M, et al. A roadmap for serum biomarkers for hepatitis B virus: Current status and future outlook[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 19( 11): 727- 745. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-022-00649-z. [4] TU T, BUDZINSKA MA, SHACKEL NA, et al. HBV DNA integration: Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications[J]. Viruses, 2017, 9( 4): 75. DOI: 10.3390/v9040075. [5] ZOULIM F, CHEN PJ, DANDRI M, et al. Hepatitis B virus DNA integration: Implications for diagnostics, therapy, and outcome[J]. J Hepatol, 2024, 81( 6): 1087- 1099. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.06.037. [6] LUCIFORA J, XIA YC, REISINGER F, et al. Specific and nonhepatotoxic degradation of nuclear hepatitis B virus cccDNA[J]. Science, 2014, 343( 6176): 1221- 1228. DOI: 10.1126/science.1243462. [7] GUIDOTTI LG, ROCHFORD R, CHUNG J, et al. Viral clearance without destruction of infected cells during acute HBV infection[J]. Science, 1999, 284( 5415): 825- 829. DOI: 10.1126/science.284.5415.825. [8] PENG B, PAN LX, LI WH. New insights on hepatitis B virus viral transcription in single hepatocytes[J]. Viruses, 2024, 16( 12): 1828. DOI: 10.3390/v16121828. [9] WONG GL, TSE YK, WONG VW, et al. Long-term safety of oral nucleos(t)ide analogs for patients with chronic hepatitis B: A cohort study of 53, 500 subjects[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 62( 3): 684- 693. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27894. [10] ZHANG YY, ZHANG BH, THEELE D, et al. Single-cell analysis of covalently closed circular DNA copy numbers in a hepadnavirus-infected liver[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2003, 100( 21): 12372- 12377. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2033898100. [11] TANG DB, ZHAO HQ, WU YM, et al. Transcriptionally inactive hepatitis B virus episome DNA preferentially resides in the vicinity of chromosome 19 in 3D host genome upon infection[J]. Cell Rep, 2021, 35( 13): 109288. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109288. [12] GUO HT, JIANG D, ZHOU TL, et al. Characterization of the intracellular deproteinized relaxed circular DNA of hepatitis B virus: An intermediate of covalently closed circular DNA formation[J]. J Virol, 2007, 81( 22): 12472- 12484. DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01123-07. [13] ZHAO KT, GUO FT, WANG JJ, et al. Limited disassembly of cytoplasmic hepatitis B virus nucleocapsids restricts viral infection in murine hepatic cells[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 77( 4): 1366- 1381. DOI: 10.1002/hep.32622. [14] WEI L, PLOSS A. Hepatitis B virus cccDNA is formed through distinct repair processes of each strand[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12( 1): 1591. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-21850-9. [15] WANG YX, NIKLASCH M, LIU TT, et al. Interferon-inducible MX2 is a host restriction factor of hepatitis B virus replication[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 72( 5): 865- 876. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.12.009. [16] QI YH, GAO ZC, XU GW, et al. DNA polymerase κ is a key cellular factor for the formation of covalently closed circular DNA of hepatitis B virus[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2016, 12( 10): e1005893. DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005893. [17] LONG QX, YAN R, HU JL, et al. The role of host DNA ligases in hepadnavirus covalently closed circular DNA formation[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2017, 13( 12): e1006784. DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006784. [18] ZHAO KT, WANG JJ, WANG ZC, et al. Hepatitis B virus hijacks MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 complex to form its minichromosome[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2025, 21( 1): e1012824. DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012824. [19] YAO QY, PENG B, LI C, et al. SLF2 interacts with the SMC5/6 complex to direct hepatitis B virus episomal DNA to promyelocytic leukemia bodies for transcriptional repression[J]. J Virol, 2023, 97( 7): e00328-23. DOI: 10.1128/jvi.00328-23. [20] XIA YC, CHENG XM, NILSSON T, et al. Nucleolin binds to and regulates transcription of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA minichromosome[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2023, 120( 49): e2306390120. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2306390120. [21] SUN Y, TENG Y, WANG LY, et al. LINC01431 promotes histone H4R3 methylation to impede HBV covalently closed circular DNA transcription by stabilizing PRMT1[J]. Adv Sci, 2022, 9( 16): 2103135. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202103135. [22] LIU W, YAO QY, SU XN, et al. Molecular insights into Spindlin1-HBx interplay and its impact on HBV transcription from cccDNA minichromosome[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14( 1): 4663. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-40225-w. [23] DECORSIÈRE A, MUELLER H, van BREUGEL PC, et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein identifies the Smc5/6 complex as a host restriction factor[J]. Nature, 2016, 531( 7594): 386- 389. DOI: 10.1038/nature17170. [24] LIU F, CAMPAGNA M, QI YH, et al. Alpha-interferon suppresses hepadnavirus transcription by altering epigenetic modification of cccDNA minichromosomes[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2013, 9( 9): e1003613. DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003613. [25] YUAN YF, ZHAO KT, YAO YX, et al. HDAC11 restricts HBV replication through epigenetic repression of cccDNA transcription[J]. Antiviral Res, 2019, 172: 104619. DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2019.104619. [26] LUCIFORA J, ARZBERGER S, DURANTEL D, et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein is essential to initiate and maintain virus replication after infection[J]. J Hepatol, 2011, 55( 5): 996- 1003. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2011.02.015. [27] LIU CY, ZHAO KT, CHEN YS, et al. Mitochondrial glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase restricts HBV replication via the TRIM28-mediated degradation of HBx[J]. J Virol, 2023, 97( 5): e00580-23. DOI: 10.1128/jvi.00580-23. [28] KORNYEYEV D, RAMAKRISHNAN D, VOITENLEITNER C, et al. Spatiotemporal analysis of hepatitis B virus X protein in primary human hepatocytes[J]. J Virol, 2019, 93( 16): e00248-19. DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00248-19. [29] ABDUL F, DIMAN A, BAECHLER B, et al. Smc5/6 silences episomal transcription by a three-step function[J]. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 2022, 29( 9): 922- 931. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-022-00829-0. [30] PENG B, JING ZY, ZHOU ZM, et al. Nonproductive hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA generates HBx-related transcripts from the HBx/enhancer I region and acquires reactivation by superinfection in single cells[J]. J Virol, 2023, 97( 1): e01717-22. DOI: 10.1128/jvi.01717-22. [31] HUANG Q, ZHOU B, CAI DW, et al. Rapid turnover of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA indicated by monitoring emergence and reversion of signature-mutation in treated chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 73( 1): 41- 52. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31240. [32] STADLER D, KÄCHELE M, JONES AN, et al. Interferon-induced degradation of the persistent hepatitis B virus cccDNA form depends on ISG20[J]. EMBO Rep, 2021, 22( 6): e49568. DOI: 10.15252/embr.201949568. [33] GUIDOTTI LG, ISHIKAWA T, HOBBS MV, et al. Intracellular inactivation of the hepatitis B virus by cytotoxic T lymphocytes[J]. Immunity, 1996, 4( 1): 25- 36. DOI: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80295-2. [34] SMEKALOVA EM, MARTINEZ MG, COMBE E, et al. Cytosine base editing inhibits hepatitis B virus replication and reduces HBsAg expression in vitro and in vivo[J]. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2024, 35( 1): 102112. DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.102112. [35] MARTINEZ MG, COMBE E, INCHAUSPE A, et al. CRISPR-Cas9 targeting of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA generates transcriptionally active episomal variants[J]. mBio, 2022, 13( 2): e02888-21. DOI: 10.1128/mbio.02888-21. [36] KREBS K, BÖTTINGER N, HUANG LR, et al. T cells expressing a chimeric antigen receptor that binds hepatitis B virus envelope proteins control virus replication in mice[J]. Gastroenterology, 2013, 145( 2): 456- 465. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.04.047. [37] WISSKIRCHEN K, KAH J, MALO A, et al. T cell receptor grafting allows virological control of Hepatitis B virus infection[J]. J Clin Invest, 2019, 129( 7): 2932- 2945. DOI: 10.1172/JCI120228. [38] GUO GL, HE WH, ZHOU ZM, et al. PreS1- targeting chimeric antigen receptor T cells diminish HBV infection in liver humanized FRG mice[J]. Virology, 2023, 586: 23- 34. DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2023.06.015. [39] LIU ZY, LI GP, LI XR, et al. CD163 impairs HBV clearance in mice by regulating intrahepatic T cell immune response via an IL-10-dependent mechanism[J]. Antiviral Res, 2025, 235: 106093. DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2025.106093. [40] YANG SQ, WANG L, PAN W, et al. MMP2/MMP9-mediated CD100 shedding is crucial for inducing intrahepatic anti-HBV CD8 T cell responses and HBV clearance[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 71( 4): 685- 698. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.05.013. [41] SONG JJ, SUN XL, ZHOU Y, et al. Early application of IFNγ mediated the persistence of HBV in an HBV mouse model[J]. Antiviral Res, 2024, 225: 105872. DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.105872. [42] LI L, BARRY V, DAFFIS S, et al. Anti-HBV response to toll-like receptor 7 agonist GS-9620 is associated with intrahepatic aggregates of T cells and B cells[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 68( 5): 912- 921. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.12.008. [43] XU XS, SHANG QH, CHEN XY, et al. Reversal of B-cell hyperactivation and functional impairment is associated with HBsAg seroconversion in chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2015, 12( 3): 309- 316. DOI: 10.1038/cmi.2015.25. [44] van BUUREN N, RAMIREZ R, TURNER S, et al. Characterization of the liver immune microenvironment in liver biopsies from patients with chronic HBV infection[J]. JHEP Rep, 2022, 4( 1): 100388. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2021.100388. [45] GUIDOTTI LG, INVERSO D, SIRONI L, et al. Immunosurveillance of the liver by intravascular effector CD8+ T cells[J]. Cell, 2015, 161( 3): 486- 500. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.03.005. [46] VENZIN V, BECCARIA CG, PERUCCHINI C, et al. CD4+ T cells license Kupffer cells to reverse CD8+ T cell dysfunction induced by hepatocellular priming[J]. Nat Immunol, 2025, 26( 8): 1352- 1366. DOI: 10.1038/s41590-025-02199-3. [47] ZHOU ZM, LI C, TAN ZX, et al. A spatiotemporally controlled recombinant cccDNA mouse model for studying HBV and developing drugs against the virus[J]. Antiviral Res, 2023, 216: 105642. DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2023.105642. [48] XU ZC, ZHAO L, ZHONG YQ, et al. A novel mouse model harboring hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA[J]. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 13( 4): 1001- 1017. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2021.11.011. [49] YUEN MF, ASSELAH T, JACOBSON IM, et al. Efficacy and safety of the siRNA JNJ-73763989 and the capsid assembly modulator JNJ-56136379(bersacapavir) with nucleos(t)ide analogues for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection(REEF-1): A multicentre, double-blind, active-controlled, randomised, phase 2b trial[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 8( 9): 790- 802. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(23)00148-6. [50] YUEN MF, LIM SG, PLESNIAK R, et al. Efficacy and safety of bepirovirsen in chronic hepatitis B infection[J]. N Engl J Med, 2022, 387( 21): 1957- 1968. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2210027. -



 PDF下载 ( 852 KB)
PDF下载 ( 852 KB)

 下载:
下载:


