非酒精性脂肪性肝病中医/中西医结合诊疗指南/共识的质量评价
DOI: 10.12449/JCH250309
Quality assessment of guidelines/consensuses on traditional Chinese medicine/integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine diagnosis and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
-
摘要:
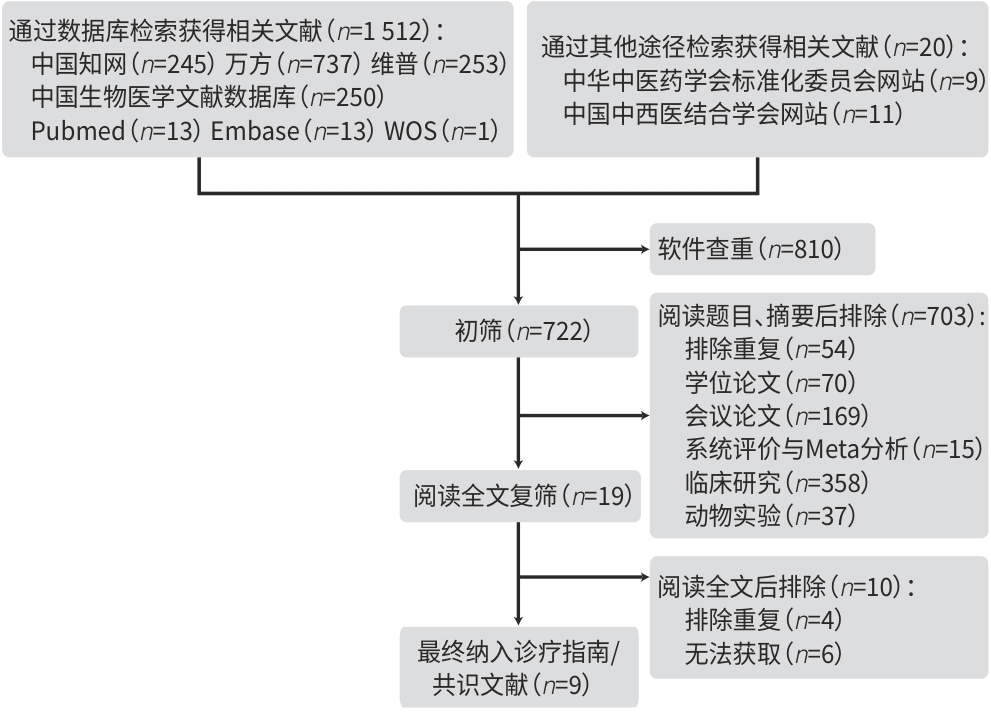
目的 评价已发表的非酒精性脂肪性肝病(NAFLD)中医/中西医结合诊疗指南/共识的方法学和报告质量,以期为今后代谢相关脂肪性肝病中医/中西医结合指南/共识的制定提供参考依据。 方法 计算机检索 PubMed、Embase、Web of Science、中国知网、万方和中国生物医学文献数据库,以及中华中医药学会和中国中西医结合学会的网站(自建库至2024年9月1日)。由两位临床研究人员分别使用指南的研究和评估工具第二版(AGREEⅡ)和国际实践指南报告规范(RIGHT)评价纳入NAFLD中医/中西医结合诊疗指南/共识的方法学质量及报告质量。 结果 通过文献筛选,最终纳入9篇指南/共识,其中指南4篇,专家共识5篇;采用AGREE Ⅱ评价9篇指南/共识不同领域得分依次为范围和目的(47.1%)、参与人员(41.0%)、严谨性(21.6%)、清晰性(40.2%)、应用性(19.1%)、独立性(19.6%)。文献推荐级别划分为:B级(修订后推荐)4篇,C级(不推荐)5篇。RIGHT评估显示,“基本信息”与“证据”报告率高,其他领域有待提升。目前,对于NAFLD的中医/中西医结合诊疗指南/共识,尚无国际标准且质量需加强以确保全面性和可信度。 结论 NAFLD中医/中西医结合诊疗指南/共识的质量仍有提升潜力,应严格遵循AGREEⅡ与RIGHT清单,以确保指南/共识的公正性、科学性与透明度。 Abstract:Objective To evaluate the methodological quality and reporting quality of published guidelines/consensuses on traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)/integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine diagnosis and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and to provide a basis for formulating guidelines/consensuses on TCM/integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine diagnosis and treatment of NAFLD in the future. Methods Databases including PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, CNKI, Wanfang Data, and CBM and the websites of China Association of Chinese Medicine and China Association of Integrative Medicine were searched for related articles published up to September 1, 2024. Two clinical researchers independently assessed the methodological quality and reporting quality of the guidelines/consensuses on TCM/integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine diagnosis and treatment of NAFLD by using Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation Ⅱ (AGREE Ⅱ) and Reporting Items for Practice Guidelines in Healthcare (RIGHT). Results A total of nine guidelines/consensuses were included after literature screening, with four guidelines and five expert consensuses. The scores of different domains assessed by AGREE Ⅱ for the nine guidelines/consensuses were as follows: scope and purpose (47.1%), stakeholder involvement (41.0%), rigor of development (21.6%), clarity of presentation (40.2%), applicability (19.0%), and editorial independence (19.6%). The recommendation level of the articles was B level (recommended after revision) for four articles and C level (not recommended) for five articles. The RIGHT assessment showed high reporting rates for “Basic Information” and “Background”, while other areas needed to be improved. Currently, there was no international standard for the guidelines/consensuses on TCM/integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine diagnosis and treatment of NAFLD, and the quality of these guidelines/consensuses needed to be enhanced to ensure comprehensiveness and credibility. Conclusion There is still potential for improving the quality of guidelines/consensuses on TCM/integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine diagnosis and treatment of NAFLD, and AGREE Ⅱ and RIGHT checklists should be strictly followed to ensure the fairness, scientific rigor, and transparency of these guidelines/consensuses. -
表 1 纳入指南/共识的基本特征
Table 1. The characteristics of the guidelines/consensus
指南名称 制定年份 指南/共识类型 制定机构 文献内容 参考文献数 参与专家数(人) 是否更新 利益冲突 基金资助 非酒精性脂肪性肝病的中西医结合诊疗共识意见[3] 2011 专家共识 中国中西医结合学会消化系统疾病专业委员会 诊断、治疗 4 106 是 未报告 未报告 非酒精性脂肪性肝病中医诊疗共识意见[4] 2011 专家共识 中华中医药学会脾胃病分会 诊断、治疗 17 109 是 未报告 未报告 非酒精性脂肪性肝病中西医结合诊疗共识意见(2017年)[6] 2017 专家共识 中国中西医结合学会消化系统疾病专业委员会 诊断、治疗 27 41 否 未报告 未报告 非酒精性脂肪性肝病中医诊疗专家共识意见(2017)[5] 2017 专家共识 中华中医药学会脾胃病分会 诊断、治疗 13 90 是 未报告 未报告 非酒精性脂肪性肝病中医诊疗指南(基层医生版)[7] 2019 诊疗指南 中华中医药学会脾胃病分会 诊断、治疗 0 18 否 未报告 未报告 肝癖(非酒精性脂肪性肝炎)诊疗方案[8] 2021 诊疗指南 国家中医药管理局华南区中医肝病诊疗中心联盟 诊断、治疗 28 51 否 未报告 未报告 穴位埋线治疗非酒精性脂肪性肝病中医实践指南[2] 2022 诊疗指南 中华中医药学会肝胆病分会 诊断、治疗 31 60 否 报告 未报告 非酒精性脂肪性肝炎中医诊疗指南[9] 2023 诊疗指南 中华中医药学会肝胆病分会 诊断、治疗、预后 34 38 否 报告 未报告 非酒精性脂肪性肝病中医诊疗专家共识(2023)[11] 2024 专家共识 中华中医药学会脾胃病分会 诊断、治疗、预后 29 27 否 报告 未报告 表 2 基于AGREEⅡ方法学质量评价结果
Table 2. Methodological quality evaluation of guidelines/consensus by AGREE Ⅱ
指南/共识 AGREEⅡ各领域得分率(%) AGREEⅡ推荐级别 目的
范文和
参与人员 严谨性 清晰性 应用性 独立性 得分率≥30%的领域数 得分率≥60%的领域数 推荐等级 非酒精性脂肪性肝病的中西医结合诊疗共识意见[3] 35.7 26.2 21.4 21.4 14.3 9.5 1 0 C 非酒精性脂肪性肝病中医诊疗共识意见[4] 33.3 28.6 24.1 21.4 14.3 9.5 1 0 C 非酒精性脂肪性肝病中西医结合诊疗共识意见(2017年)[6] 19.1 26.2 20.5 21.4 14.3 9.5 0 0 C 非酒精性脂肪性肝病中医诊疗专家共识意见(2017)[5] 38.1 31.0 21.4 40.5 14.3 9.5 3 0 B 非酒精性脂肪性肝病中医诊疗指南(基层医生版)[7] 38.1 47.6 21.4 38.1 14.3 9.5 3 0 B 肝癖(非酒精性脂肪性肝炎)诊疗方案[8] 47.6 19.1 21.4 31.0 14.3 9.5 2 0 C 穴位埋线治疗非酒精性脂肪性肝病中医实践指南[2] 92.9 78.6 21.4 73.8 26.2 47.6 4 3 B 非酒精性脂肪性肝炎中医诊疗指南[9] 83.3 85.7 21.4 92.9 45.2 61.9 5 4 B 非酒精性脂肪性肝病中医诊疗指南[11] 35.7 26.2 21.4 21.4 14.3 9.5 1 0 C 平均 47.1 41.0 21.6 40.2 19.1 19.6 表 3 基于RIGHT 报告质量评价
Table 3. Reporting quality evaluation of guidelines/consensus by RIGHT
指南/共识 RIGHT各领域报告率(%) 总体报告率(%) 基本信息 背景 证据 推荐意见 评审和
质量保证
资助和利益冲突 其他 非酒精性脂肪性肝病的中西医结合诊疗共识意见[3] 42.9 14.3 28.6 14.3 0.0 0.0 14.3 16.3 非酒精性脂肪性肝病中医诊疗共识意见[4] 42.9 28.6 42.9 14.3 0.0 0.0 14.3 20.4 非酒精性脂肪性肝病中西医结合诊疗共识意见(2017年)[6] 42.9 28.6 28.6 14.3 0.0 0.0 14.3 18.4 非酒精性脂肪性肝病中医诊疗专家共识意见(2017)[5] 42.9 28.6 100.0 14.3 0.0 0.0 14.3 28.6 非酒精性脂肪性肝病中医诊疗指南(基层医生版)[7] 42.9 14.3 100.0 14.3 0.0 0.0 14.3 26.5 肝癖(非酒精性脂肪性肝炎)诊疗方案[8] 42.9 28.6 42.9 14.3 0.0 0.0 14.3 20.4 穴位埋线治疗非酒精性脂肪性肝病中医实践指南[2] 42.9 14.3 85.7 71.4 57.1 0.0 14.3 40.8 非酒精性脂肪性肝炎中医诊疗指南[9] 42.9 28.6 100.0 71.4 57.1 14.3 14.3 46.9 非酒精性脂肪性肝病中医诊疗指南[11] 42.9 14.3 28.6 14.3 0.0 0.0 14.3 16.3 总体评价 42.9 22.2 61.9 27.0 12.7 1.6 14.3 26.1 -
[1] Chinese Society of Heptology of the Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of metabolic dysfunction-associated(non-alcoholic) fatty liver disease(Version 2024)[J]. J Pract Hepatol, 2024, 27( 4): 494- 510. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20240327-00163.中华医学会肝病学分会. 代谢相关(非酒精性)脂肪性肝病防治指南(2024年版)[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2024, 27( 4): 494- 510. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20240327-00163. [2] Branch of Hepatobiliary Diseases, Chinese Association of Chinese Medicine. Chinese medicine practice guide for acupoint catgut embedding in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 9): 1990- 1993. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.09.008.中华中医药学会肝胆病分会. 穴位埋线治疗非酒精性脂肪性肝病中医实践指南[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 9): 1990- 1993. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.09.008. [3] Digestive System Disease Professional Committee of the Chinese Society of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine. Consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of non alcoholic fatty liver disease with integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med, 2011, 31( 2): 155- 158. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2018.01.01.中国中西医结合学会消化系统疾病专业委员会. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病的中西医结合诊疗共识意见[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2011, 31( 2): 155- 158. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2018.01.01. [4] Spleen and Stomach Diseases Branch of the China Association of Chinese Medicine. Consensus on Traditional Chinese Medicine Diagnosis and Treatment of Non alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease[J]. Beijing J Tradit Chin Med, 2011, 30( 2): 83- 86. DOI: 10.16025/j.1674-1307.2011.02.003.中华中医药学会脾胃病分会. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病中医诊疗共识意见[J]. 北京中医药, 2011, 30( 2): 83- 86. DOI: 10.16025/j.1674-1307.2011.02.003. [5] Branch of Gastrointestinal Diseases, China Association of Chinese Medicine. Expert consensus on TCM diagnosis and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease(2017)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2017, 33( 12): 2270- 2274. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.12.002.中华中医药学会脾胃病分会. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病中医诊疗专家共识意见(2017)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2017, 33( 12): 2270- 2274. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.12.002. [6] Digestive System Disease Professional Committee of the Chinese Society of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine. Consensus Opinion on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Non alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine(2017)[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Dig, 2017, 25( 11): 805- 811. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2017.11.02.中国中西医结合学会消化系统疾病专业委员会. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病中西医结合诊疗共识意见(2017年)[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2017, 25( 11): 805- 811. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2017.11.02. [7] Branch of Gastrointestinal Diseases, China Association of Chinese Medicine. Guidelines for Traditional Chinese Medicine Diagnosis and Treatment of Non alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease(Grassroots Doctor Edition)[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Liver Dis, 2019, 29( 5): 483- 486.中华中医药学会脾胃病分会. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病中医诊疗指南(基层医生版)[J]. 中西医结合肝病杂志, 2019, 29( 5): 483- 486. [8] Diagnosis and Treatment Center of Hepatology of South China Alliance of TCM, National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Diagnosis and treatment scheme of Ganpi(non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J/CD]. Chin J Liver Dis Electron Version, 2021, 13( 1): 1- 9. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2021.01.001.国家中医药管理局华南区中医肝病诊疗中心联盟. 肝癖(非酒精性脂肪性肝炎)诊疗方案[J/CD]. 中国肝脏病杂志(电子版), 2021, 13( 1): 1- 9. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2021.01.001. [9] Branch of Hepatobiliary Diseases, China Association of Chinese Medicine. Diagnosis and treatment guideline for Chinese Medicine on non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 5): 1041- 1048. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.05.007.中华中医药学会肝胆病分会. 非酒精性脂肪性肝炎中医诊疗指南[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023, 39( 5): 1041- 1048. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.05.007. [10] ZHANG FQ, HU ZT, ZHANG YJ, et al. Methodology for the development of clinical practice guidelines for Chinese patent medicine(part 8): Quality evaluation with AGREE II and RIGHT[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2024, 65( 2): 185- 201. DOI: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2024.02.012.张福强, 胡紫腾, 张钰菁, 等. 中成药临床实践指南制定方法(八): 基于AGREE II和RIGHT的中成药临床实践指南质量评价[J]. 中医杂志, 2024, 65( 2): 185- 201. DOI: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2024.02.012. [11] Branch of Gastrointestinal Diseases, China Association of Chinese Medicine. Expert consensus on Traditional Chinese Medicine diagnosis and treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(2023)[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Dig, 2024, 32( 1): 1- 7.中华中医药学会脾胃病学会. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病中医诊疗专家共识(2023)[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2024, 32( 1): 1- 7. [12] FAN JG, JIN Q. A great dilemma and challenge of renaming metabolic associated fatty liver disease[J]. J Southwest Med Univ, 2022, 45( 5): 373- 376.范建高, 金倩. 代谢相关脂肪性肝病更名的困境与挑战[J]. 西南医科大学学报, 2022, 45( 5): 373- 376. [13] LIU JL, SUN JH. Renaming non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: From metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver heterogeneity to“different treatment for the same disease”[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Dig, 2024, 32( 5): 450- 454. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2024.05.15.刘嘉玲, 孙劲晖. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病更名: 从代谢功能障碍相关脂肪肝异质性到“同病异治”[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2024, 32( 5): 450- 454. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2024.05.15. [14] JIANG YR, CHEN KJ. Development and quality evaluation of evidence-based clinical practice guidelines of Chinese medicine[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med, 2016, 36( 1): 11- 15. DOI: 10.7661/CJIM.2016.01.0011.蒋跃绒, 陈可冀. 关于中医药循证临床实践指南的制定和质量评价[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2016, 36( 1): 11- 15. DOI: 10.7661/CJIM.2016.01.0011. [15] SHAO JY, HU YH, YUAN WA, et al. Research progress on preparation technology and evaluation methods of Chinese medicine placebo[J]. Drug Eval Res, 2023, 46( 5): 1125- 1130. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-6376.2023.05.024.邵靖渊, 胡薏慧, 元唯安, 等. 中药安慰剂制作工艺及评价方法的研究进展[J]. 药物评价研究, 2023, 46( 5): 1125- 1130. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-6376.2023.05.024. [16] GE L. Research progress on methodology of clinical practice guideline in the traditional Chinese medicine/integrative Chinese medicine field[J]. Chin J Drug Eval, 2022, 39( 4): 279- 284. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-3593.2022.04.001.葛龙. 中医药/中西医结合临床实践指南制订方法学研究进展与展望[J]. 中国药物评价, 2022, 39( 4): 279- 284. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-3593.2022.04.001. [17] YAO YN, CAO KG, TUO T, et al. Construction of evidence grading and recommendation system for ancient Chinese medicine books through experts questionnaire survey[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2021, 62( 7): 572- 576. DOI: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2021.07.005.姚钰宁, 曹克刚, 托托, 等. 基于专家问卷的中医古籍证据分级及推荐方法的构建[J]. 中医杂志, 2021, 62( 7): 572- 576. DOI: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2021.07.005. [18] LIANG CH, YIN DR, CUI J, et al. Application of ancient books in clinical practice guidelines and expert consensus of traditional Chinese medicine: Current status and methodological recommendations[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2024, 65( 8): 801- 809. DOI: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2024.08.007.梁昌昊, 尹丁冉, 崔靖, 等. 中医药临床实践指南和专家共识中古籍证据应用情况分析及建议[J]. 中医杂志, 2024, 65( 8): 801- 809. DOI: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2024.08.007. [19] GAO YT, DONG XL, WANG Y, et al. Research approaches of patient values and preferences in traditional Chinese medicine clinical practice guidelines[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2022, 63( 9): 819- 824. DOI: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2022.09.005.高胤桐, 董兴鲁, 王悦, 等. 中医临床实践指南中患者价值观与偏好要素的研究思路探讨[J]. 中医杂志, 2022, 63( 9): 819- 824. DOI: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2022.09.005. [20] GAO YC, XIA RY, CHAI QY, et al. Organizing patient panel: Suggestions on incorporating patient’s values and preferences into guideline development[J]. Med J Peking Union Med Coll Hosp, 2023, 14( 4): 875- 880. DOI: 10.12290/xhyxzz.2022-0528.高一城, 夏如玉, 柴倩云, 等. 组建患者小组: 将患者价值观与偏好整合融入指南制订过程的建议[J]. 协和医学杂志, 2023, 14( 4): 875- 880. DOI: 10.12290/xhyxzz.2022-0528. [21] JIN TY, YAO Y, WU SH, et al. Literature quality evaluation of health economics of traditional Chinese medicine based on PEERs[J]. Guid J Tradit Chin Med Pharm, 2022, 28( 10): 167- 171, 176. DOI: 10.13862/j.cn43-1446/r.2022.10.039.金同阳, 姚园, 吴少华, 等. 基于《药物经济学评价报告质量评估指南》的中医药卫生经济学研究文献质量评价[J]. 中医药导报, 2022, 28( 10): 167- 171, 176. DOI: 10.13862/j.cn43-1446/r.2022.10.039. [22] YAN LJ, LIANG N, ZHANG YJ, et al. Methodology for developing rapid and living guidelines of traditional Chinese medicine(RALIG-TCM)(part 4): Evidence monitoring and dynamic updates[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2024, 65( 3): 287- 291. DOI: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2024.03.011.晏利姣, 梁宁, 张钰菁, 等. 中医药快速动态指南的制定方法(四): 证据监测与动态更新[J]. 中医杂志, 2024, 65( 3): 287- 291. DOI: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2024.03.011. [23] HE WW, AN Y, ZHANG LY, et al. Methodological problems and thinking in the process of formulating clinical practice guidelines of traditional Chinese medicine and expert consensus[J/OL]. China J Chin Med, 1- 9[ 2024-12-24]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/41.1411.R.20240729. 1404.010.html. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/41.1411.R.20240729. 1404.010.html何伟伟, 安莹, 张乐怡, 等. 中医临床实践指南与专家共识制订过程中存在的方法学问题与思考[J/OL]. 中医学报, 1- 9[ 2024-12-24]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/41.1411.R.20240729. 1404.010.html. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/41.1411.R.20240729. 1404.010.html -



 PDF下载 ( 936 KB)
PDF下载 ( 936 KB)

 下载:
下载:


