免疫分子及相关免疫细胞在肝衰竭中的作用机制
DOI: 10.12449/JCH250632
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:张荣、马国娟、青磊负责研究思路的设计;罗琪、曾碧雨负责查阅相关文献,资料归纳、分析,撰写论文;付蕾、黄良江负责修改论文;姚春负责指导、审阅论文及最后定稿。
-
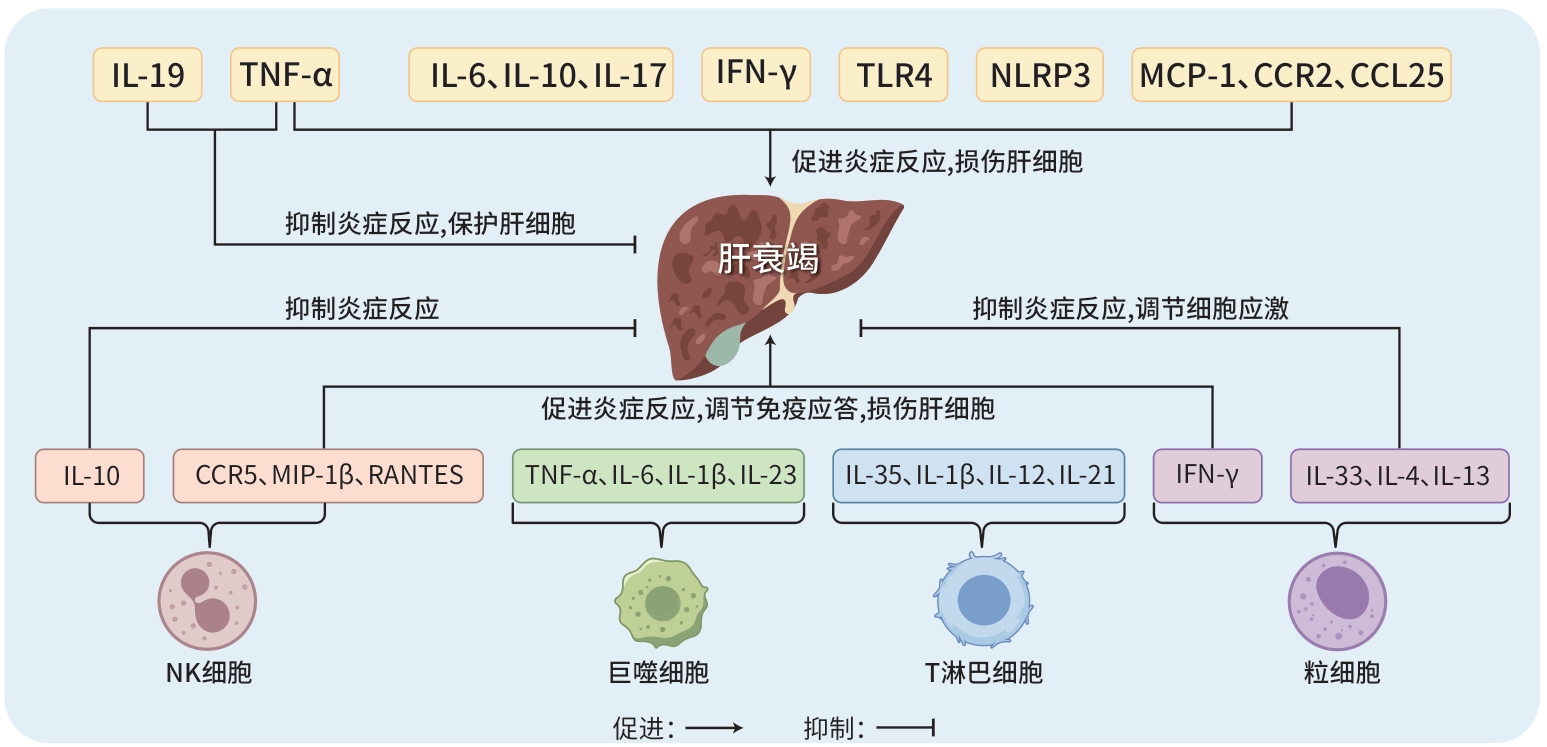
摘要: 肝衰竭是一种严重的临床综合征,以肝功能的严重障碍或失代偿为特征。目前,免疫分子在肝衰竭发病机制中的核心作用已得到证实。这些分子不仅直接参与其病理过程,还能通过调节免疫细胞行为,影响肝衰竭的进程。此外,免疫分子还具有作为肝衰竭预后评估生物标志物的潜力。本文旨在总结免疫分子在肝衰竭中的作用,并探讨基于这些免疫分子的治疗策略,以期为肝衰竭的诊疗提供新方向。Abstract: Liver failure (LF) is a severe clinical syndrome characterized by severe impairment or decompensation of liver function. At present, the key role of immune molecules in the pathogenesis of LF has been well established. These molecules not only directly participate in the pathological process of LF, but also influence the course of LF by modulating the behavior of immune cells. In addition, immune molecules can be used as potential biomarkers for evaluating the prognosis of LF. This article summarizes the role of immune molecules in LF and explores the therapeutic strategies based on these immune molecules, in order to provide new directions for the diagnosis and treatment of LF.
-
Key words:
- Immune molecules /
- Liver Failure /
- Therapeutics
-
[1] TAFESH ZH, SALCEDO RO, PYRSOPOULOS NT. Classification and epidemiologic aspects of acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2023, 27( 3): 553- 562. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2023.03.002. [2] SHAH S, GOLDBERG DS. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: Update on pathogenesis, therapeutic targets, predictive models, and liver transplantation[J]. Curr Opin Gastroenterol, 2021, 37( 3): 173- 178. DOI: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000722. [3] DĄBROWSKA A, WILCZYŃSKI B, MASTALERZ J, et al. The impact of liver failure on the immune system[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25( 17): 9522. DOI: 10.3390/ijms25179522. [4] FUJIMOTO Y, KUWAMURA M, AZUMA YT. Deficiency of interleukin-19 exacerbates lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine-induced acute liver failure[J]. J Vet Med Sci, 2020, 82( 10): 1450- 1455. DOI: 10.1292/jvms.20-0344. [5] LI L, CHEN L, LIN F, et al. Study of the expression of inflammatory factors IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, and IL-17 in liver failure complicated by coagulation dysfunction and sepsis[J]. J Inflamm Res, 2021, 14: 1447- 1453. DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S302975. [6] WEI HY, YI K, LI FF, et al. Multimodal tetrahedral DNA nanoplatform for surprisingly rapid and significant treatment of acute liver failure[J]. Adv Mater, 2024, 36( 30): e2305826. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202305826. [7] ZHAO SM, JIANG JH, JING YY, et al. The concentration of tumor necrosis factor-α determines its protective or damaging effect on liver injury by regulating Yap activity[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11( 1): 70. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-2264-z. [8] XIE H, ZENG JY, YAN X, et al. Clinical significance and properties of IFN-γ+IL-17+Th17 cells in liver injury associated with chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Digestion, 2022, 103( 6): 438- 450. DOI: 10.1159/000526924. [9] FU S, NI TZ, ZHANG MM, et al. Cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway attenuates acute liver failure through inhibiting MAdCAM1/α4β7-mediated gut-derived proinflammatory lymphocytes accumulation[J]. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2024, 17( 2): 199- 217. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2023.10.012. [10] TANG YL, ZHU L, TAO Y, et al. Role of targeting TLR4 signaling axis in liver-related diseases[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2023, 244: 154410. DOI: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154410. [11] ENGELMANN C, SHEIKH M, SHARMA S, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 is a therapeutic target for prevention and treatment of liver failure[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 73( 1): 102- 112. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.01.011. [12] LI WY, ZHANG WB, ZHANG DM, et al. Effect of lipopolysaccharide on TAK1-mediated hepatocyte PANoptosis through Toll-like receptor 4 during acute liver failure[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 129: 111612. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111612. [13] SAYAF K, BATTISTELLA S, RUSSO FP. NLRP3 inflammasome in acute and chronic liver diseases[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25( 8): 4537. DOI: 10.3390/ijms25084537. [14] ZHANG W, TAO SS, WANG T, et al. NLRP3 is dispensable for d-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver failure[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2020, 533( 4): 1184- 1190. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.10.003. [15] LI ZH, JIANG JN. The NLRP3 inflammasome mediates liver failure by activating procaspase-1 and pro-IL-1 β and regulating downstream CD40-CD40L signaling[J]. J Int Med Res, 2021, 49( 9): 3000605211036845. DOI: 10.1177/03000605211036845. [16] ZHANG X, HU YY, WANG W, et al. IRGM/Irgm1 increases autophagy to inhibit activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammatory injury induced acute liver failure[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2024, 10( 1): 272. DOI: 10.1038/s41420-024-02052-w. [17] COMERFORD I, MCCOLL SR. Atypical chemokine receptors in the immune system[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2024, 24: 753- 769. DOI: 10.1038/s41577-024-01025-5. [18] LI H, ZHAO XK, CHENG YJ, et al. Gasdermin D-mediated hepatocyte pyroptosis expands inflammatory responses that aggravate acute liver failure by upregulating monocyte chemotactic protein 1/CC chemokine receptor-2 to recruit macrophages[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25( 44): 6527- 6540. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i44.6527. [19] SUN F, WANG JW, JI XF, et al. CCL25 contributes to the pathogenesis of D-Gal/LPS-induced acute liver failure[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2024, 39( 12): 2880- 2891. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.16732. [20] DAN X, OUYANG S. The role and mechanisms of macrophage polarization and hepatocyte pyroptosis in acute liver failure[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1279264. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1279264. [21] JI XF, FAN YC, SUN F, et al. Noncanonical Wnt5a/JNK signaling contributes to the development of D-gal/LPS-induced acute liver failure[J]. Inflammation, 2022, 45( 3): 1362- 1373. DOI: 10.1007/s10753-022-01627-y. [22] KONG XR, LIU W, ZHANG XW, et al. HIF-1α inhibition in macrophages preserves acute liver failure by reducing IL-1β production[J]. FASEB J, 2023, 37( 9): e23140. DOI: 10.1096/fj.202300428RR. [23] BAO SX, ZHENG WY, YAN R, et al. miRNA-21 promotes the progression of acute liver failure via the KLF6/autophagy/IL-23 signaling pathway[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2024, 29( 5): 80. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13205. [24] LIU YH, ZHU L, ZHANG ZW, et al. C-C chemokine receptor 5 is essential for conventional NK cell trafficking and liver injury in a murine hepatitis virus-induced fulminant hepatic failure model[J]. J Transl Med, 2023, 21( 1): 865. DOI: 10.1186/s12967-023-04665-8. [25] ALI AK, KOMAL AK, ALMUTAIRI SM, et al. Natural killer cell-derived IL-10 prevents liver damage during sustained murine cytomegalovirus infection[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 2688. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02688. [26] YANG LL, ZHANG Q, SONG J, et al. Interleukin-35 suppresses CD8+ T cell activity in patients with viral hepatitis-induced acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2020, 65( 12): 3614- 3623. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-020-06077-w. [27] YU WH, LAN XQ, CAI J, et al. Critical role of IL-1β in the pathogenesis of Agrocybe aegerita galectin-induced liver injury through recruiting T cell to liver[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2020, 521( 2): 449- 456. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.10.087. [28] DU B, TENG J, YIN R, et al. Increased circulating t follicular helper cells induced via il-12/21 in patients with acute on chronic hepatitis B liver failure[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 641362. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.641362. [29] WU H, GUO CQ, LIU Z, et al. Neutrophils exacerbate acetaminophen-induced liver injury by producing cytotoxic interferon-γ[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 123: 110734. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110734. [30] XU L, YANG Y, JIANG JL, et al. Eosinophils protect against acetaminophen-induced liver injury through cyclooxygenase-mediated IL-4/IL-13 production[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 77( 2): 456- 465. DOI: 10.1002/hep.32609. [31] ZHU BB, GAO FY, LI YX, et al. Serum cytokine and chemokine profiles and disease prognosis in hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1133656. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1133656. [32] MURAKAMI S, IMAMURA M, UCHIDA T, et al. Serum interleukin-6 level predicts the prognosis for patients with alcohol-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Hepatol Int, 2023, 17( 5): 1225- 1232. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-023-10532-x. [33] UMBAUGH DS, NGUYEN NT, CURRY SC, et al. The chemokine CXCL14 is a novel early prognostic biomarker for poor outcome in acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure[J]. Hepatology, 2024, 79( 6): 1352- 1364. DOI: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000665. [34] YANG P, ZENG YM, YANG F, et al. Transmembrane TNF-α as a novel biomarker for the diagnosis of cytokine storms in a mouse model of multiple organ failure[J]. Inflammation, 2023, 46( 1): 359- 369. DOI: 10.1007/s10753-022-01738-6. [35] ZHANG EL, HUANG JB, WANG K, et al. Pterostilbene protects against lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine-induced acute liver failure by upregulating the Nrf2 pathway and inhibiting NF-κB, MAPK, and NLRP3 inflammasome activation[J]. J Med Food, 2020, 23( 9): 952- 960. DOI: 10.1089/jmf.2019.4647. [36] WANG FZ, GONG SH, WANG T, et al. Soyasaponin II protects against acute liver failure through diminishing YB-1 phosphorylation and Nlrp3-inflammasome priming in mice[J]. Theranostics, 2020, 10( 6): 2714- 2726. DOI: 10.7150/thno.40128. [37] MOHAMADI-ZARCH SM, BALUCHNEJADMOJARAD T, NOURABADI D, et al. Esculetin alleviates acute liver failure following lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine in male C57BL/6 mice[J]. Iran J Med Sci, 2021, 46( 5): 373- 382. DOI: 10.30476/ijms.2020.84909.1474. [38] MA J, XU Y, ZHANG M, et al. Geraniol ameliorates acute liver failure induced by lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine via regulating macrophage polarization and NLRP3 inflammasome activation by PPAR-γ methylation Geraniol alleviates acute liver failure[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2023, 210: 115467. DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115467. [39] WANG X, SUN YP, LI PX, et al. The protective effects of myricetin against acute liver failure via inhibiting inflammation and regulating oxidative stress via Nrf2 signaling[J]. Nat Prod Res, 2023, 37( 5): 798- 802. DOI: 10.1080/14786419.2022.2089138. [40] ZHAO X, YIN F, FU LQ, et al. Garlic-derived exosome-like nanovesicles as a hepatoprotective agent alleviating acute liver failure by inhibiting CCR2/CCR5 signaling and inflammation[J]. Biomater Adv, 2023, 154: 213592. DOI: 10.1016/j.bioadv.2023.213592. [41] ZHAO X, YIN F, HUANG YL, et al. Oral administration of grape-derived nanovesicles for protection against LPS/D-GalN-induced acute liver failure[J]. Int J Pharm, 2024, 652: 123812. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.123812. [42] WANG JL, LIU Y, DING HR, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-secreted prostaglandin E2 ameliorates acute liver failure via attenuation of cell death and regulation of macrophage polarization[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2021, 12( 1): 15. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-020-02070-2. [43] XU RX, NI BB, WANG L, et al. CCR2-overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells targeting damaged liver enhance recovery of acute liver failure[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2022, 13( 1): 55. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-022-02729-y. [44] YU YP, ZHANG QQ, WU N, et al. HNF4α overexpression enhances the therapeutic potential of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem/stromal cells in mice with acute liver failure[J]. FEBS Lett, 2022, 596( 24): 3176- 3190. DOI: 10.1002/1873-3468.14453. -



 PDF下载 ( 915 KB)
PDF下载 ( 915 KB)

 下载:
下载:


