3-羟基-3-甲基戊二酰辅酶A还原酶(HMGCR)在肝脏疾病中的作用
DOI: 10.12449/JCH250527
-
摘要: 胆固醇是细胞膜生物合成、细胞增殖与分化不可或缺的分子,肝脏在体内胆固醇代谢中扮演着核心角色,负责胆固醇的合成、摄取、分泌与转运等关键功能。肝脏中胆固醇合成的起始环节尤为重要,其异常与多种肝脏疾病的发展密切相关。研究表明,3-羟基-3-甲基戊二酰辅酶A还原酶(HMGCR)作为胆固醇生物合成中的关键限速酶,其控制特性明确,已被证实为多种肝脏疾病调控的重要靶点。本文将简要回顾胆固醇代谢的过程、HMGCR的降解与调控机制,以及抑制剂的应用,同时探讨HMGCR在多种肝脏疾病中的作用,旨在为科研和临床防治肝脏疾病提供新思路。
-
关键词:
- 肝疾病 /
- 3-羟基-3-甲基戊二酰辅酶A还原酶 /
- 胆固醇
Abstract: Cholesterol is an essential molecule for the biosynthesis of cell membranes and cell proliferation and differentiation, and the liver plays a central role in cholesterol metabolism and is responsible for the synthesis, uptake, secretion, and transport of cholesterol. The initial stages of cholesterol synthesis in the liver are particularly important, and abnormalities in such stages are closely associated with the progression of various liver diseases. Studies have shown that as a key rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMGCR) has well-defined regulatory properties and has been confirmed as an important target for the regulation of various liver diseases. This article reviews the process of cholesterol metabolism, the degradation and regulatory mechanisms of HMGCR, and the application of inhibitors, as well as the role of HMGCR in liver diseases, in order to provide new insights for scientific research and the clinical prevention and treatment of liver diseases. -
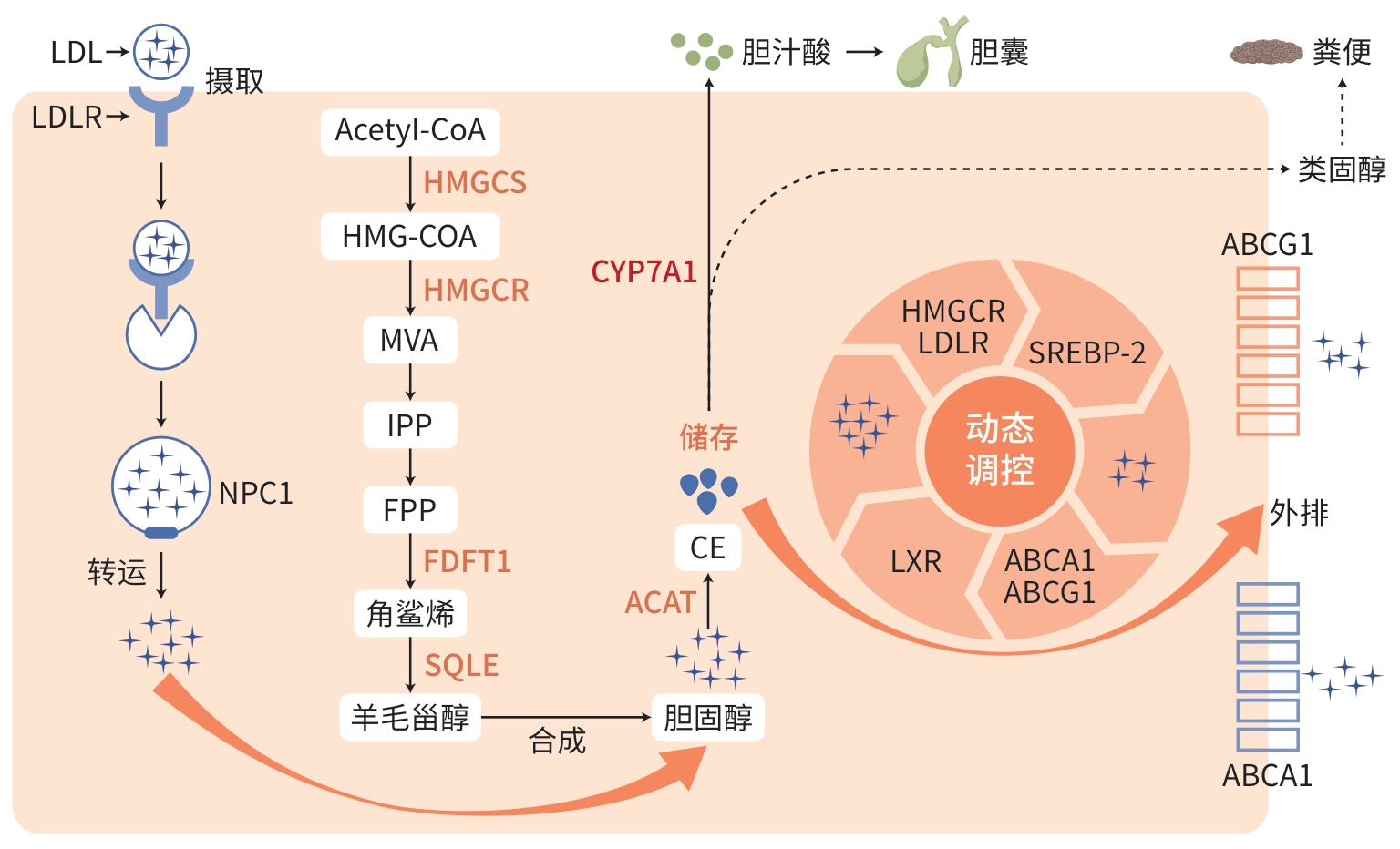
注: LDL,低密度脂蛋白;LDLR,低密度脂蛋白受体;NPC1,尼曼-匹克C1型蛋白1;Acetyl-CoA,乙酰辅酶A;HMGCS,羟甲基戊二酰辅酶A合成酶;HMG-CoA,β-羟基-β-甲基戊二酰辅酶A;HMGCR,3-羟基-3-甲基戊二酰辅酶A还原酶;MVA,甲羟戊酸;IPP,异戊烯醇焦磷酸酯;FPP,法尼基焦磷酸;FDFT1,法尼基二磷酸法尼基转移酶1;SQLE,角鲨烯环氧化酶;ACAT,胆固醇酰基转移酶;CE,胆固醇酯;CYP7A1,细胞色素P450 7A1;ABCA1,三磷酸腺苷结合盒转运体;ABCG1,ATP结合盒转运体G1;LXR,肝X受体;SREBP-2,甾醇调节元件结合蛋白-2。
图 1 胆固醇代谢机制
Figure 1. Cholesterol metabolism mechanism
-
[1] DEVARBHAVI H, ASRANI SK, ARAB JP, et al. Global burden of liver disease: 2023 update[J]. J Hepatol, 2023, 79( 2): 516- 537. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.03.017. [2] WANG JQ, LI LL, HU A, et al. Inhibition of ASGR1 decreases lipid levels by promoting cholesterol excretion[J]. Nature, 2022, 608( 7922): 413- 420. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-05006-3. [3] LIU W, CHAKRABORTY B, SAFI R, et al. Dysregulated cholesterol homeostasis results in resistance to ferroptosis increasing tumorigenicity and metastasis in cancer[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12( 1): 5103. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-25354-4. [4] HASSEN C BEN, GOUPILLE C, VIGOR C, et al. Is cholesterol a risk factor for breast cancer incidence and outcome?[J]. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, 2023, 232: 106346. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2023.106346. [5] LIANG ZC, ZHANG Z, TAN XN, et al. Lipids, cholesterols, statins and liver cancer: A Mendelian randomization study[J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1251873. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1251873. [6] YU JJ, DU YZ, SU J, et al. Preventive effect and mechanism of Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium on hypercholesterolemia rats[J]. Chin Tradit Pat Med, 2021, 43( 11): 2982- 2988. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2021.11.009.俞静静, 杜宇忠, 苏洁, 等. 陈皮对高胆固醇血症大鼠的预防作用及其机制[J]. 中成药, 2021, 43( 11): 2982- 2988. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2021.11.009. [7] YANG F, KOU JJ, LIU ZZ, et al. MYC enhances cholesterol biosynthesis and supports cell proliferation through SQLE[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9: 655889. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.655889. [8] XU HJ, ZHOU S, TANG QL, et al. Cholesterol metabolism: New functions and therapeutic approaches in cancer[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2020, 1874( 1): 188394. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188394. [9] SAHA P, SHUMATE JL, CALDWELL JG, et al. Inter-domain dynamics drive cholesterol transport by NPC1 and NPC1L1 proteins[J]. eLife, 2020, 9: e57089. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.57089. [10] van de SLUIS B, WIJERS M, HERZ J. News on the molecular regulation and function of hepatic low-density lipoprotein receptor and LDLR-related protein 1[J]. Curr Opin Lipidol, 2017, 28( 3): 241- 247. DOI: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000411. [11] BAZIOTI V, LA ROSE AM, MAASSEN S, et al. T cell cholesterol efflux suppresses apoptosis and senescence and increases atherosclerosis in middle aged mice[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13( 1): 3799. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-31135-4. [12] WANG PH, YUE ZZ, WEI XT, et al. Influence of extracts from Euphorbiae Semen before and after frosting on cholesterol efflux in Caco-2 cells through liver X receptor-adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette transporter A1 pathway[J]. Chin J Clin Pharmacol, 2023, 39( 2): 201- 205. DOI: 10.13699/j.cnki.1001-6821.2023.02.011.王佩华, 岳珠珠, 魏晓彤, 等. 千金子制霜前后提取物通过肝X受体-腺苷三磷酸结合盒转运体A1信号通路对Caco-2细胞中胆固醇外流的影响[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2023, 39( 2): 201- 205. DOI: 10.13699/j.cnki.1001-6821.2023.02.011. [13] YAN CS, ZHENG L, JIANG ST, et al. Exhaustion-associated cholesterol deficiency dampens the cytotoxic arm of antitumor immunity[J]. Cancer Cell, 2023, 41( 7): 1276- 1293. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2023.04.016. [14] CARDOSO D, PERUCHA E. Cholesterol metabolism: A new molecular switch to control inflammation[J]. Clin Sci(Lond), 2021, 135( 11): 1389- 1408. DOI: 10.1042/CS20201394. [15] LIM MYC, HO HK. Pharmacological modulation of cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase(CYP7A1) as a therapeutic strategy for hypercholesterolemia[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2024, 220: 115985. DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115985. [16] TAN JME, COOK ECL, van den BERG M, et al. Differential use of E2 ubiquitin conjugating enzymes for regulated degradation of the rate-limiting enzymes HMGCR and SQLE in cholesterol biosynthesis[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2019, 281: 137- 142. DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.12.008. [17] FAULKNER R, JO Y. Synthesis, function, and regulation of sterol and nonsterol isoprenoids[J]. Front Mol Biosci, 2022, 9: 1006822. DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1006822. [18] FAULKNER RA, YANG YY, TSIEN J, et al. Direct binding to sterols accelerates endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation of HMG CoA reductase[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2024, 121( 7): e2318822121. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2318822121. [19] JIANG LY, JIANG W, TIAN N, et al. Ring finger protein 145(RNF145) is a ubiquitin ligase for sterol-induced degradation of HMG-CoA reductase[J]. J Biol Chem, 2018, 293( 11): 4047- 4055. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001260. [20] van den BOOMEN DJH, VOLKMAR N, LEHNER PJ. Ubiquitin-mediated regulation of sterol homeostasis[J]. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2020, 65: 103- 111. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2020.04.010. [21] MENZIES SA, VOLKMAR N, van den BOOMEN DJ, et al. The sterol-responsive RNF145 E3 ubiquitin ligase mediates the degradation of HMG-CoA reductase together with gp78 and Hrd1[J]. eLife, 2018, 7: e40009. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.40009. [22] ALI N, ALLAM H, BADER T, et al. Fluvastatin interferes with hepatitis C virus replication via microtubule bundling and a doublecortin-like kinase-mediated mechanism[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8( 11): e80304. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080304. [23] ALANNAN M, TRÉZÉGUET V, AMOÊDO ND, et al. Rewiring lipid metabolism by targeting PCSK9 and HMGCR to treat liver cancer[J]. Cancers(Basel), 2022, 15( 1): 3. DOI: 10.3390/cancers15010003. [24] JIANG W, HU JW, HE XR, et al. Statins: A repurposed drug to fight cancer[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2021, 40( 1): 241. DOI: 10.1186/s13046-021-02041-2. [25] ESLAMI Z, AGHILI SS, GHAFI AG. Atorvastatin on treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients[J]. Chonnam Med J, 2024, 60( 1): 13- 20. DOI: 10.4068/cmj.2024.60.1.13. [26] WANG HJ, LIU SY, ZHOU CJ, et al. Fatal hepatic failure following atorvastatin treatment: A case report[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2023, 102( 19): e33743. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033743. [27] TORRE P, AGLITTI A, MASARONE M, et al. Viral hepatitis: Milestones, unresolved issues, and future goals[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2021, 27( 28): 4603- 4638. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i28.4603. [28] GLITSCHER M, HILDT E. Endosomal cholesterol in viral infections- A common denominator?[J]. Front Physiol, 2021, 12: 750544. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.750544. [29] HSU CS, LIU WL, LI QS, et al. Hepatitis C virus genotypes 1-3 infections regulate lipogenic signaling and suppress cholesterol biosynthesis in hepatocytes[J]. J Formos Med Assoc, 2020, 119( 9): 1382- 1395. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfma.2020.03.018. [30] LI YJ, ZHU P, LIANG Y, et al. Hepatitis B virus induces expression of cholesterol metabolism-related genes via TLR2 in HepG2 cells[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2013, 19( 14): 2262- 2269. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i14.2262. [31] LIN SH, HUANG KJ, WENG CF, et al. Exploration of natural product ingredients as inhibitors of human HMG-CoA reductase through structure-based virtual screening[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2015, 9: 3313- 3324. DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S84641. [32] THONGSRI P, PEWKLIANG Y, BORWORNPINYO S, et al. Curcumin inhibited hepatitis B viral entry through NTCP binding[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11( 1): 19125. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-98243-x. [33] NAN C. Predictive value of triglyceride to high density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio combined with γ-glutamyl transpeptidase in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hebei Med J, 2023, 45( 3): 385- 387, 391. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2023.03.015.南忱. 三酰甘油与高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值联合γ-谷氨酰转肽酶对非酒精性脂肪性肝病的预测价值[J]. 河北医药, 2023, 45( 3): 385- 387, 391. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2023.03.015. [34] TEWARI DN, BISWAS A, CHAKRABARTI AK, et al. AMFR promotes innate immunity activation and proteasomal degradation of HMGCR in response to influenza virus infection in A549 cells[J]. Virology, 2023, 587: 109875. DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2023.109875. [35] LI XZ, JIANG SY, LI GQ, et al. Synthesis of heterocyclic ring-fused analogs of HMG499 as novel degraders of HMG-CoA reductase that lower cholesterol[J]. Eur J Med Chem, 2022, 236: 114323. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114323. [36] LI ZY, ZHOU Y, JIA KW, et al. JMJD4-demethylated RIG-I prevents hepatic steatosis and carcinogenesis[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2022, 15( 1): 161. DOI: 10.1186/s13045-022-01381-6. [37] HONG T, ZOU J, YANG J, et al. Curcumin protects against bisphenol A-induced hepatic steatosis by inhibiting cholesterol absorption and synthesis in CD-1 mice[J]. Food Sci Nutr, 2023, 11( 9): 5091- 5101. DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.3468. [38] ZHAO CZ, JIANG W, ZHU YY, et al. Highland barley Monascus purpureus Went extract ameliorates high-fat, high-fructose, high-cholesterol diet induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by regulating lipid metabolism in golden hamsters[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2022, 286: 114922. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114922. [39] TONG J, LAN XT, ZHANG Z, et al. Ferroptosis inhibitor liproxstatin-1 alleviates metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in mice: Potential involvement of PANoptosis[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2023, 44( 5): 1014- 1028. DOI: 10.1038/s41401-022-01010-5. [40] RAZA S, RAJAK S, UPADHYAY A, et al. Current treatment paradigms and emerging therapies for NAFLD/NASH[J]. Front Biosci(Landmark Ed), 2021, 26( 2): 206- 237. DOI: 10.2741/4892. [41] KAMINSKY-KOLESNIKOV Y, RAUCHBACH E, ABU-HALAKA D, et al. Cholesterol induces Nrf-2- and HIF-1 α-dependent hepatocyte proliferation and liver regeneration to ameliorate bile acid toxicity in mouse models of NASH and fibrosis[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2020, 2020: 5393761. DOI: 10.1155/2020/5393761. [42] VIJAYAN DK, PERUMCHERRY RAMAN S, DARA PK, et al. In vivo anti-lipidemic and antioxidant potential of collagen peptides obtained from great hammerhead shark skin waste[J]. J Food Sci Technol, 2022, 59( 3): 1140- 1151. DOI: 10.1007/s13197-021-05118-0. [43] GUO J, XIE YA. Advances in the mechanism of immune microenvironment regulation of metastatic liver cancer[J]. Hebei Med J, 2023, 45( 8): 1238- 1243.郭驹, 谢裕安. 免疫微环境调控转移性肝癌机制研究进展[J]. 河北医药, 2023, 45( 8): 1238- 1243. [44] SAITO Y, YIN DZ, KUBOTA N, et al. A therapeutically targetable TAZ-TEAD2 pathway drives the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma via ANLN and KIF23[J]. Gastroenterology, 2023, 164( 7): 1279- 1292. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.02.043. [45] LI FY, WANG MG, MAO DW, et al. Association of lipid metabolism reprogramming with the development and progression of primary liver cancer[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2024, 40( 8): 1688- 1692. DOI: 10.12449/JCH240829.李飞燕, 王明刚, 毛德文, 等. 脂代谢重编程与原发性肝癌发生发展的关系[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40( 8): 1688- 1692. DOI: 10.12449/JCH240829. [46] FASOLATO S, PIGOZZO S, PONTISSO P, et al. PCSK9 levels are raised in chronic HCV patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Clin Med, 2020, 9( 10): 3134. DOI: 10.3390/jcm9103134. [47] ROSOFF DB, BELL AS, WAGNER J, et al. Assessing the impact of PCSK9 and HMGCR inhibition on liver function: Drug-target mendelian randomization analyses in four ancestries[J]. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2024, 17( 1): 29- 40. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2023.09.001. [48] ZHANG SZ, ZHU XD, FENG LH, et al. PCSK9 promotes tumor growth by inhibiting tumor cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Exp Hematol Oncol, 2021, 10( 1): 25. DOI: 10.1186/s40164-021-00218-1. [49] CHE L, CHI WN, QIAO Y, et al. Cholesterol biosynthesis supports the growth of hepatocarcinoma lesions depleted of fatty acid synthase in mice and humans[J]. Gut, 2020, 69( 1): 177- 186. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317581. [50] WEI MK, NURJANAH U, HERKILINI A, et al. Unspliced XBP1 contributes to cholesterol biosynthesis and tumorigenesis by stabilizing SREBP2 in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2022, 79( 9): 472. DOI: 10.1007/s00018-022-04504-x. [51] CHEN JR, DING CF, CHEN YH, et al. ACSL4 reprograms fatty acid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma via c-Myc/SREBP1 pathway[J]. Cancer Lett, 2021, 502: 154- 165. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.12.019. [52] WANG HY, SHU L, LV CR, et al. BRCC36 deubiquitinates HMGCR to regulate the interplay between ferroptosis and pyroptosis[J]. Adv Sci(Weinh), 2024, 11( 11): e2304263. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202304263. [53] SELITSKY SR, DINH TA, TOTH CL, et al. Transcriptomic analysis of chronic hepatitis B and C and liver cancer reveals microRNA-mediated control of cholesterol synthesis programs[J]. mBio, 2015, 6( 6): e01500-15. DOI: 10.1128/mBio.01500-15. [54] DING WJ, CHEN LL, XIA JG, et al. Causal association between lipid-lowering drugs and cancers: A drug target Mendelian randomization study[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2024, 103( 18): e38010. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038010. [55] JINDAL A, SARIN SK. Epidemiology of liver failure in Asia-Pacific Region[J]. Liver Int, 2022, 42( 9): 2093- 2109. DOI: 10.1111/liv.15328. [56] YANG C, YANG HS, HU JH, et al. Effect of serum total cholesterol level on prognosis of patients with liver failure[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Liver Dis, 2021, 31( 11): 1053- 1056. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2021.11.027.杨诚, 杨华升, 胡建华, 等. 血清总胆固醇水平对肝衰竭患者预后的影响[J]. 中西医结合肝病杂志, 2021, 31( 11): 1053- 1056. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2021.11.027. [57] TANAKA S, de TYMOWSKI C, STERN J, et al. Relationship between liver dysfunction, lipoprotein concentration and mortality during sepsis[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17( 8): e0272352. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0272352. [58] ALVAREZ-SOLA G, URIARTE I, LATASA MU, et al. Bile acids, FGF15/19 and liver regeneration: From mechanisms to clinical applications[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2018, 1864( 4 Pt B): 1326- 1334. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.06.025. [59] LIN Y, YAN GJ, FENG F, et al. Association between cholesterol and liver regeneration and its significance and potential value in clinical treatment of liver failure[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 3): 708- 713. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.03.044.林镛, 颜耿杰, 冯逢, 等. 胆固醇与肝再生关系及其在肝衰竭治疗中的意义和潜在价值[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 3): 708- 713. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.03.044. [60] PENG J, YU JW, XU H, et al. Enhanced liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in sterol regulatory element-binding protein(SREBP)-1c-null mice is associated with increased hepatocellular cholesterol availability[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 47( 2): 784- 799. DOI: 10.1159/000490030. [61] SLABBER CF, BACHOFNER M, SPEICHER T, et al. The ubiquitin ligase Uhrf2 is a master regulator of cholesterol biosynthesis and is essential for liver regeneration[J]. Sci Signal, 2023, 16( 787): eade8029. DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.ade8029. [62] LIEPINSH E, ZVEJNIECE L, CLEMENSSON L, et al. Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase activity is essential for mitochondrial β-oxidation of fatty acids to prevent lethal accumulation of long-chain acylcarnitines in the mouse liver[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2024, 181( 16): 2750- 2773. DOI: 10.1111/bph.16363. [63] DENG Y, ZHAO Z, SHELDON M, et al. LIFR regulates cholesterol-driven bidirectional hepatocyte-neutrophil cross-talk to promote liver regeneration[J]. Nat Metab, 2024, 6( 9): 1756- 1774. DOI: 10.1038/s42255-024-01110-y. [64] KOSHU K, MURAMATSU K, MARU T, et al. Neonatal onset of Niemann-Pick disease type C in a patient with cholesterol re-accumulation in the transplanted liver and inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Brain Dev, 2023, 45( 9): 517- 522. DOI: 10.1016/j.braindev.2023.06.006. -



 PDF下载 ( 1000 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1000 KB)

 下载:
下载:


