肿瘤坏死因子α在肝细胞癌发生发展中的作用
DOI: 10.12449/JCH241129
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:朱玲玲负责检索文献,撰写论文;张亚妮、何昱静、史婷婷、伍杨、高春参与修改论文;于晓辉、张久聪负责指导撰写文章并最后定稿。
The role of tumor necrosis factor-α in the development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
-
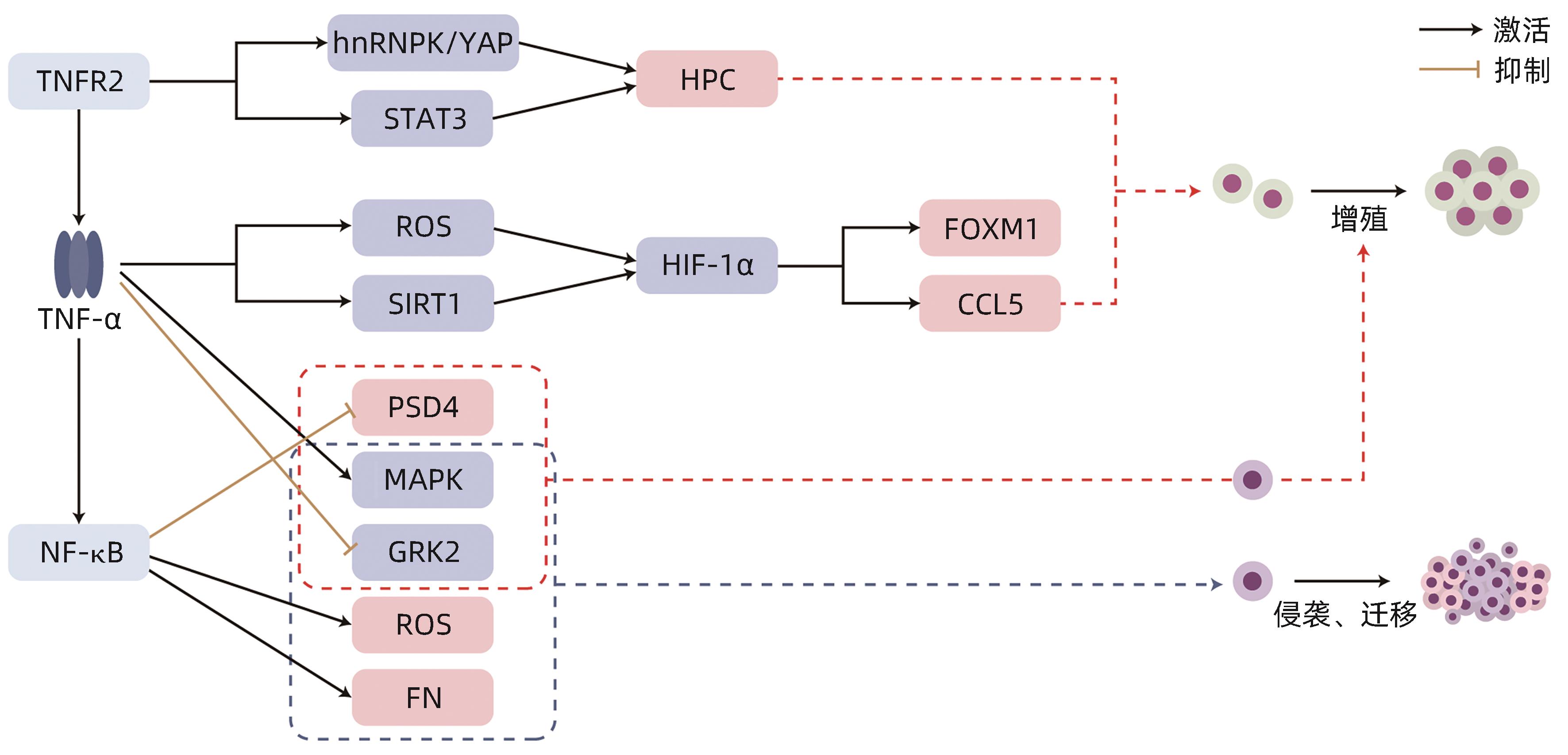
摘要: 肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)通过TNF受体介导的信号通路,参与调节肝细胞癌(HCC)细胞的增殖、侵袭、迁移乃至化疗耐药等多个生物学过程。同时,TNF-α还可发挥诱导HCC细胞凋亡的作用。部分TNF-α抑制剂已被证实可抑制HCC进展,延长生存时间。目前,TNF-α在HCC中的潜在作用机制尚未完全阐明,探究TNF-α与HCC的相互作用有益于更好地确定HCC的潜在治疗靶点。本文总结TNF-α在HCC中作用机制的最新研究进展,并介绍以TNF-α为靶点治疗HCC的可能性,以期为HCC的防治和药物研发提供理论依据及参考。Abstract: Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) is involved in the regulation of multiple biological processes such as the proliferation, invasion, migration, and chemotherapy resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells through TNF receptor-mediated signaling pathways. At the same time, TNF-α also plays a role in inducing the apoptosis of HCC cells. Some TNF-α inhibitors have been shown to inhibit the progression of HCC and prolong survival time. At present, the potential mechanism of action of TNF-α in HCC remains unclear, and exploration of the interaction between TNF-α and HCC can help to determine the potential therapeutic targets for HCC. This article summarizes the latest research advances in the mechanism of action of TNF-α in HCC and introduces the possibility of targeting TNF-α as a treatment method for HCC, in order to provide a theoretical basis for the prevention and treatment of liver cancer and drug research and development.
-
[1] CHEN YX, WEN HH, ZHOU C, et al. TNF-α derived from M2 tumor-associated macrophages promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stemness through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in SMMC-7721 hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2019, 378( 1): 41- 50. DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.03.005. [2] JANG MK, KIM HS, CHUNG YH. Clinical aspects of tumor necrosis factor-α signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2014, 20( 17): 2799- 2808. DOI: 10.2174/13816128113199990587. [3] TIEGS G, HORST AK. TNF in the liver: Targeting a central player in inflammation[J]. Semin Immunopathol, 2022, 44( 4): 445- 459. DOI: 10.1007/s00281-022-00910-2. [4] TSENG WC, LAI HC, HUANG YH, et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha: Implications of anesthesia on cancers[J]. Cancers, 2023, 15( 3): 739. DOI: 10.3390/cancers15030739. [5] LAHA D, GRANT R, MISHRA P, et al. The role of tumor necrosis factor in manipulating the immunological response of tumor microenvironment[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 656908. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.656908. [6] COUSSENS LM, WERB Z. Inflammation and cancer[J]. Nature, 2002, 420( 6917): 860- 867. DOI: 10.1038/nature01322. [7] WANG X, LIN Y. Tumor necrosis factor and cancer, buddies or foes?[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2008, 29( 11): 1275- 1288. DOI: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00889.x. [8] KALLIOLIAS GD, IVASHKIV LB. TNF biology, pathogenic mechanisms and emerging therapeutic strategies[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2016, 12( 1): 49- 62. DOI: 10.1038/nrrheum.2015.169. [9] CHEN AY, WOLCHOK JD, BASS AR. TNF in the era of immune checkpoint inhibitors: Friend or foe?[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2021, 17( 4): 213- 223. DOI: 10.1038/s41584-021-00584-4. [10] MERCOGLIANO MF, BRUNI S, MAURO F, et al. Harnessing tumor necrosis factor alpha to achieve effective cancer immunotherapy[J]. Cancers, 2021, 13( 3): 564. DOI: 10.3390/cancers13030564. [11] JING YY, SUN K, LIU WT, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α promotes hepatocellular carcinogenesis through the activation of hepatic progenitor cells[J]. Cancer Lett, 2018, 434: 22- 32. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.07.001. [12] YANG X, SHAO CC, DUAN LX, et al. Oncostatin M promotes hepatic progenitor cell activation and hepatocarcinogenesis via macrophage-derived tumor necrosis factor-α[J]. Cancer Lett, 2021, 517: 46- 54. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.05.039. [13] XIA LM, MO P, HUANG WJ, et al. The TNF-α/ROS/HIF-1-induced upregulation of FoxMI expression promotes HCC proliferation and resistance to apoptosis[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2012, 33( 11): 2250- 2259. DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgs249. [14] XU ZW, YAN SX, WU HX, et al. The influence of TNF-α and Ang II on the proliferation, migration and invasion of HepG2 cells by regulating the expression of GRK2[J]. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, 2017, 79( 4): 747- 758. DOI: 10.1007/s00280-017-3267-z. [15] XU ZW, YAN SX, WU HX, et al. Angiotensin II and tumor necrosis factor-α stimulate the growth, migration and invasion of BEL-7402 cells via down-regulation of GRK2 expression[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2019, 51( 2): 263- 274. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2018.06.007. [16] SHI JN, SONG SP, LI SX, et al. TNF-α/NF-κB signaling epigenetically represses PSD4 transcription to promote alcohol-related hepatocellular carcinoma progression[J]. Cancer Med, 2021, 10( 10): 3346- 3357. DOI: 10.1002/cam4.3832. [17] ZHANG GP, YUE X, LI SQ. Cathepsin C interacts with TNF-α/p38 MAPK signaling pathway to promote proliferation and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Res Treat, 2020, 52( 1): 10- 23. DOI: 10.4143/crt.2019.145. [18] ZONG C, MENG Y, YE F, et al. AIF1+CSF1R+MSCs, induced by TNF-α, act to generate an inflammatory microenvironment and promote hepatocarcinogenesis[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 78( 2): 434- 451. DOI: 10.1002/hep.32738. [19] MENG Y, ZHAO QD, AN LW, et al. A TNFR2-hnRNPK axis promotes primary liver cancer development via activation of YAP signaling in hepatic progenitor cells[J]. Cancer Res, 2021, 81( 11): 3036- 3050. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-3175. [20] QI DD, LU M, XU PF, et al. Transcription factor ETV4 promotes the development of hepatocellular carcinoma by driving hepatic TNF-α signaling[J]. Cancer Commun, 2023, 43( 12): 1354- 1372. DOI: 10.1002/cac2.12482. [21] LIU ZC, NING F, WANG HF, et al. Epidermal growth factor and tumor necrosis factor α cooperatively promote the motility of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines via synergistic induction of fibronectin by NF-κB/p65[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj, 2017, 1861( 11 Pt A): 2568- 2582. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.08.010. [22] KASTL L, SAUER SW, RUPPERT T, et al. TNF-α mediates mitochondrial uncoupling and enhances ROS-dependent cell migration via NF-κB activation in liver cells[J]. FEBS Lett, 2014, 588( 1): 175- 183. DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.11.033. [23] HUANG BP, LIN CS, WANG CJ, et al. Upregulation of heat shock protein 70 and the differential protein expression induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha enhances migration and inhibits apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cell HepG2[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2017, 14( 3): 284- 293. DOI: 10.7150/ijms.17861. [24] ZHU Y, CHENG Y, GUO YB, et al. Protein kinase D2 contributes to TNF-α-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition and invasion via the PI3K/GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7( 5): 5327- 5341. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.6633. [25] SHRESTHA R, BRIDLE KR, CRAWFORD DHG, et al. TNF-α-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition regulates expression of immune checkpoint molecules in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2020, 21( 4): 1849- 1860. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2020.10991. [26] DASH S, SARASHETTI PM, RAJASHEKAR B, et al. TGF-β2-induced EMT is dampened by inhibition of autophagy and TNF-α treatment[J]. Oncotarget, 2018, 9( 5): 6433- 6449. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.23942. [27] TAN WL, LUO X, LI WD, et al. TNF-α is a potential therapeutic target to overcome sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. EBioMedicine, 2019, 40: 446- 456. DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.12.047. [28] ZHOU C, SUN BY, ZHOU PY, et al. MAIT cells confer resistance to Lenvatinib plus anti-PD1 antibodies in hepatocellular carcinoma through TNF-TNFRSF1B pathway[J]. Clin Immunol, 2023, 256: 109770. DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2023.109770. [29] LI N, WANG JN, ZHANG N, et al. Cross-talk between TNF-α and IFN-γ signaling in induction of B7-H1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2018, 67( 2): 271- 283. DOI: 10.1007/s00262-017-2086-8. [30] ZHAO L, JIN Y, YANG C, et al. HBV-specific CD8 T cells present higher TNF-α expression but lower cytotoxicity in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2020, 201( 3): 289- 296. DOI: 10.1111/cei.13470. [31] ZHENG XX, CHEN XD, WU WC. The regulatory axis of PD-L1 isoform 2/TNF/T cell proliferation is required for the canonical immune-suppressive effects of PD-L1 isoform 1 in liver cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24( 7): 6314. DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076314. [32] TOKAY E, SAGKAN RI, KOCKAR F. TNF-α induces URG-4/URGCP gene expression inHepatoma cells through starvation dependent manner[J]. Biochem Genet, 2021, 59( 1): 300- 314. DOI: 10.1007/s10528-020-09972-z. [33] KOU XR, JING YY, DENG WJ, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α attenuates starvation-induced apoptosis through upregulation of ferritin heavy chain in hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J]. BMC Cancer, 2013, 13: 438. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-438. [34] SUN QM, HU B, FU PY, et al. Long non-coding RNA 00607 as a tumor suppressor by modulating NF-κB p65/p53 signaling axis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2018, 39( 12): 1438- 1446. DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgy113. [35] LI D, FU J, DU M, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma repression by TNFα-mediated synergistic lethal effect of mitosis defect-induced senescence and cell death sensitization[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 64( 4): 1105- 1120. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28637. [36] HOU JW, ZHAO RC, XIA WY, et al. PD-L1-mediated gasdermin C expression switches apoptosis to pyroptosis in cancer cells and facilitates tumour necrosis[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2020, 22( 10): 1264- 1275. DOI: 10.1038/s41556-020-0575-z. [37] VERMA HK, MERCHANT N, BHASKAR LVKS. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene promoter(TNF-α G-308A) polymorphisms increase the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in asians: A meta-analysis[J]. Crit Rev Oncog, 2020, 25( 1): 11- 20. DOI: 10.1615/CritRevOncog.2020034846. [38] LI HR, WANG YH, ZHANG M, et al. The high expression of TNF-α and NF-κB in tumor microenvironment predicts good prognosis of patients with BCLC-0-B hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Transl Cancer Res, 2019, 8( 2): 532- 541. DOI: 10.21037/tcr.2019.03.09. [39] GUO DD, QIN L, SUN JP, et al. Dynamic changes of cytokine profiles and their correlation with tumor recurrence following thermal ablation in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Technol Cancer Res Treat, 2023, 22: 15330338231190644. DOI: 10.1177/15330338231190644. [40] LU MY, YEH ML, HUANG CI, et al. Dynamics of cytokines predicts risk of hepatocellular carcinoma among chronic hepatitis C patients after viral eradication[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2022, 28( 1): 140- 153. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i1.140. [41] ZHANG M, HU J, LI HR, et al. High TNF-α and/or p38MAPK expression predicts a favourable prognosis in patients with T1N0M0 hepatocellular carcinoma: An immunohistochemical study[J]. Oncol Lett, 2019, 17( 6): 4948- 4956. DOI: 10.3892/ol.2019.10193. [42] IIDA-UENO A, ENOMOTO M, UCHIDA-KOBAYASHI S, et al. Changes in plasma interleukin-8 and tumor necrosis factor-α levels during the early treatment period as a predictor of the response to sorafenib in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, 2018, 82( 5): 857- 864. DOI: 10.1007/s00280-018-3681-x. [43] BRENNER D, BLASER H, MAK TW. Regulation of tumour necrosis factor signalling: Live or let die[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2015, 15( 6): 362- 374. DOI: 10.1038/nri3834. [44] LI W, JIAN YB. Antitumor necrosis factor-α antibodies as a noveltherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2018, 16( 2): 529- 536. DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6235. [45] LI K, LI XH, WU ZJ, et al. Adenovirus encoding XAF-1 and TNF-α in the same open reading frame efficiently inhibits hepatocellular cancer cells[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2016, 13( 6): 5169- 5176. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5193. [46] WANG HM, LIU JM, HU XM, et al. Prognostic and therapeutic values of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2016, 22: 3694- 3704. DOI: 10.12659/msm.899773. [47] WANG MD, WU MC, YANG T. The synergistic effect of sorafenib and TNF-α inhibitor on hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. EBioMedicine, 2019, 40: 11- 12. DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.01.007. [48] LEONE GM, MANGANO K, PETRALIA MC, et al. Past, present and(foreseeable) future of biological anti-TNF alpha therapy[J]. J Clin Med, 2023, 12( 4): 1630. DOI: 10.3390/jcm12041630. [49] BAI L, WANG K. Research progress of immune-related adverse reactions caused by immune checkpoint inhibitors[J]. J Changchun Univ Chin Med, 2023, 39( 2): 229- 236. DOI: 10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2023.02.025.白黎, 王珂. 免疫检查点抑制剂导致免疫相关不良反应的研究进展[J]. 长春中医药大学学报, 2023, 39( 2): 229- 236. DOI: 10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2023.02.025. [50] FISCHER R, KONTERMANN RE, PFIZENMAIER K. Selective targeting of TNF receptors as a novel therapeutic approach[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8: 401. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00401. -



 PDF下载 ( 1143 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1143 KB)


 下载:
下载: