原位肝移植术后胆道狭窄的危险因素及预后分析
DOI: 10.12449/JCH241119
Risk factors for biliary stricture and prognosis after orthotopic liver transplantation
-
摘要:
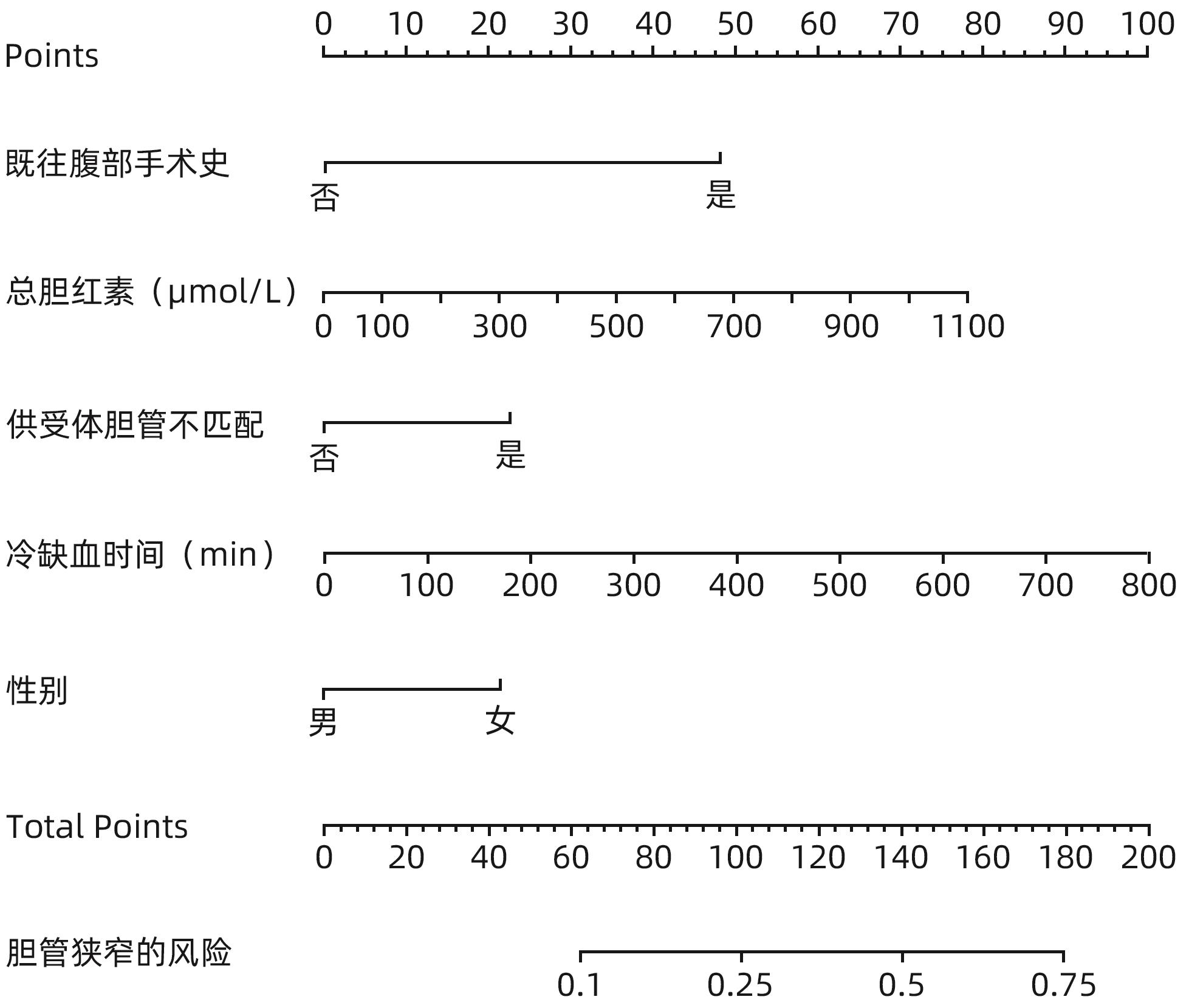
目的 探讨原位肝移植术后2年内发生胆道狭窄的危险因素并进行生存分析。 方法 回顾性分析吉林大学第一医院肝移植中心2014年1月—2022年1月495例实施的肝移植手术患者的资料。根据肝移植术后两年内是否发生胆道狭窄,将495例患者分为胆道狭窄组(n=89)和非胆道狭窄组(n=406),进行胆道狭窄的危险因素和预后分析。正态分布的计量资料两组间比较采用成组t检验;偏态分布的计量资料两组间比较采用Mann-Whitney U检验。计数资料组间比较采用χ2检验。应用Cox单因素和多因素回归分析进行危险因素分析。应用Kaplan-Meier法进行生存分析。 结果 受体性别(HR=1.808,95%CI:1.055~3.098,P=0.031)、受体术前总胆红素(HR=1.002,95%CI:1.001~1.003,P=0.001)、冷缺血时间(HR=1.003,95%CI:1.001~1.005,P=0.007)、受体既往腹部手术史(HR=3.851,95%CI:2.273~6.524,P<0.001)和供体受体胆管不匹配(HR=1.962,95%CI:1.041~3.698,P=0.037)是移植术后2年内发生胆道狭窄的独立危险因素。通过中位随访期为4.09年的随访,肝移植术后患者的1、3和5年生存率分别为92.7%、80.5%和75.4%。肝移植术后2年内发生的胆道狭窄对原位肝移植患者的生存影响无统计学意义。 结论 受体性别、受体术前总胆红素、冷缺血时间、受体既往腹部手术史和供体受体胆管不匹配是移植术后2年内发生胆道狭窄的独立危险因素。肝移植术后2年内发生的胆道狭窄并不影响肝移植患者的生存期。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the risk factors for biliary stricture within two years after orthotopic liver transplantation, and analyze the survival. Methods A retrospective analysis was performed for the data of 495 patients who underwent liver transplantation at Liver Transplantation Center of The First Hospital of Jilin University from January 2014 to January 2022, and according to the presence or absence of biliary stricture within two years after liver transplantation, the 495 patients were divided into stricture group with 89 patients and non-stricture group with 406 patients. The risk factors for biliary stricture and prognosis were analyzed. The independent-samples t-test was used for comparison of normally distributed continuous data between two groups, and the Mann-Whitney U test was used for comparison of non-normally distributed continuous data between two groups; the chi-square test was used for comparison of categorical data between two groups. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were used for the analysis of risk factors, and the Kaplan-Meier method was used for survival analysis. Results Recipient sex (hazard ratio [HR]=1.808, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.055 — 3.098, P=0.031), preoperative total bilirubin of the recipient (HR=1.002, 95%CI: 1.001 — 1.003, P=0.001), cold ischemia time (HR=1.003, 95%CI: 1.001 — 1.005, P=0.007), history of abdominal surgery for the recipient (HR=3.851, 95%CI: 2.273 — 6.524, P<0.001), and mismatch of donor-recipient bile ducts (HR=1.962, 95%CI: 1.041 — 3.698, P=0.037) were identified as independent risk factors for biliary stricture within two years after transplantation. The median follow-up time was 4.09 years, and the 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival rates were 92.7%, 80.5%, and 75.4%, respectively, after liver transplantation. The onset of biliary stricture within two years after liver transplantation had no significant impact on the survival of patients undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation. Conclusion Recipient sex, preoperative total bilirubin of the recipient, cold ischemia time, history of abdominal surgery for the recipient, and mismatch of donor-recipient bile ducts are independent risk factors for biliary stricture within two years after transplantation. The onset of biliary stricture within two years after transplantation does not affect the survival time of patients undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation. -
Key words:
- Liver Transplantation /
- Biliary Stricture /
- Risk Factors /
- Prognosis
-
表 1 两组患者的临床特征比较
Table 1. Comparison of clinical features between two groups of patients
因素 非BS组(n=406) BS组(n=89) 统计值 P值 受体性别(例) χ2=5.529 0.019 女 93 31 男 313 58 年龄(岁) 51.78±9.58 51.36±9.63 t=-0.371 0.711 手术日期(例) χ2=3.003 0.083 2020年以前 238 61 2020年及以后 168 28 肝硬化(例) χ2=3.854 0.050 否 50 18 是 356 71 乙型肝炎(例) χ2=0.179 0.672 否 168 39 是 238 50 丙型肝炎(例) χ2=0.001 0.975 否 379 83 是 27 6 恶性肿瘤(例) χ2=0.000 0.997 否 251 55 是 155 34 既往腹部手术史(例) χ2=22.250 <0.001 否 314 47 是 92 42 缝线(例) χ2=0.159 0.690 聚丙烯缝线 269 57 其他类型缝线 137 32 缝合方式(例) χ2=1.086 0.581 后连续前间断 290 62 前后均间断 76 15 前后均连续 40 12 供体受体胆管不匹配(例) χ2=5.835 0.016 否 355 69 是 51 20 白蛋白(g/L) 33.20±5.68 33.03±5.88 t=-0.256 0.798 INR 1.53±0.58 1.62±0.69 t=1.331 0.184 术前总胆红素(µmol/L) 53.8(24.1~164.6) 100.2(32.3~338.3) Z=5.147 0.002 肌酐(µmol/L) 63.2(51.6~75.9) 60.7(53.1~70.8) Z=4.114 0.356 Child-Pugh分级(例) χ2=0.403 0.818 A级 85 16 B级 307 70 C级 14 3 MELD评分(分) 10.52(7.03~15.63) 11.31(6.75~17.43) Z=0.150 0.699 热缺血时间(s) 62.0(43.0~88.0) 81.0(61.5~105.0) Z=7.107 0.008 冷缺血时间(min) 364.99±109.39 408.06±115.48 t=3.330 0.001 手术时间(min) 485.42±91.90 514.89±109.39 t=2.644 0.008 出血量(mL) 2 500(1 500~4 000) 3 000(1 450~5 300) Z=2.840 0.094 表 2 肝移植术后BS的Cox单因素和多因素分析
Table 2. Univariate and multivariate Cox analysis of the biliary stricture after liver transplantation
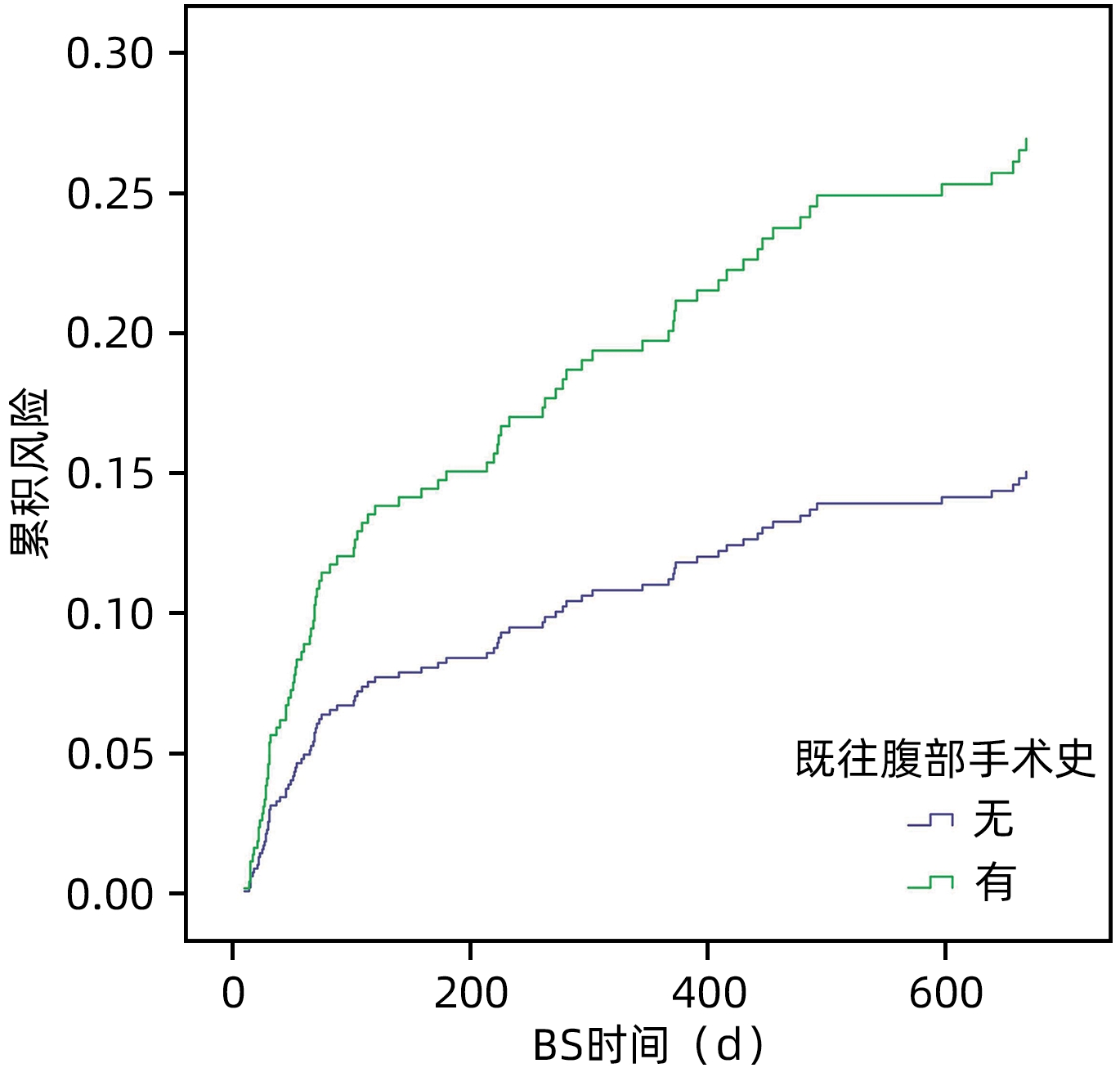
因素 单因素分析 多因素分析 HR(95%CI) P值 HR(95%CI) P值 受体性别(女/男) 1.669(1.079~2.581) 0.021 1.808(1.055~3.098) 0.031 年龄 0.997(0.976~1.019) 0.789 手术日期(2020年以前/2020年及以后) 1.487(0.951~2.326) 0.082 肝硬化(否/是) 0.595(0.355~1.000) 0.051 乙型肝炎(否/是) 0.937(0.616~1.424) 0.761 丙型肝炎(否/是) 1.092(0.477~2.502) 0.834 恶性肿瘤(否/是) 1.071(0.698~1.643) 0.753 既往腹部手术史(否/是) 2.787(1.837~4.227) <0.001 3.851(2.273~6.524) <0.001 缝线(聚丙烯缝线/其他类型缝线) 1.112(0.722~1.715) 0.629 缝合方式(后连续前间断/前后均间断/前后均连续) 1.098(0.816~1.476) 0.537 供体受体胆管不匹配(否/是) 1.785(1.085~2.937) 0.023 1.962(1.041~3.698) 0.037 白蛋白 0.997(0.961~1.034) 0.858 INR 1.225(0.906~1.658) 0.188 术前总胆红素 1.001(1.000~1.002) 0.013 1.002(1.001~1.003) 0.001 肌酐 0.995(0.987~1.002) 0.158 Child-Pugh分级(A/B/C级) 1.107(0.699~1.752) 0.664 MELD评分 1.005(0.979~1.032) 0.699 热缺血时间 1.002(1.000~1.004) 0.047 冷缺血时间 1.003(1.001~1.005) 0.001 1.003(1.001~1.005) 0.007 手术时间 1.002(1.001~1.004) 0.008 出血量 1.000(1.000~1.000) 0.075 表 3 肝移植术后患者的预后生存分析表
Table 3. Prognostic survival analysis table for patients after liver transplantation
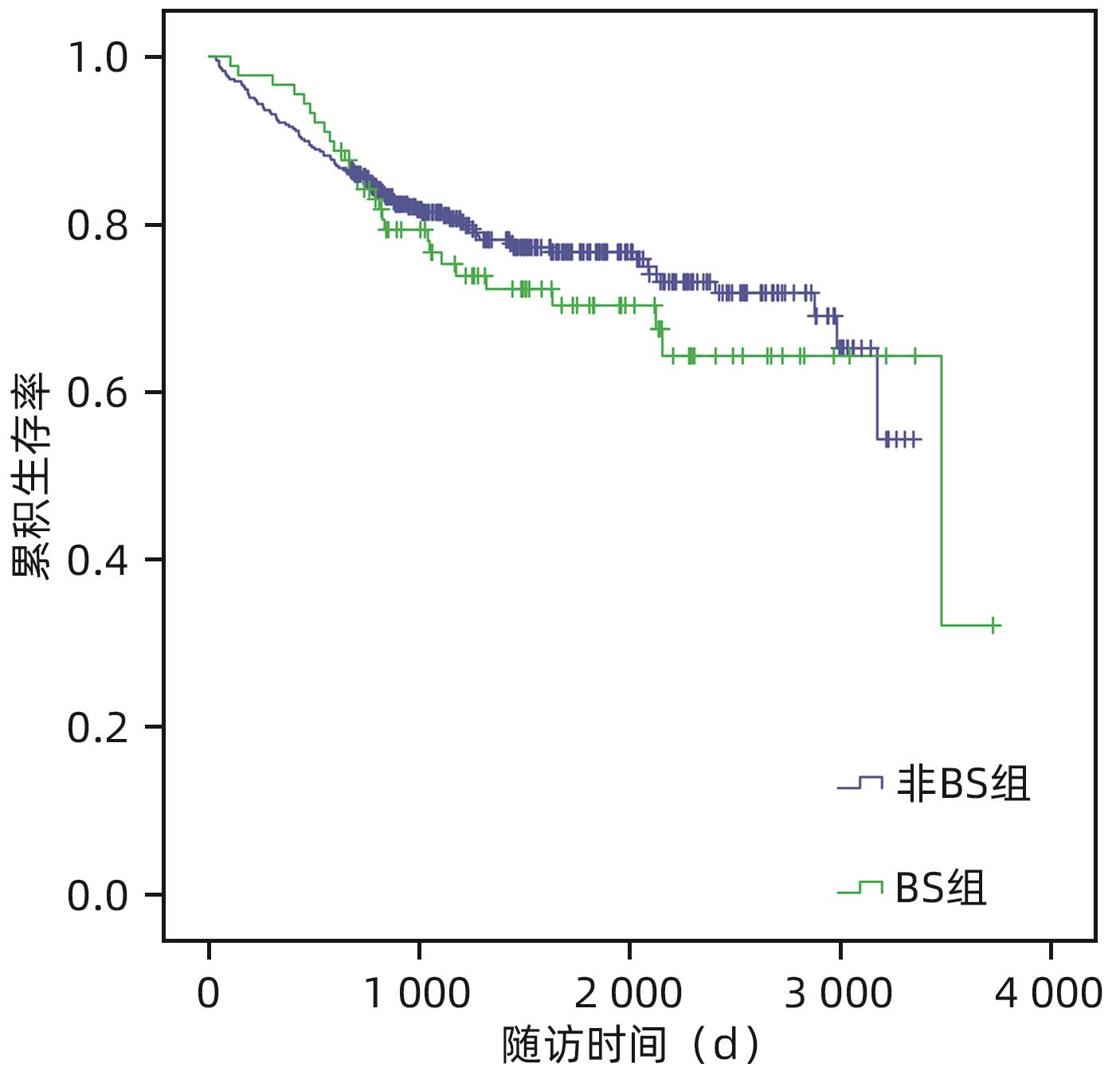
因素 例数 术后1年生存率(%) 术后3年生存率(%) 术后5年生存率(%) χ2值 P值 BS 0.629 0.430 是 89 96.6 76.6 70.3 否 406 91.9 81.4 76.7 原发病为恶性 49.920 <0.001 是 189 85.7 66.8 56.5 否 306 97.1 89.8 87.2 既往腹部手术史 2.413 0.120 是 134 91.0 78.3 70.3 否 361 93.4 81.3 77.2 供受体胆管匹配 0.104 0.747 是 424 92.2 80.7 75.6 否 71 95.8 79.3 74.5 表 4 肝移植术后发生BS患者的预后生存分析表
Table 4. Prognostic survival analysis table for patients with biliary stricture after liver transplantation
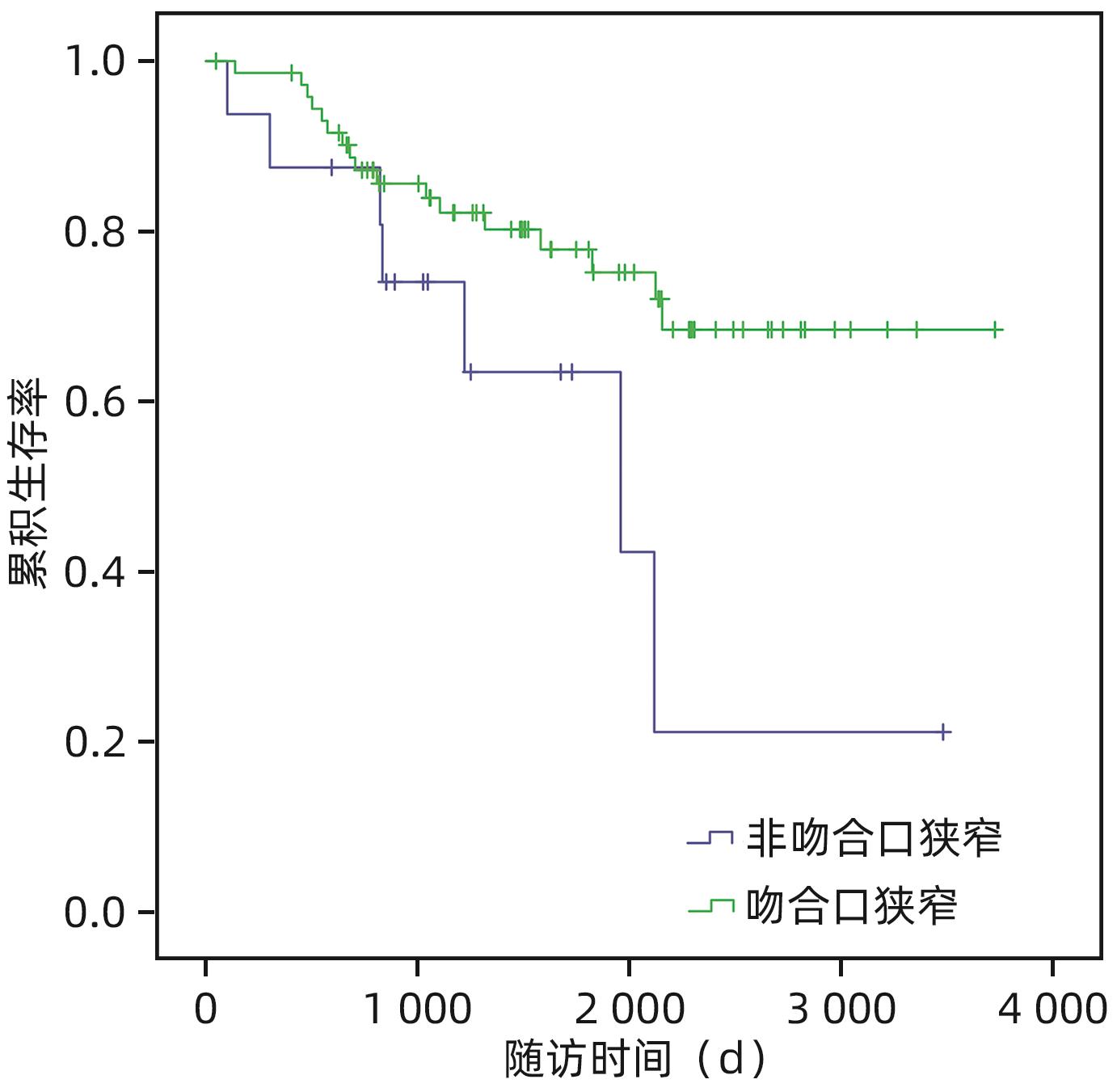
因素 例数 术后1年生存率(%) 术后3年生存率(%) 术后5年生存率(%) χ2值 P值 BS类型 4.26 0.039 非吻合口狭窄 16 87.5 74.0 63.5 吻合口狭窄 73 98.6 85.6 75.2 最窄宽度 0.289 0.591 ≤50% 56 93.9 87.9 82.7 >50% 33 98.2 80.5 66.8 狭窄长度 1.616 0.204 ≤10 mm 62 96.8 86.4 80 >10 mm 27 96.2 70.6 55.6 -
[1] HIBI T, WEI CHIEH AK, CHI-YAN CHAN A, et al. Current status of liver transplantation in Asia[J]. Int J Surg, 2020, 82S: 4- 8. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.05.071. [2] MOY BT, BIRK JW. A review on the management of biliary complications after orthotopic liver transplantation[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2019, 7( 1): 61- 71. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2018.00028. [3] COTÉ GA, SLIVKA A, TARNASKY P, et al. Effect of covered metallic stents compared with plastic stents on benign biliary stricture resolution: A randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA, 2016, 315( 12): 1250- 1257. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2016.2619. [4] AMATEAU SK, KOHLI DR, DESAI M, et al. American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy guideline on management of post-liver transplant biliary strictures: Methodology and review of evidence[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2023, 97( 4): 615- 637. e 11. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2022.10.006. [5] FENG YJ, LI JD, LI Q, et al. Progress in diagnosis and treatment of biliary anastomotic stricture after liver transplantation[J]. Organ Transplant, 2024, 15( 2): 297- 302. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2023240.冯彦杰, 李敬东, 李强, 等. 肝移植术后胆道吻合口狭窄的诊疗进展[J]. 器官移植, 2024, 15( 2): 297- 302. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2023240. [6] RAMMOHAN A, GOVIL S, VARGESE J, et al. Changing pattern of biliary complications in an evolving liver transplant unit[J]. Liver Transpl, 2017, 23( 4): 478- 486. DOI: 10.1002/lt.24736. [7] MAZILESCU LI, BERNHEIM I, TRECKMANN J, et al. Donor, recipient and surgeon sex and sex-concordance and their impact on liver transplant outcome[J]. J Pers Med, 2023, 13( 2): 281. DOI: 10.3390/jpm13020281. [8] LEGAZ I, NAVARRO NOGUERA E, BOLARÍN JM, et al. Patient sex in the setting of liver transplant in alcoholic liver disease[J]. Exp Clin Transplant, 2019, 17( 3): 355- 362. DOI: 10.6002/ect.2017.0302. [9] MAGRO B, TACELLI M, MAZZOLA A, et al. Biliary complications after liver transplantation: Current perspectives and future strategies[J]. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr, 2021, 10( 1): 76- 92. DOI: 10.21037/hbsn.2019.09.01. [10] PENG T, ZHONG YL, LIN XD, et al. Analysis and numerical investigation of bile flow dynamics within the strictured biliary duct[J]. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng, 2024, 40( 2): e3790. DOI: 10.1002/cnm.3790. [11] NEMES B, GÁMÁN G, DOROS A. Biliary complications after liver transplantation[J]. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 9( 4): 447- 466. DOI: 10.1586/17474124.2015.967761. [12] KALDAS FM, KORAYEM IM, RUSSELL TA, et al. Assessment of anastomotic biliary complications in adult patients undergoing high-acuity liver transplant[J]. JAMA Surg, 2019, 154( 5): 431- 439. DOI: 10.1001/jamasurg.2018.5527. [13] SUNDARAM V, JONES DT, SHAH NH, et al. Posttransplant biliary complications in the pre- and post-model for end-stage liver disease era[J]. Liver Transpl, 2011, 17( 4): 428- 435. DOI: 10.1002/lt.22251. [14] KEANE MG, DEVLIN J, HARRISON P, et al. Diagnosis and management of benign biliary strictures post liver transplantation in adults[J]. Transplant Rev, 2021, 35( 1): 100593. DOI: 10.1016/j.trre.2020.100593. [15] LIU DQ, SUN XD, QIU W, et al. Analysis of influencing factors for anastomotic biliary stricture after liver transplantation[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2022, 21( 2): 249- 255. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20211129-00602.刘大群, 孙晓东, 邱伟, 等. 影响肝移植术后胆管吻合口狭窄的相关因素分析[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2022, 21( 2): 249- 255. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20211129-00602. [16] FASULLO M, SHAH T, ZHOU HP, et al. Post-transplant biliary strictures: An updated review[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2022, 42( 2): 225- 232. DOI: 10.1055/s-0042-1744144. [17] VRIES YD, von MEIJENFELDT FA, PORTE RJ. Post-transplant cholangiopathy: Classification, pathogenesis, and preventive strategies[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2018, 1864( 4 Pt B): 1507- 1515. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.06.013. [18] HU XW, LI T. Diagnosis and treatment of common biliary complications after orthotopic liver transplantation in adults[J]. Organ Transplant, 2022, 13( 5): 569- 576. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2022.05.004.胡鑫文, 李亭. 成人原位肝移植术后常见胆道并发症的诊疗[J]. 器官移植, 2022, 13( 5): 569- 576. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2022.05.004. [19] PARENTE A, TIROTTA F, PINI A, et al. Machine perfusion techniques for liver transplantation- A meta-analysis of the first seven randomized-controlled trials[J]. J Hepatol, 2023, 79( 5): 1201- 1213. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.05.027. [20] AGOPIAN VG, PETROWSKY H, KALDAS FM, et al. The evolution of liver transplantation during 3 decades: Analysis of 5347 consecutive liver transplants at a single center[J]. Ann Surg, 2013, 258( 3): 409- 421. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3182a15db4. [21] SENTER-ZAPATA M, KHAN AS, SUBRAMANIAN T, et al. Patient and graft survival: Biliary complications after liver transplantation[J]. J Am Coll Surg, 2018, 226( 4): 484- 494. DOI: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2017.12.039. [22] JARLOT-GAS C, MUSCARI F, MOKRANE FZ, et al. Management of anastomotic biliary stricture after liver transplantation and impact on survival[J]. HPB, 2021, 23( 8): 1259- 1268. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2020.12.008. [23] MATAR AJ, ROSS-DRISCOLL K, KENNEY L, et al. Biliary complications following adult deceased donor liver transplantation: Risk factors and implications at a high-volume US center[J]. Transplant Direct, 2021, 7( 10): e754. DOI: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000001207. [24] AXELROD DA, LENTINE KL, XIAO HL, et al. National assessment of early biliary complications following liver transplantation: Incidence and outcomes[J]. Liver Transpl, 2014, 20( 4): 446- 456. DOI: 10.1002/lt.23829. [25] ZHANG CC, RUPP C, EXARCHOS X, et al. Scheduled endoscopic treatment of biliary anastomotic and nonanastomotic strictures after orthotopic liver transplantation[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2023, 97( 1): 42- 49. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2022.08.034. -



 PDF下载 ( 861 KB)
PDF下载 ( 861 KB)

 下载:
下载: