《2024年REDISCOVER国际指南: 交界可切除及局部晚期胰腺癌患者围手术期管理》解读
DOI: 10.12449/JCH241110
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:曾家辉、魏孔源负责指南翻译,分析讨论以及撰写论文;钱伟琨、王铮负责拟定写作思路,指导撰写文章;韩亮负责修改文章并最终定稿。
Interpretation of REDISCOVER international guidelines on the perioperative care of surgical patients with borderline-resectable and locally advanced pancreatic cancer (2024)
-
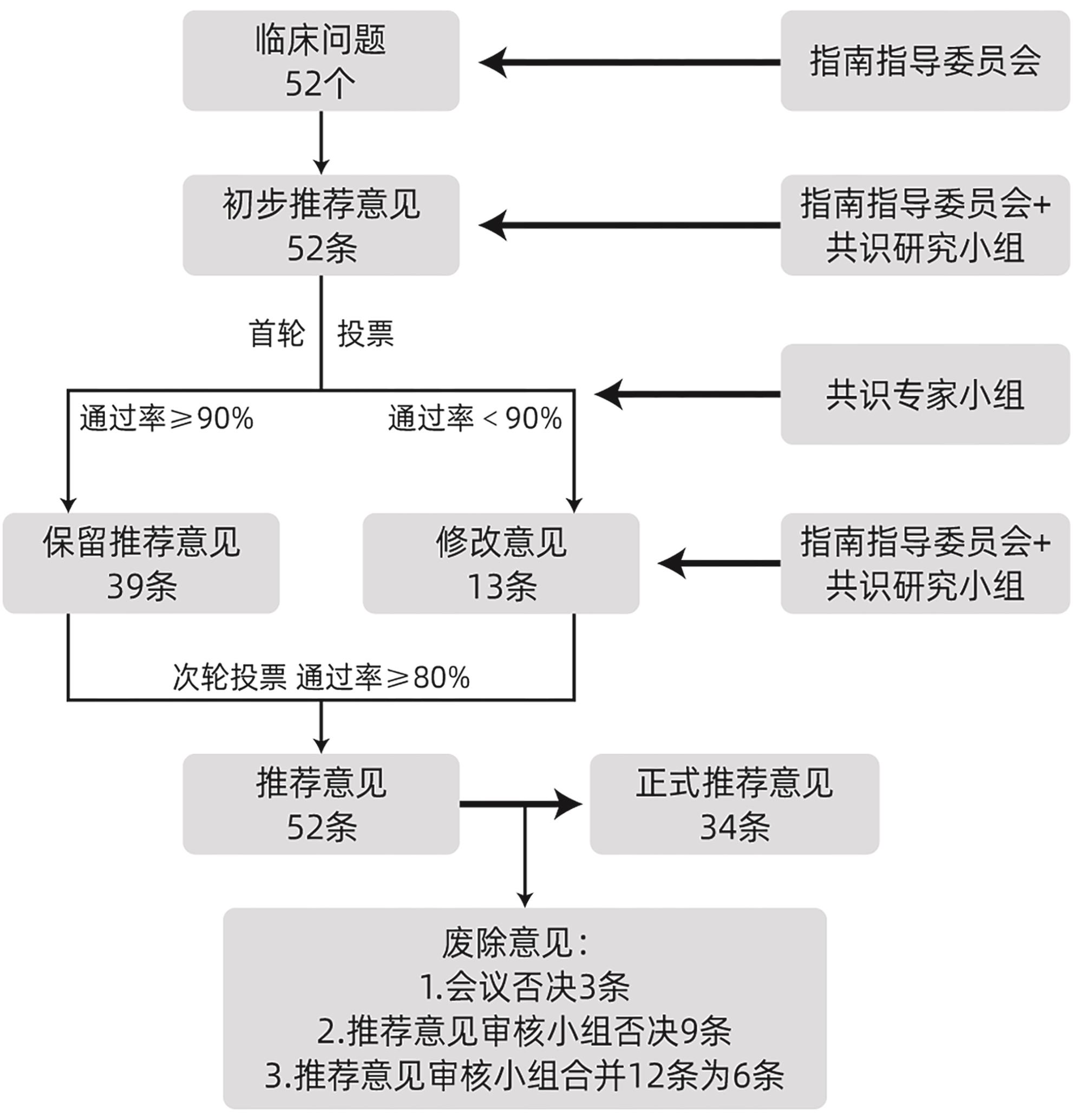
摘要: 2024年7月REDISCOVER国际指南共识小组发布了《交界可切除及局部晚期胰腺癌手术患者围手术期管理》,该规范基于目前临床存在的问题,从循证医学的角度出发,在交界可切除及局部晚期胰腺癌的诊断、分期及外科治疗等方面提出的推荐性意见具有重要意义,本文对该指南进行解读,以期更好地指导临床。Abstract: The REDISCOVER international guidelines on the perioperative care of surgical patients with borderline-resectable and locally advanced pancreatic cancer were released in July 2024, and based on the existing clinical challenges, the guidelines provide important recommendations for the diagnosis, staging, and surgical treatment of borderline-resectable and locally advanced pancreatic cancer from an evidence-based perspective. This article gives an interpretation of the guidelines, in order to better guide clinical practice.
-
Key words:
- Pancreatic Neoplasms /
- Perioperative Period /
- Practice Guideline
-
[1] SIEGEL RL, MILLER KD, FUCHS HE, et al. Cancer Statistics, 2021[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71( 1): 7- 33. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21654. [2] SESHACHARYULU P, BAINE MJ, SOUCHEK JJ, et al. Biological determinants of radioresistance and their remediation in pancreatic cancer[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2017, 1868( 1): 69- 92. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2017.02.003. [3] BEAR AS, VONDERHEIDE RH, O’HARA MH. Challenges and opportunities for pancreatic cancer immunotherapy[J]. Cancer Cell, 2020, 38( 6): 788- 802. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.08.004. [4] KATHER JN, HEIJ LR, GRABSCH HI, et al. Pan-cancer image-based detection of clinically actionable genetic alterations[J]. Nat Cancer, 2020, 1( 8): 789- 799. DOI: 10.1038/s43018-020-0087-6. [5] National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN guidelines for pancreatic adenocarcinoma(Version 2. 2023)[EB/OL].( 2023-10-22). https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/pancreatic.pdf. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/pancreatic.pdf [6] BOGGI U, DEL CHIARO M, CROCE C, et al. Prognostic implications of tumor invasion or adhesion to peripancreatic vessels in resected pancreatic cancer[J]. Surgery, 2009, 146( 5): 869- 881. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2009.04.029. [7] ISAJI S, MIZUNO S, WINDSOR JA, et al. International consensus on definition and criteria of borderline resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma 2017[J]. Pancreatology, 2018, 18( 1): 2- 11. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2017.11.011. [8] OBA A, CROCE C, HOSOKAWA P, et al. Prognosis based definition of resectability in pancreatic cancer: A road map to new guidelines[J]. Ann Surg, 2022, 275( 1): 175- 181. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003859. [9] MAGGINO L, MALLEO G, MARCHEGIANI G, et al. Outcomes of primary chemotherapy for borderline resectable and locally advanced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. JAMA Surg, 2019, 154( 10): 932- 942. DOI: 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.2277. [10] CONROY T, PFEIFFER P, VILGRAIN V, et al. Pancreatic cancer: ESMO clinical practice guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up[J]. Ann Oncol, 2023, 34( 11): 987- 1002. DOI: 10.1016/j.annonc.2023.08.009. [11] LOOS M, MACK CE, XU ATL, et al. Distal pancreatectomy: Extent of resection determines surgical risk categories[J]. Ann Surg, 2024, 279( 3): 479- 485. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000005935. [12] LOOS M, AL-SAEEDI M, HINZ U, et al. Categorization of differing types of total pancreatectomy[J]. JAMA Surg, 2022, 157( 2): 120- 128. DOI: 10.1001/jamasurg.2021.5834. [13] BOGGI U, KAUFFMANN E, NAPOLI N, et al. REDISCOVER international guidelines on the perioperative care of surgical patients with borderline-resectable and locally advanced pancreatic cancer[J]. Ann Surg, 2024, 280( 1): 56- 65. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000006248. [14] BOCKHORN M, UZUNOGLU FG, ADHAM M, et al. Borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: A consensus statement by the International Study Group of Pancreatic Surgery(ISGPS)[J]. Surgery, 2014, 155( 6): 977- 988. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2014.02.001. [15] Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network(SIGN). A guideline developer’s handbook[EB/OL].[ 2024-08-29]. https://www.sign.ac.uk/media/2038/sign50_2019.pdf. https://www.sign.ac.uk/media/2038/sign50_2019.pdf [16] Grading Tutorial[EB/OL].[ 2024-08-29]. https://www.uptodate.com/home/gradingtutorial. https://www.uptodate.com/home/gradingtutorial [17] BROUWERS MC, KHO ME, BROWMAN GP, et al. AGREE II: Advancing guideline development, reporting and evaluation in health care[J]. J Clin Epidemiol, 2010, 63( 12): 1308- 1311. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.07.001. [18] J EJ, LINSTONE HA, TUROFF M. The Delphi method: Techniques and applications[J]. Technometrics, 1976, 18( 3): 363. DOI: 10.2307/1268751. [19] AJINA R, WEINER LM. T-cell immunity in pancreatic cancer[J]. Pancreas, 2020, 49( 8): 1014- 1023. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001621. [20] NAPOLI N, KAUFFMANN EF, LOMBARDO C, et al. Postoperative results, learning curve, and outcomes of pancreatectomy with arterial resection: A single-center retrospective cohort study on 236 procedures[J]. Int J Surg, 2023, 110( 10): 6111- 6125. DOI: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000971. [21] HE JX, LV N, YANG ZY, et al. Comparing upfront surgery with neoadjuvant treatments in patients with resectable, borderline resectable or locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials[J]. Int J Surg, 2024, 110( 6): 3900- 3909. DOI: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001313. [22] BOGGI U. Resection for pancreatic cancer with arterial involvement: A paradigm shift away from unresectable to“how to do it”[J]. Surgery, 2021, 169( 5): 1036. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2020.10.047. [23] REAMES BN, BLAIR AB, KRELL RW, et al. Management of locally advanced pancreatic cancer: Results of an international survey of current practice[J]. Ann Surg, 2021, 273( 6): 1173- 1181. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003568. [24] National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN guidelines for pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Version 1.2024[EB/OL].( 2024-02-10). https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/pancreatic.pdf. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/pancreatic.pdf [25] SEELEN LWF, DOPPENBERG D, STOOP TF, et al. Minimum and optimal CA19-9 response after two months induction chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A nationwide multicenter study[J]. Ann Surg, 2024, 279( 5): 832- 841. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000006021. [26] REN L, JÄGER C, SCHORN S, et al. Arterial resection for pancreatic cancer: Feasibility and current standing in a high-volume center[J]. Ann Surg Open, 2023, 4( 3): e302. DOI: 10.1097/AS9.0000000000000302. [27] STOOP TF, MACKAY TM, BRADA LJH, et al. Pancreatectomy with arterial resection for periampullary cancer: Outcomes after planned or unplanned events in a nationwide, multicentre cohort[J]. Br J Surg, 2023, 110( 6): 638- 642. DOI: 10.1093/bjs/znac353. [28] FROMER MW, HAWTHORNE J, PHILIPS P, et al. An improved staging system for locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A critical need in the multidisciplinary era[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2021, 28( 11): 6201- 6210. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-021-10174-z. [29] BACHELLIER P, ROSSO E, FUCHSHUBER P, et al. Use of a temporary intraoperative mesentericoportal shunt for pancreatic resection for locally advanced pancreatic cancer with portal vein occlusion and portal hypertension[J]. Surgery, 2014, 155( 3): 449- 456. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2013.09.003. [30] BOGGI U, NAPOLI N, KAUFFMANN EF, et al. Pancreatectomy with resection and reconstruction of the superior mesenteric artery[J]. Br J Surg, 2023, 110( 8): 901- 904. DOI: 10.1093/bjs/znac363. [31] RATNAYAKE B, PENDHARKAR SA, CONNOR S, et al. Patient volume and clinical outcome after pancreatic cancer resection: A contemporary systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Surgery, 2022, 172( 1): 273- 283. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2021.11.029. [32] KRAUTZ C, NIMPTSCH U, WEBER GF, et al. Effect of hospital volume on in-hospital morbidity and mortality following pancreatic surgery in Germany[J]. Ann Surg, 2018, 267( 3): 411- 417. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002248. [33] VIVIAN E, BROOKS MR, LONGORIA R, et al. Improving the standard of care for all-a practical guide to developing a center of excellence[J]. Healthcare(Basel), 2021, 9( 6): 777. DOI: 10.3390/healthcare9060777. [34] GERO D, MULLER X, STAIGER RD, et al. How to establish benchmarks for surgical outcomes? A checklist based on an international expert Delphi consensus[J]. Ann Surg, 2022, 275( 1): 115- 120. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003931. [35] FARGES O, BENDERSKY N, TRUANT S, et al. The theory and practice of pancreatic surgery in France[J]. Ann Surg, 2017, 266( 5): 797- 804. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002399. [36] FARNES I, KLEIVE D, VERBEKE CS, et al. Resection rates and intention-to-treat outcomes in borderline and locally advanced pancreatic cancer: Real-world data from a population-based, prospective cohort study(NORPACT-2)[J]. BJS Open, 2023, 7( 6): zrad137. DOI: 10.1093/bjsopen/zrad137. [37] VONLANTHEN R, LODGE P, BARKUN JS, et al. Toward a consensus on centralization in surgery[J]. Ann Surg, 2018, 268( 5): 712- 724. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002965. [38] NAPOLI N, KAUFFMANN E, CACACE C, et al. Factors predicting survival in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer undergoing pancreatectomy with arterial resection[J]. Updates Surg, 2021, 73( 1): 233- 249. DOI: 10.1007/s13304-020-00883-7. [39] DIENER MK, MIHALJEVIC AL, STROBEL O, et al. Periarterial divestment in pancreatic cancer surgery[J]. Surgery, 2021, 169( 5): 1019- 1025. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2020.08.030. [40] NELSON DW, BLANCHARD TH, CAUSEY MW, et al. Examining the accuracy and clinical usefulness of intraoperative frozen section analysis in the management of pancreatic lesions[J]. Am J Surg, 2013, 205( 5): 613- 617. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2013.01.015. [41] BOGGI U, KAUFFMANN EF, NAPOLI N, et al. REDISCOVER guidelines for borderline-resectable and locally advanced pancreatic cancer: Management algorithm, unanswered questions, and future perspectives[J]. Updates Surg, 2024, 76( 5): 1573- 1591. DOI: 10.1007/s13304-024-01860-0. [42] HEGER U, SUN HH, HINZ U, et al. Induction chemotherapy in pancreatic cancer: CA 19-9 may predict resectability and survival[J]. HPB(Oxford), 2020, 22( 2): 224- 232. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2019.06.012. [43] NEWHOOK TE, VREELAND TJ, GRIFFIN JF, et al. Prognosis associated with CA19-9 response dynamics and normalization during neoadjuvant therapy in resected pancreatic adenocarcinoma[J]. Ann Surg, 2023, 277( 3): 484- 490. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000005184. [44] TSAI S, GEORGE B, WITTMANN D, et al. Importance of normalization of CA19-9 levels following neoadjuvant therapy in patients with localized pancreatic cancer[J]. Ann Surg, 2020, 271( 4): 740- 747. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003049. [45] van ROESSEL S, van VELDHUISEN E, KLOMPMAKER S, et al. Evaluation of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with resected pancreatic cancer after neoadjuvant FOLFIRINOX treatment[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2020, 6( 11): 1733- 1740. DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.3537. [46] MA M, NIU TT, HAO Q, et al. Clinical effect analysis of stereotactic radiotherapy combined with concurrent chemoradiotherapy in the treatment of pancreatic cancer[J]. Trauma Crit Care Med, 2022, 10( 5): 380- 381. DOI: 10.16048/j.issn.2095-5561.2022.05.18.马明, 牛婷婷, 郝倩, 等. 立体定向放射治疗联合同步放化疗治疗胰腺癌临床效果分析[J]. 创伤与急危重病医学, 2022, 10( 5): 380- 381. DOI: 10.16048/j.issn.2095-5561.2022.05.18. [47] WANG CY, LIU XH, WANG XH, et al. Effects of chemoradiotherapy and chemotherapy on survival of patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2018, 97( 36): e12260. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012260. [48] HOMMA Y, ENDO I, MATSUYAMA R, et al. Outcomes of lung metastasis from pancreatic cancer: A nationwide multicenter analysis[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci, 2022, 29( 5): 552- 561. DOI: 10.1002/jhbp.1127. [49] HASHIMOTO D, SATOI S, FUJII T, et al. Is surgical resection justified for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with distant abdominal organ metastasis? A position paper by experts in pancreatic surgery at the Joint Meeting of the International Association of Pancreatology(IAP)& the Japan Pancreas Society(JPS) 2022 in Kyoto[J]. Pancreatology, 2023, 23( 6): 682- 688. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2023.07.005. [50] GIANNONE F, CAPRETTI G, HILAL M ABU, et al. Resectability of pancreatic cancer is in the eye of the observer: A multicenter, blinded, prospective assessment of interobserver agreement on NCCN resectability status criteria[J]. Ann Surg Open, 2021, 2( 3): e087. DOI: 10.1097/AS9.0000000000000087. [51] GODHI SA, PARASAR K, SALUJA S, et al. Radiological and surgical implications of neoadjuvant treatment with FOLFIRINOX for locally advanced and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer[J]. Ann Surg, 2017, 265( 6): E73. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000001322. -



 PDF下载 ( 901 KB)
PDF下载 ( 901 KB)

 下载:
下载: