衰老驱动代谢相关脂肪性肝病的机制及靶向治疗策略研究进展
DOI: 10.12449/JCH250626
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:陈睿负责设计论文框架,查阅文献,撰写文章;陆伦根负责文章审校。
Advances in the mechanism of aging-driven metabolic associated fatty liver disease and related targeted therapeutic strategies
-
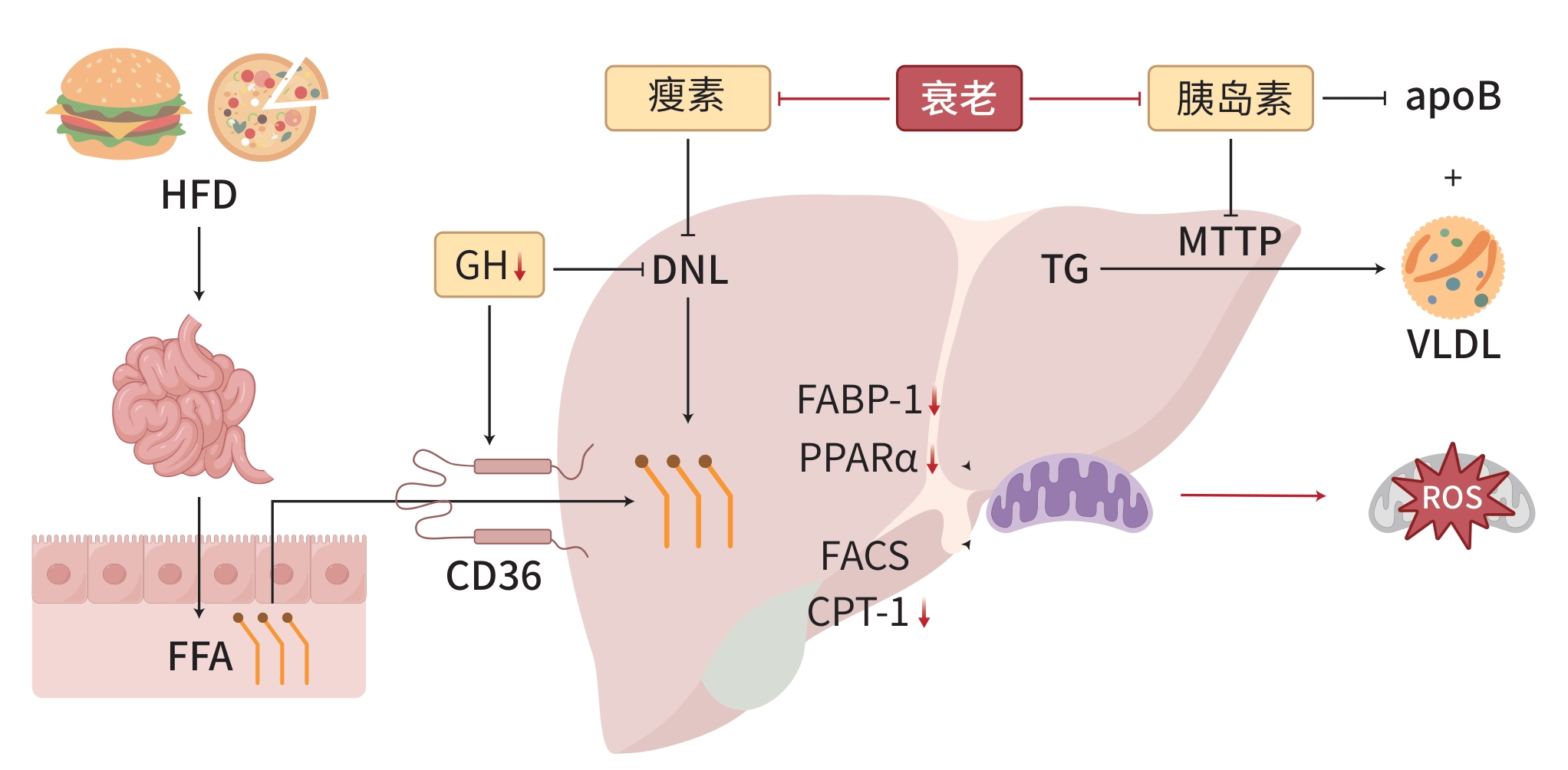
摘要: 代谢相关脂肪性肝病(MAFLD)是一种与代谢紊乱相关的肝脏疾病,其特征是肝细胞内脂肪过度沉积,与胰岛素抵抗和遗传易感性密切相关。衰老是MAFLD发展的一个重要因素,与MAFLD患者的死亡率呈正相关。MAFLD的病理生理机制涉及脂质代谢紊乱、胰岛素抵抗、炎症和氧化应激,而衰老通过进一步影响这些关键机制加剧MAFLD的病理过程。细胞衰老是机体衰老的重要因素,针对衰老细胞的治疗策略,如减少衰老细胞的数量或抑制其分泌的炎症因子,可能有助于减缓MAFLD的进展。此外,新型调节因子的筛选为MAFLD治疗新药物的开发提供了新的靶点。尽管已有多种抗衰老疗法进入临床试验阶段,但衰老对肝脏影响的机制复杂,需要进一步验证这些治疗的特异性和潜在肝损伤。将MAFLD的多系统代谢性功能障碍治疗转化为针对衰老的专门化治疗,可能为MAFLD药物研发提供新思路。Abstract: Metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is a liver disease associated with metabolic disorders, and it is characterized by excessive fat deposition in hepatocytes and is closely associated with insulin resistance and genetic susceptibility. Aging is an important factor in the progression of MAFLD and is positively correlated with the mortality rate of patients with MAFLD. The pathophysiological mechanisms of MAFLD involve lipid metabolism disorders, insulin resistance, inflammation, and oxidative stress, and aging exacerbates the pathological process of MAFLD by further affecting these key mechanisms. Cell senescence is an important factor in organismal aging, and therapeutic strategies targeting senescent cells can reduce the number of senescent cells or inhibit the inflammatory factors secreted by such cells, thereby helping to slow down the progression of MAFLD. In addition, the screening of novel regulatory factors provides new targets for the development of new drugs for MAFLD treatment. Although several anti-aging therapies have entered clinical trials, further studies are needed to validate the specificity and potential liver damage of these therapies due to the complex mechanisms of aging on the liver. Transforming multisystem metabolic dysfunction therapies for MAFLD into specialized therapies for aging may provide new ideas for MAFLD drug development.
-
[1] WONG RJ, AGUILAR M, CHEUNG R, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is the second leading etiology of liver disease among adults awaiting liver transplantation in the United States[J]. Gastroenterology, 2015, 148( 3): 547- 555. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.11.039. [2] WANG HL, LIU ZQ, FAN H, et al. Association between biological aging and the risk of mortality in individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A prospective cohort study[J]. Arch Gerontol Geriatr, 2024, 124: 105477. DOI: 10.1016/j.archger.2024.105477. [3] DONNELLY KL, SMITH CI, SCHWARZENBERG SJ, et al. Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Invest, 2005, 115( 5): 1343- 1351. DOI: 10.1172/JCI23621. [4] WEI HR, XIAO F, WEI HS. Research progress on the mechanism of endoplasmic reticulum stress in metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease[J/CD]. Chin J Liver Dis(Electronic Version), 2024, 16( 1): 13- 17. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2024.01.003.韦何锐, 肖凡, 魏红山. 内质网应激在代谢相关脂肪性肝病中的作用机制研究进展[J/CD]. 中国肝脏病杂志(电子版), 2024, 16( 1): 13- 17. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2024.01.003. [5] XU SW, WU XM, WANG SC, et al. TRIM56 protects against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by promoting the degradation of fatty acid synthase[J]. J Clin Invest, 2024, 134( 5): e166149. DOI: 10.1172/JCI166149. [6] QIU ST, CHEN JJ, BAI Y, et al. GOS ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease induced by high fat and high sugar diet through lipid metabolism and intestinal microbes[J]. Nutrients, 2022, 14( 13): 2749. DOI: 10.3390/nu14132749. [7] YOUNOSSI ZM, GOLABI P, de AVILA L, et al. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 71( 4): 793- 801. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.021. [8] FUJII H, KAWADA N, Japan Study Group Of Nafld Jsg-Nafld. The role of insulin resistance and diabetes in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21( 11): 3863. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21113863. [9] KHAN RS, BRIL F, CUSI K, et al. Modulation of insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 70( 2): 711- 724. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30429. [10] BODEN G, SHE PX, MOZZOLI M, et al. Free fatty acids produce insulin resistance and activate the proinflammatory nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in rat liver[J]. Diabetes, 2005, 54( 12): 3458- 3465. DOI: 10.2337/diabetes.54.12.3458. [11] KOYAMA Y, BRENNER DA. Liver inflammation and fibrosis[J]. J Clin Invest, 2017, 127( 1): 55- 64. DOI: 10.1172/JCI88881. [12] ZHU WW, SAHAR NE, JAVAID HMA, et al. Exercise-induced irisin decreases inflammation and improves NAFLD by competitive binding with MD2[J]. Cells, 2021, 10( 12): 3306. DOI: 10.3390/cells10123306. [13] OGRODNIK M, MIWA S, TCHKONIA T, et al. Cellular senescence drives age-dependent hepatic steatosis[J]. Nat Commun, 2017, 8: 15691. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms15691. [14] WOUDSTRA TD, DROZDOWSKI LA, WILD GE, et al. The age-related decline in intestinal lipid uptake is associated with a reduced abundance of fatty acid-binding protein[J]. Lipids, 2004, 39( 7): 603- 610. DOI: 10.1007/s11745-004-1272-9. [15] HOLT PR, BALINT JA. Effects of aging on intestinal lipid absorption[J]. Am J Physiol, 1993, 264( 1 Pt 1): G1- G6. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.1993.264.1.G1. [16] GONG ZW, TAS E, YAKAR S, et al. Hepatic lipid metabolism and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in aging[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2017, 455: 115- 130. DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2016.12.022. [17] GAWRIEH S, NOUREDDIN M, LOO N, et al. Saroglitazar, a PPAR-α/γ agonist, for treatment of NAFLD: A randomized controlled double-blind phase 2 trial[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 74( 4): 1809- 1824. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31843. [18] PI HF, LIU MY, XI Y, et al. Long-term exercise prevents hepatic steatosis: A novel role of FABP1 in regulation of autophagy-lysosomal machinery[J]. FASEB J, 2019, 33( 11): 11870- 11883. DOI: 10.1096/fj.201900812R. [19] HOUTKOOPER RH, ARGMANN C, HOUTEN SM, et al. The metabolic footprint of aging in mice[J]. Sci Rep, 2011, 1: 134. DOI: 10.1038/srep00134. [20] HAMMOUD S, IVANOVA A, OSAKI Y, et al. Tubular CPT1A deletion minimally affects aging and chronic kidney injury[J]. JCI Insight, 2024, 9( 6): e171961. DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.171961. [21] KALTENECKER D, THEMANNS M, MUELLER KM, et al. Hepatic growth hormone-JAK2-STAT5 signalling: Metabolic function, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma progression[J]. Cytokine, 2019, 124: 154569. DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.10.010. [22] SARMENTO-CABRAL A, DEL RIO-MORENO M, VAZQUEZ-BORREGO MC, et al. GH directly inhibits steatosis and liver injury in a sex-dependent and IGF1-independent manner[J]. J Endocrinol, 2021, 248( 1): 31- 44. DOI: 10.1530/JOE-20-0326. [23] GUO ZW, DU HB, GUO Y, et al. Association between leptin and NAFLD: A two-sample mendelian randomization study[J]. Eur J Med Res, 2023, 28( 1): 215. DOI: 10.1186/s40001-023-01147-x. [24] SAM DJ. Leptin and insulin sensitivity: Endogenous signals of metabolic homeostasis[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2024, 109( 5): e1402- e1403. DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgad653. [25] AKINCI B, SUBAUSTE A, AJLUNI N, et al. Metreleptin therapy for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Open-label therapy interventions in two different clinical settings[J]. Med, 2021, 2( 7): 814- 835. DOI: 10.1016/j.medj.2021.04.001. [26] ADAMCZAK M, RZEPKA E, CHUDEK J, et al. Ageing and plasma adiponectin concentration in apparently healthy males and females[J]. Clin Endocrinol(Oxf), 2005, 62( 1): 114- 118. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2004.02182.x. [27] ANWAR SD, FOSTER C, ASHRAF A. Lipid disorders and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease[J]. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am, 2023, 52( 3): 445- 457. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecl.2023.01.003. [28] NAPOLEÃO A, FERNANDES L, MIRANDA C, et al. Effects of calorie restriction on health span and insulin resistance: Classic calorie restriction diet vs. ketosis-inducing diet[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13( 4): 1302. DOI: 10.3390/nu13041302. [29] LIU YY, XU W, ZHAI T, et al. Silibinin ameliorates hepatic lipid accumulation and oxidative stress in mice with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by regulating CFLAR-JNK pathway[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2019, 9( 4): 745- 757. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2019.02.006. [30] DENTIN R, TOMAS-COBOS L, FOUFELLE F, et al. Glucose 6-phosphate, rather than xylulose 5-phosphate, is required for the activation of ChREBP in response to glucose in the liver[J]. J Hepatol, 2012, 56( 1): 199- 209. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2011.07.019. [31] CHOW JDY, LAWRENCE RT, HEALY ME, et al. Genetic inhibition of hepatic acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity increases liver fat and alters global protein acetylation[J]. Mol Metab, 2014, 3( 4): 419- 431. DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2014.02.004. [32] GUO TL, YAN WH, CUI X, et al. Liraglutide attenuates type 2 diabetes mellitus-associated non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by activating AMPK/ACC signaling and inhibiting ferroptosis[J]. Mol Med, 2023, 29( 1): 132. DOI: 10.1186/s10020-023-00721-7. [33] WANG TW, JOHMURA Y, SUZUKI N, et al. Blocking PD-L1-PD-1 improves senescence surveillance and ageing phenotypes[J]. Nature, 2022, 611( 7935): 358- 364. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-05388-4. [34] MIWA S, KASHYAP S, CHINI E, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in cell senescence and aging[J]. J Clin Invest, 2022, 132( 13): e158447. DOI: 10.1172/JCI158447. [35] WEIR HJ, YAO P, HUYNH FK, et al. Dietary restriction and AMPK increase lifespan via mitochondrial network and peroxisome remodeling[J]. Cell Metab, 2017, 26( 6): 884- 896. e 5. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.09.024. [36] MOISEEVA O, DESCHÊNES-SIMARD X, ST-GERMAIN E, et al. Metformin inhibits the senescence-associated secretory phenotype by interfering with IKK/NF-κB activation[J]. Aging Cell, 2013, 12( 3): 489- 498. DOI: 10.1111/acel.12075. [37] ZHU Y, TCHKONIA T, PIRTSKHALAVA T, et al. The Achilles’ heel of senescent cells: From transcriptome to senolytic drugs[J]. Aging Cell, 2015, 14( 4): 644- 658. DOI: 10.1111/acel.12344. [38] ISLAM MT, TUDAY E, ALLEN S, et al. Senolytic drugs, dasatinib and quercetin, attenuate adipose tissue inflammation, and ameliorate metabolic function in old age[J]. Aging Cell, 2023, 22( 2): e13767. DOI: 10.1111/acel.13767. [39] BAAR MP, BRANDT RMC, PUTAVET DA, et al. Targeted apoptosis of senescent cells restores tissue homeostasis in response to chemotoxicity and aging[J]. Cell, 2017, 169( 1): 132- 147. e 16. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.02.031. [40] CHIN AF, HAN J, CLEMENT CC, et al. Senolytic treatment reduces oxidative protein stress in an aging male murine model of post-traumatic osteoarthritis[J]. Aging Cell, 2023, 22( 11): e13979. DOI: 10.1111/acel.13979. [41] CHAUHAN D, TIAN Z, NICHOLSON B, et al. A small molecule inhibitor of ubiquitin-specific protease-7 induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells and overcomes bortezomib resistance[J]. Cancer Cell, 2012, 22( 3): 345- 358. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.08.007. [42] ZHANG L, PITCHER LE, PRAHALAD V, et al. Targeting cellular senescence with senotherapeutics: Senolytics and Senomorphics[J]. FEBS J, 2023, 290( 5): 1362- 1383. DOI: 10.1111/febs.16350. [43] SUN Y. Pathophysiological implications of cellular senescence and prospects for novel anti-aging drugs[J]. Acta Physiol Sin, 2023, 75( 6): 847- 863. DOI: 10.13294/j.aps.2023.0083.孙宇. 细胞衰老的病理生理学意义和新型抗衰老药物的发展前景[J]. 生理学报, 2023, 75( 6): 847- 863. DOI: 10.13294/j.aps.2023.0083. [44] SELVARANI R, MOHAMMED S, RICHARDSON A. Effect of rapamycin on aging and age-related diseases-past and future[J]. Geroscience, 2021, 43( 3): 1135- 1158. DOI: 10.1007/s11357-020-00274-1. [45] NOREN HOOTEN N, MARTIN-MONTALVO A, DLUZEN DF, et al. Metformin-mediated increase in DICER1 regulates microRNA expression and cellular senescence[J]. Aging Cell, 2016, 15( 3): 572- 581. DOI: 10.1111/acel.12469. [46] BARZILAI N, CRANDALL JP, KRITCHEVSKY SB, et al. Metformin as a tool to target aging[J]. Cell Metab, 2016, 23( 6): 1060- 1065. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.05.011. [47] QI XY, SONG AP, MA MY, et al. Curcumol inhibits ferritinophagy to restrain hepatocyte senescence through YAP/NCOA4 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Cell Prolif, 2021, 54( 9): e13107. DOI: 10.1111/cpr.13107. [48] BABOOTA RK, RAWSHANI A, BONNET L, et al. BMP4 and Gremlin 1 regulate hepatic cell senescence during clinical progression of NAFLD/NASH[J]. Nat Metab, 2022, 4( 8): 1007- 1021. DOI: 10.1038/s42255-022-00620-x. [49] HUA YQ, ZENG Y, XU J, et al. Naringenin alleviates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in middle-aged Apoe-/-mice: Role of SIRT1[J]. Phytomedicine, 2021, 81: 153412. DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153412. [50] KRIZHANOVSKY V, YON M, DICKINS RA, et al. Senescence of activated stellate cells limits liver fibrosis[J]. Cell, 2008, 134( 4): 657- 667. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.06.049. -



 PDF下载 ( 1061 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1061 KB)

 下载:
下载:


