超声内镜下选择性食管胃静脉曲张来源支穿刺组织胶封闭术与传统内镜治疗的随机对照研究
DOI: 10.12449/JCH250617
Safety and efficacy of puncture cyanoacrylate selective seal under endoscopic ultrasound versus traditional endoscopy in treatment of gastroesophageal varices: A randomized controlled trial
-
摘要:
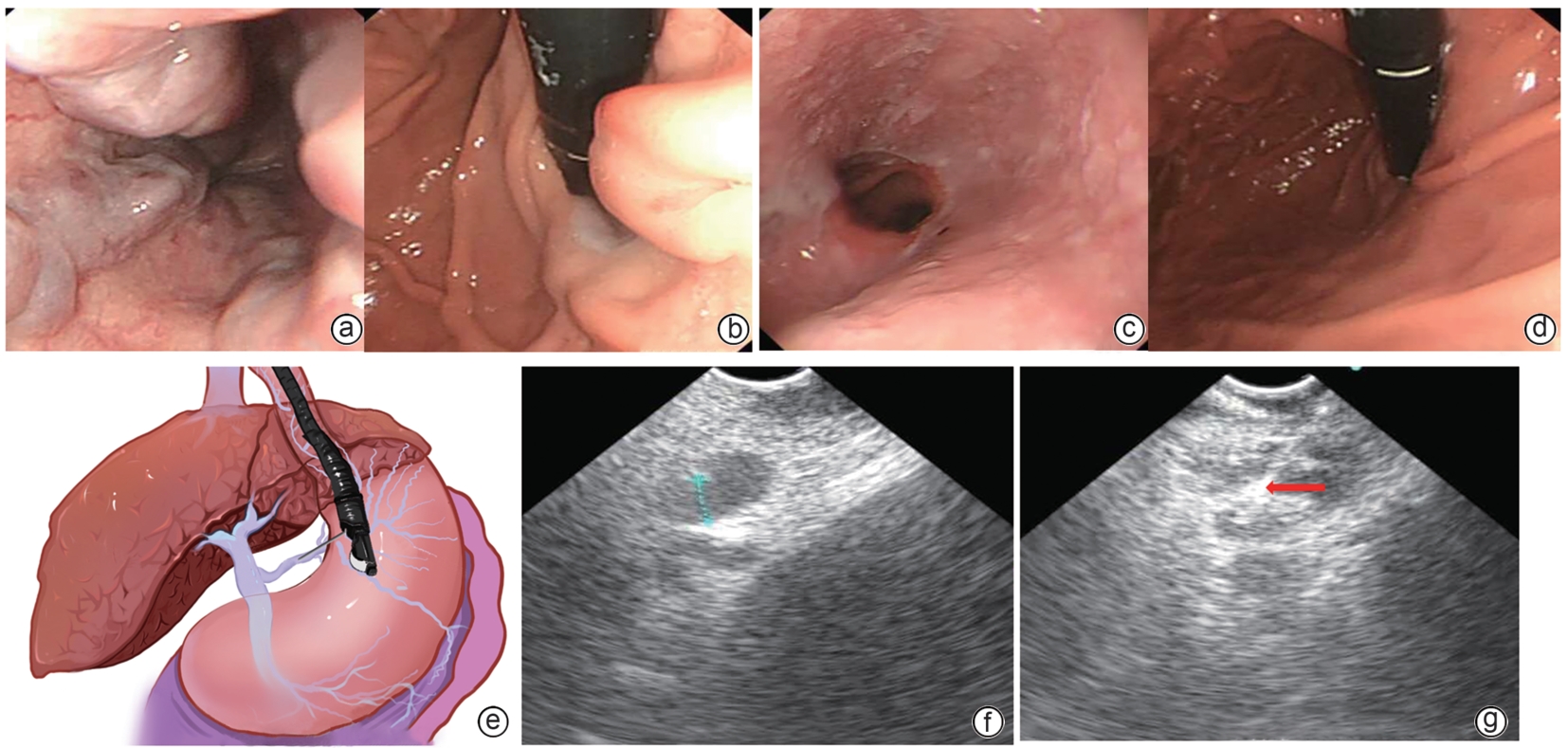
目的 探讨超声内镜下食管胃静脉曲张(GOV)来源支组织胶栓塞封闭术(PCSS)的安全性及疗效。 方法 纳入2023年3月1日—12月31日于首都医科大学附属北京地坛医院行GOV出血二级预防内镜治疗的肝硬化患者共100例,随机分为PCSS组和传统内镜治疗组,术后随访6个月,比较两组的疗效和并发症情况,主要观察指标为GOV的硬化减轻或消失率,次要观察指标为静脉曲张再出血和死亡。正态分布及近似正态分布的定量资料2组间比较采用成组t检验,非正态分布的定量资料2组间比较采用Wilcoxon非参数检验;定性资料2组间比较采用χ2检验或Fisher确切概率法。 结果 PCSS组50例,脱落1例;传统内镜治疗组50例,脱落3例。患者年龄、性别、Child-Pugh分级、静脉曲张程度、胃静曲张分型等基线资料在两组间差异均无统计学意义(P值均>0.05)。PCSS组内镜治疗的次数(t=-15.671,P=0.001)、总组织胶使用量(t=-2.830,P=0.006)、术后静脉曲张的实变减轻或根除率(χ2=7.078,P=0.029)均明显优于传统内镜治疗组。两组术后再出血率、不良反应及并发症发生率均很低,且差异均无统计学意义(P值均>0.05)。 结论 PCSS与传统内镜治疗相比,在不降低安全性的前提下,显著增加疗效。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the safety and efficacy of puncture cyanoacrylate selective seal (PCSS) under endoscopic ultrasound in the treatment of gastroesophageal varices (GOV). Methods A total of 100 patients with liver cirrhosis who underwent endoscopic therapy for the secondary prevention of GOV bleeding in Beijing Ditan Hospital, Capital Medical University, from March 1 to December 31, 2023 were enrolled and randomly divided into PCSS group and traditional endoscopy group. The patients were followed up for 6 months after surgery, and the two groups were compared in terms of clinical outcome and complications. The primary outcome measure was the rate of alleviation or disappearance of GOV, and the secondary outcome measure was variceal rebleeding and death. The independent-samples t test was used for comparison of normally distributed or approximately normally distributed quantitative data between two groups, and the Wilcoxon non-parametric test was used for comparison of non-normally distributed quantitative data between two groups; the chi-square test or the Fisher’s exact test was used for comparison of qualitative data between two groups. Results There were 50 patients in the PCSS group, among whom 1 patient was lost to follow-up, and there were 50 patients in the traditional endoscopy group, among whom 3 patients were lost to follow-up. There were no significant differences between the two groups in baseline data such as age, sex, Child-Pugh class, varices grade, and GOV typing (all P>0.05). Compared with the traditional endoscopy group, the PCSS group had significantly better results of the number of endoscopic treatment sessions (t=-15.671, P=0.001), the total amount of tissue adhesive used (t=-2.830, P=0.006), and the rate of alleviation or eradication of varices sclerosis (χ2=7.078, P=0.029). Both groups had low rates of postoperative rebleeding, adverse reactions, and complications, and there were no significant differences between the two groups (all P>0.05). Conclusion Compared with traditional endoscopy, PCSS can significantly enhance treatment outcome while maintaining safety standards. -
表 1 PCSS组和传统内镜治疗组的基线资料比较
Table 1. Comparison of baseline data between PCSS group and control group
指标 PCSS组(n=49) 传统内镜治疗组(n=47) 统计值 P值 年龄(岁) 55(48~65) 57(46~67) Z=-0.583 0.560 男/女(例) 33/16 25/22 χ2=2.887 0.097 总胆红素(μmol/L) 21.10(13.05~31.75) 14.85(10.10~23.25) Z=-1.880 0.600 白蛋白(g/L) 33.95±5.05 34.94±0.35 t=-0.915 0.490 国际标准化比值 1.37±0.18 1.28±0.18 t=2.240 0.624 Child-Pugh分级(例) χ2=0.030 0.863 A级 40 39 B/C级 9 8 食管静脉曲张程度(例) χ2=1.009 0.315 G2 10 6 G3 39 41 胃静脉曲张(例) χ2=0.922 >0.05 GOV1 40 38 GOV2 9 9 肝硬化病因(例) χ2=4.689 0.096 病毒性肝炎 24 33 酒精性肝病 9 4 其他 16 10 表 2 PCSS与传统内镜方法对GOV的治疗情况和疗效比较
Table 2. Comparison of PCSS and traditional endostherapy in the treatment of GOV
指标 PCSS组(n=49) 传统内镜治疗组(n=47) 统计值 P值 首次治疗组织胶使用量(mL) 3.63±1.83 3.07±1.67 t=1.532 0.129 总组织胶使用量(mL) 3.82±1.88 4.88±1.72 t=-2.830 0.006 首次治疗硬化剂使用量(支) 2.92±1.17 2.35±1.02 t=2.172 0.075 总硬化剂使用量(mL) 33.70±1.20 32.10±1.25 t=0.620 0.538 内镜治疗次数 1.08±0.28 2.20±0.41 t=-15.671 0.001 术后6个月曲张静脉变化(例) χ2=7.078 0.029 根除 12 4 实变减轻 37 40 无变化或加重 0 3 术后6个月再出血(例) 2 1 >0.05 表 3 PCSS与传统内镜方法治疗GOV的安全性比较
Table 3. Comparison of the safety profiles between PCSS and traditional endotherapy in the treatment of GOV
不良反应及并发症 PCSS组
(n=49)传统内镜治疗组
(n=47)腹痛(例) 1 2 恶心呕吐(例) 0 1 发热(例) 1 1 新发门静脉血栓(例) 0 1 异位栓塞(例) 1 0 总发生率[例(%)] 3(6.1) 5(10.6) -
[1] MAYDEO A, PATIL G. How to approach a patient with gastric varices[J]. Gastroenterology, 2022, 162( 3): 689- 695. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.12.277. [2] WENDY TAN AY, CHIENG JY. Endoscopic variceal ligation as primary prophylaxis for esophageal variceal bleeding at a Malaysian tertiary hospital[J]. Med J Malaysia, 2018, 73( 6): 361- 364. [3] GARCIA-TSAO G, SANYAL AJ, GRACE ND, et al. Prevention and management of gastroesophageal varices and variceal hemorrhage in cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2007, 46( 3): 922- 938. DOI: 10.1002/hep.21907. [4] ZHANG MY, LI P, MOU HJ, et al. Clip-assisted endoscopic cyanoacrylate injection for gastric varices with a gastrorenal shunt: A multicenter study[J]. Endoscopy, 2019, 51( 10): 936- 940. DOI: 10.1055/a-0977-3022. [5] Esophagogastric Varices Group of Chinese Society of Digestive Endoscopology. Trial protocol for endoscopic diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal varicose veins and bleeding(2009)[J]. China Contin Med Educ, 2010, 2( 6): 21- 26.中华医学会消化内镜学分会食管胃静脉曲张学组. 消化道静脉曲张及出血的内镜诊断和治疗规范试行方案(2009年)[J]. 中国继续医学教育, 2010, 2( 6): 21- 26. [6] KAPLAN DE, RIPOLL C, THIELE M, et al. AASLD Practice Guidance on risk stratification and management of portal hypertension and varices in cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2024, 79( 5): 1180- 1211. DOI: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000647. [7] ZHANG S, ZHANG XB, LIU YD, et al. Endoscopic management of esophagogastric varices in patients with liver cirrhosis[J/OL]. Chin J Gastrointestial Endoscopy(Electronic Editon), 2024, 11( 3): 191- 194. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-7157.2024.03.010.张帅, 张晓彬, 刘迎娣, 等. 肝硬化食管胃静脉曲张的内镜管理[J/OL]. 中华胃肠内镜电子杂志, 2024, 11( 3): 191- 194. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-7157.2024.03.010. [8] de FRANCHIS R, BOSCH J, GARCIA-TSAO G, et al. Baveno VII- Renewing consensus in portal hypertension[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 76( 4): 959- 974. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.12.022. [9] KRIGE J, JONAS E, KOTZE U, et al. Defining the advantages and exposing the limitations of endoscopic variceal ligation in controlling acute bleeding and achieving complete variceal eradication[J]. World J Gastrointest Endosc, 2020, 12( 10): 365- 377. DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v12.i10.365. [10] ALI SM, WU SB, XU HW, et al. A prospective study of endoscopic injection sclerotherapy and endoscopic variceal ligation in the treatment of esophageal varices[J]. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A, 2017, 27( 4): 333- 341. DOI: 10.1089/lap.2016.0436. [11] SCHUMAN BM, BECKMAN JW, TEDESCO FJ, et al. Complications of endoscopic injection sclerotherapy: a review[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 1987, 82: 823- 830. [12] O’ROURKE J, TODD A, SHEKHAR C, et al. EUS-guided thrombin injection and coil implantation for gastric varices: Feasibility, safety, and outcomes[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2024, 100( 3): 549- 556. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2024.01.044. [13] TSENG Y, MA LL, LUO TC, et al. Patient response to endoscopic therapy for gastroesophageal varices based on endoscopic ultrasound findings[J]. Gut Liver, 2018, 12( 5): 562- 570. DOI: 10.5009/gnl17471. [14] CARNEIRO FOAA, RETES FA, MATUGUMA SE, et al. Role of EUS evaluation after endoscopic eradication of esophageal varices with band ligation[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2016, 84( 3): 400- 407. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2016.02.006. [15] IRISAWA A, SAITO A, OBARA K, et al. Endoscopic recurrence of esophageal varices is associated with the specific EUS abnormalities: Severe periesophageal collateral veins and large perforating veins[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2001, 53( 1): 77- 84. DOI: 10.1067/mge.2001.108479. [16] SOMEBERG KA. TIPS: safe, effective, better?[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 1997, 92( 9): 1412- 1416. [17] LIANG A, BRAR S, ALMAGHRABI M, et al. Primary prevention of hepatic encephalopathy post-TIPS: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2023, 102( 38): e35266. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035266. [18] ZHANG H, XIAO JQ, TU JJ, et al. Prevention of variceal rebleeding in cirrhotic patients with spontaneous portosystemic shunts: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus endoscopic treatment[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 33( 5): 752- 761. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000002079. [19] KHAKWANI A, TRIVEDI M, AFZAL M, et al. Use of balloon occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration(BRTO) for treatment of gastric varices: A narrative review[J]. Cureus, 2023, 15( 4): e38233. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.38233. [20] MOHAN BP, CHANDAN S, KHAN SR, et al. Efficacy and safety of endoscopic ultrasound-guided therapy versus direct endoscopic glue injection therapy for gastric varices: Systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Endoscopy, 2020, 52( 4): 259- 267. DOI: 10.1055/a-1098-1817. [21] SAMANTA J, NABI Z, FACCIORUSSO A, et al. EUS-guided coil and glue injection versus endoscopic glue injection for gastric varices: International multicentre propensity-matched analysis[J]. Liver Int, 2023, 43( 8): 1783- 1792. DOI: 10.1111/liv.15630. [22] GRALNEK IM, CAMUS DUBOC M, GARCIA-PAGAN JC, et al. Endoscopic diagnosis and management of esophagogastric variceal hemorrhage: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy(ESGE) Guideline[J]. Endoscopy, 2022, 54( 11): 1094- 1120. DOI: 10.1055/a-1939-4887. -



 PDF下载 ( 1855 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1855 KB)


 下载:
下载: