大黄灵仙方对胆固醇结石豚鼠模型胆囊Cajal间质细胞中scf/c-kit信号通路的影响
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.02.019
Effect of Dahuang Lingxian prescription on the scf/c-kit signaling pathway in gallbladder interstitial cells of Cajal in a guinea pig model of cholesterol gallstone
-
摘要:
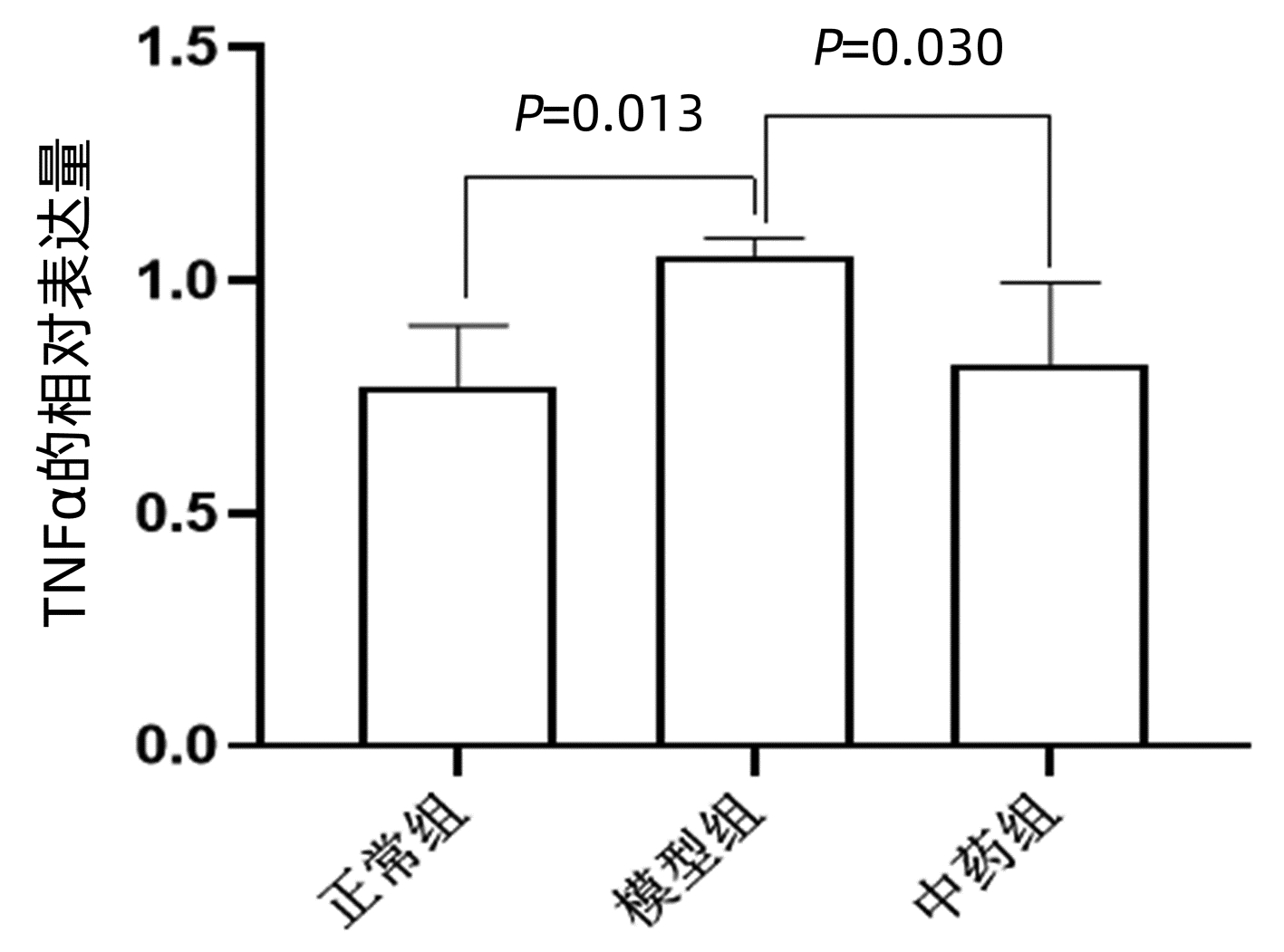
目的 观察在大黄灵仙方的调控下干细胞生长因子(scf)、酪氨酸激酶受体(c-kit)的表达水平,探讨其影响胆囊动力学改变的可能机制,为大黄灵仙方预防胆石症的发生及复发提供理论依据。 方法 将45只SPF级健康雄性豚鼠随机分为正常组、模型组、中药组,其中正常组予正常饲料喂养,模型组、中药组予高脂致石饲料喂养,喂养8周后分别从各组中随机抽取5只豚鼠,肉眼观察下结石形成超过4只,则判断为模型建立成功。造模成功后中药组予大黄灵仙方灌胃,模型组予等体积生理盐水灌胃,连续灌胃给药8周后取豚鼠胆囊组织,HE染色观察观察胆囊组织的病理学改变,Western blot测定胆囊组织中TNFα的表达水平,免疫组化测定胆囊平滑肌组织中scf、c-kit的蛋白表达水平。符合正态分布的计量资料多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,进一步两两比较采用LSD多重比较法。 结果 HE染色显示模型组胆囊组织炎症明显,中药组胆囊组织内炎症程度较模型组明显减轻。Western blot结果表明在模型组中,胆囊组织中TNFα的表达水平最高,中药组次之,正常组最低(P值均<0.05);免疫组化结果表明豚鼠胆囊平滑肌组织中scf、c-kit蛋白在正常组、中药组中的表达水平显著高于模型组(P值均<0.05)。 结论 大黄灵仙方能增强胆囊动力功能,其作用机制可能与上调胆囊Cajal间质细胞中的scf、c-kit信号通路有关。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the expression levels of scf and c-kit under the regulation of Dahuang Lingxian prescription and the possible mechanism of its effect on gallbladder dynamics, and to provide a theoretical basis for Dahuang Lingxian prescription in preventing the development and recurrence of cholesterol gallstone. Methods A total of 45 specific pathogen-free healthy male guinea pigs were randomly divided into normal group, model group, and traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) group. The guinea pigs in the normal group were fed with normal diet, and those in the model group and the TCM group were fed with high-fat lithogenic diet. After 8 weeks of feeding, 5 guinea pigs were randomly selected from each group, and successful modeling was determined if gallstone was observed with the naked eye in more than 4 guinea pigs. After successful modeling, the guinea pigs in the TCM group were given Dahuang Lingxian prescription by gavage, and those in the model group were given an equal volume of normal saline by gavage. After 8 consecutive weeks of administration by gavage, gallbladder tissue samples were collected, and HE staining was used to observe the pathological changes of gallbladder tissue; Western blot was used to measure the expression level of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in gallbladder tissue; immunohistochemistry was used to measure the protein expression levels of scf and c-kit in gallbladder smooth muscle tissue. A one-way analysis of variance was used for comparison of normally distributed continuous data between multiple groups, and the least significant difference multiple comparison method was used for further comparison between two groups. Results HE staining showed marked inflammation of gallbladder tissue in the model group, and compared with the model group, the TCM group had a significantly lower degree of inflammation. Western blot showed that the model group had the highest expression level of TNF-α in gallbladder tissue, followed by the TCM group and the normal group (P < 0.05); immunohistochemistry showed that compared with the model group, the normal group and the TCM group had significantly higher protein expression levels of scf and c-kit in gallbladder smooth muscle tissue (P < 0.05). Conclusion Dahuang Lingxian prescription can enhance the dynamic function of the gallbladder, possibly by upregulating the scf/c-kit signaling pathway in interstitial cells of Cajal in gallbladder. -
Key words:
- Dahuang Lingxian Formula /
- Gallstones /
- Interstitial Cells of Cajal /
- Signal Transduction /
- Guinea Pigs
-
抗病毒治疗是慢性乙型肝炎(CHB)的关键措施,其中恩替卡韦(ETV) 是治疗HBV的一线核苷(酸)类似物(NAs) 之一。尽管其他研究曾报道了长期ETV治疗CHB的疗效和安全性,但其在中国慢性CHB(主要为基因型B和C)患者中的临床数据仍然有限。
马来酸ETV是正大天晴药业股份有限公司开发的ETV衍生物,多中心、随机、双盲双模拟、阳性药物对照临床研究显示其治疗48周时与原研ETV在治疗CHB时等效,基于上述结果,国家食品药品管理局已经批准其上市。作为此项研究的主要研究者,北京大学第一医院于岩岩教授对其长期疗效和安全性进行了进一步研究:此前已经报告144周的马来酸ETV治疗中国慢性CHB(主要为基因型B和C)患者有效而且安全。更长疗程的药物治疗效果和安全性如何,尚无知晓。
2022年7月6日于岩岩教授团队在线发表研究论文,旨在更新马来酸ETV治疗中国患者240周疗程的病毒学、血清学和生化结果。CHB受试者被随机分配接受0.5 mg/d ETV(A组)或0.5 mg/d马来酸ETV(B组)治疗48周,此后所有受试者从第49周开始接受0.5 mg/d马来酸ETV治疗。定期对患者进行随访,监测血清HBV标志物、肝生化等指标,记录不良事件(AE)。主要终点是治疗结束时每组HBV DNA的下降。次要终点包括治疗结束时HBV DNA不可测(<20 IU/mL) 的比率、HBeAg消失率、HBeAg血清转化率和血清ALT复常率。137例(A组71例) HBeAg阳性CHB患者和46例(A组21例)HBeAg阴性CHB患者完成了240周的治疗和随访。两组的基线特征可比。在HBeAg阳性CHB组,240周时两组的HBV DNA较基线下降平均值可比(A:6.67 log10 IU/mL vs B:6.74 log10 IU/mL;P>0.05),血清HBV DNA不可测率(A:91.55% vs B:87.88%;P>0.05)、HBeAg血清学转换率(A:26.98% vs B:20.97%;P>0.05)和ALT复常率(A:87.32% vs B:83.61%;P>0.05)均在组间可比。在HBeAg阴性CHB组,240周时两组的HBV DNA较基线下降平均值可比(A:6.05 log10 IU/mL vs B:6.10 log10 IU/mL;P>0.05),血清HBV DNA不可测比例(A:100% vs B:100%)和ALT复常率(A:90.91% vs B:95.45%)(P>0.05)也可比。在耐药方面,HBeAg阴性CHB组耐药率为0;HBeAg阳性CHB组144周时耐药率1.16%,此后直至240周新增1例ETV耐药。安全性方面,没有因为AE导致停药,无肝癌或死亡病例。
总之,作为国产抗HBV药物代表之一的马来酸ETV,长期治疗中国CHB(主要是基因型B或C)是安全有效的。
摘译自XU JH, FAN YN, YU YY, et al. 240-week entecavir maleate treatment in Chinese chronic hepatitis B predominantly genotype B or C[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2022, 29(10): 862-867. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.13724.
(北京大学第一医院感染疾病科 徐京杭 报道)
-
表 1 大黄灵仙方对TNFα、scf、c-kit表达水平的影响
Table 1. Effect of Dahuang Lingxian formula on the expression of TNFα, scf and c-kit
组别 TNFα c-kit SCF 正常组 3.48±1.791)2) 29.35±8.971)2) 28.11±5.631)2) 模型组 26.42±3.87 13.32±2.01 15.46±3.14 中药组 17.35±2.751) 21.11±2.721) 23.08±6.411) F值 108.91 14.70 10.28 P值 <0.05 <0.05 <0.05 注:与模型组比较,1)P<0.05;与中药组比较,2)P<0.05。 -
[1] STINTON LM, SHAFFER EA. Epidemiology of gallbladder disease: cholelithiasis and cancer[J]. Gut Liver, 2012, 6(2): 172-187. DOI: 10.5009/gnl.2012.6.2.172. [2] SHABANZADEH DM. Incidence of gallstone disease and complications[J]. Curr Opin Gastroenterol, 2018, 34(2): 81-89. DOI: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000418. [3] LAMBERTS MP. Indications of cholecystectomy in gallstone disease[J]. Curr Opin Gastroenterol, 2018, 34(2): 97-102. DOI: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000419. [4] PENG YY, TAN YY. Analysis of the role of Cajal interstitial cells in the formation of gallstones[J]. Labeled Immunoassays Clin Med, 2016, 23(7): 817-819. DOI: 10.11748/bjmy.issn.1006-1703.2016.07.028.彭雅亚, 谭宇彦. Cajal间质细胞在胆囊结石形成中的作用分析[J]. 标记免疫分析与临床, 2016, 23(7): 817-819. DOI: 10.11748/bjmy.issn.1006-1703.2016.07.028. [5] ZHAO JN, FAN Y, WU SD. Advances in the relationship between Cajal-like interstitial cells of the gallbladder and cholesterol stone formation in the gallbladder[J]. Med Recapitulate, 2019, 25(21): 4180-4184, 4190. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2019.21.004.赵健楠, 范莹, 吴硕东. 胆囊Cajal样间质细胞与胆囊胆固醇结石形成关系的研究进展[J]. 医学综述, 2019, 25(21): 4180-4184, 4190. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2019.21.004. [6] XU JH, FAN Y. Effect of cholesterol on Cajal-like interstitial cells of guinea pig gallbladder isolated and cultured in vitro[J]. Chin J Clin Res, 2019, 32(11): 1457-1461. DOI: 10.13429/j.cnki.cjcr.2019.11.001.许金煌, 范莹. 胆固醇对体外分离培养的豚鼠胆囊Cajal样间质细胞的影响[J]. 中国临床研究, 2019, 32(11): 1457-1461. DOI: 10.13429/j.cnki.cjcr.2019.11.001. [7] YU Y, YIN X, TANG QL, et al. Study on the regulation of NF-κB signaling pathway-related factor genes by Dahuang Lingxian formula to affect the inflammatory response of bile duct cells[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2020, 31(5): 1034-1037. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2020.05.003.俞渊, 尹星, 唐乾利, 等. 大黄灵仙方调控NF-κB信号通路相关因子基因影响胆管细胞炎性反应的研究[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2020, 3(5): 1034-1037. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2020.05.003. [8] WANG QJ, TANG QL, YU Y, et al. Dahuang Lingxian formula capsule regulates TGF-β1 mRNA and Smad2 in bile duct endothelial cells[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2014, 25(12): 2833-2835. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2014.12.006.王清坚, 唐乾利, 俞渊, 等. 大黄灵仙胶囊调节胆管内皮细胞TGF-β1mRNA、Smad2/3mRNA表达的实验研究[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2014, 25(12): 2833-2835. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2014.12.006. [9] FENG H, WANG F, WANG C. C-Kit expression in the gallbladder of guinea pig with chronic calculous cholecystitis and the effect of Artemisia capillaris Thunb on interstitial cells of Cajal[J]. Iran J Basic Med Sci, 2016, 19(7): 720-725. [10] CHEN Q. Experimental methodology of Chinese pharmacology[M]. Beijing: People's Health Publishing House, 1994: 215.陈奇. 中药药理学实验方法学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 1994: 215. [11] ANSTÖTZ M, LEE SK, NEBLETT TI, et al. Experience-dependent regulation of Cajal-retzius cell networks in the developing and adult mouse hippocampus[J]. Cereb Cortex, 2018, 28(2): 672-687. DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhx153. [12] ORTIZ-HIDALGO C, de LEON BOJORGE B, ALBORES-SAAVEDRA J. Stromal tumor of the gallbladder with phenotype of interstitial cells of Cajal: a previously unrecognized neoplasm[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2000, 24(10): 1420-1423. DOI: 10.1097/00000478-200010000-00013. [13] LAVOIE B, BALEMBA OB, NELSON MT, et al. Morphological and physiological evidence for interstitial cell of Cajal-like cells in the guinea pig gallbladder[J]. J Physiol, 2007, 579(Pt 2): 487-501. DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.122861. [14] PASTERNAK A, GAJDA M, GIL K, et al. Evidence of interstitial Cajal-like cells in human gallbladder[J]. Folia Histochem Cytobiol, 2012, 50(4): 581-585. DOI: 10.5603/19673. [15] CHEN L, YU B. Telocytes and interstitial cells of Cajal in the biliary system[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2018, 22(7): 3323-3329. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13643. [16] FAUSSONE-PELLEGRINI MS, VANNUCCHI MG, LEDDER O, et al. Plasticity of interstitial cells of Cajal: a study of mouse colon[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2006, 325(2): 211-217. DOI: 10.1007/s00441-006-0174-8. [17] MEI F, HAN J, HUANG Y, et al. Plasticity of interstitial cells of cajal: a study in the small intestine of adult Guinea pigs[J]. Anat Rec (Hoboken), 2009, 292(7): 985-993. DOI: 10.1002/ar.20928. [18] TORIHASHI S, NISHI K, TOKUTOMI Y, et al. Blockade of kit signaling induces transdifferentiation of interstitial cells of cajal to a smooth muscle phenotype[J]. Gastroenterology, 1999, 117(1): 140-148. DOI: 10.1016/s0016-5085(99)70560-3. [19] MEI F, ZHU J, GUO S, et al. An age-dependent proliferation is involved in the postnatal development of interstitial cells of Cajal in the small intestine of mice[J]. Histochem Cell Biol, 2009, 131(1): 43-53. DOI: 10.1007/s00418-008-0515-7. [20] HUIZINGA JD, THUNEBERG L, KLVPPEL M, et al. W/kit gene required for interstitial cells of Cajal and for intestinal pacemaker activity[J]. Nature, 1995, 373(6512): 347-349. DOI: 10.1038/373347a0. [21] ISOZAKI K, HIROTA S, NAKAMA A, et al. Disturbed intestinal movement, bile reflux to the stomach, and deficiency of c-kit-expressing cells in Ws/Ws mutant rats[J]. Gastroenterology, 1995, 109(2): 456-464. DOI: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90333-x. [22] ISOZAKI K, HIROTA S. Gain-of-function mutations of receptor tyrosine kinases in gastrointestinal stromal tumors[J]. Curr Genomics, 2006, 7(8): 469-475. DOI: 10.2174/138920206779315755. [23] MA WW, LI CQ, YU HL, et al. The oxysterol 27-hydroxycholesterol increases oxidative stress and regulate Nrf2 signaling pathway in astrocyte cells[J]. Neurochem Res, 2015, 40(4): 758-766. DOI: 10.1007/s11064-015-1524-2. [24] CHUA NK, COATES HW, BROWN AJ. Cholesterol, cancer, and rebooting a treatment for athlete's foot[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2018, 10(437): eaat3741. DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aat3741. [25] WAN JF, CHU SF, ZHOU X, et al. Ursodeoxycholic acid protects interstitial Cajal-like cells in the gallbladder from undergoing apoptosis by inhibiting TNF-α expression[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2018, 39(9): 1493-1500. DOI: 10.1038/aps.2017.206. 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 向文耀,李仕雄,吕日英. 恩替卡韦治疗后慢性乙型肝炎低病毒血症患者序贯联合艾米替诺福韦治疗的效果研究. 中国现代医学杂志. 2024(08): 15-20 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(1)
-




 PDF下载 ( 3342 KB)
PDF下载 ( 3342 KB)

 下载:
下载:



 百度学术
百度学术

