内质网应激在非酒精性脂肪性肝病中的作用及相关靶向治疗
DOI: 10.12449/JCH241126
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:李岫滟负责查阅文献,撰写论文;曾玲负责归纳文献,分析资料;雷娜、宋虹霏负责拟定思路,修改论文;王东、穆杰负责指导撰写并最后定稿。
The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and related targeted therapies
-
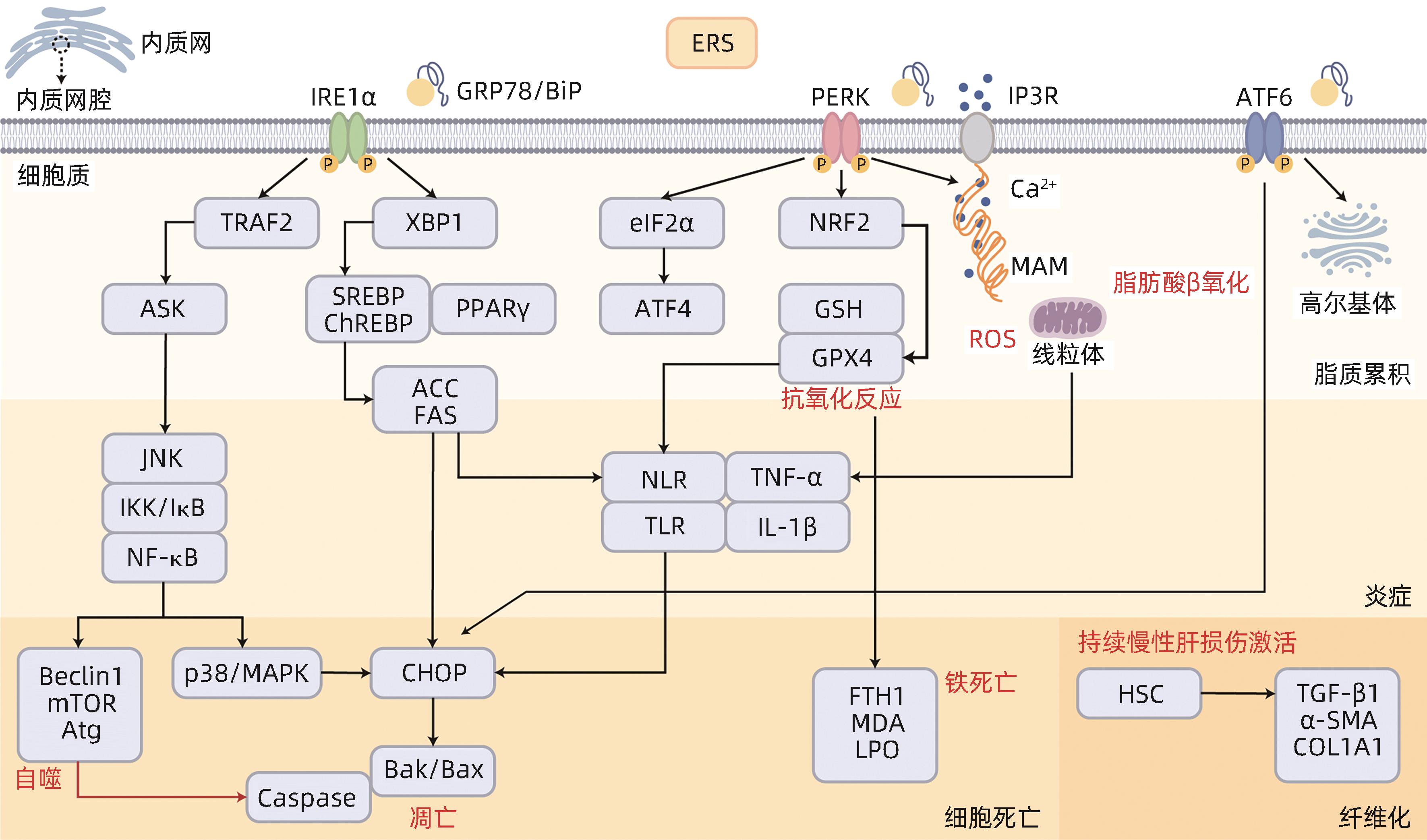
摘要: 非酒精性脂肪性肝病(NAFLD)是以肝脂肪变性为主要特征的一系列疾病谱的概括,是一种代谢相关性疾病,也是肝纤维化、肝硬化和肝癌的重要风险因子。内质网是调节脂代谢的核心场所,而非折叠蛋白反应是内质网应激(ERS)的重要过程。基于内质网在代谢相关疾病中的重要应激作用,本文将从ERS角度,探寻其与NAFLD之间的影响机制,对NAFLD病理发展过程中脂质代谢、炎症反应、细胞死亡、纤维化及ERS靶向治疗的相关研究进展进行综述。Abstract: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a series of diseases characterized by hepatic steatosis and is also a metabolism-associated disease and an important factor for liver fibrosis, liver cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Endoplasmic reticulum is a core organelle for the regulation of lipid metabolism, and unfolded protein response is an important process of endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS). Based on the important stress role of endoplasmic reticulum in metabolism-associated diseases, this article explores the influencing mechanism between ERS and NAFLD and reviews the research advances in lipid metabolism, inflammatory response, hepatocyte death, fibrosis, and ERS-targeted therapies in the pathological development of NAFLD.
-
[1] POWELL EE, WONG VWS, RINELLA M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Lancet, 2021, 397( 10290): 2212- 2224. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32511-3. [2] LAZARUS JV, MARK HE, ANSTEE QM, et al. Advancing the global public health agenda for NAFLD: A consensus statement[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 19( 1): 60- 78. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-021-00523-4. [3] ZHOU JH, ZHOU F, WANG WX, et al. Epidemiological features of NAFLD from 1999 to 2018 in China[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 71( 5): 1851- 1864. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31150. [4] YANG RX, FAN JG. A new understanding of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its rename[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 8): 1775- 1779. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.08.002.杨蕊旭, 范建高. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病新认识与再更名[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023, 39( 8): 1775- 1779. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.08.002. [5] FANG YL, CHEN H, WANG CL, et al. Pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescence: From“two hit theory” to“multiple hit model”[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2018, 24( 27): 2974- 2983. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i27.2974. [6] FLESSA CM, KYROU I, NASIRI-ANSARI N, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD): Current evidence and perspectives[J]. Curr Obes Rep, 2021, 10( 2): 134- 161. DOI: 10.1007/s13679-021-00431-3. [7] LEBEAUPIN C, VALLÉE D, HAZARI Y, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling and the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 69( 4): 927- 947. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.06.008. [8] XIA SW, WANG ZM, SUN SM, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and protein degradation in chronic liver disease[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2020, 161: 105218. DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105218. [9] CULLINAN SB, ZHANG D, HANNINK M, et al. Nrf2 is a direct PERK substrate and effector of PERK-dependent cell survival[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2003, 23( 20): 7198- 7209. DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.20.7198-7209.2003. [10] SHEN JS, CHEN X, HENDERSHOT L, et al. ER stress regulation of ATF6 localization by dissociation of BiP/GRP78 binding and unmasking of Golgi localization signals[J]. Dev Cell, 2002, 3( 1): 99- 111. DOI: 10.1016/s1534-5807(02)00203-4. [11] MARRA F, SVEGLIATI-BARONI G. Lipotoxicity and the gut-liver axis in NASH pathogenesis[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 68( 2): 280- 295. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.11.014. [12] ZHANG KZ, WANG SY, MALHOTRA J, et al. The unfolded protein response transducer IRE1α prevents ER stress-induced hepatic steatosis[J]. EMBO J, 2011, 30( 7): 1357- 1375. DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.52. [13] LIU CZ, ZHOU B, MENG MY, et al. FOXA3 induction under endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 75( 1): 150- 162. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.01.042. [14] XIAO GZ, ZHANG T, YU SB, et al. ATF4 protein deficiency protects against high fructose-induced hypertriglyceridemia in mice[J]. J Biol Chem, 2013, 288( 35): 25350- 25361. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.470526. [15] MAO H, CHEN W, CHEN LX, et al. Potential role of mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane proteins in diseases[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2022, 199: 115011. DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115011. [16] CHEN XQ, ZHANG FF, GONG Q, et al. Hepatic ATF6 increases fatty acid oxidation to attenuate hepatic steatosis in mice through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor Α[J]. Diabetes, 2016, 65( 7): 1904- 1915. DOI: 10.2337/db15-1637. [17] YAMAZAKI H, HIRAMATSU N, HAYAKAWA K, et al. Activation of the Akt-NF-kappaB pathway by subtilase cytotoxin through the ATF6 branch of the unfolded protein response[J]. J Immunol, 2009, 183( 2): 1480- 1487. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900017. [18] CHEN J, ZHANG MH, ZHU MM, et al. Paeoniflorin prevents endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated inflammation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells via the IRE1α/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Food Funct, 2018, 9( 4): 2386- 2397. DOI: 10.1039/c7fo01406f. [19] LEI N, SONG HF, ZENG L, et al. Persistent lipid accumulation leads to persistent exacerbation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation in progressive NASH via the IRE1α/TRAF2 complex[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28( 7): 3185. DOI: 10.3390/molecules28073185. [20] LEBEAUPIN C, PROICS E, de BIEVILLE CH, et al. ER stress induces NLRP3 inflammasome activation and hepatocyte death[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2015, 6( 9): e1879. DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2015.248. [21] LATIF MU, SCHMIDT GE, MERCAN S, et al. NFATc1 signaling drives chronic ER stress responses to promote NAFLD progression[J]. Gut, 2022, 71( 12): 2561- 2573. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325013. [22] GENG YN, FABER KN, de MEIJER VE, et al. How does hepatic lipid accumulation lead to lipotoxicity in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease?[J]. Hepatol Int, 2021, 15( 1): 21- 35. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-020-10121-2. [23] SENFT D, RONAI ZA. UPR, autophagy, and mitochondria crosstalk underlies the ER stress response[J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 2015, 40( 3): 141- 148. DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.01.002. [24] GONZÁLEZ-RODRÍGUEZ A, MAYORAL R, AGRA N, et al. Impaired autophagic flux is associated with increased endoplasmic reticulum stress during the development of NAFLD[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2014, 5( 4): e1179. DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2014.162. [25] ZHOU YP, ZHONG L, YU SJ, et al. Inhibition of stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase 1 ameliorates hepatic steatosis by inducing AMPK-mediated lipophagy[J]. Aging, 2020, 12( 8): 7350- 7362. DOI: 10.18632/aging.103082. [26] BEIER JI, BANALES JM. Pyroptosis: An inflammatory link between NAFLD and NASH with potential therapeutic implications[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 68( 4): 643- 645. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.01.017. [27] JIA Q, WANG J, LI W. Relationship between endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling pathway PERK and atherosclerotic plaque stability[J]. Clin Misdiagnosis Mistherapy, 2023, 36( 12): 56- 61. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3429.2023.12.012.贾乾, 王洁, 李雯. 内质网应激信号通路PERK与动脉粥样硬化斑块稳定性的关系[J]. 临床误诊误治, 2023, 36( 12): 56- 61. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3429.2023.12.012. [28] DEMIREL-YALCINER T, SOZEN E, OZALTIN E, et al. Alpha-Tocopherol supplementation reduces inflammation and apoptosis in high cholesterol mediated nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Biofactors, 2021, 47( 3): 403- 413. DOI: 10.1002/biof.1700. [29] RUAN L, LI FH, LI SB, et al. Effect of different exercise intensities on hepatocyte apoptosis in HFD-induced NAFLD in rats: The possible role of endoplasmic reticulum stress through the regulation of the IRE1/JNK and eIF2α/CHOP signal pathways[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2021, 2021: 6378568. DOI: 10.1155/2021/6378568. [30] KANDA T, MATSUOKA S, YAMAZAKI M, et al. Apoptosis and non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2018, 24( 25): 2661- 2672. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i25.2661. [31] MARCHI S, PATERGNANI S, MISSIROLI S, et al. Mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum calcium homeostasis and cell death[J]. Cell Calcium, 2018, 69: 62- 72. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceca.2017.05.003. [32] YE L, LI XQ, WANG JQ. Association between endoplasmic reticulum stress and ferroptosis in liver diseases[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 4): 980- 985. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.04.036.叶露, 李秀芹, 王建青. 肝脏疾病中内质网应激与铁死亡的关系[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023, 39( 4): 980- 985. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.04.036. [33] WEI S, QIU TM, WANG NN, et al. Ferroptosis mediated by the interaction between Mfn2 and IREα promotes arsenic-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Environ Res, 2020, 188: 109824. DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.109824. [34] JIANG Z, SUN H, MIAO JE, et al. The natural flavone acacetin protects against high-fat diet-induced lipid accumulation in the liver via the endoplasmic reticulum stress/ferroptosis pathway[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2023, 640: 183- 191. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.12.014. [35] KISSELEVA T, BRENNER D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 18( 3): 151- 166. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-020-00372-7. [36] HERNÁNDEZ-GEA V, HILSCHER M, ROZENFELD R, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress induces fibrogenic activity in hepatic stellate cells through autophagy[J]. J Hepatol, 2013, 59( 1): 98- 104. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.02.016. [37] ZHANG YQ, WEN J, LIU DQ, et al. Demethylenetetrahydroberberine alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome and oxidative stress in mice[J]. Life Sci, 2021, 281: 119778. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119778. [38] YOO T, JOO SK, KIM HJ, et al. Disease-specific eQTL screening reveals an anti-fibrotic effect of AGXT2 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 75( 3): 514- 523. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.04.011. [39] PETITO-DA-SILVA TI, SOUZA-MELLO V, BARBOSA-DA-SILVA S. Empaglifozin mitigates NAFLD in high-fat-fed mice by alleviating insulin resistance, lipogenesis and ER stress[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2019, 498: 110539. DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2019.110539. [40] NASIRI-ANSARI N, NIKOLOPOULOU C, PAPOUTSI K, et al. Empagliflozin attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD) in high fat diet fed ApoE(-/-) mice by activating autophagy and reducing ER stress and apoptosis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22( 2): 818. DOI: 10.3390/ijms22020818. [41] YANG J, AO N, DU J, et al. Protective effect of liraglutide against ER stress in the liver of high-fat diet-induced insulin-resistant rats[J]. Endocrine, 2015, 49( 1): 106- 118. DOI: 10.1007/s12020-014-0480-y. [42] MANTOVANI A, PETRACCA G, BEATRICE G, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: An updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Metabolites, 2021, 11( 2): 73. DOI: 10.3390/metabo11020073. [43] MOSBAH I BEN, ALFANY-FERNÁNDEZ I, MARTEL C, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibition protects steatotic and non-steatotic livers in partial hepatectomy under ischemia-reperfusion[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2010, 1( 7): e52. DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2010.29. [44] OZCAN U, YILMAZ E, OZCAN L, et al. Chemical chaperones reduce ER stress and restore glucose homeostasis in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes[J]. Science, 2006, 313( 5790): 1137- 1140. DOI: 10.1126/science.1128294. [45] LOOMBA R, LAWITZ E, MANTRY PS, et al. The ASK1 inhibitor selonsertib in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A randomized, phase 2 trial[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67( 2): 549- 559. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29514. -



 PDF下载 ( 1161 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1161 KB)

 下载:
下载:


