咖啡酸在重症急性胰腺炎小鼠模型中的作用及其机制
DOI: 10.12449/JCH250418
-
摘要:
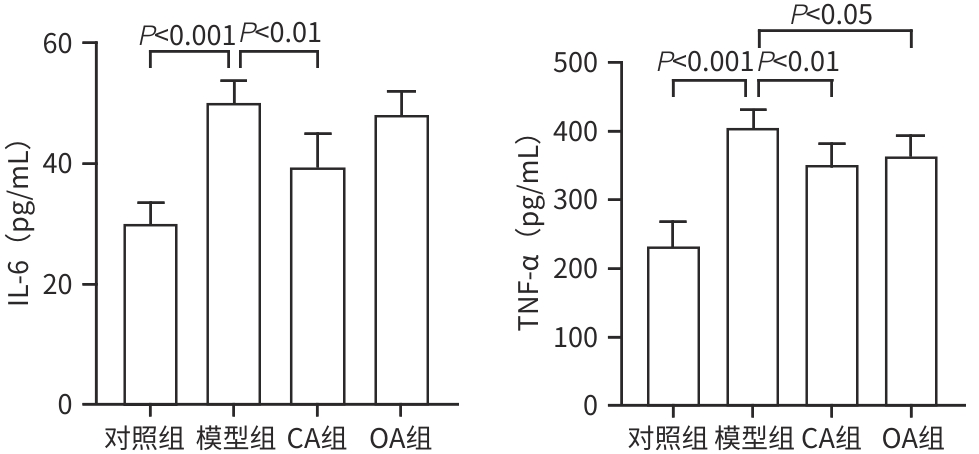
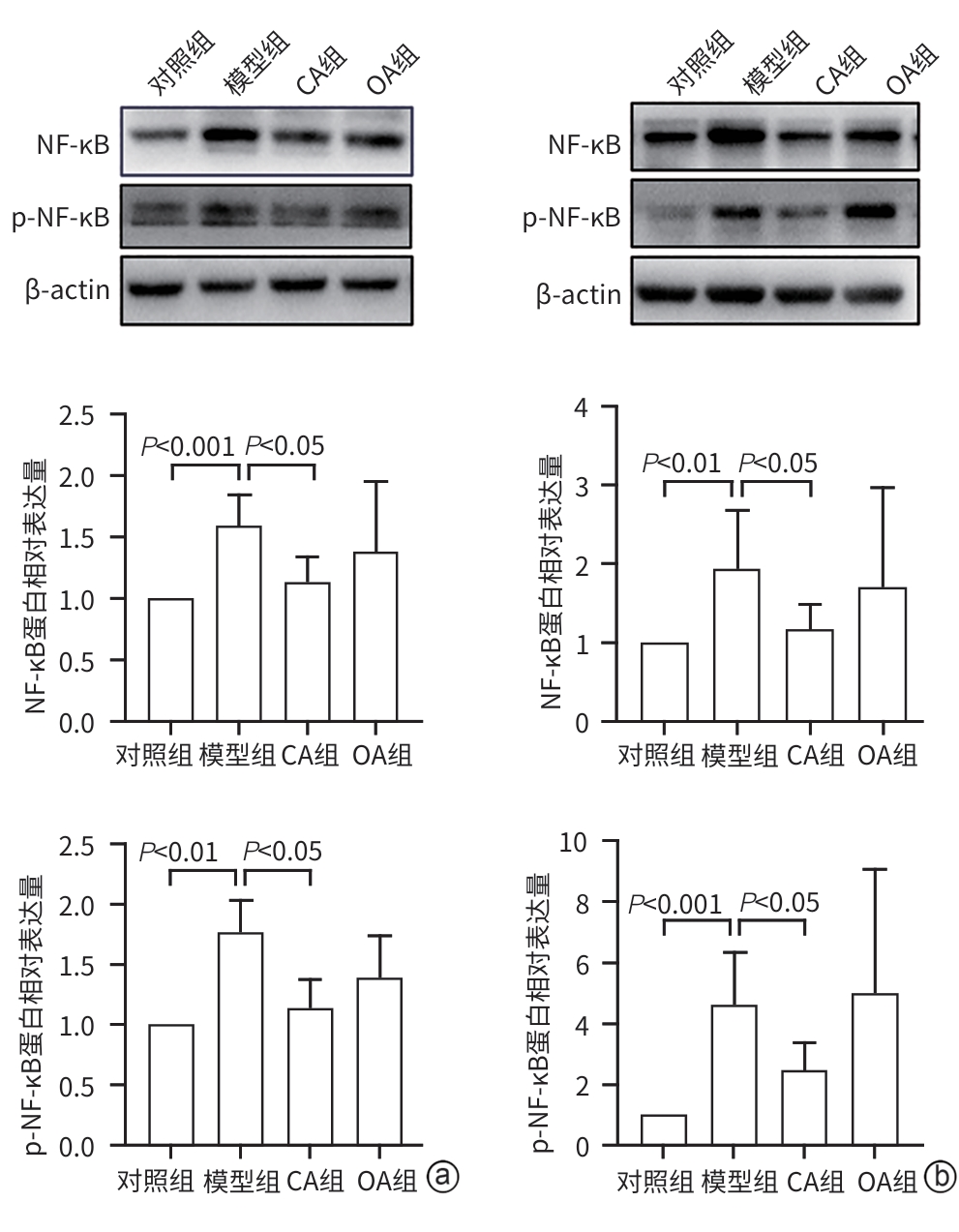
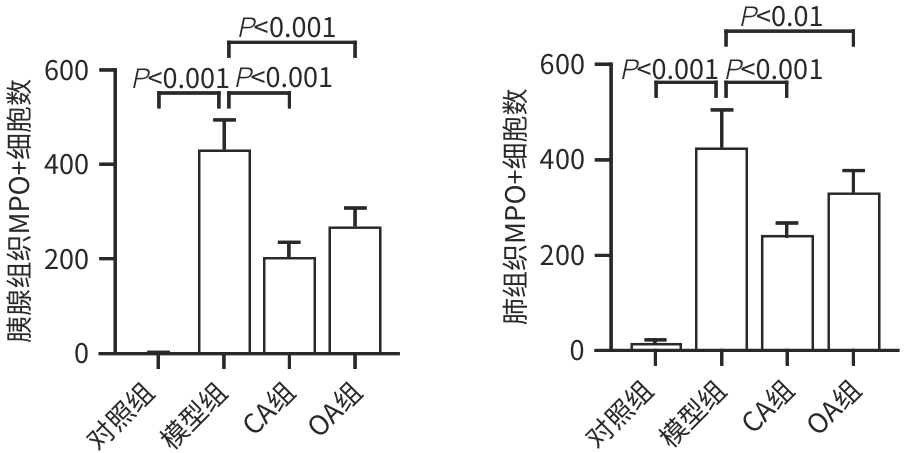
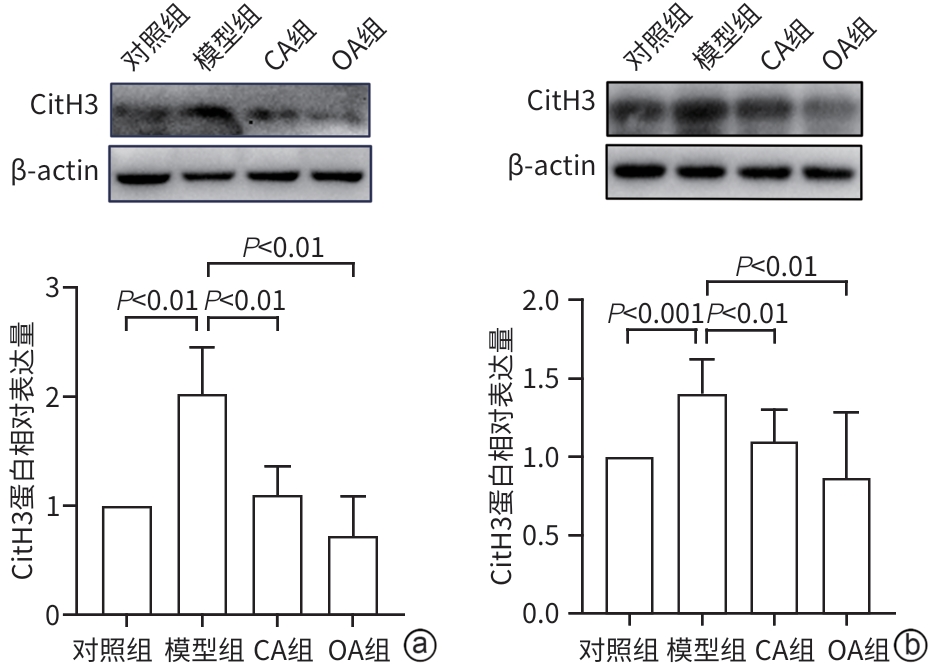
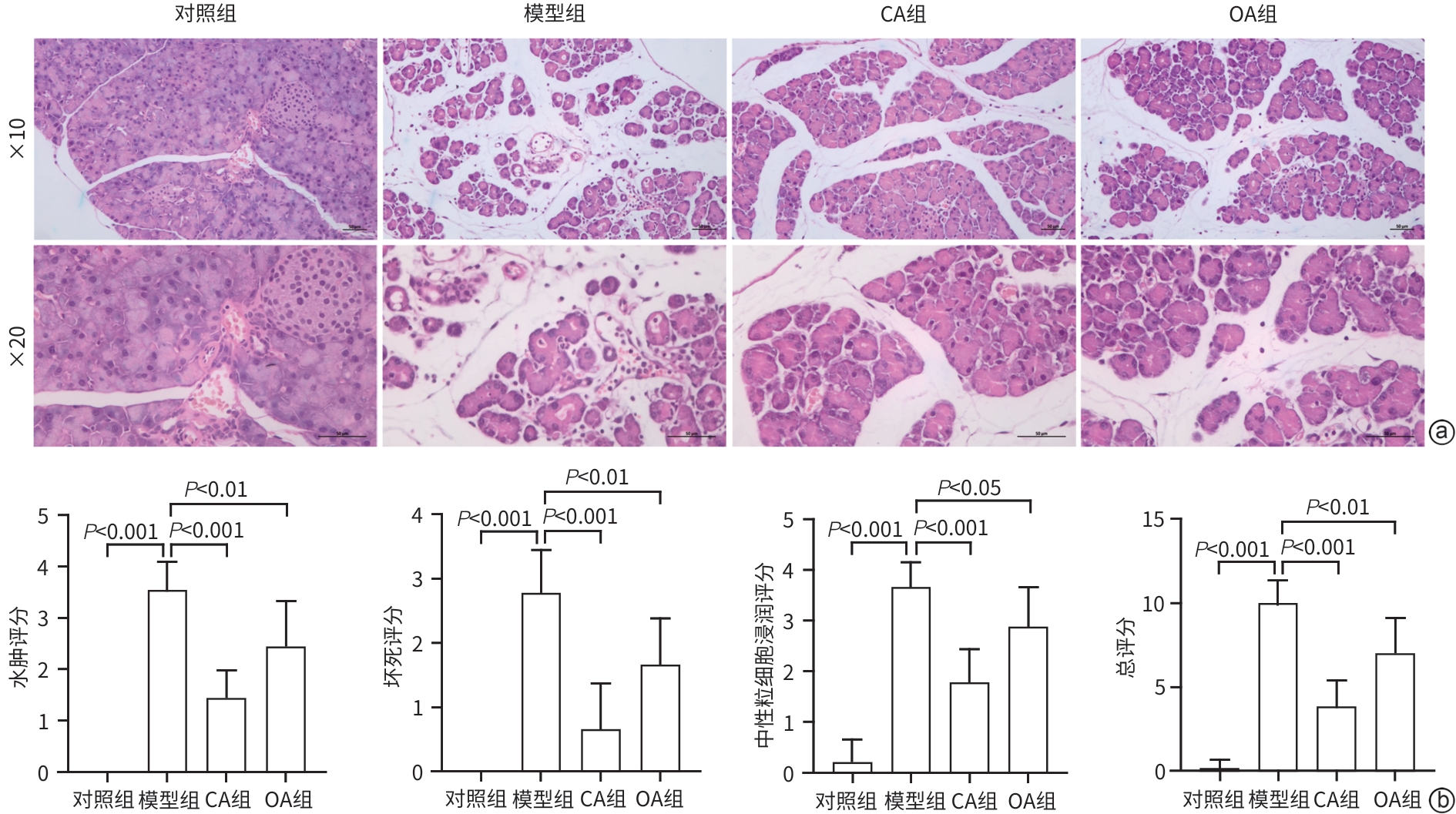
目的 研究咖啡酸(CA)对雨蛙素联合脂多糖诱导的重症急性胰腺炎的影响及潜在机制,以期为重症急性胰腺炎治疗提供潜在新型药物的研究基础。 方法 将6周龄C57BL/6J小鼠分为4组:对照组、模型组、CA组及醋酸奥曲肽(OA)组,每组6只。除对照组注射生理盐水外,其余各组通过腹腔注射雨蛙素联合脂多糖构建重症急性胰腺炎小鼠模型,在初次注射雨蛙素1 h后,CA组及OA组小鼠分别给予CA腹腔注射或OA皮下注射3次,每次间隔8 h。造模24 h后观察小鼠一般情况,收集血清和胰腺、肺、结肠组织。通过HE染色观察胰腺、肺组织病理变化。检测小鼠血清α-淀粉酶、脂肪酶、TNF-α、IL-6、ALT、AST和Cr水平。RT-PCR检测胰腺、肺组织促炎因子表达,通过髓过氧化物酶(MPO)免疫组化观察中性粒细胞浸润程度,Western Blot检测胰腺和肺组织核因子-κB(NF-κB)活化,中性粒细胞胞外陷阱(NET)形成标志物瓜氨酸化组蛋白H3(CitH3)水平,以及结肠组织ZO-1表达水平。计量资料多组间数据比较采用单因素方差分析,进一步两两比较采用Dunnett’s t检验。 结果 与对照组比较,模型组小鼠胰腺及肺组织损伤严重,血清α-淀粉酶、脂肪酶活性,以及血清、肺组织中促炎因子IL-6、IL-1β和TNF-α水平均显著升高(P值均<0.05),胰腺及肺组织中NF-κB活化、中性粒细胞浸润及NET形成均显著增加(P值均<0.05)。与模型组相比,CA组小鼠胰腺及肺组织病理损伤减轻,血清α-淀粉酶活性以及血清、肺组织中促炎因子IL-6、IL-1β和TNF-α水平均下调(P值均<0.05),胰腺及肺组织NF-κB活化、中性粒细胞浸润及NET形成均减少(P值均<0.05)。 结论 CA可减轻雨蛙素联合脂多糖诱导的SAP小鼠模型的症状,抑制中性粒细胞募集及NET形成可能是其部分作用机制。 -
关键词:
- 胰腺炎 /
- 小鼠, 近交C57BL /
- 咖啡酸 /
- 模型, 动物
Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect and potential mechanism of caffeic acid (CA) on severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) induced by caerulein combined with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and to provide a basis for the research on novel drugs for the treatment of SAP. Methods C57BL/6J mice, aged 6 weeks, were divided into control group, model group, CA group, and octreotide acetate (OA) group, with 6 mice in each group. The mice in the control group were given injection of normal saline, and those in the other groups were given intraperitoneal injection of caerulein combined with LPS to establish a mouse model of SAP. At 1 hour after the first injection of caerulein, the mice in the CA group and the OA group were given intraperitoneal injection of CA or subcutaneous injection of OA at an interval of 8 hours. The general status of the mice was observed after 24 hours of modeling, and serum, pancreas, lung, and colon samples were collected. HE staining was used to observe the histopathological changes of the pancreas and lungs, and the serum levels of α-amylase, lipase, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, and creatinine were measured. RT-PCR was used to measure the expression of proinflammatory factors in the pancreas and lungs; myeloperoxidase (MPO) immunohistochemistry was used to observe the degree of neutrophil infiltration; Western blot was used to measure the activation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and the level of citrullinated histone H3 (CitH3), a marker for the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), in the pancreas and lungs, as well as the expression level of ZO-1 in colon tissue. A one-way analysis of variance was used for comparison of continuous data between multiple groups, and the Dunnett’s t-test was used for further comparison between two groups. Results Compared with the control group, the model group had severe injury in the pancreas and lungs and significant increases in the activity of serum α- amylase and lipase and the levels of the proinflammatory cytokines IL-6, interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and TNF-α in serum and lung tissue (all P<0.05), as well as significant increases in NF-κB activation, neutrophil infiltration, and the formation of NETs in the pancreas and lungs (all P<0.05). Compared with the model group, the CA group had alleviated pathological injury of the pancreas and lungs and significant reductions in the activity of serum α-amylase and the levels of the proinflammatory cytokines IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α in serum and lung tissue (all P<0.05), as well as significant reductions in NF-κB activation, neutrophil infiltration, and the formation of NETs in the pancreas and lungs (all P<0.05). Conclusion CA can alleviate SAP induced by caerulein combined with LPS in mice, possibly by inhibiting neutrophil recruitment and the formation of NETs. -
Key words:
- Pancreatitis /
- Mice, Inbred C57BL /
- Caffeic Acid /
- Models, Animal
-
表 1 胰腺炎组织病理评分表
Table 1. Histopathological scale of pancreatitis
评分 水肿 坏死 炎性细胞浸润 0 无水肿 无坏死 炎性细胞数0~1个 1 局限性小叶间水肿 坏死细胞1~4个 炎性细胞数2~10个 2 弥漫性小叶间水肿 坏死细胞5~10个 炎性细胞数11~20个 3 腺泡增大,小叶间隔增宽 坏死细胞11~16个 炎性细胞数21~30个 4 明显小叶分隔 坏死细胞>16个 炎性细胞数>30个 表 2 PCR引物序列
Table 2. PCR primer sequence
基因 种属 序列 IL-6 小鼠 上游:5´-GGGACTGATGCTGGTGACAAC-3´ 下游:5´-CAACTCTTTTCTCATTTCCACGA-3´ IL-1β 小鼠 上游:5´-GCTTCAGGCAGGCAGTATCA-3´ 下游:5´-TGCAGTTGTCTAATGGGAACG-3´ TNF-α 小鼠 上游:5´-CCCTCCAGAAAAGACACCATG-3´ 下游:5´-CACCCCGAAGTTCAGTAGACAG-3´ β-actin 小鼠 上游:5´-GAGACCTTCAACACCCCAGC-3´ 下游:5´-ATGTCACGCACGATTTCCC-3´ -
[1] Drafting Group of Guidelines for Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Diagnosis and Treatment of Severe Acute Pancreatitis, Chinese Association of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Guidelines for integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine diagnosis and treatment of severe acute pancreatitis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2024, 40( 6): 1114- 1125. DOI: 10.12449/JCH240608.中华中医药学会《重症急性胰腺炎中西医结合诊疗指南》起草组. 重症急性胰腺炎中西医结合诊疗指南[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40( 6): 1114- 1125. DOI: 10.12449/JCH240608 [2] LI HX, ZHAO LY, WANG YY, et al. Roles, detection, and visualization of neutrophil extracellular traps in acute pancreatitis[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 974821. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.974821. [3] LIU XX, ZHENG Y, MENG ZA, et al. Gene regulation of neutrophils mediated liver and lung injury through NETosis in acute pancreatitis[J]. Inflammation, 2024. DOI: 10.1007/s10753-024-02071-w.[ Online ahead of print] [4] BRINKMANN V, REICHARD U, GOOSMANN C, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria[J]. Science, 2004, 303( 5663): 1532- 1535. DOI: 10.1126/science.1092385. [5] MERZA M, HARTMAN H, RAHMAN M, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps induce trypsin activation, inflammation, and tissue damage in mice with severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2015, 149( 7): 1920- 1931. e 8. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.08.026. [6] PETROV MS, SHANBHAG S, CHAKRABORTY M, et al. Organ failure and infection of pancreatic necrosis as determinants of mortality in patients with acute pancreatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2010, 139( 3): 813- 820. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.06.010. [7] JIN T, LI L, ZHANG XY, et al. Interpretation of《Integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine practice guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of acute pancreatitis》[J]. Chin J Bases Clin Gen Surg, 2024, 31( 2): 205- 211.金涛, 李兰, 张潇颖, 等.《急性胰腺炎中西医结合诊疗指南》解读[J]. 中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2024, 31( 2): 205- 211. [8] LAN WP, GUO W, ZHOU X, et al. Research trends on traditional Chinese medicine and acute pancreatitis: A bibliometric analysis from 2007 to mid-2023[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10( 5): e25659. DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25659. [9] YAO WY, ZHOU YF, QIAN AH, et al. Emodin has a protective effect in cases of severe acute pancreatitis via inhibition of nuclear factor-κB activation resulting in antioxidation[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2015, 11( 2): 1416- 1420. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2789. [10] SHENG B, ZHAO L, ZANG XF, et al. Quercetin inhibits caerulein-induced acute pancreatitis through regulating miR-216b by targeting MAP2K6 and NEAT1[J]. Inflammopharmacology, 2021, 29( 2): 549- 559. DOI: 10.1007/s10787-020-00767-7. [11] TARASIUK A, BULAK K, TALAR M, et al. Chlorogenic acid reduces inflammation in murine model of acute pancreatitis[J]. Pharmacol Rep, 2021, 73( 5): 1448- 1456. DOI: 10.1007/s43440-021-00320-5. [12] MIAO MS, XIANG LL. Pharmacological action and potential targets of chlorogenic acid[J]. Adv Pharmacol, 2020, 87: 71- 88. DOI: 10.1016/bs.apha.2019.12.002. [13] AZUMA K, IPPOUSHI K, NAKAYAMA M, et al. Absorption of chlorogenic acid and caffeic acid in rats after oral administration[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2000, 48( 11): 5496- 5500. DOI: 10.1021/jf000483q. [14] HUANG XJ, XI Y, PAN QY, et al. Caffeic acid protects against IL-1β- induced inflammatory responses and cartilage degradation in articular chondrocytes[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 107: 433- 439. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.161. [15] LIU DS, WU XL, LI JX, et al. Comparative study in acute pancreatitis rat models induced by three different methods[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2016, 36( 10): 2315- 2318. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2016.10.003.刘大晟, 吴先林, 李接兴, 等. 三种不同造模方法建立大鼠急性胰腺炎模型的对比[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2016, 36( 10): 2315- 2318. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2016.10.003. [16] XIAO LY, ZHANG J, XU ZG, et al. Effects of acute pancreatitis mouse model induced by caerulein and lipopolysaccharides[J]. Basic Clin Med, 2017, 37( 10): 1384- 1388. DOI: 10.16352/j.issn.1001-6325.2017.10.007.肖鲁瑶, 张杰, 徐志刚, 等. 雨蛙素及脂多糖诱导小鼠急性胰腺炎效果分析[J]. 基础医学与临床, 2017, 37( 10): 1384- 1388. DOI: 10.16352/j.issn.1001-6325.2017.10.007. [17] BAO WQ, LIANG L, YAO BH, et al. Research progress in the construction of animal models of severe acute pancreatitis[J]. J Inn Mong Med Univ, 2022, 44( 6): 649- 654. DOI: 10.16343/j.cnki.issn.2095-512x.2022.06.026.鲍伟奇, 梁鲁, 姚碧辉, 等. 重症急性胰腺炎动物模型构建方法的研究进展[J]. 内蒙古医科大学学报, 2022, 44( 6): 649- 654. DOI: 10.16343/j.cnki.issn.2095-512x.2022.06.026. [18] MAYERLE J, SENDLER M, HEGYI E, et al. Genetics, cell biology, and pathophysiology of pancreatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2019, 156( 7): 1951- 1968. e 1. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.11.081. [19] AKBARSHAHI H, ROSENDAHL AH, WESTERGREN-THORSSON G, et al. Acute lung injury in acute pancreatitis-Awaiting the big leap[J]. Respir Med, 2012, 106( 9): 1199- 1210. DOI: 10.1016/j.rmed.2012.06.003. [20] XU L, XU MM, XIE YH, et al. Preparing a mice model of severe acute pancreatitis via a combination of caerulein and lipopolysaccharide intraperitoneal injection[J]. J Vis Exp, 2024: 207. DOI: 10.3791/66780. [21] SHI H, CHEN H, TAN P, et al. Mitigation effects of cryptotanshinone on severe acute pancreatitis in mice induced by cerulein combined with lipopolysaccharides[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med, 2022, 42( 1): 83- 88. DOI: 10.7661/j.cjim.20211115.339.石昊, 陈浩, 谭鹏, 等. 隐丹参酮缓解雨蛙素联合脂多糖诱导的小鼠重症急性胰腺炎的作用探讨[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2022, 42( 1): 83- 88. DOI: 10.7661/j.cjim.20211115.339. [22] CHEN X, CHEN X, YAN D, et al. GV-971 prevents severe acute pancreatitis by remodeling the microbiota-metabolic-immune axis[J]. Nat Commun, 2024, 15( 1): 8278. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-52398-z. [23] LI XY, HE C, ZHU Y, et al. Role of gut microbiota on intestinal barrier function in acute pancreatitis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2020, 26( 18): 2187- 2193. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i18.2187. [24] DERVENIS C, SMAILIS D, HATZITHEOKLITOS E. Bacterial translocation and its prevention in acute pancreatitis[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg, 2003, 10( 6): 415- 418. DOI: 10.1007/s00534-002-0727-5. [25] GE P, LUO YL, OKOYE CS, et al. Intestinal barrier damage, systemic inflammatory response syndrome, and acute lung injury: A troublesome trio for acute pancreatitis[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2020, 132: 110770. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110770. [26] WANG ZJ, LI F, LIU J, et al. Intestinal microbiota- an unmissable bridge to severe acute pancreatitis-associated acute lung injury[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 913178. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.913178. [27] Branch of Gastrointestinal Diseases, China Association of Chinese Medicine. Expert consensus on TCM diagnosis and treatment of acute pancreatitis(2017)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2017, 33( 11): 2052- 2057. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.11.002.中华中医药学会脾胃病分会. 急性胰腺炎中医诊疗专家共识意见(2017)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2017, 33( 11): 2052- 2057. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.11.002. [28] ZHANG W, DUAN JY, MA MH, et al. Effects of different ratios of herba artemisias capillaris and rhubarb on chlorogenic acid and anthraquinones[J]. Feed Ind, 2023, 44( 18): 99- 106. DOI: 10.13302/j.cnki.fi.2023.18.015.张伟, 段佳燚, 马铭环, 等. 茵陈-大黄不同配比对绿原酸和蒽醌类成分的影响[J]. 饲料工业, 2023, 44( 18): 99- 106. DOI: 10.13302/j.cnki.fi.2023.18.015. [29] WENG ZY, DUAN YJ, XIAO R, et al. Pharmacokinetics of chlorogenic acid extracted from Lonicera japonica thunb.in mice[J]. Food Ind, 2023, 44( 3): 120- 125.翁子依, 段义君, 肖瑞, 等. 小鼠体内金银花提取物绿原酸的药动学研究[J]. 食品工业, 2023, 44( 3): 120- 125. [30] AI GL. Evaluation of quality study lonicerae japonicaeflos extract[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of TCM, 2017.艾光丽. 金银花提取物的质量研究[D]. 成都: 成都中医药大学, 2017. [31] SU GY. Study on caffeic acid and chlorogenic acid in suppressingages-induced inflammation[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2018.苏国莹. 咖啡酸和绿原酸抑制AGEs诱导的炎症反应[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2018. [32] MAKHIJA R, KINGSNORTH AN. Cytokine storm in acute pancreatitis[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg, 2002, 9( 4): 401- 410. DOI: 10.1007/s005340200049. [33] SUN YL. Protective effect and mechanism of caffeic acid onlipopoly‑ saccharide-induced acute lung injury[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2022.孙雅丽. 咖啡酸对脂多糖诱导急性肺损伤的保护作用及机制研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2022. [34] OIVA J, MUSTONEN H, KYLÄNPÄÄ ML, et al. Patients with acute pancreatitis complicated by organ dysfunction show abnormal peripheral blood polymorphonuclear leukocyte signaling[J]. Pancreatology, 2013, 13( 2): 118- 124. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2013.01.010. [35] PAN BH, LI YZ, LIU Y, et al. Circulating CitH3 is a reliable diagnostic and prognostic biomarker of septic patients in acute pancreatitis[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 766391. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.766391. [36] LEPPKES M, MAUERÖDER C, HIRTH S, et al. Externalized decondensed neutrophil chromatin occludes pancreatic ducts and drives pancreatitis[J]. Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 10973. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10973. [37] HAN F, DING ZF, SHI XL, et al. Irisin inhibits neutrophil extracellular traps formation and protects against acute pancreatitis in mice[J]. Redox Biol, 2023, 64: 102787. DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102787. [38] LING X, NIE C, SHENG LP, et al. Disulfiram relieves severe acute pancreatitis by inhibiting GSDMD-dependent NETs formation[J]. J Dig Dis, 2023, 24( 5): 359- 368. DOI: 10.1111/1751-2980.13211. [39] YU CM, WANG Y, REN SC, et al. Caffeic acid modulates activation of neutrophils and attenuates sepsis-induced organ injury by inhibiting 5-LOX/LTB4 pathway[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 125( Pt A): 111143. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111143. [40] HUANG B, ZANG FN, SHA Y. Analysis of the effect of different mode of octreotide administration in the treatment of acute pancreatitis[J]. Syst Med, 2023, 8( 15): 67- 70. DOI: 10.19368/j.cnki.2096-1782.2023.15.067.黄蓓, 臧夫宁, 沙跃. 奥曲肽不同用药方式治疗急性胰腺炎的效果分析[J]. 系统医学, 2023, 8( 15): 67- 70. DOI: 10.19368/j.cnki.2096-1782.2023.15.067. [41] LIU QS, WANG GH, CHEN FY. Effect of ulinastatin and octreotide in the treatment of severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Pract Clin J Integr Tradit Chin West Med, 2023, 23( 9): 100- 103. DOI: 10.13638/j.issn.1671-4040.2023.09.028.刘青松, 王国华, 陈福英. 乌司他丁和奥曲肽联合治疗重症急性胰腺炎的疗效[J]. 实用中西医结合临床, 2023, 23( 9): 100- 103. DOI: 10.13638/j.issn.1671-4040.2023.09.028. [42] LIU F, YAO J, ZHANG LQ. Effects of Honeysuckle extract combined with Octreotide on acinar cell damage repair, immunological indicators, and p38MAPK/ATF2 levels in rats with pancreatitis[J]. Chin J Anat, 2023, 46( 6): 497- 501, 524. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1633.2023.06.006.刘斐, 姚杰, 张丽骞. 金银花提取物联合奥曲肽对胰腺炎大鼠腺泡细胞损伤修复、免疫学指标及p38MAPK/ATF2水平的影响[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2023, 46( 6): 497- 501, 524. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1633.2023.06.006. -



 PDF下载 ( 5001 KB)
PDF下载 ( 5001 KB)

 下载:
下载: