肿瘤坏死因子超家族因子14(LIGHT)在慢性肝病中的作用机制
DOI: 10.12449/JCH250427
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:马亚鹏负责收集资料,撰写论文;马亚楠负责课题设计,拟定写作思路,指导撰写文章并最后定稿。
Mechanism of action of tumor necrosis factor superfamily member 14 in chronic liver diseases
-
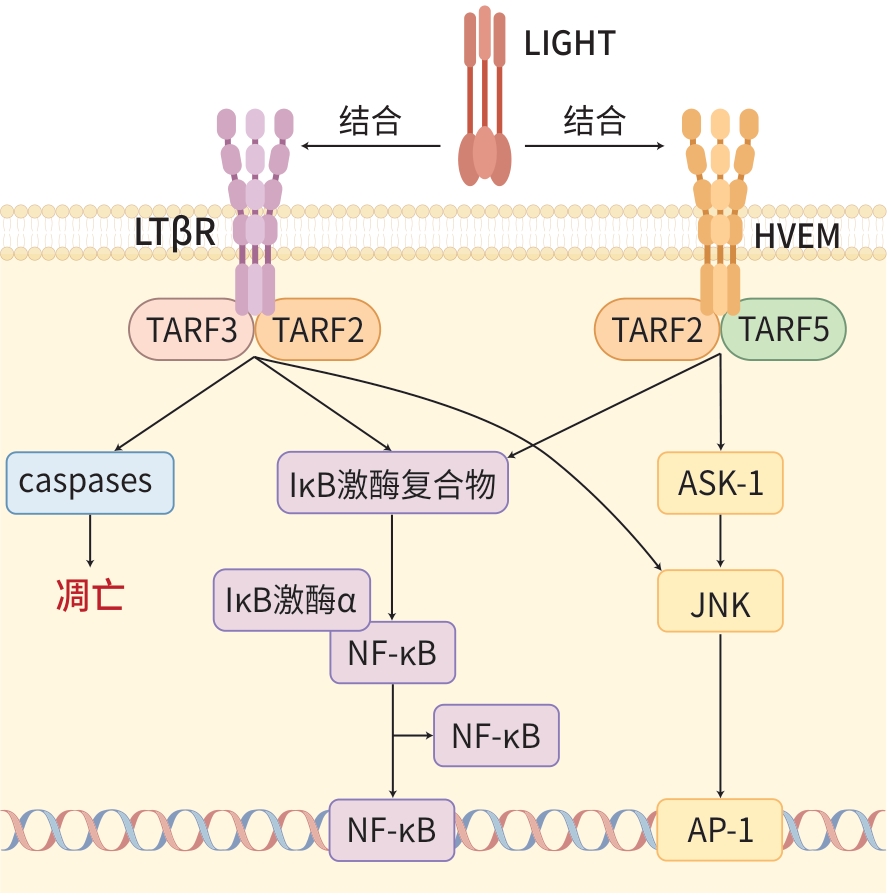
摘要: 肿瘤坏死因子超家族因子14是肿瘤坏死因子超家族的新成员之一,主要通过与功能性受体疱疹病毒侵入介质、淋巴毒素β受体、可溶性诱饵受体3结合介导不同生物学效应,在炎症性疾病、纤维化疾病、抗肿瘤免疫中发挥重要的调节作用。近年来,肿瘤坏死因子超家族因子14在慢性肝病发生发展中的机制及在治疗中的作用日益受到重视。Abstract: Tumor necrosis factor superfamily member 14 (TNFSF14) is a new member of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily member, and it mediates diverse biological functions through binding with herpes virus entry mediator, lymphotoxin-β receptor, and soluble decoy receptor 3, thereby exerting an important regulatory effect in inflammatory diseases, fibrotic diseases, and anti-tumor immunity. In recent years, the mechanism of LIGHT in the development and progression of liver diseases and its role in treatment have attracted more and more attention.
-
Key words:
- Tumor Necrosis Factors /
- Liver Diseases /
- Signal Transduction
-
[1] YOUNOSSI ZM, WONG G, ANSTEE QM, et al. The global burden of liver disease[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 21( 8): 1978- 1991. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.04.015. [2] SHUPTRINE CW, PEREZ VM, SELITSKY SR, et al. Shining a LIGHT on myeloid cell targeted immunotherapy[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2023, 187: 147- 160. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejca.2023.03.040. [3] MAURI DN, EBNER R, MONTGOMERY RI, et al. LIGHT, a new member of the TNF superfamily, and lymphotoxin alpha are ligands for herpesvirus entry mediator[J]. Immunity, 1998, 8( 1): 21- 30. DOI: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80455-0. [4] CROFT M, SIEGEL RM. Beyond TNF: TNF superfamily cytokines as targets for the treatment of rheumatic diseases[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2017, 13( 4): 217- 233. DOI: 10.1038/nrrheum.2017.22. [5] WARE CF. Targeting the LIGHT-HVEM pathway[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2009, 647: 146- 155. DOI: 10.1007/978-0-387-89520-8_10. [6] PIAO WJ, KASINATH V, SAXENA V, et al. LTβR signaling controls lymphatic migration of immune cells[J]. Cells, 2021, 10( 4): 747. DOI: 10.3390/cells10040747. [7] ZOU GM, HU WY. LIGHT regulates CD86 expression on dendritic cells through NF-kappaB, but not JNK/AP-1 signal transduction pathway[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2005, 205( 3): 437- 443. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.20420. [8] LIANG CJ, XU YC, LI GM, et al. Downregulation of DcR3 sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2017, 10: 417- 428. DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S127202. [9] ŠEDÝ JR, RAMEZANI-RAD P. HVEM network signaling in cancer[J]. Adv Cancer Res, 2019, 142: 145- 186. DOI: 10.1016/bs.acr.2019.01.004. [10] FROMM G, de SILVA S, SCHREIBER TH. Reconciling intrinsic properties of activating TNF receptors by native ligands versus synthetic agonists[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1236332. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1236332. [11] STEINBERG MW, CHEUNG TC, WARE CF. The signaling networks of the herpesvirus entry mediator(TNFRSF14) in immune regulation[J]. Immunol Rev, 2011, 244( 1): 169- 187. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01064.x. [12] BORGHI A, VERSTREPEN L, BEYAERT R. TRAF2 multitasking in TNF receptor-induced signaling to NF-κB, MAP kinases and cell death[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2016, 116: 1- 10. DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.03.009. [13] CELIK S, SHANKAR V, RICHTER A, et al. Proinflammatory and prothrombotic effects on human vascular endothelial cells of immune-cell-derived LIGHT[J]. Eur J Med Res, 2009, 14( 4): 147- 156. DOI: 10.1186/2047-783x-14-4-147. [14] HAYBAECK J, ZELLER N, WOLF MJ, et al. A lymphotoxin-driven pathway to hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Cell, 2009, 16( 4): 295- 308. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.08.021. [15] LI GQ, SHANG YH, CAO ZH, et al. Role of TNFSF14 and its receptors LTβR and HVEM in pathogenesis of virus hepatitis[J]. Chin J Immunol, 2015, 31( 12): 1591- 1594. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2015.12.002.李桂清, 尚宇航, 曹朝晖, 等. TNFSF14及其受体LTβR和HVEM在病毒肝炎中的作用[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2015, 31( 12): 1591- 1594. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2015.12.002. [16] WASHBURN ML, KOVALEV GI, KOROLEVA E, et al. LIGHT induces distinct signals to clear an AAV-expressed persistent antigen in the mouse liver and to induce liver inflammation[J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5( 5): e10585. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010585. [17] LAI DM, LV ZJ, LU XH, et al. LIGHT amplification by NF-κB contributes to TLR3 signaling pathway-induced acute hepatitis[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2023, 2023: 3732315. DOI: 10.1155/2023/3732315. [18] ZHANG YL, JIANG WZ, FAN Y, et al. Engineering enhancement of the immune response to HBV DNA vaccine in mice by the use of LIGHT gene adjuvant[J]. J Virol Methods, 2008, 153( 2): 142- 148. DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2008.07.013. [19] JIANG WZ, CHEN R, KONG XB, et al. Immunization with adenovirus LIGHT-engineered dendritic cells induces potent T cell responses and therapeutic immunity in HBV transgenic mice[J]. Vaccine, 2014, 32( 35): 4565- 4570. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.06.039. [20] MA SY, CHEN XH, TAN QH, et al. An engineered novel lentivector specifically transducing dendritic cells and eliciting robust HBV-specific CTL response by upregulating autophagy in T cells[J]. Cell Cycle, 2018, 17( 10): 1220- 1234. DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2018.1471312. [21] OTTERDAL K, HAUKELAND JW, YNDESTAD A, et al. Increased serum levels of LIGHT/TNFSF14 in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Possible role in hepatic inflammation[J]. Clin Transl Gastroenterol, 2015, 6( 7): e95. DOI: 10.1038/ctg.2015.23. [22] HERRERO-CERVERA A, VINUÉ Á, BURKS DJ, et al. Genetic inactivation of the LIGHT(TNFSF14) cytokine in mice restores glucose homeostasis and diminishes hepatic steatosis[J]. Diabetologia, 2019, 62( 11): 2143- 2157. DOI: 10.1007/s00125-019-4962-6. [23] MIAO XL, GUO Y, ZENG S, et al. HES5-mediated repression of LIGHT transcription may contribute to apoptosis in hepatocytes[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2021, 7( 1): 308. DOI: 10.1038/s41420-021-00707-6. [24] SAUNDERS BM, RUDNICKA C, FILIPOVSKA A, et al. Shining LIGHT on the metabolic role of the cytokine TNFSF14 and the implications on hepatic IL-6 production[J]. Immunol Cell Biol, 2018, 96( 1): 41- 53. DOI: 10.1111/imcb.1002. [25] AGOSTINO M, ROONEY J, HERAT L, et al. TNFSF14-derived molecules as a novel treatment for obesity and type 2 diabetes[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22( 19): 10647. DOI: 10.3390/ijms221910647. [26] XU Y, PENG WP, HAN D, et al. Maiwei Yangfei decoction prevents bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2021, 22( 5): 1306. DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.10741. [27] SCHIMMEL K, ICHIMURA K, REDDY S, et al. Cardiac fibrosis in the pressure overloaded left and right ventricle as a therapeutic target[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 9: 886553. DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.886553. [28] MANRESA MC, CHIANG AWT, KURTEN RC, et al. Increased production of LIGHT by T cells in eosinophilic esophagitis promotes differentiation of esophageal fibroblasts toward an inflammatory phenotype[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 159( 5): 1778- 1792. e 13. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.07.035. [29] STEELE H, CHENG J, WILLICUT A, et al. TNF superfamily control of tissue remodeling and fibrosis[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1219907. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1219907. [30] KANAI S, FUJIWARA H, MIZUNO S, et al. Increased expression of TNFRSF14 and LIGHT in biliary epithelial cells of patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2024, 56( 2): 305- 311. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2023.08.057. [31] ELßNER C, GOEPPERT B, LONGERICH T, et al. Nuclear translocation of RELB is increased in diseased human liver and promotes ductular reaction and biliary fibrosis in mice[J]. Gastroenterology, 2019, 156( 4): 1190- 1205. e 14. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.11.018. [32] YUAN ZH, WANG J, ZHANG HR, et al. Triptolide increases resistance to bile duct ligation-induced liver injury and fibrosis in mice by inhibiting RELB[J]. Front Nutr, 2022, 9: 1032722. DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1032722. [33] LIANG QS, XIE JG, YU CP, et al. Splenectomy improves liver fibrosis via tumor necrosis factor superfamily 14(LIGHT) through the JNK/TGF-β1 signaling pathway[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2021, 53( 3): 393- 406. DOI: 10.1038/s12276-021-00574-2. [34] SKEATE JG, OTSMAA ME, PRINS R, et al. TNFSF14: Lighting the way for effective cancer immunotherapy[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 922. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00922. [35] HAN B, WU LQ, MA X, et al. Synergistic effect of IFN-γ gene on LIGHT-induced apoptosis in HepG2 cells via down regulation of Bcl-2[J]. Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol, 2011, 39( 4): 228- 238. DOI: 10.3109/10731199.2010.538403. [36] LI J, SHEN F, WU D, et al. Expression level of Bcl-XL critically affects sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to LIGHT-enhanced and interferon-gamma-induced apoptosis[J]. Oncol Rep, 2007, 17( 5): 1067- 1075. [37] CHEN MC, HSU TL, LUH TY, et al. Overexpression of bcl-2 enhances LIGHT- and interferon-gamma-mediated apoptosis in Hep3BT2 cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2000, 275( 49): 38794- 38801. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M003292200. [38] MAKER AV, ITO H, MO QX, et al. Genetic evidence that intratumoral T-cell proliferation and activation are associated with recurrence and survival in patients with resected colorectal liver metastases[J]. Cancer Immunol Res, 2015, 3( 4): 380- 388. DOI: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-14-0212. [39] QIAO GL, QIN JZ, KUNDA N, et al. LIGHT elevation enhances immune eradication of colon cancer metastases[J]. Cancer Res, 2017, 77( 8): 1880- 1891. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-1655. [40] CHENG JM, LI YY, WANG XH, et al. Response stratification in the first-line combined immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma at genomic, transcriptional and immune repertoire levels[J]. J Hepatocell Carcinoma, 2021, 8: 1281- 1295. DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S326356. [41] QIU YY, ZHANG J, ZENG FY, et al. Roles of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors(PPARs) in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD)[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2023, 192: 106786. DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106786. [42] AMELIMOJARAD M, AMELIMOJARAD M, CUI XN. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis identified GBP2 connected to PPARα activity and liver cancer[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14( 1): 20745. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-70832-6. -



 PDF下载 ( 870 KB)
PDF下载 ( 870 KB)

 下载:
下载:


