多元判别分析评分与FIB-4诊断慢性HBV感染者肝纤维化程度的准确性比较
DOI: 10.12449/JCH250412
Accuracy of multivariate discriminant analysis versus fibrosis-4 in evaluating the liver fibrosis degree in patients with chronic HBV infection
-
摘要:
目的 比较多元判别分析评分(MDA)和FIB-4对HBV感染者肝纤维化程度的诊断准确性,探讨MDA作为诊断疾病进展指标的可能性。 方法 纳入2010年4月—2024年4月在广西医科大学第一附属医院行肝活检的HBV感染者263例,收集患者临床资料。根据病理结果,分为非显著纤维化组(F<2,n=126)和显著纤维化组(F≥2,n=137),分析MDA、FIB-4与肝纤维化程度的相关性,比较两者评估显著性肝纤维化的准确性;62例患者完成随访,根据末次随访时是否发展为肝硬化分为进展组(n=21)与未进展组(n=41),分析并比较MDA、FIB-4诊断疾病进展的效能。符合正态分布的计量资料两组间比较采用成组t检验;非正态分布的计量资料两组间比较采用Mann-Whitney U检验,多组间比较采用Kruskal-Wallis H检验,进一步两两比较采用Bonferroni法。计数资料的组间比较采用χ²检验。采用Spearman相关法进行相关性分析。采用Wilcoxon符号秩和检验对基线与随访终点的资料进行配对分析;二元Logistic回归分析患者进展为肝硬化的影响因素。利用受试者操作特征曲线(ROC曲线)分析指标的诊断效能,ROC曲线下面积(AUC)的比较采用Z检验,采用配对χ²检验比较两指标的灵敏度、特异度和准确率。 结果 FIB-4、MDA与肝纤维化程度的相关系数分别为0.378、-0.325(P值均<0.001)。FIB-4诊断显著性肝纤维化的AUC、灵敏度、特异度、阳性预测值、阴性预测值及准确率分别为0.688、64.96%、68.87%、67.42%、63.36%、65.40%,最佳截断值为1.01;MDA诊断显著性肝纤维化AUC、灵敏度、特异度、阳性预测值、阴性预测值及准确率分别为0.653、52.55%、78.57%,72.73%、60.37%、65.02%,最佳截断值为0.29;MDA的灵敏度低于FIB-4(P=0.004),但特异度较高(P=0.001)。基线时,进展组患者年龄较未进展组大(t=2.611,P=0.011)。在进展组,与基线时相比,随访终点时FIB-4升高、MDA降低(P值均<0.001);未进展组无明显变化(P值均>0.05)。多因素Logistic回归分析结果显示,AST(OR=0.940,95%CI:0.885~0.998,P<0.05)、MDA(OR=0.445,95%CI:0.279~0.710,P<0.001)是疾病进展的独立影响因素;对于诊断疾病进展为肝硬化,MDA的AUC为0.893,最佳截断值为-0.01。 结论 MDA诊断显著性肝纤维化的准确性与FIB-4相当;MDA<-0.01对于诊断肝纤维化发展为肝硬化有较高的准确性,有助于减少临床上肝活检的需要。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the accuracy of multiple discriminant analysis (MDA) versus fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) in assessing liver fibrosis degree in patients with HBV infection, as well as the possibility of MDA as an indicator for disease progression. Methods A total of 263 patients with HBV infection who underwent liver biopsy in The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University from April 2010 to April 2024 were included, and their clinical data were collected. According to the results of pathological examination, they were divided into non-significant fibrosis group (F<2) with 126 patients and significant fibrosis group (F≥2) with 137 patients. The correlation of MDA and FIB-4 with liver fibrosis degree was analyzed, and MDA and FIB-4 were compared in terms of their accuracy in assessing significant liver fibrosis. A total of 62 patients completed follow-up, and according to the presence or absence of progression to liver cirrhosis at the last follow-up visit, they were divided into progressive group with 21 patients and non-progressive group with 41 patients; the efficacy of MDA and FIB-4 in diagnosing disease progression was analyzed and compared. The independent-samples t test was used for comparison of normally distributed continuous data between groups, and the Mann-Whitney U test was used for comparison of non-normally distributed continuous data between groups; the Kruskal-Wallis H test was used for comparison between multiple groups, and the Bonferroni method was used for further comparison between two groups. The chi-square test was used for comparison of categorical data. The Spearman’s correlation coefficient was used for correlation analysis. The Wilcoxon signed rank sum test was used for the analysis of baseline data and data at the end of follow-up, and the binary Logistic regression analysis was used to investigate the influencing factors for progression to liver cirrhosis. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to investigate the diagnostic efficacy of indicators, the Z-test was used for comparison of the area under the ROC curve (AUC), and the paired chi-square test was used for comparison of the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of the two indicators. Results The correlation coefficient between FIB-4 and liver fibrosis degree was 0.378, while the correlation coefficient between MDA and liver fibrosis degree was -0.325 (both P<0.001). FIB-4 had an AUC of 0.688, a sensitivity of 64.96%, a specificity of 68.87%, a positive predictive value of 67.42%, a negative predictive value of 63.36%, an accuracy of 65.40%, and a cut-off value of 1.01, while MDA had an AUC of 0.653, a sensitivity of 52.55%, a specificity of 78.57%, a positive predictive value of 72.73%, a negative predictive value of 60.37%, an accuracy of 65.02%, and a cut-off value of 0.29, suggesting that compared with FIB-4, MDA had a lower sensitivity (P=0.004) and a higher specificity (P=0.001). The progressive group had a significantly higher age than the non-progressive group at baseline (t=2.611, P=0.011). For the progressive group, there was an increase in FIB-4 and a reduction in MDA from baseline to the end of follow-up (both P<0.001), while the non-progressive group showed no significant changes (both P>0.05). The multivariate Logistic regression analysis showed that aspartate aminotransferase (odds ratio [OR]=0.940, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.885 — 0.998, P<0.05) and MDA (OR=0.445, 95%CI: 0.279 — 0.710, P<0.001) were independent influencing factors for disease progression. MDA had an AUC of 0.893 and an optimal cut-off value of -0.01 in diagnosing the disease progression of liver cirrhosis. Conclusion MDA has a comparable accuracy to FIB-4 in the diagnosis of significant liver fibrosis, and MDA<-0.01 has a high accuracy in diagnosing the progression of liver fibrosis to liver cirrhosis, which can help to reduce the need for liver biopsy in clinical practice. -
Key words:
- Hepatitis B Virus /
- Hepatic Fibrosis /
- Diagnosis
-
表 1 显著性与非显著性肝纤维化HBV感染者临床资料比较
Table 1. Clinical data of HBV infected patients with significant and non-significant fibrosis
临床特征 显著肝纤维化组(n=137) 非显著肝纤维化组(n=126) 统计值 P值 性别[例(%)] χ²=0.180 0.671 女 37(27.01) 37(29.37) 男 100(72.99) 89(70.63) HBeAg[例(%)] χ²=0.013 0.911 阳性 40(29.20) 36(28.57) 阴性 97(70.80) 90(71.43) 抗病毒[例(%)] χ²=5.946 0.015 否 98(71.53) 72(57.14) 是 39(28.47) 54(42.86) lg HBV DNA(IU/mL) 4.20(2.70~5.72) 3.42(2.70~5.68) Z=-1.022 0.307 年龄(岁) 39.00(35.00~47.00) 38.00(32.00~47.00) Z=-1.570 0.118 Alb(g/L) 41.10(38.30~43.30) 41.65(39.80~43.95) Z=-1.810 0.071 ALT(g/L) 32.00(22.00~47.00) 28.00(19.25~38.00) Z=-2.110 0.035 AST(g/L) 31.00(24.00~43.00) 26.00(20.00~32.00) Z=-4.070 <0.001 ALP(U/L) 69.00(59.00~90.00) 65.00(55.00~81.75) Z=-1.580 0.115 PLT(109/L) 174.20(139.10~226.70) 214.25(180.18~246.53) Z=-4.740 <0.001 FIB-4 1.18(0.81~1.92) 0.86(0.66~1.18) Z=-5.270 <0.001 MDA 0.11(-2.71~3.59) 2.65(0.43~4.50) Z=-4.280 <0.001 炎症分级1)[例(%)] χ²=60.020 <0.001 G0 8(5.84) 6(4.76) G1 31(22.63) 80(63.49) G2 49(35.77) 35(27.78) G3 42(30.66) 5(3.97) G4 7(5.11) 0 METAVIR评分2)[例(%)] χ²=263.000 <0.001 F0 0 46(36.51) F1 0 80(63.49) F2 63(45.99) 0 F3 48(35.04) 0 F4 26(18.98) 0 注:1)根据病理结果将组织炎症程度分为G0~G4级;2)METAVIR评分用于评价肝脏纤维化程度,由轻到重分为F0~F4。
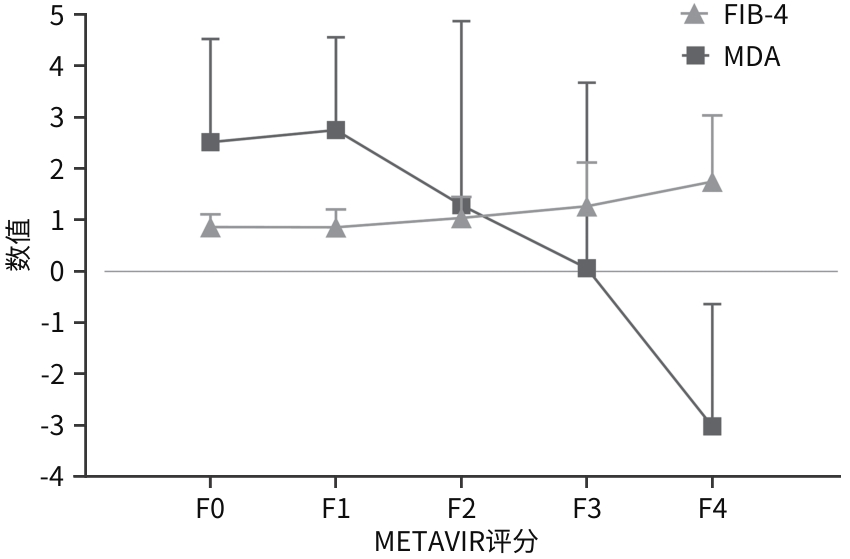
表 2 FIB-4、MDA在不同METAVIR评分患者中的比较
Table 2. Comparison of FIB-4 and MDA in patients with different METAVIR scores
组别 例数 FIB-4 MDA F0组 46 0.86(0.63~1.11) 2.52(0.81~4.53) F1组 80 0.86(0.66~1.21) 2.75(0.33~4.56) F2组 63 1.04(0.73~1.45) 1.29(-1.08~4.88) F3组 48 1.27(0.89~2.13)1)4) 0.06(-3.02~3.68)1)4) F4组 26 1.75(0.95~3.04)1)2)4) -3.02(-8.55~-0.64)1)2)3)4) H值 -40.584 -36.030 P值 P<0.001 P<0.001 注:与F1组比较,1)P<0.05;与F2组比较,2)P<0.05;与F3比较,3)P<0.05;与F0比较,4)P<0.05。
表 3 FIB-4、MDA对显著性肝纤维化的诊断效能
Table 3. Diagnostic efficacy of FIB-4 and MDA for significant liver fibrosis
血清学模型 AUC(95%CI) 最佳截断值 灵敏度(%) 特异度(%) 阳性预测值(%) 阴性预测值(%) 准确率(%) P值 FIB-4 0.688(0.625~0.752) 1.01 64.96 68.87 67.42 63.36 65.40 <0.001 MDA 0.653(0.586~0.719) 0.29 52.55 78.57 72.73 60.37 65.02 <0.001 表 4 进展组与未进展组中FIB-4和MDA变化情况
Table 4. Changes in FIB-4 and MDA in the progression group and non-progression group
组别 例数 基线 随访终点 差值及其95%CI Z值 P值 进展组 21 FIB-4 1.27(0.85~1.45) 1.89(1.67~2.68) 0.86(0.53~1.79) 4.015 <0.001 MDA 1.74(0.07~2.75) -2.20(-4.72~-0.20) -3.72(-6.37~-2.42) 3.945 <0.001 未进展组 41 FIB-4 0.84(0.70~1.16) 1.01(0.70~1.33) 0.07(-0.07~0.19) 0.978 0.328 MDA 2.86(0.65~4.45) 3.31(0.86~4.78) 0.35(-0.76~1.51) 0.667 0.505 注:差值指随访终点与基线的差值。
表 5 慢性HBV感染者进展为肝硬化二元logistic回归分析
Table 5. Binary Logistic regression analysis for progression of chronic HBV infection to cirrhosis
自变量 单因素分析 多因素分析 β值 SE P值 OR(95%CI) β值 SE P值 OR(95%CI) 男性 -0.85 0.65 0.196 0.429(0.119~1.546) 规律抗病毒 -0.60 0.68 0.375 0.549(0.146~2.066) HBeAg阳性 -0.98 0.83 0.238 0.374(0.073~1.918) 随访结束时年龄 0.05 0.03 0.086 1.053(0.993~1.117) Alb -0.25 0.09 0.003 0.778(0.658~0.919) ALT 0.02 0.01 0.047 1.024(1.001~1.049) 0.08 0.04 0.050 1.083(1.000~1.172) AST 0.04 0.02 0.030 1.046(1.004~1.088) -0.06 0.03 0.044 0.940(0.885~0.998) ALP 0.02 0.01 0.104 1.023(0.995~1.052) PLT -0.03 0.01 <0.001 0.969(0.953~0.986) FIB-4 2.55 0.74 <0.001 12.855(2.998~55.113) MDA -0.54 0.15 <0.001 0.585(0.438~0.781) -0.81 0.24 <0.001 0.445(0.279~0.710) 表 6 FIB-4、MDA在诊断疾病进展中的准确性
Table 6. The accuracy of FIB-4 and MDA in diagnosing disease progression
血清学模型 AUC(95%CI) 最佳截断值 灵敏度(%) 特异度(%) 阳性预测值(%) 阴性预测值(%) 准确率(%) P值 FIB-4 0.871(0.781~0.961) 1.37 85.71 80.49 68.00 89.19 80.65 <0.001 MDA 0.893(0.813~0.974) -0.01 80.95 85.37 73.91 89.74 83.87 <0.001 -
[1] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Consensus on the diagnosis and therapy of hepatic fibrosis(2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 10): 2163- 2172. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.10.007.中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会消化病学分会, 中华医学会感染病学分会. 肝纤维化诊断及治疗共识(2019年)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35( 10): 2163- 2172. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.10.007. [2] LIAO ZH, XIE ZY. Research progress in molecular mechanism of hepatic fibrosis and related therapeutic targets[J]. J Jilin Univ(Med Edit), 2024, 50( 5): 1450- 1456. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240532.廖昭辉, 谢正元. 肝纤维化发病的分子机制及其相关治疗靶点的研究进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2024, 50( 5): 1450- 1456. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240532. [3] SAPMAZ FP, BÜYÜKTURAN G, SAKIN YS, et al. How effective are APRI, FIB-4, FIB-5 scores in predicting liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients?[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2022, 101( 36): e30488. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030488. [4] BELLAN M, CASTELLO LM, PIRISI M. Candidate biomarkers of liver fibrosis: A concise, pathophysiology-oriented review[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2018, 6( 3): 317- 325. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2018.00006. [5] DONG XQ, WU Z, ZHAO H, et al. Evaluation and comparison of thirty noninvasive models for diagnosing liver fibrosis in Chinese hepatitis B patients[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2019, 26( 2): 297- 307. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.13031. [6] ATTALLAH AM, SHIHA GE, OMRAN MM, et al. A discriminant score based on four routine laboratory blood tests for accurate diagnosis of severe fibrosis and/or liver cirrhosis in Egyptian patients with chronic hepatitis C[J]. Hepatol Res, 2006, 34( 3): 163- 169. DOI: 10.1016/j.hepres.2005.12.004. [7] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B(version 2022)[J]. Infect Dis Info, 2023, 36( 1): 1- 17. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8134.2023.01.01.中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会感染病学分会. 慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2022年版)[J]. 传染病信息, 2023, 36( 1): 1- 17. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8134.2023.01.01. [8] MALLET V, DHALLUIN-VENIER V, ROUSSIN C, et al. The accuracy of the FIB-4 index for the diagnosis of mild fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2009, 29( 4): 409- 415. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2008.03895.x. [9] WANG H, XUE L, YAN R, et al. Comparison of FIB-4 and APRI in Chinese HBV-infected patients with persistently normal ALT and mildly elevated ALT[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2013, 20( 4): e3-10. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.12010. [10] BEDOSSA P, POYNARD T. An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C. The METAVIR Cooperative Study Group[J]. Hepatology, 1996, 24( 2): 289- 293. DOI: 10.1002/hep.510240201. [11] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Chinese guidelines on the management of liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 11): 2408- 2425. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.11.006.中华医学会肝病学分会. 肝硬化诊治指南[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35( 11): 2408- 2425. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.11.006. [12] SRINIVASA BABU A, WELLS ML, TEYTELBOYM OM, et al. Elastography in chronic liver disease: Modalities, techniques, limitations, and future directions[J]. Radiographics, 2016, 36( 7): 1987- 2006. DOI: 10.1148/rg.2016160042. [13] ZHU L, YANG JR, HE LL, et al. Advances on the application of transient elastography in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis[J/CD]. Chin J Liver Dis(Electronic Version), 2023, 15( 3): 16- 22. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2023.03.003.朱璐, 杨君茹, 何玲玲, 等. 瞬时弹性成像在肝纤维化诊断中的应用研究进展[J/CD]. 中国肝脏病杂志(电子版), 2023, 15( 3): 16- 22. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2023.03.003. [14] ZHANG Q, MA Z. Progress on influencing factors and biomarkers for hepatic fibrosis progression of hepatitis C[J/CD]. Chin J Exp Clin Infect Dis(Electronic Edition), 2024, 18( 1): 1- 6. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-1358.2024.01.001.张麒, 马臻. 丙型肝炎肝纤维化进展影响因素及标志物研究进展[J/CD]. 中华实验和临床感染病杂志(电子版), 2024, 18( 1): 1- 6. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-1358.2024.01.001. [15] WANG Y, WANG M, ZHANG GH, et al. Clinical diagnosis, staging, and therapeutic principles of liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37( 1): 17- 21. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.01.004.王宇, 王民, 张冠华, 等. 肝硬化的诊断、分期及治疗原则[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2021, 37( 1): 17- 21. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.01.004. [16] CHEN W, HONG RT, LIU XC, et al. Value of fibrosis-4, aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index, and globulin-platelet index in the diagnosis of significant liver fibrosis in autoimmune hepatitis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36( 9): 1955- 1959. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.09.009.陈薇, 洪汝涛, 刘晓昌, 等. FIB-4、APRI和GPI模型对自身免疫性肝炎显著肝纤维化的诊断价值[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36( 9): 1955- 1959. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.09.009. [17] KIM WR, BERG T, ASSELAH T, et al. Evaluation of APRI and FIB-4 scoring systems for non-invasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 64( 4): 773- 780. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.11.012. [18] JIANG YM, LIU J, YOU NN, et al. Evaluation of serum non-invasive methods for the diagnosis of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Int J Epidemiol Infect Dis, 2022, 49( 4): 238- 241. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn331340-20211209-00240.蒋艳明, 刘静, 尤宁宁, 等. 血清无创方法诊断慢性乙型肝炎病毒感染者肝纤维化的效果评价[J]. 国际流行病学传染病学杂志, 2022, 49( 4): 238- 241. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn331340-20211209-00240. [19] DONG JJ, WANG YY, LIU K, et al. Diagnostic value of γ-glutamyl transpeptidase-to-platelet ratio index for hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. Chin J Infect Dis, 2017, 35( 11): 670- 674. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6680.2017.11.006.董菁菁, 王允野, 刘昆, 等. γ-谷氨酰转肽酶和血小板比值指数对慢性乙型肝炎肝纤维化的诊断价值[J]. 中华传染病杂志, 2017, 35( 11): 670- 674. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6680.2017.11.006. [20] HUANG CM, YANG Z, NIE YQ, et al. Value of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase-to-platelet ratio in predicting liver fibrosis stage in chronic hepatitis B patients in Guangdong, China[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34( 6): 1204- 1208. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.06.015.黄春明, 杨湛, 聂玉强, 等. GGT/PLT比值对广东地区慢性乙型肝炎患者肝纤维化分期的预测价值[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2018, 34( 6): 1204- 1208. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.06.015. [21] DONG BT, LYU GR, CHEN YP, et al. Comparison of two-dimensional shear wave elastography, magnetic resonance elastography, and three serum markers for diagnosing fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B: A meta-analysis[J]. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 15( 9): 1077- 1089. DOI: 10.1080/17474124.2021.1880894. [22] XIAO GQ, YANG JY, YAN LN. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index and fibrosis-4 index for detecting liver fibrosis in adult patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A systemic review and meta-analysis[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 61( 1): 292- 302. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27382. [23] GORDON SC, LAMERATO LE, RUPP LB, et al. Antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis B virus infection and development of hepatocellular carcinoma in a US population[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2014, 12( 5): 885- 893. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.09.062. -



 PDF下载 ( 879 KB)
PDF下载 ( 879 KB)

 下载:
下载:


