环状RNA hsa_circ_0091579对肝癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭的影响
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.05.029
Effect of circRNA hsa_circ_0091579 on the proliferation, migration, and invasion of hepatoma cells
-
摘要:
目的 探究环状RNA(circRNA)hsa_circ_0091579在肝细胞癌(HCC)细胞系中的表达及其对HCC细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭的影响。 方法 体外培养人肝癌细胞系SMMC-7721、HuH-7、MHCC-97H、HepG2和人正常肝细胞系HL-7702。从细胞中提取RNA,用实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)检测hsa_circ_0091579在HCC细胞系及人正常肝细胞系中的表达,并进行对比。针对hsa_circ_0091579的环化拼接位点设计siRNA,在体外HepG2和HuH-7细胞中转染hsa_circ_0091579 siRNA,并用qRT-PCR验证其有效性。实验分为siRNA组(hsa_circ_0091579 siRNA)和NC组(negative control siRNA),并在HepG2和HuH-7细胞中用CCK8实验、流式细胞术、划痕实验以及Transwell实验分别研究hsa_circ_0091579对细胞增殖、凋亡、迁移和侵袭的影响。使用双荧光素酶报告基因实验对预测的靶点进行验证。计量资料两组间比较采用t检验。 结果 与hsa_circ_0091579在人正常肝细胞系HL-7702中的表达水平相比,其在HCC细胞系SMMC-7721、HuH-7、MHCC-97H、HepG2中的表达水平均明显升高(t值分别为14.27、36.34、26.70、36.16,P值均 < 0.001)。与NC组相比,hsa_circ_0091579 siRNA可在HepG2和HuH-7细胞中有效沉默hsa_circ_0091579(t值分别为14.22、27.20,P值分别为0.005、0.001)。CCK8实验和流式细胞术结果显示,与NC组相比,siRNA组HepG2和HuH-7细胞的增殖活性明显降低,凋亡率明显升高,差异均有统计学意义(P值均 < 0.05);划痕实验和Transwell实验显示,与NC组相比,siRNA组HepG2和HuH-7细胞的迁移和侵袭能力明显减弱(t值分别为19.63、13.61、20.75、18.45,P值分别为0.003、0.005、0.002、0.003)。荧光素酶报告基因实验结果显示,与NC组相比,miR-149、miR-490-5p和miR-502-5p均能明显降低野生型荧光素酶质粒的活性(t值分别为10.01、9.13、61.49,P值分别为0.010、0.012、 < 0.001)。 结论 hsa_circ_0091579在HCC细胞系中高表达,可能通过抑制miR-149、miR-490-5p和miR-502-5p发挥其癌基因的作用。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the expression of circular RNA (cirRNA) hsa_circ_0091579 in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lines and its effect on the proliferation, migration, and invasion of HCC cells. Methods Human HCC cell lines SMMC-7721, Huh-7, MHCC-97H, and HepG2 and normal human liver cell line HL-7702 were cultured in vitro. RNA was extracted from cells and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to measure the expression of hsa_circ_0091579 in HCC cell lines and normal human liver cell line. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) was designed for the cyclic splicing site of hsa_circ_0091579, and HepG2 and Huh-7 cells were transfected with hsa_circ_0091579 siRNA in vitro; qRT-PCR was used to verify transfection efficiency. The experiment was divided into siRNA group (transfected with hsa_circ_0091579 siRNA) and NC group (transfected with negative control siRNA), and CCK-8 assay, flow cytometry, wound healing assay, and Transwell assay were used to investigate the effect of hsa_circ_0091579 on cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion in HepG2 and Huh-7 cells. Dual luciferase reporter gene assay was used to verify the predicted target. The t-test was used for comparison of continuous data between the two groups. Results Compared with the normal human liver cell line HL-7702, the HCC cell lines SMMC-7721, Huh-7, MHCC-97H, and HepG2 had a significant increase in the expression level of hsa_circ_0091579 (t=14.27, 36.34, 26.70, and 36.16, all P < 0.001). Compared with the NC group, hsa_circ_0091579 siRNA effectively silenced hsa_circ_0091579 in HepG2 and Huh-7 cells (t=14.22 and 27.20, P=0.005 and 0.001). CCK-8 assay and flow cytometry showed that compared with the NC group, the siRNA group had a significant reduction in the proliferative activity of HepG2 and Huh-7 cells and a significant increase in apoptosis rate (all P < 0.05); wound healing assay and Transwell assay showed that compared with the NC group, the siRNA group had significant reductions in the migration and invasion abilities of HepG2 and Huh-7 cells (t=19.63, 13.61, 20.75, and 18.45, P=0.003, 0.005, 0.002, and 0.003). Luciferase reporter assay showed that compared with the NC group, miR-149, miR-490-5p, and miR-502-5p significantly reduced the activity of wild-type luciferase plasmids (t=10.01, 9.13, and 61.49, P=0.010, P=0.012, and P < 0.001). Conclusion Hsa_circ_0091579 is highly expressed in HCC cell lines and may play the role of oncogene by inhibiting miR-149, miR-490-5p, and miR-502-5p. -
Key words:
- Carcinoma, Hepatocellular /
- DNA, Circular /
- Cell Physiological Phenomena
-
肝细胞癌(HCC)是一种常见的恶性肿瘤,位居全球第三大癌症相关死亡原因[1],具有侵袭性、预后差、治疗机会有限的临床特点。目前,手术是HCC最常见的治疗方式,但很多HCC发现时已是晚期,无法进行手术切除,导致患者预后很差[2]。因此,进一步了解HCC进展的分子机制,寻找有效的治疗靶点具有重要意义。
越来越多的证据[3-4]表明,环状RNA(circular RNA,circRNA)失调在多种肿瘤的发生和发展中发挥重要作用。circRNA是一类内源性非编码RNA,具有高度保守性;与线性RNA相比,它具有共价闭合环结构,因而比较稳定且不易被RNA外切酶降解[5-6]。circRNAs广泛存在于真核生物体内,具有基因调控潜能,从而参与了增殖、侵袭、迁移、自噬、凋亡和代谢等多种细胞生物学进程[7-9]。据报道[10-11],circRNAs在很多疾病中异常表达,参与了这些疾病的进展,并与预后密切相关。随着高通量测序和生物信息学的发展,许多circRNAs被发现在HCC中异常表达,可作为HCC的生物学标志物,并参与了HCC的发生与发展[12-14]。
Zhang等[15]研究发现,hsa_circ_0091579可能在HCC进展中起到关键作用,并可能作为HCC患者预后的潜在生物标志物。然而,在HCC中,并无hsa_circ_0091579相关功能及机制研究。因此,本研究在HCC细胞系中检测hsa_circ_0091579的表达,并探索其对HCC细胞增殖和迁移的影响。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 细胞培养及转染
体外培养购买于ATCC公司的人HCC细胞系SMMC-7721、HuH-7、MHCC-97H、HepG2和人正常肝细胞系HL-7702。培养基为含10%胎牛血清(Gibco,USA)的DMEM高糖培养基(Gibco)。培养于37 ℃、5% CO2的环境中。采用Lipofectamine 3000试剂(Invitrogen,USA)将hsa_circ_0091579 siRNA及阴性对照(negative control,NC)转染入细胞内,使用实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)评估转染效率。
1.2 RNA提取及qRT-PCR
根据说明书,使用Trizol试剂(Invitrogen)从细胞中提取总RNA,并使用分光光度计测定RNA的纯度和浓度。取1 μg总RNA,采用PrimeScript-RT试剂盒(Takara Bio,Japan)将RNA逆转录成cDNA。以DNA为模板,使用SYBR Select Master Mix试剂盒(Applied Biosystems,USA)及ABI Prism 7900检测系统(Applied Biosystems)进行qRT-PCR反应。hsa_circ_0091579的表达以GAPDH为内参,采用2-△△Ct法计算相对表达量。
1.3 CCK8细胞增殖实验
细胞增殖能力采用CCK-8实验进行分析。细胞以5×103/孔的密度接种于96孔板,并转染siRNA,在37 ℃、5% CO2的环境中培养。转染24、48或72 h后,将10 μl CCK-8试剂(Transgen Biotech,USA)添加至每个孔中,并在37 ℃下孵育1 h。根据说明书在450 nm波长下测量吸光度。
1.4 细胞凋亡实验
细胞凋亡采用流式细胞术进行分析。将细胞接种于培养板中,培养24 h后进行转染。转染48 h后收集细胞,用PBS洗涤,并使用Annexin V-FITC/PI凋亡检测试剂盒(Solarbio)对细胞进行双重染色,用FlowJo软件分析细胞凋亡率。
1.5 细胞迁移实验
通过细胞划痕实验研究细胞迁移能力。将细胞接种于6孔板,培养24 h后进行转染。用10 μl无菌吸头尖划伤单层细胞制造划痕,用PBS洗涤细胞3次以冲掉划下的细胞。加入无血清的DMEM高糖培养基置于细胞培养箱中继续培养24 h。使用光学显微镜对0 h和24 h的划痕进行拍照记录,计算细胞迁移率。
1.6 细胞侵袭实验
使用Transwell小室(Thermo Fisher Scientific)研究细胞侵袭能力。转染后的细胞消化并用无血清的DMEM培养基重悬,添加到涂有基质胶的Transwell上室,下室加入含有10%血清的DMEM培养基。小室置于细胞培养箱中培养24 h后,轻轻去除膜上的细胞,膜下的细胞用甲醇固定,结晶紫染色并计数。
1.7 靶点预测及荧光素酶报告基因实验
使用Circular RNA Interactome (https://circinteractome.nia.nih.gov/index.html)数据库对hsa_circ_0091579的靶microRNA(miRNA)进行预测。利用pmirGLO载体(Promega)分别构建野生型(wt)和突变型(mut)荧光素酶报告基因质粒。将荧光素酶报告基因质粒和miRNA mimics共转染入HepG2细胞,用双荧光素酶报告基因系统(Promega)测定荧光素酶活性。
1.8 统计学方法
采用SPSS 20.0进行统计分析。所有实验均至少重复3次,计量资料以x±s表示,两组间比较采用t检验。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 hsa_circ_0091579在HCC细胞系中的表达
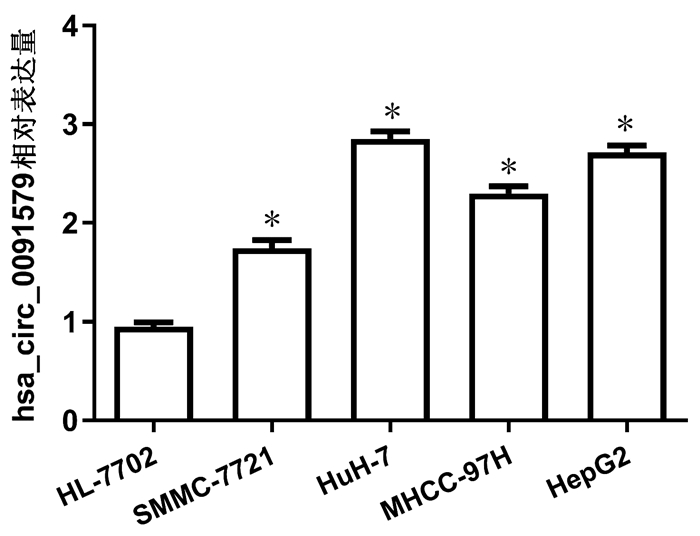
通过qRT-PCR检测了人HCC细胞系和人正常肝细胞系中hsa_circ_0091579的表达情况,并进行了对比。结果显示,人HCC细胞系SMMC-7721、HuH-7、MHCC-97H、HepG2中hsa_circ_0091579的表达水平明显高于人正常肝细胞系HL-7702,差异均有统计学意义(t值分别为14.27、36.34、26.70、36.16,P值均 < 0.001)(图 1)。
2.2 hsa_circ_0091579 siRNA设计及转染
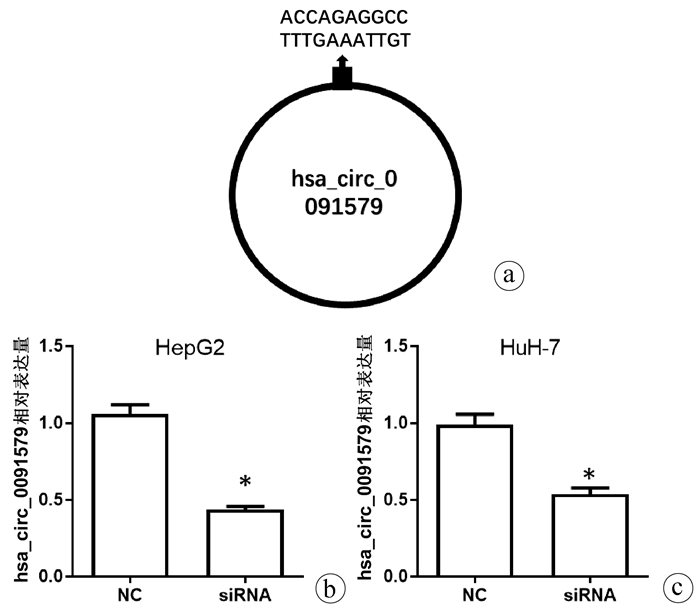
针对hsa_circ_0091579的环化拼接位点设计siRNA,siRNA靶序列为ACCAGAGGCCTTTGAAATTGT(图 2a),qRT-PCR结果显示,在HepG2和HuH-7细胞中转染hsa_circ_0091579 siRNA能够明显降低hsa_circ_0091579的表达水平(t值分别为14.22、27.20,P值分别为0.005、0.001)(图 2b)。
2.3 沉默hsa_circ_0091579对HCC细胞增殖和凋亡的影响
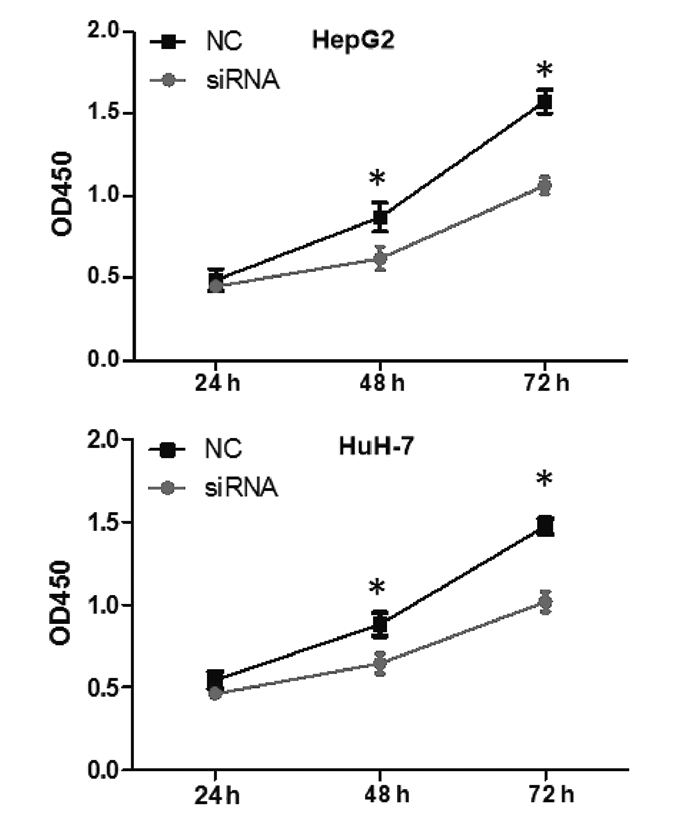
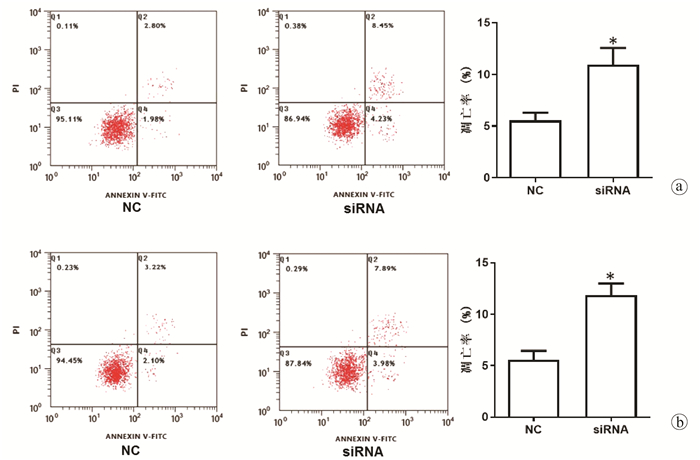
在HepG2和HuH-7细胞中转染hsa_circ_0091579 siRNA,CCK8实验和流式细胞术结果显示,与NC组相比,沉默hsa_circ_0091579能够在48 h和72 h明显抑制HepG2和HuH-7细胞的增殖活性(P值均 < 0.05)(图 3),并能够明显加速HepG2和HuH-7细胞的凋亡(t值分别为9.50、25.89,P值分别为0.011、0.002)(图 4)。
2.4 沉默hsa_circ_0091579对HCC细胞迁移和侵袭的影响
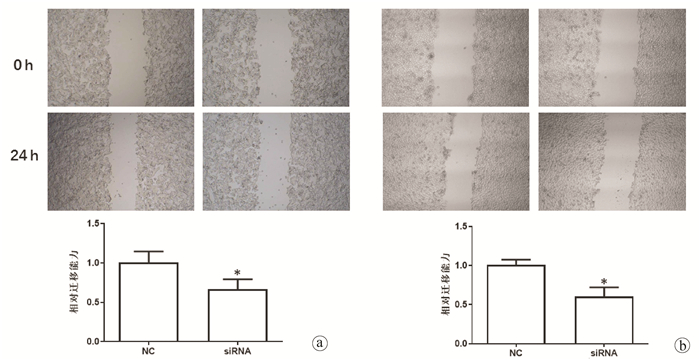
划痕实验和Transwell实验结果显示,与NC组相比,沉默hsa_circ_0091579能够明显抑制HepG2和HuH-7细胞的迁移和侵袭能力(t值分别为19.63、13.61、20.75、18.45,P值分别为0.003、0.005、0.002、0.003)(图 5、6)。
2.5 hsa_circ_0091579靶miRNAs预测及验证
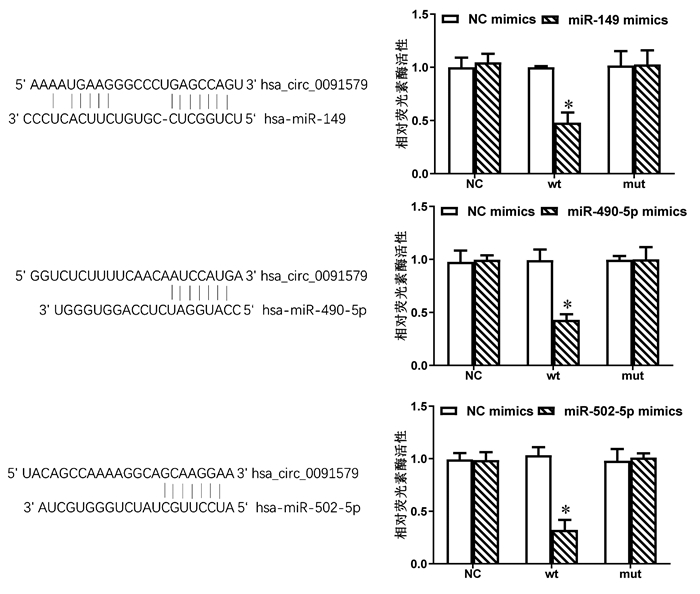
通过Circular RNA Interactome数据库,发现miR-149、miR-490-5p和miR-502-5p可能是hsa_circ_0091579的靶miRNAs。荧光素酶报告基因实验结果显示,与NC组相比,miR-149、miR-490-5p和miR-502-5p均能明显降低野生型荧光素酶质粒的活性(t值分别为10.01、9.13、61.49,P值分别为0.010、0.012、 < 0.001)(图 7)。
3. 讨论
到目前为止,HCC进展的机制仍不清楚,然而,越来越多的证据[16-17]表明,HCC的发生可能是由HBV感染、癌基因激活、抑癌基因失活所引起。近年来,非编码RNA已成为肝癌研究的热点。一些研究[18-19]已表明肿瘤特异性非编码RNA可以应用于生存预测和治疗干预。部分异常调控的miRNAs和长链非编码RNA(long non- coding RNAs, lncRNAs)是HCC耐药性形成的重要调节因子,肿瘤特异性miRNAs和lncRNAs可作为HCC新的治疗靶点和预后标志物[20]。
在与HCC相关的非编码RNA中,circRNA日益受到关注[21-22]。例如,异常表达circRNAs可用于区分HCC和健康人群,预测患者预后,并与肿瘤大小、分化程度、微血管浸润、转移、TNM分期及甲胎蛋白水平等临床因素密切相关,提示异常表达的circRNAs可作为一种新的HCC诊断和预后的无创生物标志物[23]。circABCB10在HCC组织和细胞系中的表达明显增加,并通过调节miR-670-3p/HMG20A轴促进HCC的进展,可能是HCC的潜在治疗靶点[24]。circ-0003418在HCC组织和细胞株表达下调,具有抗肝癌作用,通过抑制Wnt/β-catenin途径促进HCC细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭,并提高HCC细胞对顺铂的敏感性[25]。
本研究选取了hsa_circ_0091579作为研究对象。2018年,Zhang等[15]使用circRNA微阵列分析检测了3例HCC伴癌栓患者肿瘤组织和配对正常肝组织中circRNA的表达谱,发现hsa_circ_0091579在癌组织中高表达;随后他们用qRT-PCR在75对肿瘤组织和配对正常肝组织中进行了验证,并进一步发现hsa_circ_0091579的高表达与HCC患者总体生存率差密切相关;但他们并没有对hsa_circ_0091579在HCC细胞系中的表达和功能做进一步研究。在此基础上,笔者推测hsa_circ_0091579可能在HCC的发生和进展过程中发挥重要的作用,因而做了进一步探索。本研究结果显示,hsa_circ_0091579在HCC细胞系中同样高表达,这与其在人体组织中的高表达相符。进一步的功能实验表明,在体外通过siRNA沉默hsa_circ_0091579后,HCC细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭活性明显降低,凋亡明显加快。因此,笔者认为hsa_circ_0091579可发挥癌基因的作用促进HCC进展,此结果也可解释Zhang等[15]研究所报道的hsa_circ_0091579高表达能够影响HCC患者生存率。
在多种癌症中,circRNAs发挥其功能的一个重要机制是靶向结合部分肿瘤相关miRNAs,并抑制这些miRNAs的功能[26]。本研究中,通过生物信息学预测发现miR-149、miR-490-5p和miR-502-5p可能是hsa_circ_0091579的靶miRNAs,并通过荧光素酶报告基因实验进行了验证。已有研究[27-29]证实miR-149、miR-490-5p和miR-502-5p在HCC中发挥抑癌基因的作用,抑制肿瘤进展。因此,笔者认为hsa_circ_0091579可能通过抑制上述具有抑癌作用的miRNAs发挥其癌基因的作用。
综上,本研究结果表明,hsa_circ_0091579在HCC细胞系中高表达;在体外HCC细胞系中沉默hsa_circ_0091579能够抑制HCC细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭。hsa_circ_0091579可能通过抑制miR-149、miR-490-5p和miR-502-5p发挥癌基因的作用,其有希望成为有效的临床治疗靶点用于HCC的治疗。
-
-
[1] CRAIG AJ, von FELDEN J, GARCIA-LEZANA T, et al. Tumour evolution in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 17(3): 139-152. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-019-0229-4. [2] CHEN F, FANG Y, ZHAO R, et al. Evolution in medicinal chemistry of sorafenib derivatives for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Eur J Med Chem, 2019, 179: 916-935. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.06.070. [3] QIU M, XIA W, CHEN R, et al. The circular RNA circPRKCI promotes tumor growth in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Cancer Res, 2018, 78(11): 2839-2851. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-2808. [4] TAN S, GOU Q, PU W, et al. Circular RNA F-circEA produced from EML4-ALK fusion gene as a novel liquid biopsy biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Cell Res, 2018, 28(6): 693-695. DOI: 10.1038/s41422-018-0033-7. [5] JECK WR, SHARPLESS NE. Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs[J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2014, 32(5): 453-461. DOI: 10.1038/nbt.2890. [6] MEMCZAK S, JENS M, ELEFSINIOTI A, et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency[J]. Nature, 2013, 495(7441): 333-338. DOI: 10.1038/nature11928. [7] TANG Q, HANN SS. Biological roles and mechanisms of circular RNA in human cancers[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2020, 13: 2067-2092. DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S233672. [8] LI J, SUN D, PU W, et al. Circular RNAs in cancer: Biogenesis, function, and clinical significance[J]. Trends Cancer, 2020, 6(4): 319-336. DOI: 10.1016/j.trecan.2020.01.012. [9] HUANG A, ZHENG H, WU Z, et al. Circular RNA-protein interactions: Functions, mechanisms, and identification[J]. Theranostics, 2020, 10(8): 3503-3517. DOI: 10.7150/thno.42174. [10] HAN B, CHAO J, YAO H. Circular RNA and its mechanisms in disease: From the bench to the clinic[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2018, 187: 31-44. DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.01.010. [11] ZHANG TR, HUANG WQ. Angiogenic circular RNAs: A new landscape in cardiovascular diseases[J]. Microvasc Res, 2020, 129: 103983. DOI: 10.1016/j.mvr.2020.103983. [12] XIONG DD, FENG ZB, LAI ZF, et al. High throughput circRNA sequencing analysis reveals novel insights into the mechanism of nitidine chloride against hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2019, 10(9): 658. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-019-1890-9. [13] ZOU H, XU X, LUO L, et al. Hsa_circ_0101432 promotes the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by adsorbing miR-1258 and miR-622[J]. Cell Cycle, 2019, 18(19): 2398-2413. DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1618120. [14] WEI X, ZHENG W, TIAN P, et al. Oncogenic hsa_circ_0091581 promotes the malignancy of HCC cell through blocking miR-526b from degrading c-MYC mRNA[J]. Cell Cycle, 2020, 19(7): 817-824. DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1731945. [15] ZHANG C, ZHANG C, LIN J, et al. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0091579 serves as a diagnostic and prognostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 51(1): 290-300. DOI: 10.1159/000495230. [16] ZUO Q, HE J, ZHANG S, et al. PPARγ coactivator-1α suppresses metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting Warburg effect by PPARγ-dependent WNT/β-catenin/pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isozyme 1 axis[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 73(2): 644-660. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31280. [17] CHATURVEDI VK, SINGH A, DUBEY SK, et al. Molecular mechanistic insight of hepatitis B virus mediated hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Microb Pathog, 2019, 128: 184-194. DOI: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.01.004. [18] XIONG DD, DANG YW, LIN P, et al. A circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network identification for exploring underlying pathogenesis and therapy strategy of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Transl Med, 2018, 16(1): 220. DOI: 10.1186/s12967-018-1593-5. [19] O'BRIEN A, ZHOU T, TAN C, et al. Role of non-coding RNAs in the progression of liver cancer: Evidence from experimental models[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2019, 11(11): 1652. DOI: 10.3390/cancers11111652. [20] WEI L, WANG X, LV L, et al. The emerging role of microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 147. DOI: 10.1186/s12943-019-1086-z. [21] QIU L, XU H, JI M, et al. Circular RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: Biomarkers, functions and mechanisms[J]. Life Sci, 2019, 231: 116660. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116660. [22] QIU LP, WU YH, YU XF, et al. The emerging role of circular RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Cancer, 2018, 9(9): 1548-1559. DOI: 10.7150/jca.24566. [23] JIANG YL, SHANG MM, DONG SZ, et al. Abnormally expressed circular RNAs as novel non-invasive biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis[J]. World J Gastrointest Oncol, 2019, 11(10): 909-924. DOI: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i10.909. [24] FU Y, CAI L, LEI X, et al. Circular RNA ABCB10 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by increasing HMG20A expression by sponging miR-670-3p[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2019, 19: 338. DOI: 10.1186/s12935-019-1055-z. [25] CHEN H, LIU S, LI M, et al. circ_0003418 inhibits tumorigenesis and cisplatin chemoresistance through Wnt/β-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2019, 12: 9539-9549. DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S229507. [26] GURIA A, SHARMA P, NATESAN S, et al. Circular RNAs-the road less traveled[J]. Front Mol Biosci, 2019, 6: 146. DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2019.00146. [27] CHENG JL, LI DJ, LV MY, et al. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 regulates the invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma by acting on S1PR1 through miR-149[J]. Cancer Gene Ther, 2020. DOI:10.1038/s41417-020-0203-x. [Online ahead of print] [28] CHEN W, YE L, WEN D, et al. MiR-490-5p inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion by directly regulating ROBO1[J]. Pathol Oncol Res, 2019, 25(1): 1-9. DOI: 10.1007/s12253-017-0305-4. [29] CHEN S, LI F, CHAI H, et al. miR-502 inhibits cell proliferation and tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma through suppressing phosphoinositide 3-kinase catalytic subunit gamma[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2015, 464(2): 500-505. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.06.168. 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 严文英,方伟,张景华,黄谷,杨瑞山. LncRNA DNM3OS对急性髓系白血病细胞的进展影响研究. 中国临床药理学杂志. 2022(14): 1623-1627 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 依马木买买提江·阿布拉,佟庆,杨欢,易超. HBV感染相关性肝癌患者血清环状RNA circ_0000591表达及其沉默对HepG2.2.15细胞凋亡的影响. 中华医院感染学杂志. 2022(19): 2920-2924 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(1)
-




 PDF下载 ( 4588 KB)
PDF下载 ( 4588 KB)


 下载:
下载:







 下载:
下载:






 百度学术
百度学术