1990—2021年全球和中国急性病毒性肝炎疾病负担分析
DOI: 10.12449/JCH251010
An analysis of the disease burden of acute viral hepatitis in China and globally from 1990 to 2021
-
摘要:
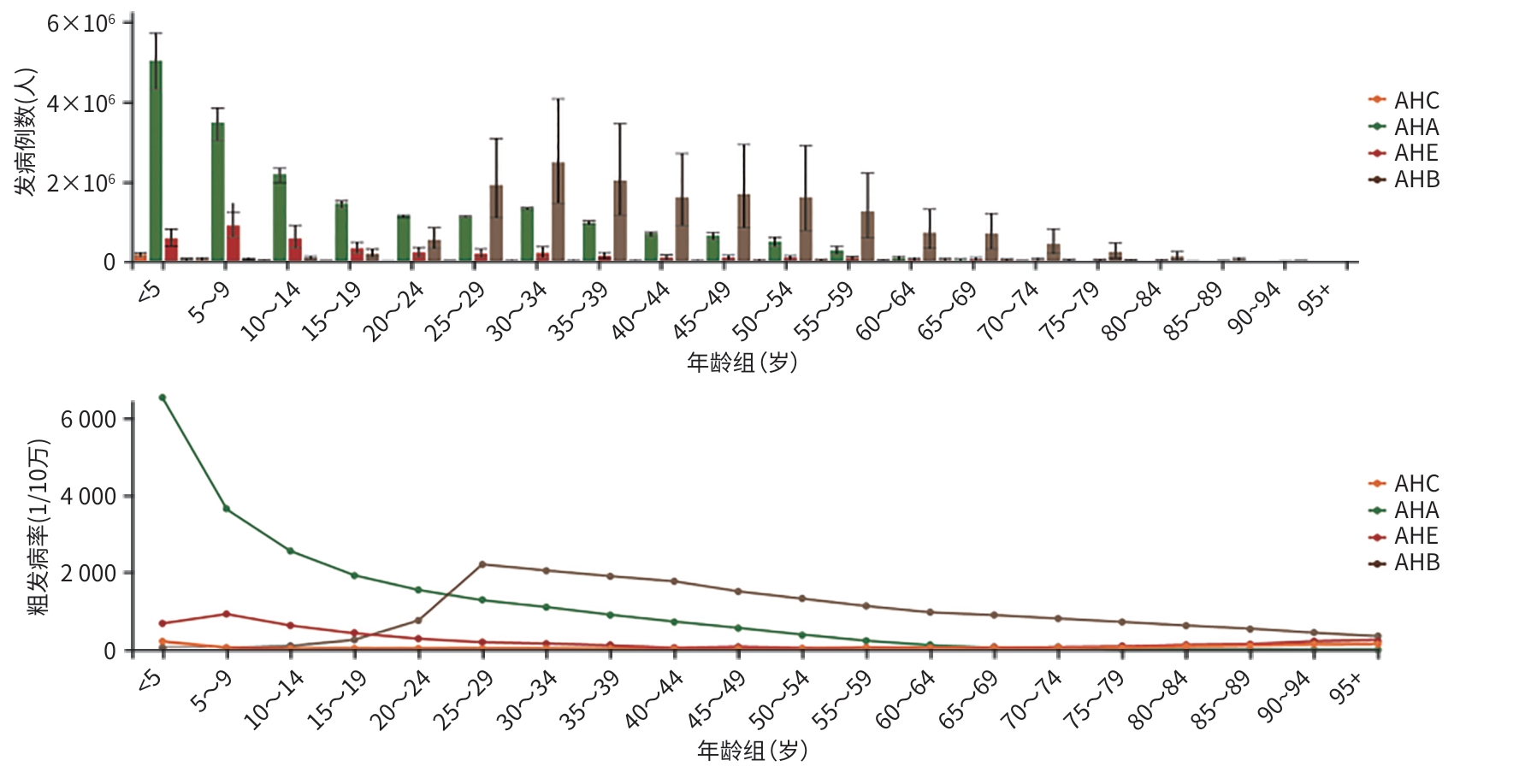
目的 分析1990—2021年全球与中国急性病毒性肝炎(AVH)疾病负担的变化趋势,为优化防控策略提供依据。 方法 基于2021年全球疾病负担数据库(GBD 2021),提取1990—2021年全球和中国AVH的发病、死亡和伤残调整生命年(DALY)等疾病负担数据,按地区、年龄、性别及肝炎类型分组,采用Joinpoint回归模型计算平均年度变化百分比(AAPC)及95%可信区间(95%CI)。 结果 1990—2021年期间,全球AVH的年龄标准化发病率、死亡率和DALY率均呈现下降趋势,平均每年分别下降1.02%(95%CI:-1.10%~-0.94%,P<0.001)、3.97%(95%CI:-4.12%~-3.82%,P<0.001)和3.64%(95%CI:-3.84%~-3.44%,P<0.001);中国相应的指标均呈下降趋势,分别为1.63%(95%CI:-1.70%~-1.57%,P<0.001)、9.24%(95%CI:-9.51%~-8.97%,P<0.001)和7.93%(95%CI:-8.15%~-7.71%,P<0.001)。中国AVH的疾病负担在全球中的占比持续降低,新发病例占比从1990年的24%降至2021年的15%,死亡病例占比从19%降至4%,DALY占比从16%降至4%。1990—2021年在全球范围内,AVH的发病、死亡及DALY高峰均集中在<5岁儿童群体;在中国发病高峰虽然仍以<5岁儿童为主要发病人群,但近年来,25~29岁青壮年人群发病率呈上升趋势,其中以急性乙型肝炎的病例增长最为突出(占该年龄段的59%),而死亡和DALY负担则集中于中老年人群。男性AVH的疾病负担均高于女性。从疾病类型分布来看,急性甲型肝炎是AVH发病的主要类型,在全球和中国分别占64%和48%;而急性乙型肝炎是导致死亡和DALY负担的主要类型,其在全球和中国分别占死亡病例的50%和80%,以及DALY的47%和69%。 结论 1990—2021年全球与中国AVH疾病负担均呈下降趋势,但近年来在我国青壮年人群发病率呈上升趋势,尤以急性乙型肝炎增高为主,需实施精准防控策略。 -
关键词:
- 肝炎, 病毒性, 人 /
- 全球疾病负担 /
- 中国
Abstract:Objective To analyze the changing trend of the disease burden of acute viral hepatitis (AVH) globally and in China from 1990 to 2021, and to provide a basis for optimizing prevention and control strategies. Methods Related data were extracted from the Global Burden of Disease 2021 database, including incidence rate, mortality rate, and disability-adjusted life years (DALY) for AVH globally and in China from 1990 to 2021, and the patients were divided into groups according to region, age, sex, and type of hepatitis. The Joinpoint regression model was used to calculate average annual percentage change (AAPC) and its 95% confidence interval (CI). Results From 1990 to 2021, there was a tendency of reduction in the age-standardized incidence rate, mortality rate, and DALY rate of AVH globally, with an average annual reduction of 1.02% (95%CI: -1.10% to -0.94%, P<0.001), 3.97% (95%CI: -4.12% to -3.82%, P<0.001), and 3.64% (95%CI: -3.84% to -3.44%, P<0.001), respectively; in China, there was also a tendency of reduction in these indicators, with an average annual reduction of 1.63% (95%CI: -1.70% to -1.57%, P<0.001), 9.24% (95%CI: -9.51% to -8.97%, P<0.001), and 7.93% (95%CI: -8.15% to -7.71%, P<0.001), respectively. In addition, China’s share of the global disease burden of AVH continued to decrease; the proportion of new cases decreased from 24% in 1990 to 15% in 2021, the proportion of deaths decreased from 19% to 4%, and the proportion of DALY decreased from 16% to 4%. From 1990 to 2021 globally, the peaks in the incidence rate, mortality, and DALY of AVH were observed in children under 5 years of age; in China, although the peak incidence rate of the disease was still observed in children under 5 years of age, there was a tendency of increase in the incidence rate of AVH among young adults aged 25 — 29 years in recent years, with the most significant increase in the cases of acute hepatitis B (accounting for 59% of the cases in this age group), while the disease burden of mortality and DALY mainly affected the middle-aged and elderly populations. The disease burden of AVH in the male population was higher than that in the female population. As for the distribution of disease types, acute hepatitis A was the predominant type of AVH, accounting for 64% globally and 48% in China, whereas acute hepatitis B was the leading cause of mortality and DALY, accounting for 50% of deaths globally, 80% of deaths in China, 47% of DALY globally, and 69% of DALY in China. Conclusion There is a tendency of reduction in the disease burden of AVH globally and in China from 1990 to 2021, but there is a tendency of increase in the incidence rate of AVH among young adults in China, especially acute hepatitis B. It is necessary to implement targeted prevention and control strategies. -
Key words:
- Hepatitis, Viral, Human /
- Global Burden of Disease /
- China
-
表 1 1990和2021年全球AVH及其各分型的发病、死亡、DALY情况及1990—2021年的AAPC情况
Table 1. The condition of incidence, deaths, DALYs, and corresponding AAPC for AVH and its subtypes globally in 1990 and 2021
全球数据 1990年 2021年 1990—2021年 人群1)
(95%UI)标化率2)(1/10万)
(95%UI)人群1)
(95%UI)标化率2)(1/10万)
(95%UI)AAPC(%)
(95%CI)P值 发病情况 AVH 266 388 077
(243 212 898~
289 980 844)4 660.03
(4 212.96~
5 125.09)250 774 458
(234 361 297~
268 115 472)3 411.51
(3 201.79~
3 631.26)-1.02
(-1.10~-0.94)<0.001 AHA 173 428 526
(156 873 679~
193 086 773)2 970.52
(2 650.90~
3 352.56)160 860 122
(152 201 085~
170 430 684)2 273.72
(2 150.13~
2 403.76)-0.86
(-0.95~-0.77)<0.001 AHB 71 669 350
(57 918 394~
86 076 473)
1 316.12
(1 063.13~
1 587.65)63 533 726
(50 445 999~
78 878 535)784.73
(627.37~
968.45)-1.64
(-1.75~-1.53)<0.001 AHC 5 625 288
(4 933 813~
6 428 419)103.71
(91.49~
117.03)7 009 910
(6 182 801~
7 885 767)92.64
(82.13~
104.65)-0.38
(-0.42~-0.33)<0.001 AHE 15 664 913
(12 846 345~
19 042 336)269.68
(224.04~
322.68)19 370 701
(16 103 891~
23 239 012)260.41
(215.39~
312.21)-0.12
(-0.13~-0.11)<0.001 死亡情况 AVH 160 352
(139 544~180 112)3.18
(2.76~3.59)71 846
(58 045~92 908)0.92
(0.73~1.20)-3.97
(-4.12~-3.82)<0.001 AHA 95 016
(77 825~113 851)1.81
(1.46~2.19)26 902
(18 387~42 454)0.35
(0.24~0.57)-5.14
(-5.38~-4.90)<0.001 AHB 51 854
(36 312~68 169)1.09
(0.78~1.43)36 025
(26 239~44 621)0.45
(0.33~0.57)-2.80
(-2.88~-2.72)<0.001 AHC 10 074
(3 692~18 327)0.21
(0.08~0.40)5 474
(2 465~9 111)0.07
(0.03~0.11)-3.66
(-3.79~-3.52)<0.001 AHE 3 409
(1 390~5 143)0.07
(0.03~0.11)3 445
(1 885~5 842)0.05
(0.02~0.08)-1.37
(-1.53~-1.21)<0.001 DALY情况 AVH 9 841 371
(8 674 224~
11 047 444)177.42
(156.17~199.28)4 228 048
(3 342 182~
5 559 113)56.74
(44.11~75.55)-3.64
(-3.84~-3.44)<0.001 AHA 6 353 303
(5 277 676~
7 398 360)111.19
(92.34~130.13)1 817 363
(1 275 384~
2 792 339)24.95
(17.32~39.12)-4.74
(-4.92~-4.57)<0.001 AHB 2 776 343
(1 835 331~
3 732 870)52.68
(35.83~69.08)1 914 972
(1 407 012~
2 381 815)25.19
(18.32~31.15)-2.36
(-2.47~-2.26)<0.001 AHC 497 967
(185 511~887 491)9.67
(3.59~17.27)266 088
(117 650~455 055)3.41
(1.48~5.88)-3.29
(-3.46~-3.12)<0.001 AHE 213 758
(94 817~320 232)3.89
(1.78~5.68)229 625
(127 411~374 728)3.18
(1.73~5.23)-0.66
(-0.84~-0.48)<0.001 注:1)发病情况和死亡情况单位均为“例”,DALY单位为“人年”。2)发病、死亡、DALY对应的标化率分别为ASIR、ASMR、ASDR。
表 2 1990和2021年中国AVH及其各分型的发病、死亡、DALY情况及1990—2021年的AAPC情况
Table 2. The condition of incidence, deaths, DALYs and corresponding AAPC for AVH and its subtypes in China in 1990 and 2021
中国数据 1990年 2021年 1990—2021年 人群1)
(95%UI)标化率2)(1/10万)
(95%UI)人群1)
(95%UI)标化率2)(1/10万)
(95%UI)AAPC(%)
(95%CI)P值 发病情况 AVH 65 757 649
(58 813 343~
72 787 654)5 493.59
(4 952.39~
6 048.17)39 808 671
(35 070 968~
45 585 506)3 301.09
(2 985.10~
3 671.53)-1.63
(-1.70~-1.57)<0.001 AHA 30 531 306
(28 419 939~
32 850 030)2 613.64
(2 419.93~
2 829.61)19 209 161
(17 977 606~
20 381 837)1 903.58
(1 758.35~
2 046.41)-1.02
(-1.05~-0.10)<0.001 AHB 29 200 407
(22 793 003~
35 818 278)2 378.19
(1 865.66~
2 893.99)16 032 339
(11 361 942~
21 674 277)978.33
(711.35~
1 302.24)-2.87
(-2.99~-2.76)<0.001 AHC 976 188
(847 445~
1 122 754)89.07
(77.57~
102.12)666 818
(558 915~
771 329)55.22
(48.25~63.34)-1.55
(-1.69~-1.42)<0.001 AHE 5 049 748
(4 038 586~
6 218 766)412.68
(336.93~
502.59)3 900 352
(3 209 998~
4 724 584)363.96
(297.43~447.62)-0.41
(-0.44~-0.38)<0.001 死亡情况 AVH 31 234
(26 123~36 926)3.22
(2.70~3.82)3 018
(2 354~3 958)0.16
(0.13~0.21)-9.24
(-9.51~-8.97)<0.001 AHA 12 334
(8 463~17 323)1.24
(0.84~1.75)376
(247~543)0.02
(0.01~0.03)-12.42
(-12.87~-11.97)<0.001 AHB 16 094
(11 439~21 648)1.69
(1.21~2.25)2 424
(1 835~3 240)0.13
(0.10~0.17)-8.10
(-8.62~-7.58)<0.001 AHC 2 005
(737~3 906)0.21
(0.08~0.41)73
(43~149)0
(0~0.01)-12.02
(-13.02~-11.01)<0.001 AHE 800
(248~1 530)0.09
(0.03~0.17)144
(80~291)0.01
(0~0.01)-7.73
(-7.97~-7.48)<0.001 DALY情况 AVH 1 656 678
(1 415 696~1 939 344)152.77
(130.33~178.95)179 098
(140 781~224 381)11.88
(9.32~15.03)-7.93
(-8.15~-7.71)<0.001 AHA 723 349
(515 993~982 603)65.65
(46.74~89.96)50 929
(37 153~68 437)4.08
(2.90~5.63)-8.57
(-8.85~-8.29)<0.001 AHB 802 752
(555 930~1058 589)74.90
(52.05~98.66)114 254
(87 684~146 707)6.81
(5.27~8.61)-7.55
(-8.09~-7.01)<0.001 AHC 89 581
(35 216~167 126)8.40
(3.30~15.75)3 408
(2 180~5 829)0.22
(0.15~0.37)-11.04
(-11.76~-10.32)<0.001 AHE 40 995
(17 057~69 596)3.82
(1.52~6.57)10 507
(7 282~15 750)0.76
(0.52~1.12)-5.10
(-5.28~-4.93)<0.001 注:1)发病情况和死亡情况单位均为“例”,DALY单位为“人年”。2)发病、死亡、DALY对应的标化率分别为ASIR、ASMR、ASDR。
-
[1] DI COLA G, FANTILLI AC, PISANO MB, et al. Foodborne transmission of hepatitis A and hepatitis E viruses: A literature review[J]. Int J Food Microbiol, 2021, 338: 108986. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108986. [2] SHUKLA NB, POLES MA. Hepatitis B virus infection: Co-infection with hepatitis C virus, hepatitis D virus, and human immunodeficiency virus[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2004, 8( 2): 445- 460, viii. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2004.02.005. [3] World Health Organization. Global hepatitis report 2024[R/OL].( 2024)[ 2024-10-02]. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240091672. https: //www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240091672 [4] CAO GY, JING WZ, LIU J, et al. Countdown on hepatitis B elimination by 2030: The global burden of liver disease related to hepatitis B and association with socioeconomic status[J]. Hepatol Int, 2022, 16( 6): 1282- 1296. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-022-10410-y. [5] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association, et al. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B(version 2022)[J]. J Pract Hepatol, 2023, 26( 3): 457- 478. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8134.2023.01.01.中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会感染病学分会. 慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2022年版)[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2023, 26( 3): 457- 478. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8134.2023.01.01. [6] TANG X, WANG P, HUANG S, et al. Trend of gastrointestinal and liver diseases in China: Results of the global burden of disease study, 2019[J]. Chin Med J(Engl), 2024, 137( 19): 2358- 2368. DOI: 10.1097/cm9.0000000000002975. [7] GBD 2021 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability(YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years(DALYs), and healthy life expectancy(HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021[J]. Lancet, 2024, 403( 10440): 2133- 2161. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00757-8. [8] NEGRO F, LOK AS. Hepatitis D: A review[J]. JAMA, 2023, 330( 24): 2376- 2387. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2023.23242. [9] ZENG DY, LI JM, LIN S, et al. Global burden of acute viral hepatitis and its association with socioeconomic development status, 1990-2019[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 75( 3): 547- 556. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.04.035. [10] HOU SS, SHI JD, YIN X, et al. Disease burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases in China from 1990 to 2019[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2022, 43( 10): 1554- 1561. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20211009-00773.侯珊珊, 施劲东, 尹欣, 等. 1990-2019年中国慢性阻塞性肺疾病的疾病负担情况分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2022, 43( 10): 1554- 1561. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20211009-00773. [11] CHEN X, CHEN YF. Analysis of the disease burden of pneumoconiosis globally and in China from 1990 to 2019[J]. Chin J Industrial Hygiene Occupational Dis, 2023, 41( 6): 417- 424. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121094-20221019-00478.陈相, 陈彦凡. 1990至2019年全球和中国尘肺病的疾病负担分析[J]. 中华劳动卫生职业病杂志, 2023, 41( 6): 417- 424. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121094-20221019-00478. [12] LIU DW, LI C, LI YY, et al. Benign prostatic hyperplasia burden comparison between China and United States based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. World J Urol, 2023, 41( 12): 3629- 3634. DOI: 10.1007/s00345-023-04658-8. [13] WEI JH, CHEN LZ, HUANG SB, et al. Time trends in the incidence of spinal pain in China, 1990 to 2019 and its prediction to 2030: The global burden of disease study 2019[J]. Pain Ther, 2022, 11( 4): 1245- 1266. DOI: 10.1007/s40122-022-00422-9. [14] LI XC, ZHANG YY, ZHANG QY, et al. Global burden of viral infectious diseases of poverty based on Global Burden of Diseases Study 2021[J]. Infect Dis Poverty, 2024, 13( 1): 71. DOI: 10.1186/s40249-024-01234-z. [15] CHEN HM, SU JT, TONG C, et al. Characteristics of deaths induced by viral hepatitis among registered residents in Beijing from 2005 to 2020[J]. Int J Virol, 2024, 31( 3): 233- 237. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4092.2024.03.012.陈红梅, 苏健婷, 佟超, 等. 2005—2020年北京市户籍居民病毒性肝炎死亡特征分析[J]. 国际病毒学杂志, 2024, 31( 3): 233- 237. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4092.2024.03.012. [16] GBD 2019 Hepatitis B Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of hepatitis B, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 7( 9): 796- 829. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00124-8. [17] GBD 2019 Europe Hepatitis B& C Collaborators. Hepatitis B and C in Europe: An update from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. Lancet Public Health, 2023, 8( 9): e701- e716. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-2667(23)00149-4. [18] HAN Y, LI Y, WANG S, et al. Temporal trend analysis of acute hepatitis B virus infection in China, 1990-2019[J]. Epidemiol Infect, 2024, 152: e48. DOI: 10.1017/s095026882400044x. [19] SHIFFMAN ML. Management of acute hepatitis B[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2010, 14( 1): 75- 91; viii-ix. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2009.11.013. [20] HUANG DL, LAI HY, SHI X, et al. Global temporal trends and projections of acute hepatitis E incidence among women of childbearing age: Age-period-cohort analysis 2021[J]. J Infect, 2024, 89( 4): 106250. DOI: 10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106250. [21] ZHANG M, ZHANG YX, JIANG SJM, et al. Changing trends in disease burden of viral hepatitis B and its risk factors among Chinese residents from 1990 to 2019: an analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. China Public Health, 2024, 40( 5): 593- 597. DOI: 10.11847/zgggws1142491.张敏, 张裕晓, 江山佳美, 等. 中国居民1990-2019年乙型病毒性肝炎及其危险因素所致疾病负担变化趋势分析[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2024, 40( 5): 593- 597. DOI: 10.11847/zgggws1142491. [22] YUAN L, ZHANG SJ. Effects of gender and sex hormones on susceptibility to hepatitis B virus and its immune response[J]. Henan Med Res, 2019, 28( 10): 1919- 1921. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-437X.2019.10.092.袁磊, 张水军. 性别与性激素对乙肝病毒易感性及其免疫应答的影响[J]. 河南医学研究, 2019, 28( 10): 1919- 1921. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-437X.2019.10.092. [23] LIU SS, YU XH, CAI JW. Changing trend of the disease burden of liver cirrhosis in China from 1990 to 2019[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2024, 40( 4): 726- 733. DOI: 10.12449/JCH240414.刘珊山, 于晓辉, 秦建伟. 1990—2019年中国肝硬化疾病负担变化趋势分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40( 4): 726- 733. DOI: 10.12449/JCH240414. [24] SHI L, BAO CL, WEN Y, et al. Analysis and comparison of the trends in burden of rheumatic heart disease in China and worldwide from 1990 to 2019[J]. BMC Cardiovasc Disord, 2023, 23( 1): 517. DOI: 10.1186/s12872-023-03552-w. -



 PDF下载 ( 154921 KB)
PDF下载 ( 154921 KB)


 下载:
下载: