NLRP3炎症小体在自身免疫性肝炎中的作用机制
DOI: 10.12449/JCH241027
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:王丽菲、罗龙龙负责检索文献,撰写论文;邢国静、卢利霞、李斌参与修改论文;于晓辉、张久聪负责拟定写作思路,指导撰写文章并最后定稿。
Research advances in the mechanism of action of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome in autoimmune hepatitis
-
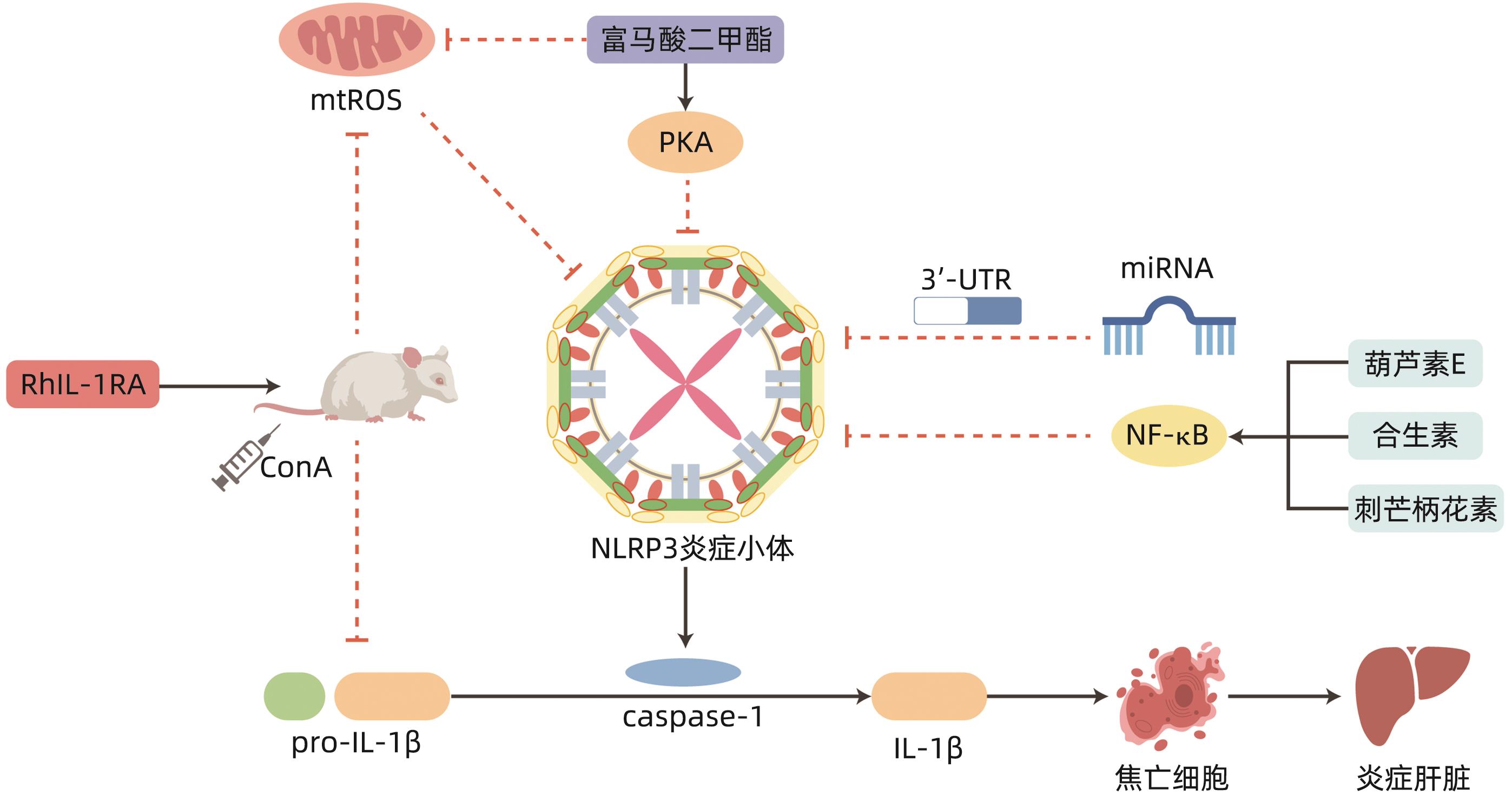
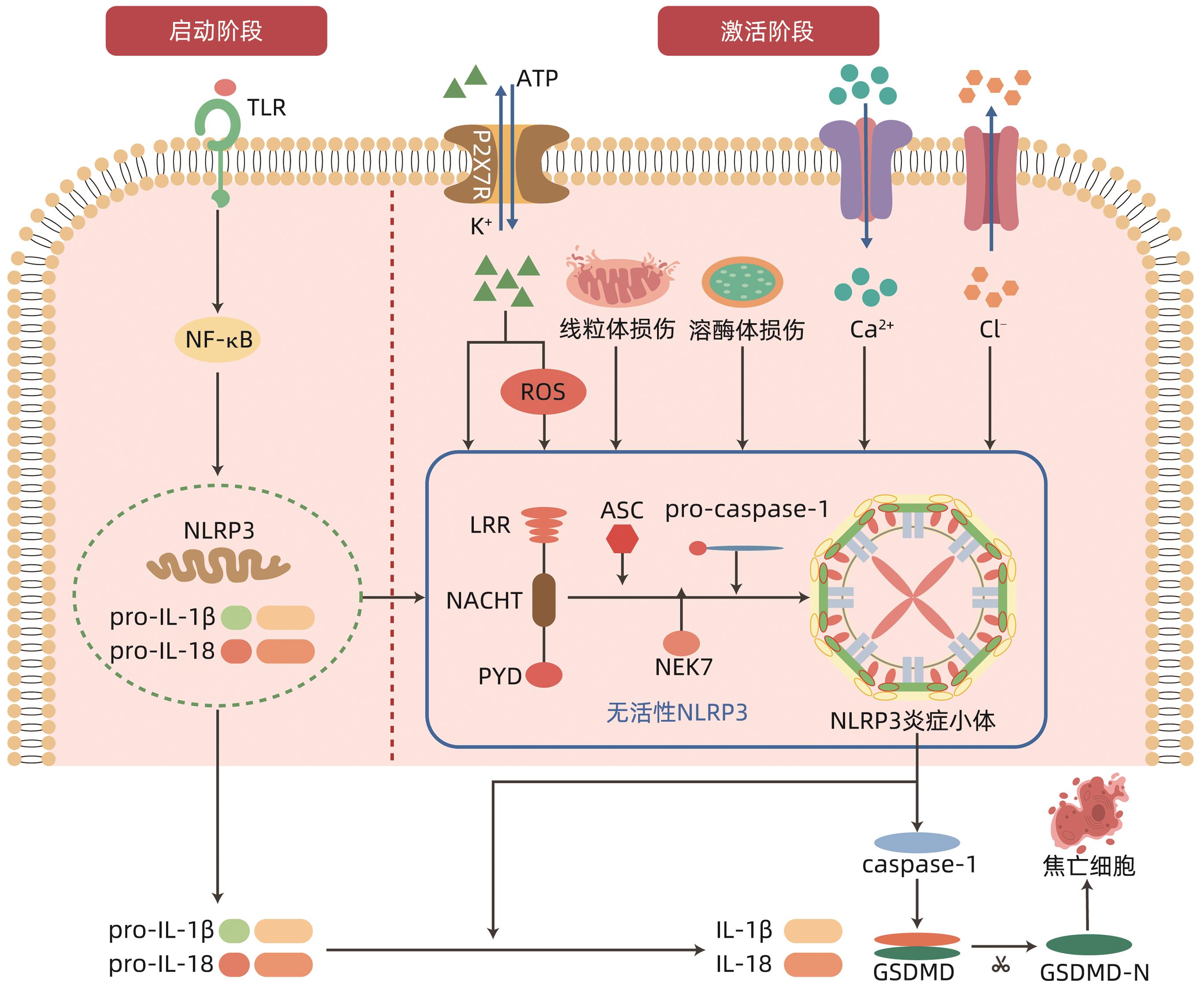
摘要: 自身免疫性肝炎(AIH)是由自身免疫系统攻击肝细胞所致的慢性肝炎,目前关于AIH的发病机制尚不十分明确。炎症小体是先天免疫的重要组成部分,参与多种病理生理学过程。研究表明核苷酸结合寡聚化结构域样受体蛋白3(NLRP3)炎性小体相关的炎性反应在AIH的发病机制中起重要作用,其主要介导促炎因子的释放和细胞焦亡,进而参与AIH的病理生理过程。因此,可以通过抑制NLRP3炎性小体的激活来延缓AIH发生发展,从而为AIH的防治提供新思路。
-
关键词:
- 肝炎, 自身免疫性 /
- NLR家族,热蛋白结构域包含蛋白3 /
- 治疗学
Abstract: Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is chronic hepatitis caused by the attack of live cells by the immune system, and at present, the pathogenesis of AIH remains unclear. Inflammasomes are important components of innate immunity and are involved in a variety of pathophysiological processes. Studies have shown that inflammatory response associated with nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) plays an important role in the pathogenesis of AIH, which mainly mediates the release of proinflammatory factors and pyroptosis, thereby participating in the pathophysiological process of AIH. Therefore, the development and progression of AIH can be delayed by inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes, which provides new ideas for the prevention and treatment of AIH. -
-
[1] FISCHER HP, GOLTZ D. Autoimmune liver diseases[J]. Pathologe, 2020, 41( 5): 444- 456. DOI: 10.1007/s00292-020-00807-7. [2] SHIFFMAN ML. Autoimmune hepatitis: Epidemiology, subtypes, and presentation[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2024, 28( 1): 1- 14. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2023.06.002. [3] MURATORI L, LOHSE AW, LENZI M. Diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis[J]. BMJ, 2023, 380: e070201. DOI: 10.1136/bmj-2022-070201. [4] KOMORI A. Recent updates on the management of autoimmune hepatitis[J]. Clin Mol Hepatol, 2021, 27( 1): 58- 69. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2020.0189. [5] PAPE S, SNIJDERS RJALM, GEVERS TJG, et al. Systematic review of response criteria and endpoints in autoimmune hepatitis by the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 76( 4): 841- 849. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.12.041. [6] LU Y, SUN FF, ZENG Z, et al. Research advances on autoimmune hepatitis[J/CD]. Chin J Liver Dis(Electronic Version), 2022, 14( 4): 1- 9. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2022.04.001.路遥, 孙芳芳, 曾湛, 等. 自身免疫性肝炎研究进展[J/CD]. 中国肝脏病杂志(电子版), 2022, 14( 4): 1- 9. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2022.04.001. [7] LI Z, GUO JL, BI LQ. Role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in autoimmune diseases[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2020, 130: 110542. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110542. [8] RUMPRET M, von RICHTHOFEN HJ, PEPERZAK V, et al. Inhibitory pattern recognition receptors[J]. J Exp Med, 2022, 219( 1): e20211463. DOI: 10.1084/jem.20211463. [9] LEU SY, TSANG YL, HO LC, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation, metabolic danger signals, and protein binding partners[J]. J Endocrinol, 2023, 257( 2): e220184. DOI: 10.1530/JOE-22-0184. [10] SCHMIDT FI, LU A, CHEN JW, et al. A single domain antibody fragment that recognizes the adaptor ASC defines the role of ASC domains in inflammasome assembly[J]. J Exp Med, 2016, 213( 5): 771- 790. DOI: 10.1084/jem.20151790. [11] NAMBAYAN RJT, SANDIN SI, QUINT DA, et al. The inflammasome adapter ASC assembles into filaments with integral participation of its two Death Domains, PYD and CARD[J]. J Biol Chem, 2019, 294( 2): 439- 452. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004407. [12] MOLLA MD, AYELIGN B, DESSIE G, et al. Caspase-1 as a regulatory molecule of lipid metabolism[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2020, 19( 1): 34. DOI: 10.1186/s12944-020-01220-y. [13] FU JN, WU H. Structural mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and activation[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2023, 41: 301- 316. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-081022-021207. [14] BLEVINS HM, XU YM, BIBY S, et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome pathway: A review of mechanisms and inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory diseases[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2022, 14: 879021. DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.879021. [15] BOUCHER D, MONTELEONE M, COLL RC, et al. Caspase-1 self-cleavage is an intrinsic mechanism to terminate inflammasome activity[J]. J Exp Med, 2018, 215( 3): 827- 840. DOI: 10.1084/jem.20172222. [16] DUBYAK GR, MILLER BA, PEARLMAN E. Pyroptosis in neutrophils: Multimodal integration of inflammasome and regulated cell death signaling pathways[J]. Immunol Rev, 2023, 314( 1): 229- 249. DOI: 10.1111/imr.13186. [17] SWANSON KV, DENG M, TING JPY. The NLRP3 inflammasome: Molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2019, 19( 8): 477- 489. DOI: 10.1038/s41577-019-0165-0. [18] PELEGRIN P. P2X7 receptor and the NLRP3 inflammasome: Partners in crime[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2021, 187: 114385. DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114385. [19] SHARIF H, WANG L, WANG WL, et al. Structural mechanism for NEK7-licensed activation of NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. Nature, 2019, 570( 7761): 338- 343. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1295-z. [20] BERINGER A, MIOSSEC P. IL-17 and IL-17-producing cells and liver diseases, with focus on autoimmune liver diseases[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2018, 17( 12): 1176- 1185. DOI: 10.1016/j.autrev.2018.06.008. [21] BUTCHER MJ, ZHU JF. Recent advances in understanding the Th1/Th2 effector choice[J]. Fac Rev, 2021, 10: 30. DOI: 10.12703/r/10-30. [22] WU YN, ZHANG R, SONG XC, et al. C6orf120 gene knockout in rats mitigates concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis via regulating NKT cells[J]. Cell Immunol, 2022, 371: 104467. DOI: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2021.104467. [23] LAN PX, FAN YH, ZHAO Y, et al. TNF superfamily receptor OX40 triggers invariant NKT cell pyroptosis and liver injury[J]. J Clin Invest, 2017, 127( 6): 2222- 2234. DOI: 10.1172/JCI91075. [24] SMYK DS, MAVROPOULOS A, MIELI-VERGANI G, et al. The role of invariant NKT in autoimmune liver disease: Can vitamin D act as an immunomodulator?[J]. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 2018: 8197937. DOI: 10.1155/2018/8197937. [25] SIRBE C, SIMU GL, SZABO I, et al. Pathogenesis of autoimmune hepatitis-cellular and molecular mechanisms[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22( 24): 13578. DOI: 10.3390/ijms222413578. [26] CHRISTEN U, HINTERMANN E. Animal models for autoimmune hepatitis: Are current models good enough?[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 898615. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.898615. [27] LUAN JY, ZHANG XY, WANG SF, et al. NOD-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome-dependent IL-1β accelerated ConA-induced hepatitis[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 758. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00758. [28] LIU ZJ, SUN MY, LIU WH, et al. Deficiency of purinergic P2X4 receptor alleviates experimental autoimmune hepatitis in mice[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2024, 221: 116033. DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116033. [29] WANG H, WANG GD, LIANG YJ, et al. Redox regulation of hepatic NLRP3 inflammasome activation and immune dysregulation in trichloroethene-mediated autoimmunity[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2019, 143: 223- 231. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.08.014. [30] WANG H, WANG GD, ANSARI GAS, et al. Trichloroethene metabolite dichloroacetyl chloride induces apoptosis and compromises phagocytosis in Kupffer cells: Activation of inflammasome and MAPKs[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13( 12): e0210200. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210200. [31] WANG KC, WU WR, JIANG XW, et al. Multi-omics analysis reveals the protection of gasdermin D in concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis[J]. Microbiol Spectr, 2022, 10( 5): e0171722. DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.01717-22. [32] GUAN YL, GU YY, LI H, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation mechanism and its role in autoimmune liver disease[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin, 2022, 54( 11): 1577- 1586. DOI: 10.3724/abbs.2022137. [33] HUANG Y, XU W, ZHOU RB. NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cell death[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2021, 18( 9): 2114- 2127. DOI: 10.1038/s41423-021-00740-6. [34] XIE HB, PENG JL, ZHANG XS, et al. Effects of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation on trichloroethylene-mediated kidney immune injury[J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 2022, 244: 114067. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.114067. [35] LU FB, CHEN DZ, CHEN L, et al. Attenuation of experimental autoimmune hepatitis in mice with bone mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes carrying microRNA-223-3p[J]. Mol Cells, 2019, 42( 12): 906- 918. DOI: 10.14348/molcells.2019.2283. [36] HUANG C, XING X, XIANG XY, et al. MicroRNAs in autoimmune liver diseases: From diagnosis to potential therapeutic targets[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2020, 130: 110558. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110558. [37] YU YN, DONG H, ZHANG Y, et al. MicroRNA-223 downregulation promotes HBx-induced podocyte pyroptosis by targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. Arch Virol, 2022, 167( 9): 1841- 1854. DOI: 10.1007/s00705-022-05499-3. [38] LA ROSA F, MANCUSO R, AGOSTINI S, et al. Pharmacological and epigenetic regulators of NLRP3 inflammasome activation in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Pharmaceuticals, 2021, 14( 11): 1187. DOI: 10.3390/ph14111187. [39] LIU D, CHENG HL, LUO JF. Exogenous hydrogen sulfide miR-211-5p targeting TLR4 pathway mitigates liver damage in autoimmune hepatitis mice[J]. Immunol J, 2022, 38( 10): 838- 845. DOI: 10.13431/j.cnki.immunol.j.20220117.刘丹, 程海林, 罗剑锋. MiR-211-5p靶向TLR4通路减轻自身免疫性肝炎小鼠肝损害[J]. 免疫学杂志, 2022, 38( 10): 838- 845. DOI: 10.13431/j.cnki.immunol.j.20220117. [40] CHEN L, LU FB, CHEN DZ, et al. BMSCs-derived miR-223-containing exosomes contribute to liver protection in experimental autoimmune hepatitis[J]. Mol Immunol, 2018, 93: 38- 46. DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2017.11.008. [41] de CARVALHO RIBEIRO M, SZABO G. Role of the inflammasome in liver disease[J]. Annu Rev Pathol, 2022, 17: 345- 365. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-032521-102529. [42] COLL RC, SCHRODER K, PELEGRÍN P. NLRP3 and pyroptosis blockers for treating inflammatory diseases[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2022, 43( 8): 653- 668. DOI: 10.1016/j.tips.2022.04.003. [43] SHI FL, NI ST, LUO SQ, et al. Dimethyl fumarate ameliorates autoimmune hepatitis in mice by blocking NLRP3 inflammasome activation[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2022, 108: 108867. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108867. [44] SANGINETO M, GRABHERR F, ADOLPH TE, et al. Dimethyl fumarate ameliorates hepatic inflammation in alcohol related liver disease[J]. Liver Int, 2020, 40( 7): 1610- 1619. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14483. [45] RAMOS-TOVAR E, MURIEL P. NLRP3 inflammasome in hepatic diseases: A pharmacological target[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2023, 217: 115861. DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115861. [46] LIU GW, ZHAO WX, BAI JM, et al. Formononetin protects against concanavalin-A-induced autoimmune hepatitis in mice through its anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory properties[J]. Biochem Cell Biol, 2021, 99( 2): 231- 240. DOI: 10.1139/bcb-2020-0197. [47] SILVESTRE GFG, DE LUCENA RP, SILVA ALVES H DA. Cucurbitacins and the immune system: Update in research on anti- inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory mechanisms[J]. Curr Med Chem, 2022, 29( 21): 3774- 3789. DOI: 10.2174/0929867329666220107153253. [48] MOHAMED GA, IBRAHIM SRM, EL-AGAMY DS, et al. Cucurbitacin E glucoside alleviates concanavalin A-induced hepatitis through enhancing SIRT1/Nrf2/HO-1 and inhibiting NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathways[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2022, 292: 115223. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115223. [49] LIU QQ, YANG H, KANG X, et al. A synbiotic ameliorates con A-induced autoimmune hepatitis in mice through modulation of gut microbiota and immune imbalance[J]. Mol Nutr Food Res, 2023, 67( 7): e2200428. DOI: 10.1002/mnfr.202200428. [50] KANG YB, KUANG XY, YAN H, et al. A novel synbiotic alleviates autoimmune hepatitis by modulating the gut microbiota-liver axis and inhibiting the hepatic TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway[J]. mSystems, 2023, 8( 2): e0112722. DOI: 10.1128/msystems.01127-22. -



 PDF下载 ( 1474 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1474 KB)

 下载:
下载: