microRNA-223-3p靶向微管相关蛋白1B抑制肝星状细胞活化的机制研究
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.12.015
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:谢文涛负责实验操作,撰写论文;鱼康康负责课题设计,指导并修改论文;程琦负责指导实验,修改论文;李宁负责课题设计,指导撰写论文并定稿。
Mechanism of microRNA-223-3p inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation by targeting microtubule-associated protein 1B
-
摘要:
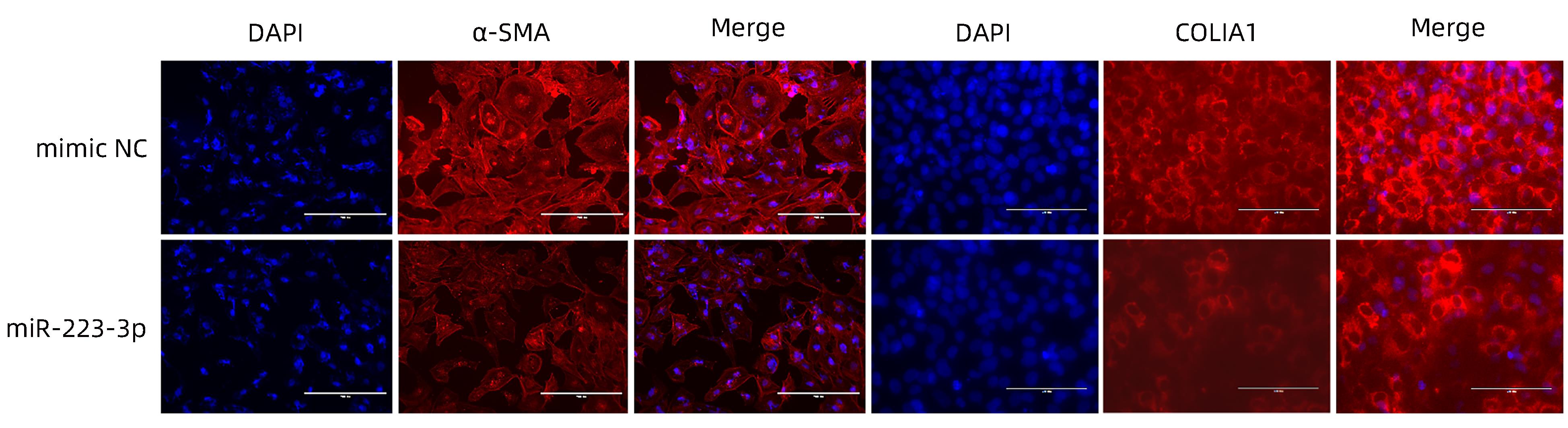
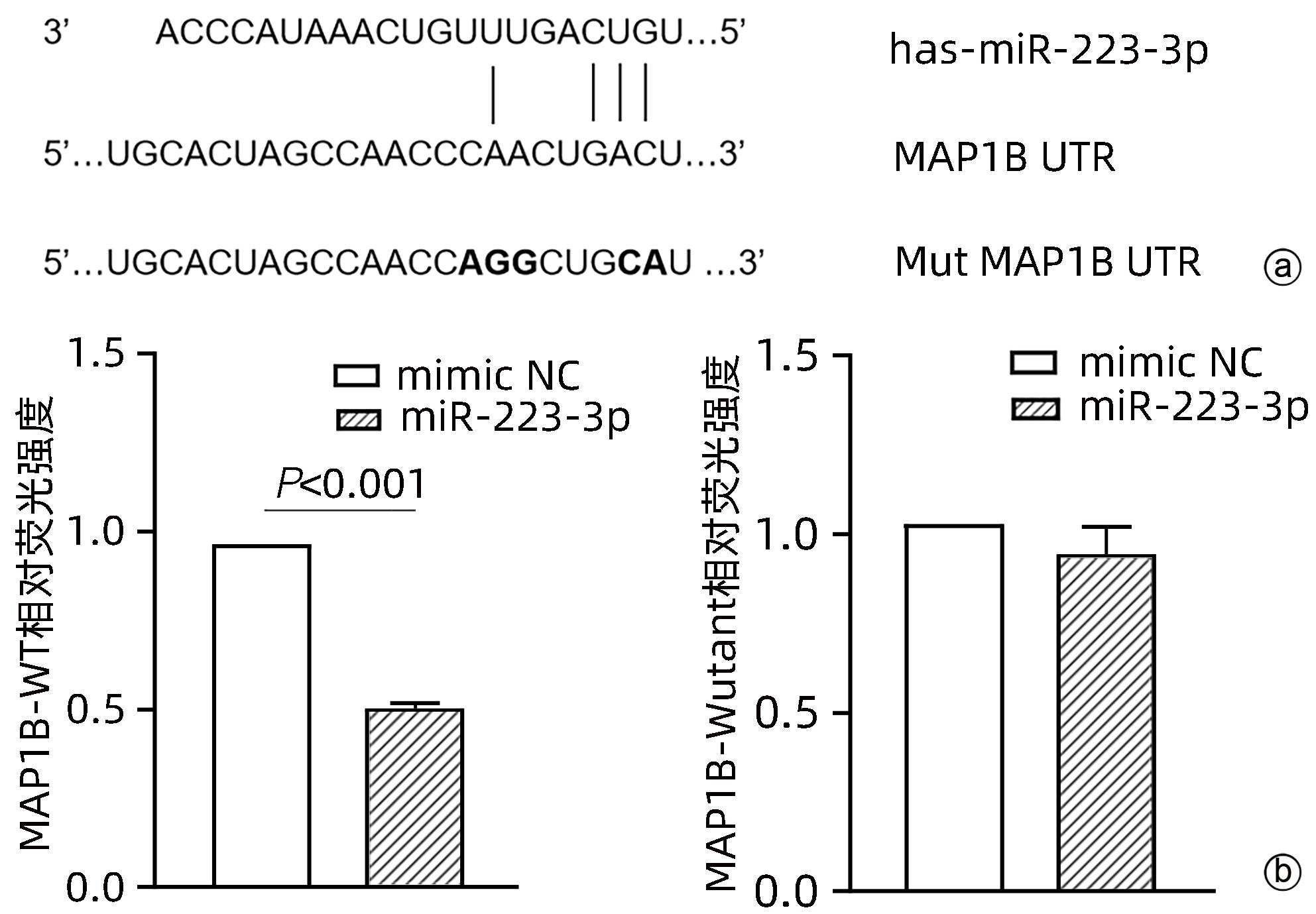
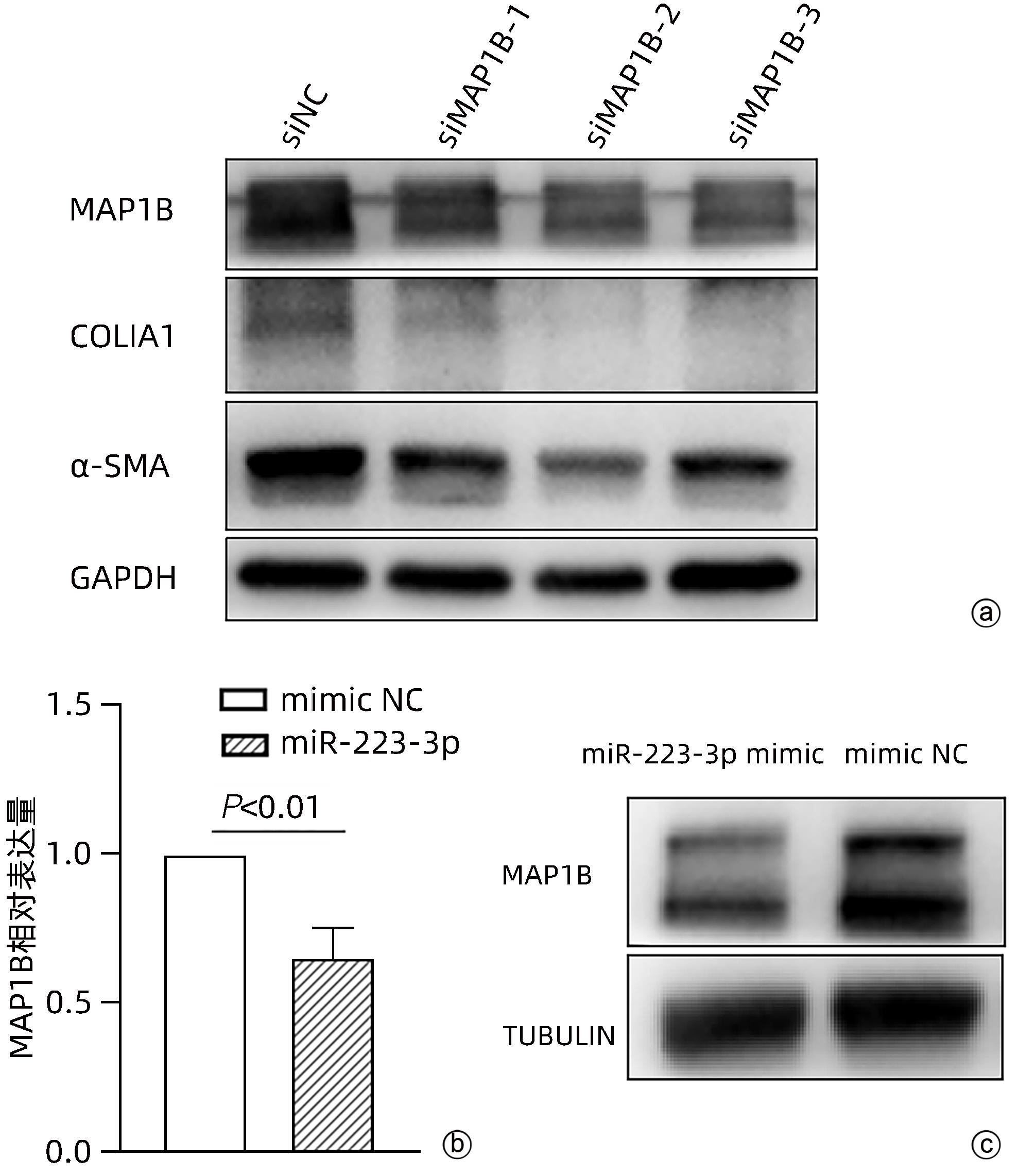
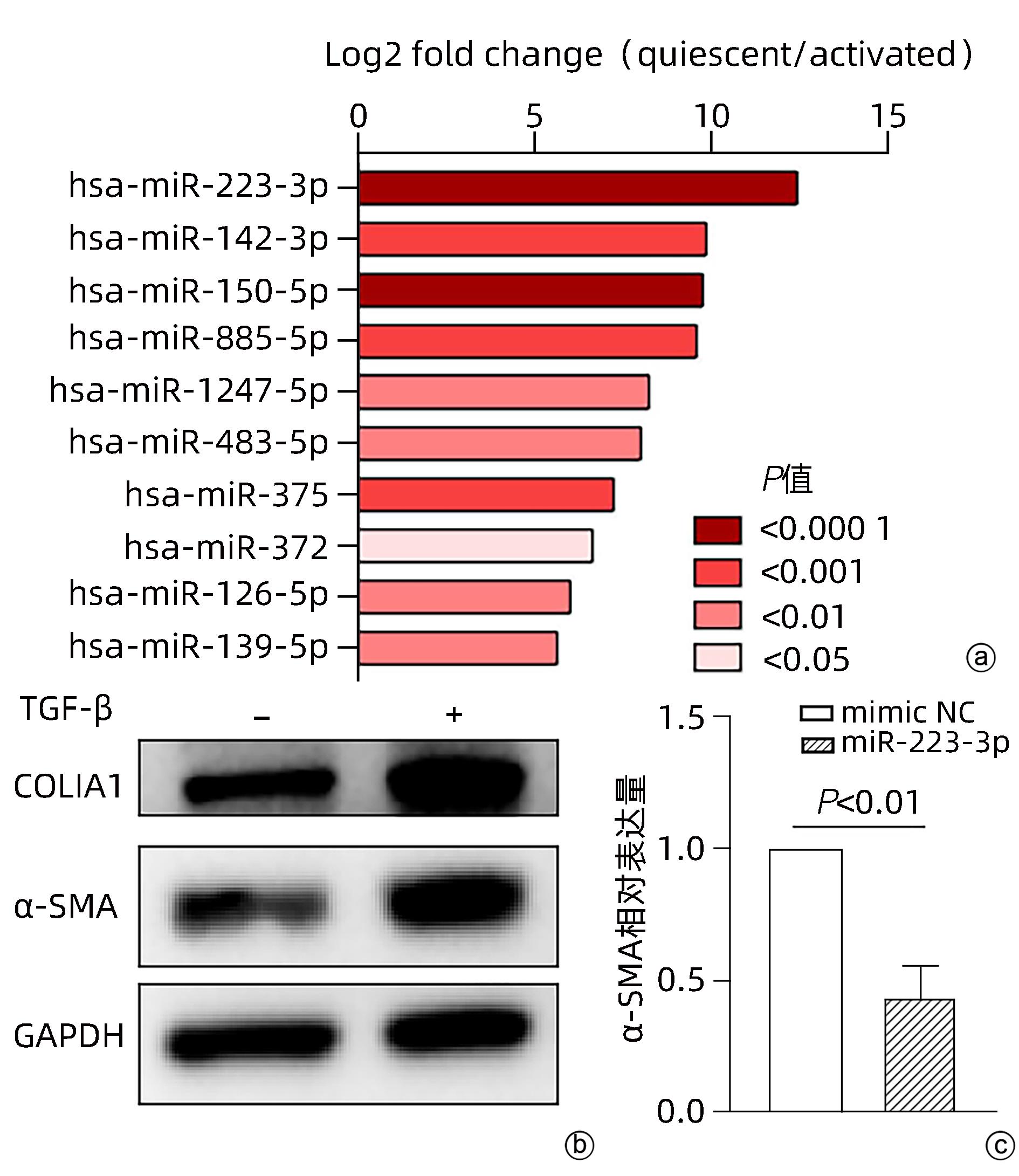
目的 探讨microRNA-223-3p (miR-223-3p)对肝星状细胞活化的影响及机制。 方法 选取人肝星状细胞系LX2细胞为研究对象,采用TGF-β刺激LX2细胞的方式构建肝星状细胞活化模型,通过实时荧光定量PCR检测miR-223-3p在肝星状细胞活化过程中表达水平变化;转染miR-223-3p mimic至LX2细胞,通过实时荧光定量PCR、蛋白免疫印迹法(Western Blot)及细胞免疫荧光明确miR-223-3p对肝星状细胞活化的调控作用;通过双荧光素酶报告基因实验验证miR-223-3p与靶基因MAP1B的关系;转染MAP1B的siRNA至LX2细胞,通过Western Blot明确抑制MAP1B表达对肝星状细胞活化的影响;转染miR-223-3p至LX2细胞,通过实时荧光定量PCR和Western Blot验证miR-223-3p对MAP1B的调控作用。计量资料两组间比较采用成组t检验。 结果 与静息状态相比,肝星状细胞处于活化状态时,miR-223-3p表达水平下降(t=9.12,P<0.001)。过表达miR-223-3p能抑制肝星状细胞活化标志物平滑肌肌动蛋白及Ⅰ型胶原的mRNA(t值分别为8.35、12.23,P值均<0.01)和蛋白(t值分别为16.24、20.90,P值均<0.001)表达水平。双荧光素酶报告基因实验证实MAP1B是miR-223-3p的潜在靶基因。与对照组相比,过表达miR-223-3p的LX2上MAP1B的mRNA表达(t=5.95,P<0.01)及蛋白表达(t=11.12,P<0.001)水平均显著降低。 结论 miR-223-3p可通过靶向MAP1B抑制肝星状细胞活化。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of microRNA-223-3p (miR-223-3p) on hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation and its mechanism. Methods Human HSC LX2 cells were selected for the study, and LX2 cells were stimulated by TGF-β to establish a model of HSC activation; quantitative real-time PCR was used to measure the change in the expression level of miR-223-3p during HSC activation. After LX2 cells were transfected with miR-223-3p mimic, quantitative real-time PCR, Western blot, and immunofluorescence assay were used to clarify the regulatory effect of miR-223-3p on HSC activation, and dual-luciferase reporter assay was used to verify the association between miR-223-3p and the target gene MAP1B. After LX2 cells were transfected with MAP1B siRNA, Western blot was used to clarify the influence of inhibiting MAP1B expression on HSC activation; after LX2 cells were transfected with miR-223-3p, quantitative real-time PCR and Western blot were used to verify the regulatory effect of miR-223-3p on MAP1B. The independent-samples t test was used for comparison of continuous data between two groups. Results HSC in the activated state had a significant reduction in the expression level of miR-223-3p compared with those in the resting state (t=9.12, P<0.001). Overexpression of miR-223-3p inhibited the mRNA and protein expression levels of the markers for HSC activation alpha-smooth muscle actin and collagen type Ⅰ (mRNA expression: t=8.35 and 12.23, both P<0.01; protein expression: t=16.24 and 20.90, both P<0.001). The dual-luciferase reporter assay confirmed that MAP1B was a potential target gene of miR-223-3p. Compared with the control group, LX2 cells with miR-223-3p overexpression had significant reductions in the mRNA and protein expression levels of MAP1B (mRNA expression: t=5.95, P<0.01; protein expression: t=11.12, P<0.001). Conclusion This study shows that miR-223-3p can inhibit HSC activation by targeting MAP1B. -
Key words:
- Hepatic Fibrosis /
- Microtubule-Associated Proteins /
- Hepatic Stellate Cells /
- MicroRNAs
-
-
[1] TRAUTWEIN C, FRIEDMAN SL, SCHUPPAN D, et al. Hepatic fibrosis: Concept to treatment[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 62( 1 Suppl): S15- S24. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.02.039. [2] WANG XL, HE Y, MACKOWIAK B, et al. microRNAs as regulators, biomarkers and therapeutic targets in liver diseases[J]. Gut, 2021, 70( 4): 784- 795. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322526. [3] BAO SX, ZHENG JM, LI N, et al. Serum microRNA levels as a noninvasive diagnostic biomarker for the early diagnosis of hepatitis B virus-related liver fibrosis[J]. Gut Liver, 2017, 11( 6): 860- 869. DOI: 10.5009/gnl16560. [4] TSUCHIDA T, FRIEDMAN SL. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 14( 7): 397- 411. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.38. [5] TRIVEDI P, WANG S, FRIEDMAN SL. The power of plasticity-metabolic regulation of hepatic stellate cells[J]. Cell Metab, 2021, 33( 2): 242- 257. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.10.026. [6] RODERBUG C, TRAUTWEIN C. Cell-specific functions of miRNA in the liver[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 66( 3): 655- 656. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.09.015. [7] HUANG C, ZHENG JM, CHENG Q, et al. Serum microRNA-29 levels correlate with disease progression in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J]. J Dig Dis, 2014, 15( 11): 614- 621. DOI: 10.1111/1751-2980.12185. [8] LAKNER AM, STEUERWALD NM, WALLING TL, et al. Inhibitory effects of microRNA 19b in hepatic stellate cell-mediated fibrogenesis[J]. Hepatology, 2012, 56( 1): 300- 310. DOI: 10.1002/hep.25613. [9] ZHANG R, LI WH, JIANG XD, et al. Ferulic acid combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells attenuates the activation of hepatic stellate cells and alleviates liver fibrosis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 863797. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.863797. [10] ZHANG J, JIAO JJ, CERMELLI S, et al. miR-21 inhibition reduces liver fibrosis and prevents tumor development by inducing apoptosis of CD24+ progenitor cells[J]. Cancer Res, 2015, 75( 9): 1859- 1867. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-1254. [11] DING RR, ZHENG JM, LI N, et al. DZNep, an inhibitor of the histone methyltransferase EZH2, suppresses hepatic fibrosis through regulating miR-199a-5p/SOCS7 pathway[J]. PeerJ, 2021, 9: e11374. DOI: 10.7717/peerj.11374. [12] OKSUZ Z, SERIN MS, KAPLAN E, et al. Serum microRNAs; miR-30c-5p, miR-223-3p, miR-302c-3p and miR-17-5p could be used as novel non-invasive biomarkers for HCV-positive cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2015, 42( 3): 713- 720. DOI: 10.1007/s11033-014-3819-9. [13] TESSEMA M, YINGLING CM, PICCHI MA, et al. Epigenetic repression of CCDC37 and MAP1B links chronic obstructive pulmonary disease to lung cancer[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2015, 10( 8): 1181- 1188. DOI: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000592. [14] ARASAKI K, NAGASHIMA H, KUROSAWA Y, et al. MAP1B-LC1 prevents autophagosome formation by linking syntaxin 17 to microtubules[J]. EMBO Rep, 2018, 19( 8): e45584. DOI: 10.15252/embr.201745584. [15] HERNANDEZ-GEA V, GHIASSI-NEJAD Z, ROZENFFLD R, et al. Autophagy releases lipid that promotes fibrogenesis by activated hepatic stellate cells in mice and in human tissues[J]. Gastroenterology, 2012, 142( 4): 938- 946. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.12.044. [16] TUOHETAHUNTIL M, MOLENAAR MR, SPEE B, et al. Lysosome-mediated degradation of a distinct pool of lipid droplets during hepatic stellate cell activation[J]. J Biol Chem, 2017, 292( 30): 12436- 12448. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.778472. -



 PDF下载 ( 1203 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1203 KB)

 下载:
下载: